Cross-chain track research report: Why is the LayerZero full-chain interoperability protocol valued at 3 billion US dollars (Part 1)
foreword
foreword
In just one year, LayerZero, a full-chain interoperability protocol, once again raised $120 million at a valuation of $3 billion, three times the previous valuation. Investors include a16z, ChristiesInc, and Sequoia Capital.
This article is the first part, focusing on LayerZero's technical solution and evaluating its advantages and disadvantages.
1. LayerZero technical principle
secondary title
1.1. Overview
Note that LayerZero does not focus on cross-chain assets, but cross-chain messages on the upper layer. As the underlying protocol, it has an inclusive relationship with the application layer of cross-chain assets. The more specific cross-chain assets are Stargate, also developed by Layerzero Labs.
secondary title
1.2. What is a light node?The communication between cross-chains is mainly done through external verification or light nodes on the chain. First of all, a light node is a node operation mode, as well as a full node (Full Node) and an archive node (Archive Node). Different nodes of the same chain are the deleted version of the chain information,
With multiple Merkle Roots in the block header, Merkle tree verification can be used to determine whether a transaction actually exists in this block.
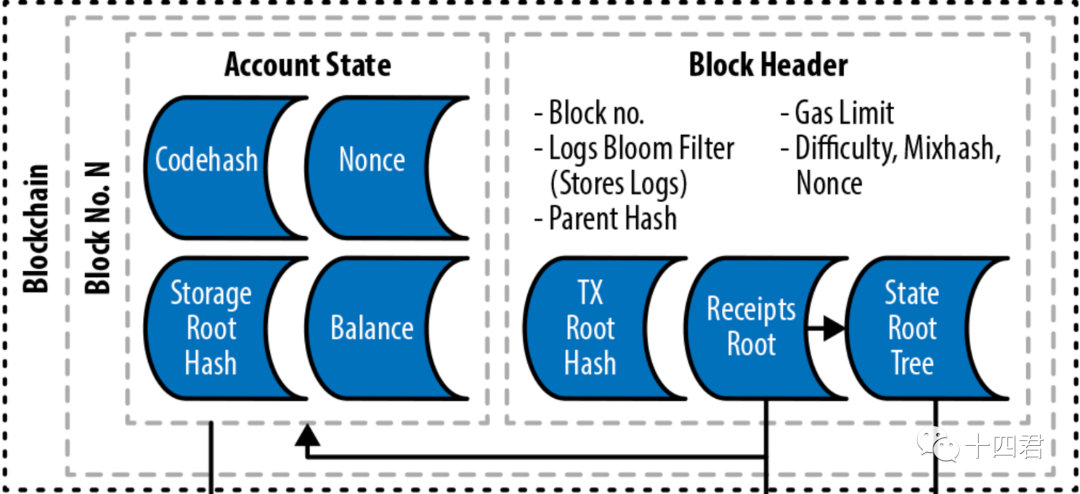
image description
Ethereum's EVM virtual machine architecture diagram comes from the official GITHUB
The benefit of running verification on the chain with light nodes is that it completely eliminates the interference of the external role of the notary, and achieves a high degree of decentralization based on the security of the chain itself, making it safer.but in this wayThe cost of cross-chain will be extremely high, and will eventually be distributed to users with cross-chain needs
. The author once estimated the cost of storing metadata in KB in NFT.[Source Code Interpretation] What exactly is the NFT you bought?
secondary title
1.2. What is an ultra-light node?
The ultra-light node Ultra-Light Node (ULN) is actually very simple. Compared with the light node, the ultra-light node will perform the same verification as the light node on the chain, but instead of retaining all the block headers in order, they are determined by the decentralized oracle machine on demand. streaming.
The benefit is that it does not rely on the light node to start the block header data stream from scratch.
A certain degree of security loss corresponds to a great degree of cost reduction. What is right and wrong depends on how everyone weighs it based on their own scenarios. Referring to the design of social protocols such as lens, the value of social attention information will not be too great, so in doing In the case of good application layer isolation, it is also very advisable to optimistically do meta transactions, and optimistically perform first and then trace back.
first level title
In the LayerZero official white paper in the figure below, the green part is the key role of information transmission between the two chains, namely Oracle and Relayer.
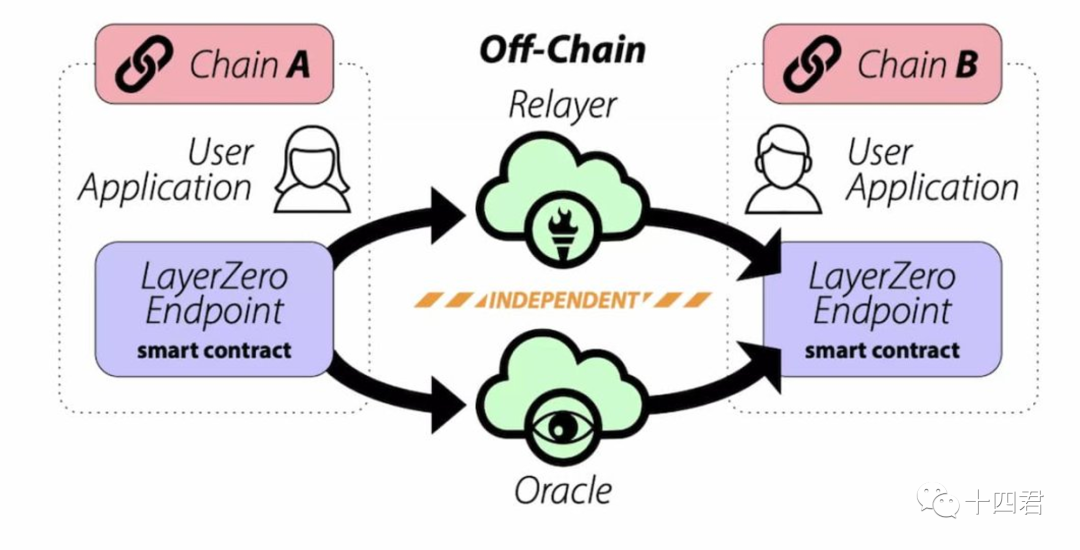
LayerZero official white paper comes from the official website
secondary title
2.1. Positioning of Oracle and Relayer
In simple terms, the main function of the Oracle (oracle machine) is to let the contract on the target chain know when to verify and what the answer to the verification is. The Relayer (repeater) is responsible for providing the proof process required to verify the transaction and the specific content of the cross-chain information.
The author also mentioned in the previous 4337 research report that the current 4337 contract still needs to be connected to the off-chain oracle price service in order to truly realize the function of multi-currency payment transaction fees:Extended reading
In short, Oracle is the notary role in the LayerZero cross-chain. It may be due to such a malicious assessment. The security of the oracle is almost equal to the value of Defi on the chain. Too many loan products rely on the oracle to provide prices. If they If you are willing to do evil, then you can do things with higher yields.
secondary title
2.2. Division of labor between Oracle and Relayer
The role of the oracle machine is to transfer the Blockhash and Block Receiptsroot where the cross-chain request on the source chain is located to the target chain.
Blockhash Block hash, which tells the contract on the target chain which block contains the user's cross-chain request.
Block Receiptsroot is used to verify the messages passed by the transaction relayer.
The role of the repeater is to pass the path information required by the Receipt and Merkle Proof where the cross-chain message is located to the contract on the target chain for verification.
Among them, the receipt refers to the transaction receipt information, which mainly includes the transaction execution result, transaction hash and transaction event log.
Transaction execution result: whether the transaction itself on the source chain is successful.
Transaction hash: the globally unique hash of each transaction.
The path information here is the red arrow in the figure below, for example, after the relayer informs the nodes on the chain of L2 -> Hash 0-0 -> Hash 1 information in sequence. Comparing the TopHash given by the oracle and the second calculation based on the information contract given by the relayer means that the relayer is correct.
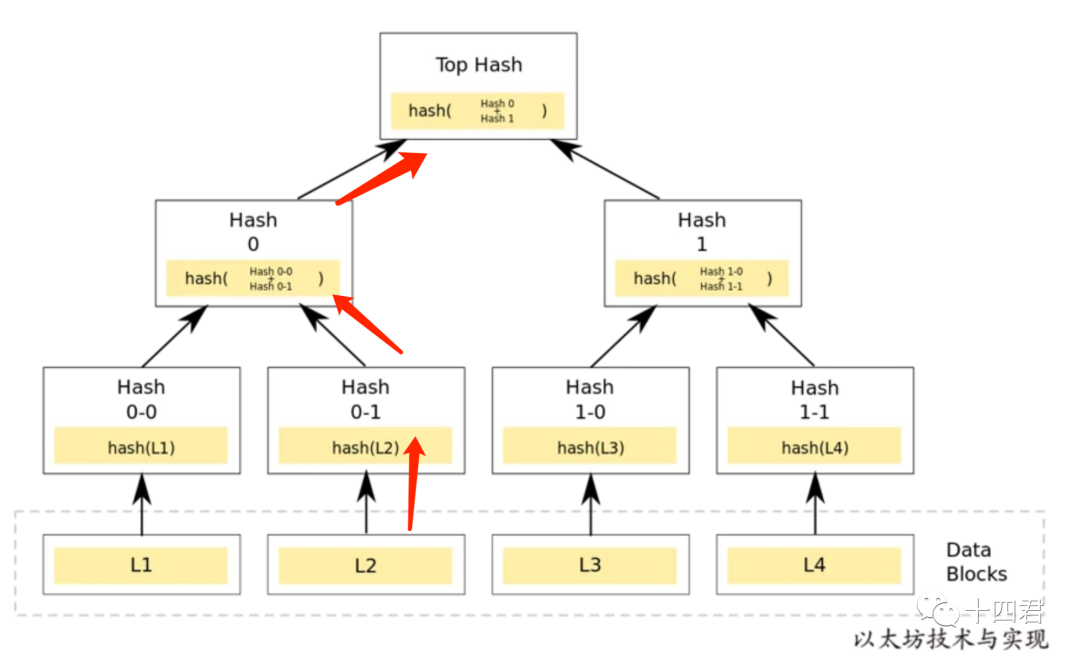
secondary title
After understanding the work of the cross-chain role in the intermediate area, let's cross a transaction from ChainA to ChainB. Both the left and right boxes in the figure below interact with the endpoint contract (EndPoint) on their respective chains.
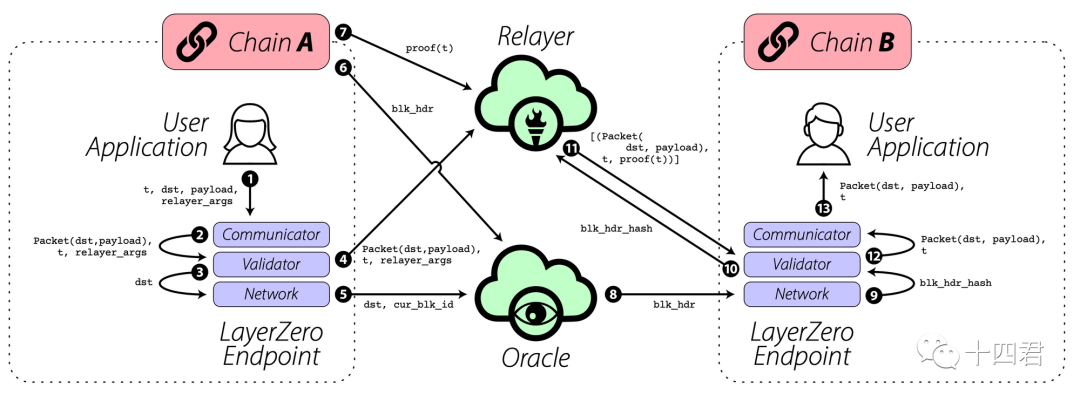
image description
LayerZero official white paper comes from the official website
The overall process is outlined as follows:
A transaction begins when a user application (UA) initiates a transaction (i.e. performs some action on-chain). This transaction is then broken down into parts (proof and block header) with the assistance of LayerZero endpoints via oracles and relayers. Once the oracle and repeater send their respective messages on the target chain (sign the transaction on the chain), and the LayerZero Endpoint (contract) verifies the correctness of the information, the message will be converted and executed on the target chain.
The detailed steps are as follows (see the picture above):
Step 1: User application UA (such as Stargate bridge) LayerZero's communicator (Communicator) sends a request, including the transaction identifier t, the data transferred from A to B (payload payload), or pointing to the user application intelligence on Chain B Contract identifier or relayer (relayer_args) and other transaction information.
Step 2: The communicator sends the data to the validator (Validator) in the form of a LayerZero packet
Step 3: The validator sends the transaction identifier and the identifier of the smart contract on chain B to the network layer (NetWork). The work of the network layer is also triggered, and the information to be transmitted needs to send the block header of the source chain A to the target chain B through oracle.
Step 4: The validator forwards this information (packet) to the relayer. After being notified, the repeater will take the transaction proof (Proof in step 7) and store it off-chain, and send it to Chain B (step 11). The endpoint of chain B can also initiate an application to obtain the result of the specified block hash ( Step 10).
Step 5: The network layer sends the identifier of the smart contract on Chain B together with the block ID of the transaction block to the oracle. When the oracle is notified it fetches the block header of the current block on Chain A (step 6) and sends it to Chain B (step 8).
It can be seen that at this time, the parts 6, 7, 8, 10, and 11 are actually embedded in the links of repeaters and oracles.
Step 9: The network layer sends the obtained block hash to the validator (triggering the verification of the ultra-light node).
Step 12: The validator ensures that the transaction is valid and committed by looking at the transaction proof and block header stored at the network layer. If the block header and the transaction proof match, the transaction information (Packet) is sent to the communicator.
The overall cross-chain is the gas fee charged when the first transaction is executed on the source chain, and there are 3 corresponding transactions on the target chain, consisting of repeater + oracle + Layer Zero: Executor (an EOA account).
3. How to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of the LayerZero protocol
secondary title
3.1. Is it dangerous to rely on oracles?If there is only one relayer or one oracle machine, it may indeed be dangerous (it is no longer the management scope of the protocol itself), but what layerZero currently implements isAny application can customize its own relayer or even choose a different oracle
to support your system.
Even if some relayers are down or do not work or work incorrectly for a certain purpose, in the gradual market competition, a many-to-many selection pattern will be formed, and decentralized mutual supervision will be formed between the respective games, similar to the miner mechanism.
Even if oracle 1 and relay A collude maliciously, this is an isolated risk because only applications that use both oracle 1 as an oracle and relay A as information will be affected.
And LayerZero is only the bottom-level mechanism for transmitting information. As for how to use the upper-layer application after the information is transmitted, it can be independently defined and security hardened. As far as the protocol itself is concerned, he does not store funds or data, which will reduce the possibility of him being attacked.
Currently, LayerZero has been officially audited by more than 30 versions, including Quantstamp, Zokyo, Zellic and Trail of Bits, etc. Additionally, he currently hosts a $15 million bug bounty through ImmuneFi, the largest live bug bounty program in the entire industry! , LayerZero has awarded nearly $1 million to white hats for disclosures to date.
secondary title
3.2. Comparing the advantages of cross-chain products at the protocol layer
Consistent with the previous conclusions, the extremely low cost of cross-chain security verification is a bright spot, and the same loss is the security of the highly trusted oracle machine. In addition to security factors (after all, it can be reinforced at the application layer), Versatility and extremely low protocol access costs for developers are a big hidden advantage I see.
Stronger general scalabilityCurrently, there are IBC protocol of Cosmos ecology and XCMP cross-chain protocol of Polkadot ecology that are cross-chain at the protocol layer. The reason why they have limitations in scalability is that for Ethereum to verify transactions on other public chains,Then the corresponding light nodes must be deployed on Ethereum
. Such a high Gas cost makes it difficult for many EVM compatible chains (ETH/BSC/Polygon/L2, etc.) to support the IBC protocol, which greatly limits the versatility of the IBC protocol, so it is still only available in the relatively small Cosmos run between ecological chains.
Lower developer access complexityFrom the very beginning, the workload of the underlying protocol is placed on the minimalist contract access design, and the upper limit of the demand scenario for message cross-chain is extremely high, such as cross-chain lending, income aggregation and transactions are just the beginning. Because it is convenient and easy to develop, the protocol is currently used in more than 30 chain Dapps (Including decentralized exchanges PancakeSwap, SushiSwap, TraderJoe, Uniswap, etc.
) has passed more than millions of messages, and the application bridge on it has locked a total value of more than 7 billion U.S. dollars (the recent TVL of the post is 400 million U.S. dollars).
In the aforementioned locked-in casting mode, the generated packaging tokens are a fragmentation of multi-chain funds, while LayerZero uses non-encapsulated assets, which can support EVM and non-EVM, a unified liquidity layer, and When assets cross-chain, complex transactions such as original chain exchange, bridging, target chain exchange, and pledge can be bundled.
3.3. Summary

image description
Interpretation of the cross-chain solution: https://research.web3 caff.com/zh/archives/7592Cross-chain is one of the important investment tracks under the multi-chain structure.The future is highly certain, the business model is clear, and the market has already achieved high revenue at an immature stage
, as a communication protocol embedded in the basic code of various Dapps, the protocol itself has become one of the most basic Lego building blocks.
【Next part notice】
The last part is the implementation and advantages and disadvantages of LayerZero's technical solution."shisi"The next article will further expand the comparison of LZ's market situation, and comprehensively evaluate the major cross-chain models. It has been submitted to the research channel of the Web3 Caff platform (the head paid research platform, and the 14 Jun fans joint activity is underway, which can be used
15-day membership extension for referral code).
Read the original text: https://research.web3 caff.com/zh/archives/7592
https://medium.com/layerzero-official/layerzero-an-omnichain-interoperability-protocol-b 4 3d 2 ae 975 b 6
https://blog.li.fi/layerzero-a-deep-dive-6 a 46555967 f 5
https://layerzero.gitbook.io/docs/
https://github.com/LayerZero-Labs/Audits/tree/main/audits
https://blog.li.fi/navigating-arbitrary-messaging-bridges-a-comparison-framework-8720 f 302 e 2 aa
https://web3 caff.com/zh/archives/37040
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/1322
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Ji-3 XKfquPlP 7 upnUWEaHQ
https://stargate.finance/overview
https://blog.ethereum.org/2015/11/15/merkling-in-ethereum
https://layerzero.network/pdf/LayerZero_Whitepaper_Release.pdf
https://github.com/LayerZero-Labs



