Inventory of 12 "new generation agreements" in one article

Since BRC 20 was launched on March 8, it has been enthusiastically sought after by users, project parties and CEX, and has become the focus of the market. At the same time, new standard protocols have emerged in an endless stream, receiving a lot of funds.
secondary title
BRC 20: Bitcoin FT protocol on the shoulders of Ordinals
The BRC 20 token standard was developed by Twitter user@domodataBitcoin's experimental fungible token (FT) standard created on March 8, 2023. As a new token standard, BRC 20 is developed based on the native Ordinals protocol of the Bitcoin network.
The Ordinals protocol is a scheme for numbering the smallest unit of the Bitcoin network, "Satoshi". It is also an NFT protocol based on the Bitcoin network. "Satoshi" is the basic unit in the Bitcoin network. One "Satoshi" is equal to 100 millionths a bitcoin. The Ordinals protocol assigns a unique serial number to each "Satoshi" according to the order in which "Satoshi" is mined, making it non-homogeneous. When "Satoshi" is transferred, it follows the first-in, first-out rule. Since both the numbering scheme and the transfer scheme are order-dependent, the protocol is named Ordinals.
Satoshi"Satoshi", and added to the Bitcoin transaction to form an inscription. Based on the Ordinals system, these Satoshis can be tracked. Because these inscriptions are unique, permanent, traceable, and transferable, Bitcoin NFT is derived. The Ordinals protocol does not need to rely on sidechains or tokens outside of Bitcoin, and can be used without any changes to the Bitcoin network.
BRC 20 is essentially a Bitcoin NFT, which is a set of data in a fixed format that is engraved on "Satoshi", turning "Satoshi" into a digital asset with custom attributes and rules. Through the agreed data format for deploying, minting and transferring tokens, users can use the Ordinal protocol to inscribe inscriptions on "Satoshi" in a fixed format, thereby realizing the functions of deploying, minting and transferring tokens. Combined with the corresponding indexing tools, the entire process of token issuance and circulation based on the Bitcoin network can be realized.
As a very early technical experiment, BRC 20 has some shortcomings (and also provides room for latecomers to patch):
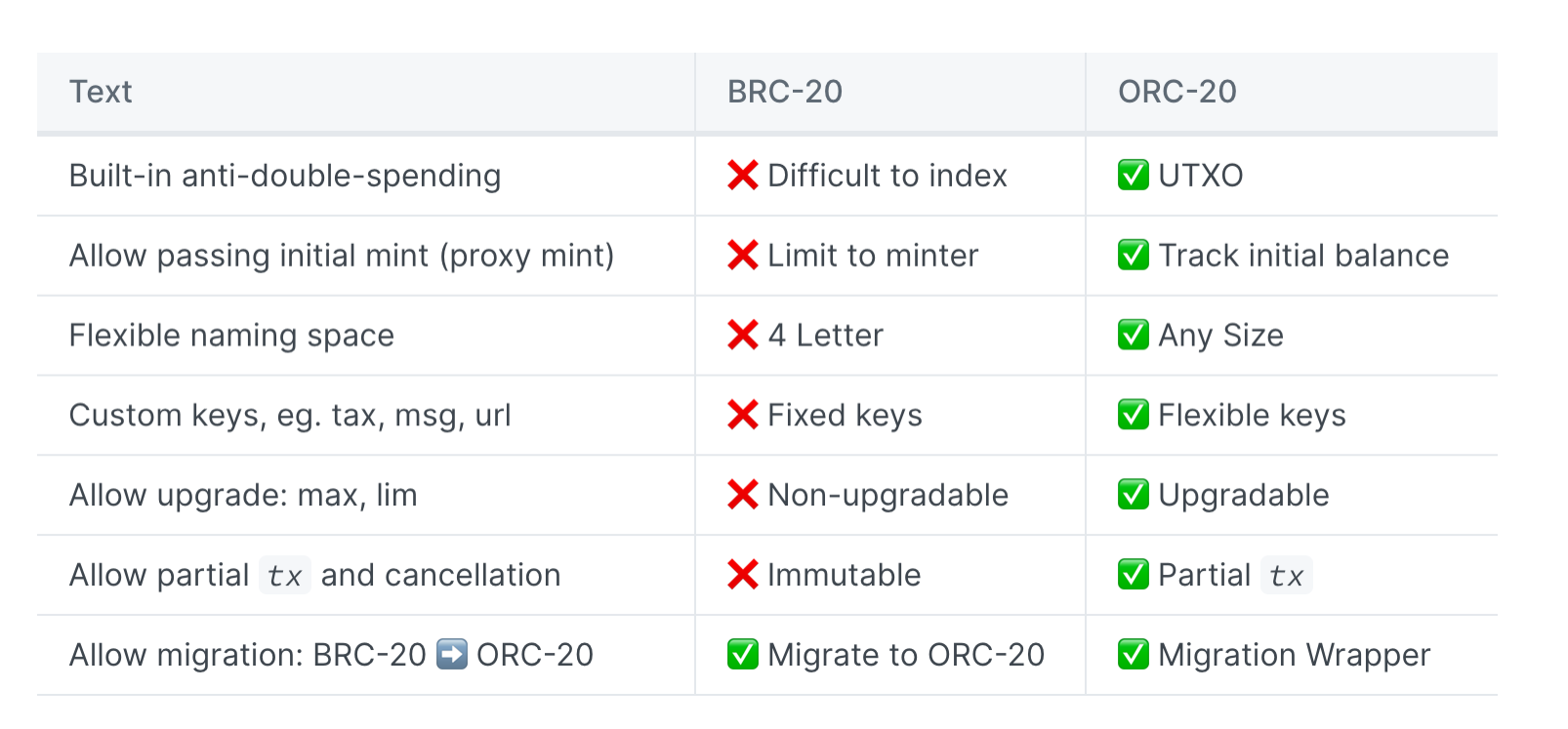
1. The total supply and the maximum amount of tokens minted each time are fixed, cannot be changed, and lack flexibility;
2. The length of the token name is limited, only 4 characters are allowed;
secondary title
ORC 20: backward compatible with BRC 20, improving adaptability, scalability and security
Soon, there was an "upgrade of BRC 20" - the ORC 20 protocol standard.
ORC 20 is an open token standard for Bitcoin ordinals, created by OrcDAO to enhance some key features of BRC 20. It aims to be backward compatible with BRC 20, improve adaptability, scalability and security, and eliminate the possibility of double spending. in particular:
1. Added an identifier (ID) that can identify a specific token;
2. Allows the creation of token names of any length;
3. Introduced the function of modifying the total supply and modifying the maximum number of tokens minted each time;
4. Added UTXO model to prevent double-spending attacks.
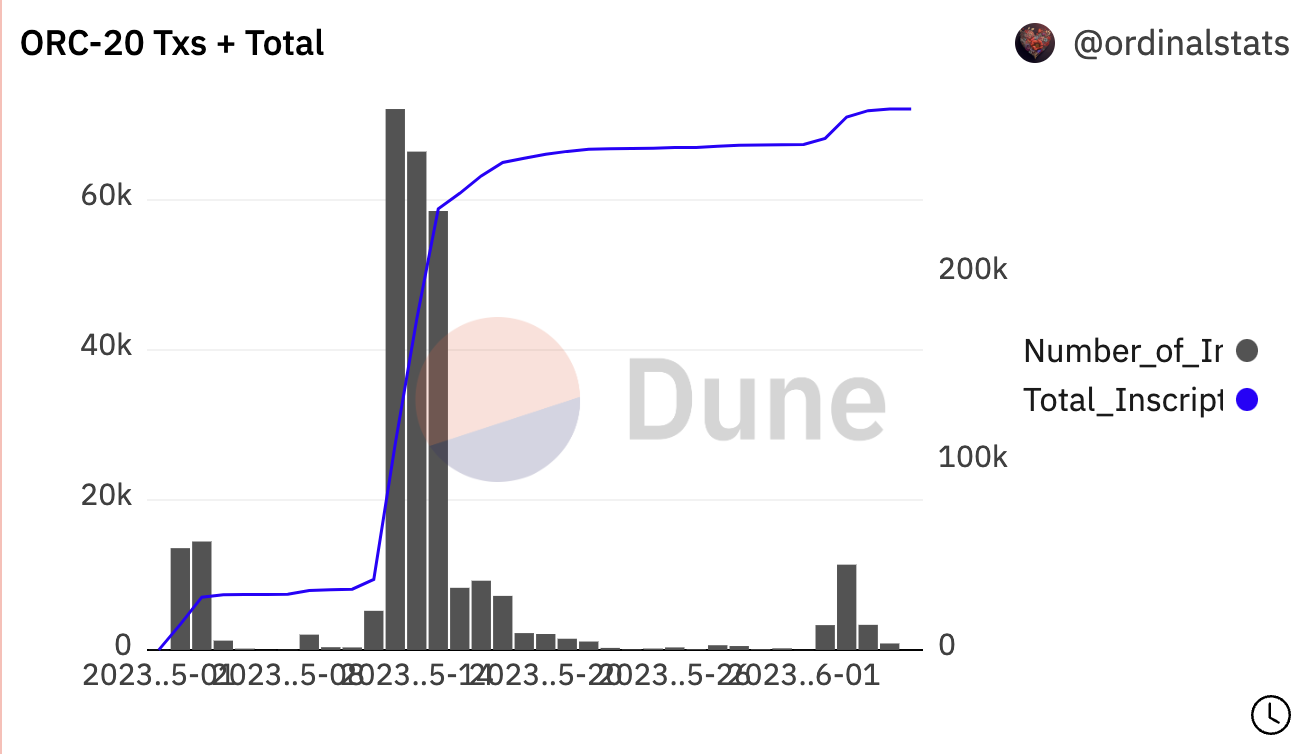
According to Dune data, as of June 6, the total transaction volume of ORC 20 was about 288,132, with a transaction value of about 21.25 BTC.
secondary title
BRC 21: Minting cross-chain tokens on Bitcoin
BRC 21 was proposed by Alexei Zamyatin, the founder of the cross-chain interoperability project Interlay, with the goal of minting fully decentralized, cross-chain tokens on Bitcoin. The protocol allows minting L1 assets (e.g. ETH, SOL, DOT) and stablecoins (e.g. DAI, LUSD) on the Bitcoin network and spending them on the Lightning Network.
Its technical components include:
1. Custom indexer: responsible for verifying BRC 21 coin minting, transfer, redemption and other operations on the Bitcoin network, as well as the smart contract status on the initial chain;
2. Startchain smart contract: responsible for processing coin minting and redemption operations on the Startchain;
3. Relay (BTCRelay): As a light client on the Bitcoin network to achieve the effect of smart contracts, it is necessary to verify and analyze the inclusion of transactions on the Bitcoin network.
secondary title
BRC 42: Another cross-chain upgrade version of BRC 20
BRC 42 is an extension to the BRC 20 standard, connecting BRC 20 tokens with Ethereum or other chains in a fully decentralized manner, which unlocks more DeFi use cases for BRC 20 tokens, such as DEX exchange, lending, etc. . Its technical characteristics are:
1. Custom indexer: verify the operation of BRC 20 cross-chain bridging Bitcoin, and the contract status on the destination chain. The indexer keeps track of every tracked BRC 20 token"out of the bridge"The total amount of tokens.
2. The destination chain contract handles the bridge-out and bridge-in operations on the destination chain.
3. Relay (BTCRelay): A BTClight client implemented as a smart contract on the destination chain, which can verify that the main chain of BTC transactions contains and parses them.
The main use case of BRC 42 is to unlock the DeFi scenarios of BRC 20 tokens, such as trading on AMM DEX, using them as collateral in lending agreements, creating auctions, etc.
secondary title
BRC 721: Introduces a decentralized and trustless approach to collection creation and verification
The BRC 721 protocol introduces a decentralized and trustless method of set creation and verification, similar to the ERC 721 standard on the Ethereum blockchain. The BRC 721 protocol aims to simplify the collection creation and verification process by providing a single source of truth without upfront payment. This protocol specifies the data structure of a collection and its items in a manifest. Lists and validation rules determine whether an ordinal inscription belongs to a certain set.
For details, see SevenUp DAO《secondary title》。
BRC 721 E: Allows Migration of Immutable, Verifiable ERC 721 NFTs to Ordinals
Bitcoin NFT market Ordinals Market and Bitcoin Miladys have jointly released the BRC 721 E standard, allowing immutable, verifiable ERC 721 NFTs to be migrated to Ordinals without prior embedding of the entire NFT family.
When bridging NFT, BRC 721 E encodes data directly into a destruction transaction, which also serves as an on-chain inscription request, and the destruction transaction will specify a Bitcoin address to receive the inscription (airdrop).
Additionally, the standard works by indexers collecting data from both chains, providing rich dynamic metadata on Bitcoin at very low cost. The standard also has the capability for future upgrades and additional on-chain data.
secondary title
GBRC 721: Save on-chain resources and optimize block space
GBRC 721 (Generativebrc 721), proposed by developer @0xJerry543 on Twitter on May 23, he believes, "Currently high network fees and block space usage make creating on-chain NFOs (NonFungible Ordinals) very inefficient costly, it is time to optimize this process to make NFOs more accessible and sustainable."
GBRC 721 can save all on-chain resources while achieving 50% -90% block space optimization. The process consists of three main operations:
Create a BRC 721 collection using the deploy action;
Use the mint operation to mint an irreplaceable serial number;
Convert NonFungible Ordinal to Standard Ordinal Glyph.
OrdiBots is the first NFT series based on GBRC 721, a collection of 1000 robot inscriptions consisting of 26 different characteristics, using the new standard can reduce block space by 55%, greatly reducing the cost of inscriptions.

SRC 20: more "on-chain" than ordinal storage
Both BRC 20 and ORC 20 are based on Ordinals, the principle is to write arbitrary files in the data of Bitcoin transactions. However, this process consumes most of the distributed ledger's capacity, enabling nodes to prune or eliminate witness data. Furthermore, not all nodes are required to persist or propagate this witness data.
The SRC 20 standard uses Stamps (stamps) to write text. Since the information is stored in UTXO, each node must store it, so it is more "on-chain" than the ordinal number, but there is also a problem: the space is limited, so only Accepts 24 x 24 pixel images or 8 color depth PNG, GIF.
The text used to deploy, mint and transfer SRC 20 tokens is also in JSON format, very similar to BRC 20.
Currently, the SRC 20 casting system is temporarily closed due to an upgrade. It is reported that the ecosystem is being built and the transfer function will be launched.
BRC 30: Introducing a staking mechanism for BRC 20 tokens and Bitcoin to the Bitcoin network
On June 1, OKX released the BRC 30 standard. As an enhanced version of the BRC 20 protocol, it adopts the design principles of BRC 20 and introduces equity operation functions such as deposit, casting, and withdrawal. The proposal aims to introduce a staking mechanism for BRC 20 tokens and Bitcoins to the Bitcoin network.
With the introduction of BRC 30, users can stake their own BRC 20 tokens and Bitcoin and receive corresponding BRC 30 tokens in return. BRC 30 tokens can be seen as an extension of the functionality of BRC 20 tokens, while adding a description of the equity mechanism.
In this way, BRC 20 token holders can put their digital assets to work, earn passive income without having to sell these tokens, actively participate in the Bitcoin network ecosystem, and increase the underlying value of their tokens.
According to reports, the purpose of introducing BRC 30 and its pledge function is to allow BRC 20 token holders to participate in digital asset-related activities and obtain passive income opportunities. Additionally, staking operations incentivize users to continue holding their assets, potentially reducing selling pressure in the market and contributing to a more stable token ecosystem.
By implementing BRC 30, OKX hypothesizes that holders of BRC 20 tokens and Bitcoins have an alternative means of income that does not solely rely on buying and selling tokens on exchanges.
FERC 20: Let the concept of fair launch of BRC 20 return to Ethereum
FERC 20 aims to implement the fair launch (Fairlaunch) spirit of BRC 20 on Ethereum (and other EVM chains) through smart contracts, allowing more community participation. FERC 20 is based on the ERC 20 standard protocol, so it has features that BRC 20 does not have, including but not limited to:
It is convenient to transfer money in the wallet familiar to the user, without downloading new wallet software;
It can be used in the powerful DeFi ecosystem of Ethereum, including DEX, lending, multi-signature, etc.;
FERC 20 tokens have no owner authority, that is, no owner tokens;
The number of Tick characters can be upgraded;
There is no pre-mining, and the total amount of tokens is mined from zero until the hard cap is reached;
Highly decentralized, the system architecture is serverless, including search, search and other functions, all carried out in smart contracts;
Instead of the BRC 20 generation platform, users interact directly with the contract.
proposer@jackygu 2020 It is believed that the main difficulty in realizing BRC 20 on Ethereum lies in how to implement more effective protection against witches and smart contract robots on the Bitcoin chain on Ethereum, so as to maintain the fairness of participants. For this reason, on the basis of the ERC 20 standard contract, 3 sets of attributes are added:
Freezing period: When the user mints coins for the first time, he will enter the freezing period. If he wants to continue minting coins during the freezing period, he needs to pay a tip to the platform. For every additional coin, the tip is doubled. For example: 0.00025 ETH will be paid for the first coin minting during the freezing period, 0.0005 ETH will be paid for the second time, and 0.001 ETH will be paid for the third time... It should be noted that for FERC 20 with a freezing period set, batch coins cannot be minted (Rollup Mint).
Position conditions: Deployers can set position conditions to prevent large-scale rapid minting of witch accounts. Holdings include NFTs and other ERC 20 tokens.
Pre-sale/crowdfunding: Deployers can set the pre-sale/crowdfunding price of tokens to charge a certain fee when minting coins.
FERC 20 reached a small climax on June 1, minter DAU reached 13,519, and the number of Tokens was 116.
Related reading: DodoResearch'sFrom the on-chain data of FERC-20, we can see the activity curve of new concepts in the current market》
DRC 20、LTC 20
When the BTC ecology is hot, the "relatives" of Bitcoin also come to share a share. LTC 20 is a token protocol launched by community developers on the Litecoin network, providing users with text, pictures, videos, Audio and other functions casted on NFT.
For details, see Sammi Simi "Detailed explanation of LTC-20 agreement: development status, advantages and potential risks》。
DRC 20 is a token agreement on the DOGE chain. It is as cheap as LTC, and only needs a little Gas fee to engrave tokens.
The launch of the LTC 20 and DRC 20 protocols has led to a sharp increase in the transaction volume on the DOGE and LTC chains. On May 15, the single transaction volume of DOGE exceeded 650,000. The active addresses of LTC increased by nearly 4 times within a week, and the giant whale became active , LTC hit a record high with 576,700 transactions on May 9.
In general, the "X" RC standard has attracted widespread attention from the entire cryptocurrency industry, and a group of new-generation protocols have provided new solutions for the transaction and management of digital assets, which has also become a new round of hot narrative The field of intensive occurrence, by the way, triggered a certain wealth effect. However, with the development of technology and ecology, there are still uncertainties in the security, scope of use cases, and duration of "X" RC. In any case, the "X" RC standard has become an important part of the Bitcoin ecosystem and has gradually spread to more encrypted ecosystems.



