Hermits across bull-bear cycles: crypto market makers
Summary
first level title
Summary
The business of traditional financial market makers began to sprout in the early 19th century, and now it has shown the characteristics of mature development, diversified trading varieties, and relatively stable business and income. As an important participant in the financial market, market makers have played a unique role in providing market liquidity and market efficiency. With the continuous expansion of the market size, more and more institutions and investment banks have also joined the market-making business and become an important source of income. The market-making business of the overall market also gathers to the head, and the competition is fierce. In order to seize the market and customers, market makers are constantly upgrading algorithms, technology, risk control, and compliance, and are gradually getting involved in the encryption field.
Compared with traditional finance, the market maker business in the encrypted market is not much different in essence. But the operating model, technology, risk management and supervision are very different. First of all, in terms of market size, the encryption market is still relatively small compared to the traditional financial market, and the market size of the encryption industry is also relatively small. The liquidity of the encrypted market is relatively low and fluctuates greatly, and market makers need to be more cautious in risk management; secondly, the market maker team in the encrypted market is also called a banker. Because the trading process of the encrypted market is difficult to be supervised, and there is no strict market maker system to constrain it. The relationship between exchanges, project parties and market makers has become more complicated. Then, the market maker business is not only generated in the centralized exchange, but also involves market making on the chain, and based on this, some middleware and protocols for market making services have begun to appear; the last point is that in terms of technical architecture, the encryption industry Higher technical capabilities are required to ensure the security of transactions.
The market-making business in the encryption market is a blue ocean, which gives every investor opportunities but also risks. At present, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) are tightening supervision on the encryption market, and many institutions and businesses are affected. Coupled with the bear market and frequent thunderstorms of large institutions, it is even more challenging for market makers to manage risks. Beyond that, crypto market makers face market fragmentation/interoperability, capital inefficiency, regulatory uncertainty, and still-improving exchange technology/connectivity.
Even so, crypto market makers still have a lot of room for development and profitability. Crypto market makers will also present some development characteristics of traditional financial market makers in the future:
(1) Market-making participants are gradually diversified;
(2) Diversification of market-making varieties;
(4) The head effect of market makers is becoming more and more obvious.
In the field of investment, you can focus on centralized small market-making strategies or service projects, tools to solve interoperability, and CeDeFi projects.
first level title
Market makers refer to institutions or individuals that provide liquidity in financial markets. Its main responsibility is to provide liquidity and market depth for the securities trading market. A market maker typically trades between buyers and sellers in a securities exchange market and provides a quote on the market so that other traders can place a buy or sell trade on that quote. Market makers are usually composed of investment banks, securities companies or professional institutions. They play an important role in the market and help to maintain market stability and liquidity. Market makers typically trade in one or more markets simultaneously and provide liquidity by buying and selling the same asset in order to provide trading opportunities to market participants.
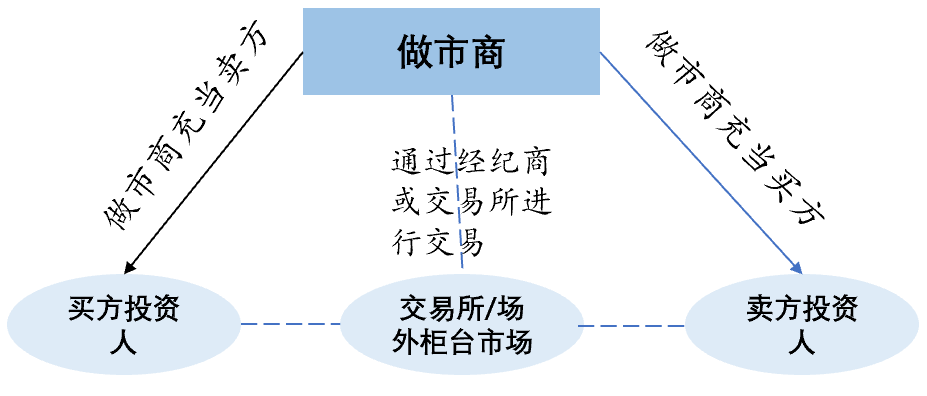
image description
secondary title
1.1 Industry Overview
text
1.1.1 Industry Functions and Customers Served
The role of market makers in the financial market is very important and unique from other market participants. Especially in terms of providing liquidity and market efficiency. Specifically, market makers undertake six main functions:
Provide liquidity: Provide liquidity between buyers and sellers to make the market more active.
Continuous quotation: Market makers continue to quote and provide buying and selling prices at any time, which is convenient for market participants to conduct transactions.
Risk management: Market makers need to manage transaction risks, maintain a healthy risk-benefit ratio, and protect the interests of themselves and their customers.
Provide consulting: Market makers can provide market information and analysis to help customers make better trading decisions.
Increase market efficiency: The existence of market makers can increase market efficiency, reduce the price difference between buyers and sellers, and improve market efficiency and competitiveness.
Provide innovative products: Launch new products according to market demand to meet the different investment needs of customers.
The customers of market makers mainly include the following categories:
Traders: Market makers provide traders with liquidity and help them conduct fast and efficient transactions.
Investment institutions: market makers provide liquidity and services for investment institutions, helping them with asset allocation and risk management.
Individual investors: Market makers provide individual investors with liquidity and services to help them trade financial products such as stocks and futures.
Other financial institutions: Market makers also provide liquidity and services to other financial institutions such as banks and insurance companies.
text
1.1.2 The development history of the market maker track
The development process of the market maker track can be divided into five stages:
Before the 19th century: the initial stage of market makers, matching transactions in the traditional counter market. The market-making system is one of the oldest securities trading systems. It originated from the traditional over-the-counter market. In order to facilitate transactions and reduce transaction costs, traders assume the role of market makers themselves and provide bilateral quotations for other traders or customers. Most of them are traditional methods such as on-site communication and telephone communication.
19th century-1970s: Standardized exchanges appeared and developed rapidly, and market makers provided liquidity in the market. After the 19th century, major exchanges in the United States, such as the American Exchange and the Chicago Stock Exchange, were established one after another. At that time, market makers were mainly active on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in the United States. During that period, market makers were largely based on human trading, not computer programs. Market makers provide market liquidity based on the quotations of buyers and sellers on the trading books of the stock exchange.
1990s: In the late 20th century, with the rise of institutional investors and retail discount brokers, the market share of market makers’ internal matching platform transactions continued to increase. On the one hand, with the rise of institutional investors such as mutual funds and pension funds in the United States, institutional investors’ demand for large transactions has increased significantly, and large investment banks represented by Goldman Sachs can provide comprehensive services for institutional investors. On the other hand, the volume of retail securities transactions undertaken by retail discount brokers such as Robinhood and Charles Schwab has surged, and such discount brokers mainly transfer orders to market maker platforms in exchange for market maker Payment for this (called Payment for Order Flow). With the globalization of financial markets, market makers have begun to expand their operations globally, while also facing increasing competition. During this period, market makers began to adopt more complex and advanced trading strategies and techniques to improve trading efficiency and profitability.
21st century: With the continuous innovation and development of financial markets, the role of market makers has gradually been expanded and consolidated. In the 21st century, market makers began to enter emerging markets, such as the cryptocurrency market and options market, while also adopting more advanced technological means, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
text
1.1.3 Market Size and Competitive Environment
According to data from financial industry regulator FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority), as of September 2021, the number of legal market makers registered in the United States exceeds 500. These market makers are registered with and regulated by FINRA. According to the U.S. Office of the Currency (OCC), from 2012 to 2018, the total transaction revenue of U.S. commercial bank holding companies remained at around 50 billion US dollars. Although some years represented by 2018 were dragged down by the secondary market, the transaction revenue decreased year-on-year. The decline, but the overall fluctuation is small, showing a growing trend. Since 2019, the transaction income of the banking industry has further increased. In 2019, 2020, and 2021, the total transaction income of Bank of America Holdings Co., Ltd. will be 75.126, 79.512, and 78.946 billion U.S. dollars, respectively. The size or market share of a market maker company is often related to the degree of liquidity it provides in the market. Specifically, the market share of a market maker can be measured by the following indicators:
Trading volume ratio: The trading volume ratio of a market maker in a certain market can reflect its trading activity and influence in the market.
(2) Quote depth: The quote depth of a market maker in a certain market, that is, the quantity and price it is ready to trade, can reflect the degree of liquidity it provides in the market.
(3) Trading efficiency: the trading efficiency of a market maker in a certain market, that is, its ability to conduct transactions quickly and efficiently.
In short, the market share of a market maker is an important indicator that can reflect its performance in terms of transaction activity, liquidity provision capability, and transaction efficiency in the market.
The more well-known market maker companies are as follows:
Jane Street: A quantitative trading company headquartered in New York City, USA, established in 2000, mainly focusing on trading in stocks, futures, foreign exchange and other fields.
Citadel Securities: a financial company headquartered in Chicago, USA, established in 2002, is one of the world's largest market makers, mainly involved in the transactions of stocks, futures, foreign exchange, bonds and other fields.
IMC Trading: A financial company headquartered in Amsterdam, the Netherlands, established in 1989, is one of the world's leading market makers, involving transactions in stocks, futures, foreign exchange and other fields.
Susquehanna International Group: A financial company headquartered in Philadelphia, USA, founded in 1987, is one of the world's largest option market makers and also involves transactions in other fields.
Jump Trading: A quantitative trading company headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, USA, founded in 1999. The company is committed to using advanced algorithms and advanced technology to conduct transactions in order to find profit opportunities. Jump Trading involves various markets such as stocks, futures, foreign exchange, and digital currency on a global scale.
1.2 Necessary conditions for a market maker company
Establishing a market maker company requires a high degree of financial strength, technical capabilities and market insight. At the same time, it needs to meet the regulatory requirements of financial regulators, and it is difficult to face a highly competitive market environment and high risk management pressure.
text
1.2.1 Understand the market
Market makers need an in-depth understanding of market rules, liquidity, trading varieties, and traders' behavior patterns in order to make correct trading decisions. They need to understand the trends and opportunities in the market in order to gain an edge in the market. There are several ways to understand the market:
Research market information and data: Market makers need to study the historical and current trading data of the market in order to understand the market and price fluctuations. Market makers can obtain market information by using trading software or market data providers.
Communicate with other traders: Market makers can learn about market conditions by communicating with other traders. For example, they can attend trading conferences or online forums to exchange ideas and market updates with other traders.
With the help of trading strategies and models: Market maker firms can use trading strategies and models to predict market trends and price fluctuations. These models may include methods such as technical analysis, fundamental analysis and quantitative analysis.
text
1.2.2 Establish a technology platform
Market maker companies need an efficient and stable technology platform that can support real-time trading and data analysis. The platform needs to include algorithms for fast execution of transactions, high-speed data transmission and processing systems, and secure transaction settlement systems. Specifically, market maker companies need to have the following five types of technologies:
Trading technology: including securities, futures, options, etc. These technologies include the use of trading platforms, order management, risk control, etc.
Data analysis technology: understand market conditions and trends. These techniques include data mining, machine learning, artificial intelligence, etc.
Risk management technology: to ensure the safety and stability of transactions. These technologies include risk control, fund management, market monitoring, etc.
Software development techniques: developing and maintaining trading systems and trading tools. These technologies include programming languages, database management, software testing, and more.
text
1.2.3 Determining capital needs
Market maker firms require substantial capital to support their trading activities. You need to determine how much capital you need to enter the market and identify sources of capital. Here's how to determine how much capital you need:
Calculating Market Liquidity Requirements: Market liquidity requirements are the amount of funds that a market maker must provide in order to execute buy and sell transactions in the market. The method of determining liquidity needs includes measuring market trading volume, trading frequency, and open interest and other indicators, so as to estimate the amount of funds that need to be invested.
Consider Margin Requirements: Many exchanges and markets require market makers to provide margin to ensure that the market maker's trading activity in the market is compliant. You need to understand the market margin requirements and reserve enough funds to meet the margin requirements.
Consider market volatility: Market volatility can cause market makers to suffer losses. You need to take market volatility into account and reserve enough funds to cover market risks.
To sum up, determining how much capital a market maker needs needs to consider various factors, and it needs to be analyzed and calculated according to the specific conditions of different markets. It should be noted that capital demand is a dynamic process that needs to be constantly adjusted according to market changes and company business expansion.
text
Market makers need to manage risk to ensure the safety and stability of transactions. You need to develop risk management strategies, including transaction risk, liquidity risk, market risk and operational risk, etc.
Market risk management is about making sure that trading remains on track despite adverse market conditions. For example, market makers can employ measures such as hedging strategies, leverage controls, and trading restrictions to manage market risk. Operational risk is to ensure that errors or mistakes do not occur during the trading process. For example, market makers can establish good trading processes and trading rules, and strengthen measures such as internal audit and monitoring to manage operational risks. Technical risk management is to ensure the stability and security of the trading system. For example, market makers can employ measures such as backup and recovery strategies, network security measures, and data encryption to manage technical risk. Credit risk management is to ensure that there will be no default or loss of non-performing assets during the transaction process. For example, market makers can manage credit risk with measures such as credit assessment and monitoring, margin management, and risk control.
secondary title
1.3 Operation Mode and Market Making System
On the trading platform, market makers provide liquidity through two-way quotations (buying and selling), so its operation mode generally includes the following steps:
Select the target: select one or more markets or products, such as stocks, futures, foreign exchange, etc., according to the trading strategy, cooperation model and risk preference.
Market analysis: analyze the selected market or target to understand its characteristics, trends and changes. And specify the corresponding strategy according to the analysis results.
Provide quotations: Market makers will provide two-way quotations, that is, buying and selling quotations, according to their trading strategies and market conditions, to provide liquidity.
Risk control: Market makers will monitor and control transaction risks, and conduct risk management and hedging operations as needed.

Profit: Market makers make profits through transaction spreads and handling fees, but there are also risks that may lead to losses.
Figure 2. The operating mode of market makers in the trading platform
Under the above operation mode, there are actually two driving systems: quotation-driven system and order-driven system. In the quote-driven system, market makers provide investors with bilateral quotes for buying and selling for gambling transactions, and guide the transaction price to change through the update of quotes. The order-driven (Order driven) system is also known as the auction trading system. Investors transmit the buying and selling orders to the exchange through the network, and the computer host of the exchange matches the buying and selling orders into transactions according to the principle of time priority and price priority, forming continuous transactions. price.
secondary title
1.4 Profit Model
The profit model of market makers is usually to obtain profits from the bid-ask spread. The market maker will quote both buying and selling prices on the trading platform at the same time, which is called "two-way quotation". When a customer places an order, the market maker will immediately execute the transaction, and then sell at a higher price or buy the same security at a lower price to obtain a profit from the difference. This difference is usually called Spread income or Facilitation revenues. . Market makers can also make profits through high-frequency trading, hedging, and arbitrage. Among them, high-frequency trading refers to a trading strategy that uses high-speed algorithms and automated systems for fast trading. Hedging refers to using opposite transactions to reduce risk, and arbitrage refers to taking advantage of different prices in the market to obtain profits. In addition, market makers also have a kind of inventory revenue (Inventory revenues), which reflects the gains and losses brought about by changes in securities values when market makers hold positions, as well as dividends, interest and other holding income.
The profitability of market makers also needs to consider transaction costs. The cost of market-making business mainly includes three aspects: transaction costs such as brokerage commissions and liquidation fees paid when buying and selling securities; financing costs for raising capital for market-making business; The cost of hedging due to risk exposure, as well as risk costs such as credit risk and counterparty risk that cannot be eliminated. However, since market makers usually conduct a large number of transactions, they can reduce transaction costs through economies of scale and efficient technology, and gain profits from it.
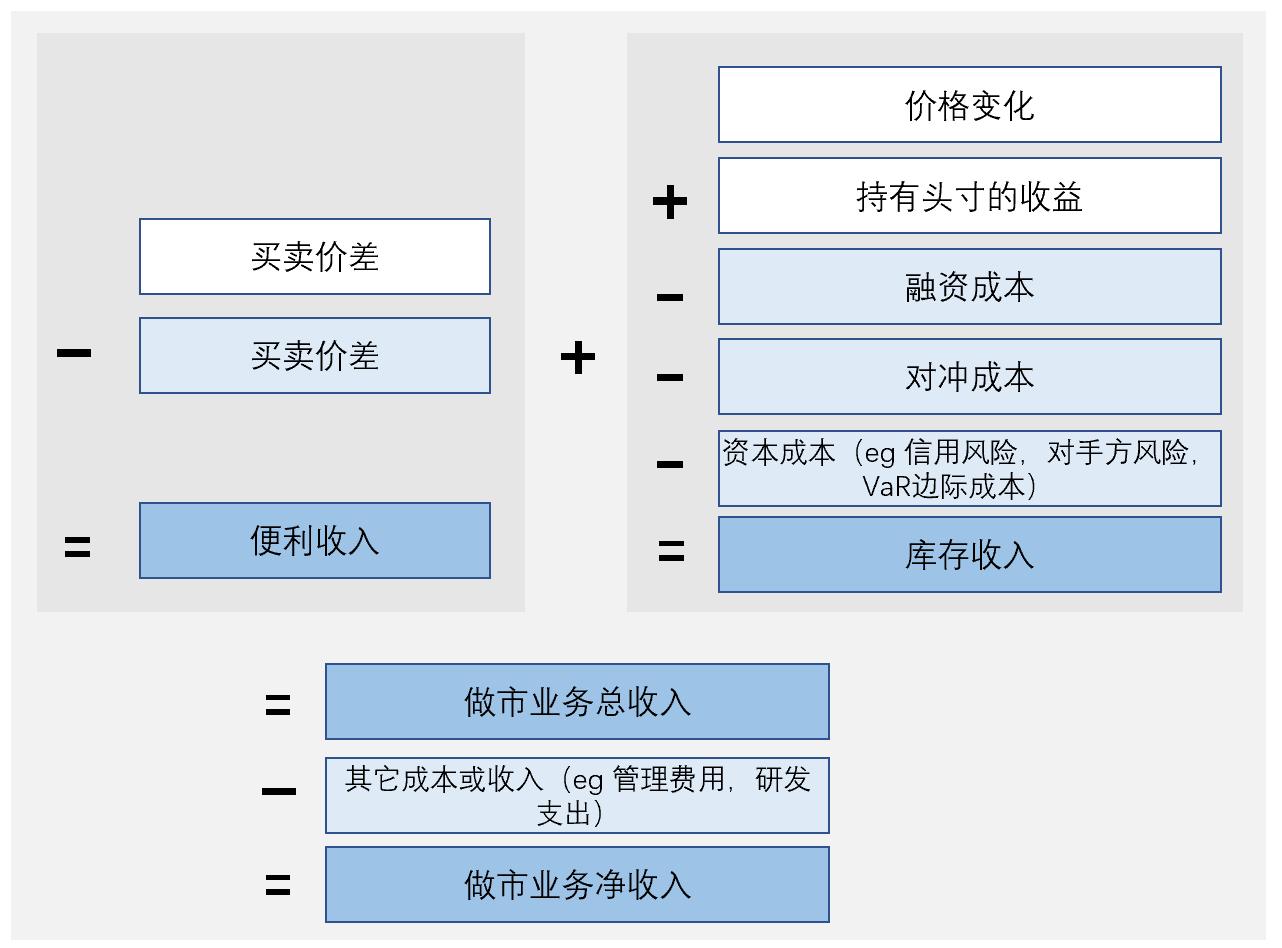
image description
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of revenue and cost accounts of market makers (Source: Committee on the Global Financial System, Ping An Securities Research Institute)
secondary title
1.5 Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Market makers are directly involved in the liquidity and price formation of the securities market, and their trading strategies and behaviors may have an impact on the market, so they need to be supervised by regulatory agencies. Supervision can effectively ensure that market maker companies abide by trading rules and market order, prevent market manipulation and improper trading behavior, protect the interests of investors, and maintain the fairness, transparency and stability of the market. At the same time, supervision can also promote the compliant operation of market maker companies, strengthen the requirements for risk management and information disclosure, improve market confidence and transparency, reduce market volatility, and promote the healthy development of the market. Therefore, it is necessary for market makers to be regulated not only to protect the interests of investors, but also to maintain the healthy operation of the entire market.
Here we mainly consider the regulatory policies that market maker institutions in the United States are subject to. In the United States, the supervision of market maker companies is relatively strict. These companies need to strictly adhere to the regulatory requirements of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), and comply with securities regulations. In addition, market maker firms also need to comply with compliance and anti-money laundering requirements. Regulatory agencies strictly supervise the transactions and business of market maker companies, including the review of trading systems and algorithms, the inspection of risk control systems, and the requirements for data protection. In terms of regulation, the U.S. securities market has a sound regulatory system, and there will be corresponding penalties for violations. Therefore, market maker companies need to attach great importance to regulatory compliance risks in their daily operations. Specific sectors and regulatory laws are as follows:
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): Responsible for regulating the securities market, including the registration and supervision of market maker firms.
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA): Regulates securities broker-dealer and market-maker firms to ensure compliance with securities regulations.
"Securities Act" (Securities Act): stipulates the registration and issuance requirements of securities, and involves the business of market makers.
National Securities Markets Improvement Act (National Securities Markets Improvement Act): An overhaul of the regulation of the securities markets, which also has implications for the business of market makers.
secondary title
1.6 Future Development Trend
A market maker is a circuit that develops as the securities market matures, and it plays an important role in the financial market. With the development of the financial market, the market demand for market makers will continue to exist. However, at this stage, the development is relatively mature, and the market is gradually becoming saturated. It is difficult for new institutions to squeeze into this track. Therefore, more and more market maker teams use the encrypted market as their main layout point.
In general, the long-term challenges faced by market makers are as follows:
Technical risk: As the market continues to change, market maker companies need to continuously upgrade and improve their technical architecture to ensure the stable operation of the system and avoid risks and losses caused by technical problems.
Legal risk: Market maker companies need to abide by the laws and regulations of various countries, including financial supervision, securities laws and intellectual property laws, otherwise they will face legal sanctions and losses.
Market risk: Market changes and uncertainties will bring risks and challenges to market maker companies, such as market volatility, decline in trading volume, and insufficient liquidity, all of which will affect the profitability of market maker companies.
Operational risk: Market maker companies need to process a large amount of transactions and data, and need to establish an effective risk management and internal control system to prevent risks and losses caused by internal operational errors or violations.
Opportunities and challenges coexist. With the continuous development of the global financial market and the increasing complexity and scale of securities market transactions, market maker companies will have more opportunities to participate in the market by providing liquidity services and market manufacturing, so as to obtain higher profits. Moreover, with the rapid development of the encryption market, market maker companies can also obtain more opportunities by providing market manufacturing services and liquidity provision for encrypted assets. At the same time, market maker companies can improve their market manufacturing capabilities by developing and applying new technical tools and algorithms, better adapt to market demand, and gain more market share.
first level title
2. Crypto market market makers
Market makers in the encryption industry are not much different from traditional finance in essence. They all provide liquidity for the market, quickly open and close positions, and obtain bid-ask spreads. But the operating model, technology, risk management and supervision are very different. First of all, in terms of market size, the encryption market is still relatively small compared to the traditional financial market, and the market size of the encryption industry is also relatively small. Secondly, the liquidity of the encryption market is relatively low and the volatility is high, and market makers need to be more cautious in risk management; then, the market maker team in the encryption market is also called a banker. Because the trading process of the encryption market is difficult to be supervised, and there is no strict market maker system to constrain it; the last point is that in terms of technical architecture, the encryption industry needs to have higher technical capabilities to ensure the security of transactions.
Provide liquidity and depth to the crypto market;
Provide stable prices to the market and attract more traders. It can be said that market makers are the key link for project parties, exchanges, and investors to operate normally in the encryption market.
secondary title
2.1 Development History
The development of market makers in the crypto market can be divided into 3 stages:
Early days (2009-2012): With the birth of Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency exchanges and market makers began to emerge. These market makers are primarily composed of individuals and small teams that aim to provide liquidity and trading opportunities.
Period of Great Change (2018-present): The slump in the cryptocurrency market in 2018 led to the collapse of many exchanges and market makers, but it also brought an opportunity and reshuffle to the market. After integration and adjustments, the trading volume of the cryptocurrency market has gradually recovered, and the services and models of market makers have also been continuously optimized and upgraded. At the same time, with the continuous introduction and improvement of policies and regulations in various countries, the supervision and compliance of encrypted market makers has gradually become an important trend in the market. At this stage, some traditional financial companies began to get involved in the cryptocurrency market, such as Jane Street, Susquehanna, etc.
At present, the services of encrypted market makers are not limited to exchanges, but have gradually expanded to over-the-counter transactions and decentralized exchanges, providing important support and guarantee for the development and maturity of the market.
secondary title
2.2 The operation mode of encrypted market maker
The operation mode of encrypted market makers is similar to that of traditional financial market makers, mainly to provide liquidity and market depth for the cryptocurrency market, and at the same time obtain profits from it. Crypto market makers usually trade on multiple exchanges, and crypto market makers' transactions are usually automated and connected to exchanges through API interfaces. In the market, quotes are provided through their own funds and algorithmic models to attract buyers and sellers to trade. Some crypto market makers also offer over-the-counter trading services, allowing bulk and customized trades. Due to the volatility and uncertainty of the encrypted market, encrypted market makers need to adjust their market strategies in real time, including transaction size, quotation range, and hedging risks.
The encryption market-making process generally includes the following steps:
Screen currency pairs: Select one or more groups of currency pairs, usually depending on market liquidity and market maker volume capabilities.
Quotes: Bid and ask prices are formulated and published in the exchange's depth of trade table.
Risk management: Risk management is a very important step during market maker trading. Market makers use various tools and strategies to control their risks, such as trading limits, stop loss orders, and hedging.

Settlement and liquidation: Once the transaction is completed, the market maker needs to perform settlement and liquidation, including charging fees to buyers and sellers and paying relevant taxes and fees.
Figure 4. Encrypted market-making business operation model
In addition to the above steps, market makers also need to constantly monitor market conditions, including market liquidity, competitors' actions, and market risks, in order to adjust their strategies and quotations in a timely manner.
text
The market-maker strategy is a risk-neutral spread arbitrage strategy, which belongs to the high-frequency trading strategy in the quantitative trading strategy and follows the principle of buying low and selling high. The basic principle is: between the selling price and the buying price of the market, insert a commissioned buy order and a commissioned sell order. If the inserted two orders are all executed, the market maker will get the price difference between the bid and the order, and the entire After the process, the positions held by the market makers do not change. If there is still a surplus after deducting various transaction fees from the price difference between the buying and selling orders, then the market maker has obtained a corresponding profit. Common market-making strategies include spread strategies, hedging strategies, quantitative trading strategies, etc.
Market-making strategies are divided into spot market-making strategies and futures market-making strategies according to different markets. The spot market-making strategy has four modules: short-term trend judgment, market making, rebalancing and main cycle. Futures market-making strategies are more complicated, including complex logic such as market-making timing selection, net position processing, lock-up, shifting, and counterparty lightening.
2.2.2 OTC transactions
The way crypto market makers provide over-the-counter trading services is usually by establishing contact with counterparties and negotiating prices and transaction details with them. Specifically, encrypted market makers will publish their market-making prices on trading platforms or other off-exchange channels, waiting for counterparties to accept and trade. In addition, encrypted market makers can also use their own liquidity pools to provide real-time quotes and trading opportunities to counterparties when needed to meet their liquidity needs. At the same time, encrypted market makers can also provide clearing and settlement services for counterparties to ensure the smooth progress of transactions and the safety of funds.
secondary title
2.3 Market-making technical threshold
Encrypted market makers need to fully overlap with traditional market makers in technology, but encrypted market makers need to master more technologies, the most important thing is blockchain technology. Cryptocurrency transactions are based on blockchain technology, so crypto market makers must understand blockchain technology and its application in cryptocurrency transactions in order to understand the nature and technical details of transactions. Learn how exchanges and wallets interact with the blockchain, and how to identify and resolve issues such as transaction delays due to network congestion or other issues.
Secondly, for the encryption industry, the security of assets is also very important. Due to certain security risks in cryptocurrency transactions, encrypted market makers need to master relevant security technologies to protect the security of the trading system. Specific technologies include multi-signature technology, cold wallet storage, secure communication protocol, transaction monitoring and anti-fraud technology, data backup and recovery technology, etc.
Other technologies are not limited to:
Data analysis and machine learning: The cryptocurrency market fluctuates greatly, so crypto market makers need to have certain data analysis capabilities, including market analysis, price trend forecasting, etc. Machine learning technology can help market makers make more accurate trading decisions.
Social media and online marketing: The cryptocurrency market has strong social characteristics, so encrypted market makers need to have certain social media and online marketing capabilities in order to interact and communicate with potential customers.
secondary title
2.4 Exchanges and market makers
The relationship between digital currency exchanges and market maker teams is delicate. Some crypto exchanges may have their own team of market makers, but many choose to work with third-party market makers. There are two forms of cooperation between exchanges and market makers:
Work directly with crypto exchanges
Market makers cooperate directly with encrypted exchanges to provide on-site market-making services. Exchanges often provide some market maker plans, which require the cooperation of these teams and provide trading interfaces, but these are passive trading interfaces and cannot take the initiative to take orders. If you want to actively quote and take orders, it can only be done internally by the exchange, directly or indirectly embedded in the exchange matching system.
At this time, market makers need to obtain information such as the order book and market depth of the exchange through the API interface, and then use their own algorithms and trading strategies for market pricing and transaction matching.
Exchanges need to provide market makers with relevant module interfaces, usually including market data, order withdrawals, recharge reminders, etc.
Indirect cooperation with crypto exchanges
Market makers cooperate with encrypted exchanges through other intermediaries or platforms to provide off-exchange market-making services. At this time, the market maker needs to negotiate with the intermediary or platform to determine the cooperation method and details, and obtain the market information of the exchange through the API interface or other channels, and then conduct over-the-counter transactions.
It should be noted that crypto exchanges do not have to use market makers to provide liquidity. Some exchanges may use other means to increase liquidity, such as using technologies such as deep pools or order book matching engines. When cooperating with an encrypted exchange, market makers need to negotiate with the exchange on cooperation details, fee allocation, trading volume, etc., to ensure smooth cooperation and obtain considerable benefits. At the same time, market makers need to strictly abide by the rules and regulatory requirements of the exchange to ensure the legal compliance of transactions.
From the analysis of the trading mechanism, the market makers connected with the exchange are largely involved in the price determination process, which can restrain those who try to manipulate the currency price to a certain extent, improve the expectations of investors and project parties, and stabilize market sentiment.
Around 2017 and 2018, a large number of new exchanges went online, leading the concept of "trading is mining". In the early stage of some exchanges' operations, 120% cashback was even used to attract market traders to participate in transactions based on the transaction volume.
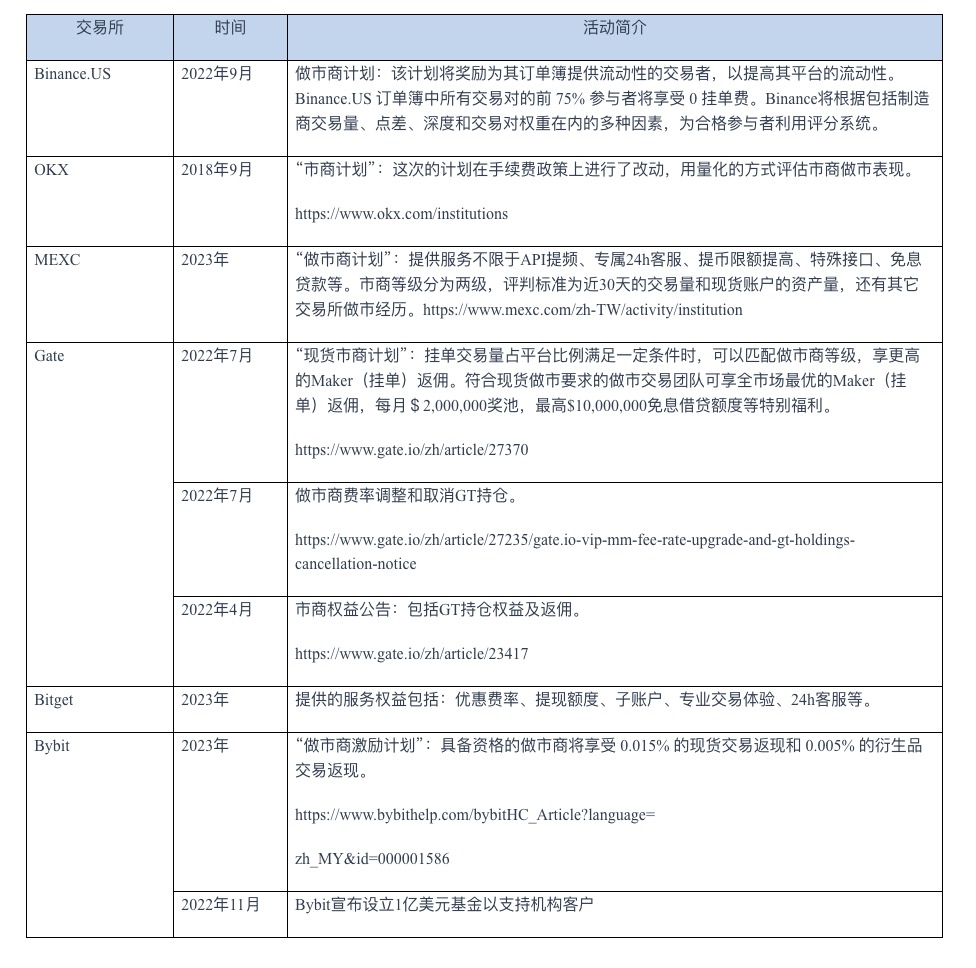
In order to attract more excellent market-making teams to carry out market-making on exchanges, major exchanges have launched their own service solutions. First of all, the trading platform itself needs to have more service products, including more spot trading pairs and futures types, value preservation products (low interest rate lending services, etc.), and provide more trading strategies and algorithm services. Secondly, a reasonable and attractive rebate ratio. In the end, the risk management and reputation of the exchange is the most important. Here is a list of some of the exchanges' activities for market makers.
image description
Table 1. Market maker activity by exchange
It can be seen from the above list of activities that since Gate launched the global market maker plan in 2021, there have been constant market maker competitions to attract market maker teams. At the same time, the market-making fee rate and GT positions are constantly being adjusted. In addition, some services are also provided for market makers, including 0-interest loan lines.
Market makers will participate in the spot, futures, and options markets, and the threshold is getting higher and higher. Correspondingly, the exchange will also grant different privileges in different participating markets. In general, the exchange can give preferential treatment to market makers in the following items:
Fee discount
leveraged funds
deposit and withdrawal amount
Institutional client accounts/accounting system
secondary title
2.5 Project party and market maker
image description
Figure 5. Market maker and participant relationship
In the encrypted market, the liquidity of project tokens is as important as products, teams, and operations. The relationship between the project party and the market maker is mainly established through the market maker providing liquidity services to the project party. Project parties, especially new projects in the ICO or IEO stage, need a market maker team for price management. Market makers play three roles:
Make up for the shortcomings of insufficient market liquidity;
Stabilize the currency price to prevent the project from failing if the price is too high or too low;
Market value management to improve the market recognition of the project. These tasks are handed over to a professional market maker team, which costs less than the project team's own operations.
The project party will choose some well-known encryption exchanges to cooperate with market makers to obtain better liquidity and higher market recognition, which requires the project to provide a certain amount of tokens to market makers as initial circulation. Market makers agree to provide active liquidity to the order book for at least 90% of the contract’s life, in exchange for receiving 2-5% of the project’s total token supply. For market makers, cooperating with well-known project parties can improve their popularity and reputation in the market and help attract more trading pairs for transactions. Therefore, in the encrypted market, the cooperative relationship between project parties and market makers is very important.
In addition to providing liquidity, market makers will also provide additional services to project parties, including formulating strategies for token prices (especially STG) and helping teams cash out
secondary title
2.6 The Profit Model of Encrypted Market Makers
Like traditional market makers, encrypted market makers also make profits through the price difference between buying and selling transactions. However, in the absence of regulation in the crypto market, this spread can be large, the market volatile and the returns more volatile.
Crypto market makers also have two sources of income:
Help the project party to make a market;
Assist exchanges in maintaining sufficient liquidity and trading volume.
Among them, in cooperation with the project party, the profit model of the market maker is usually the following two:
Market makers provide over-the-counter trading services to help project parties increase liquidity, obtain trading volume, and earn profits from it. Market makers make profits by bearing the bid-ask spread and transaction fees between the two parties.
Market makers cooperate with project parties to become token liquidity providers and participate in token liquidity mining. Market makers are rewarded with tokens when the token’s liquidity increases. In addition, market makers can also gain benefits by providing market depth, participating in airdrops and promotions of project parties, etc.
In cooperation with exchanges, there are also two profit models:
Provide liquidity services: Market makers improve market liquidity by providing cryptocurrency buying and selling services, thereby helping exchanges attract more users and trading volume. Some crypto exchanges pay market makers additional liquidity fees.
As the number of market makers increases and the competition becomes stronger, in order to win more markets, market makers will narrow the price difference between quotations, resulting in a decrease in revenue.
secondary title
How to select a market maker team or evaluate market maker performance is very important for crypto market participants. Common indicators for evaluating a market-making team include the market maker's trading volume and trading frequency, the accuracy and stability of quotations, profit margins and risk management capabilities, market share and reputation. But for exchanges, market takers, and project parties, what is more important is the performance of market makers in providing liquidity. Reference indicators for liquidity performance include quotation depth, accuracy, update frequency and transaction efficiency.
first level title
3. Risk analysis and management of encrypted market makers
secondary title
3.1 Regulation and Compliance
Crypto market makers currently remain in a regulatory gray area and are not yet supported by clear legal and regulatory frameworks in most countries and regions. This means that crypto market makers are generally not required to adhere to the strict regulatory standards set forth in traditional financial markets, nor are they regulated by the corresponding regulators. However, in some countries and regions, regulators have begun to explore how to regulate encrypted market makers to ensure market transparency, fairness and stability.
Regulatory agencies involved in market makers in the encrypted market include the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), which have certain regulatory responsibilities for the encrypted market. The SEC is responsible for supervising the securities nature of encrypted assets, and the CFTC is Regulate transactions such as encrypted derivatives contracts. In addition, ESMA, the European Union's financial market regulator, has also begun to explore the regulatory framework of the encryption market, aiming to ensure the transparency and stability of the encryption market.
Examples of these regulators in recent years include:
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) announced in July 2020 that Coinbase and other crypto exchanges can register as brokers and exchanges and provide market maker services for digital assets on their trading platforms. This shows that the SEC has begun to explore the regulation of encrypted market makers.
The Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) released a cryptocurrency management guide in 2019, which mentioned how crypto traders and market makers should comply and need to apply for a license to engage in these activities. This shows that FINMA has begun to regulate crypto market makers.
The Singapore Stock Exchange (SGX) launched SGX iSTOX, a digital currency trading platform, in 2020 and has developed a regulatory framework with market makers to ensure its compliance and transparency. This shows that SGX has begun to explore the supervision of encrypted market makers and has begun to cooperate with market makers.
These cases show that regulators have begun to explore the regulation of encrypted market makers and have developed some relevant guidelines and regulatory frameworks. With the continuous development of the encryption market in the future, it will become increasingly important for regulators to supervise encrypted market makers.
In terms of compliance, encrypted market makers also need to comply with various regulations, which vary from country to country, but some common compliance requirements include:
KYC (Know Your Customer): Market makers need to comply with KYC regulations, ensuring that customers’ identities are verified and recorded.
AML (Anti-Money Laundering): Market makers need to comply with AML regulations to prevent cryptocurrencies from being used for money laundering and other illegal activities.
Transaction transparency: Market makers need to provide transaction transparency, including public transaction data, market depth and other information, to ensure fair and transparent transactions.
In addition, some countries or regions may have other regulatory requirements, such as regulations in the fields of taxation, securities or futures, etc.
secondary title
3.2 Market risk
Market makers face multiple risks in the crypto market, including:
Liquidity risk: Market makers need to provide liquidity to support market transactions, but if there is a large number of sellers or buyers in the market, it may be difficult for market makers to provide sufficient liquidity in a timely manner, resulting in transaction delays or failures.
Counterparty risk: Due to the anonymity and decentralization of the cryptocurrency market, market makers may not be able to determine the credit status and transaction intentions of their counterparties, thus facing counterparty risk, that is, market makers cannot honor their counterparty's transactions.
Risk of market-making funds: Market-making funds are similar to traditional financial market-making. To put it bluntly, the scale of market-making funds and the efficiency of capital circulation determine the level of market makers. Especially when it comes to deposit and withdrawal, it is the first threshold for market making. The market-making team generally opens accounts with Silvergate bank and Signature bank. But the two crypto-friendly banks have recently faced bankruptcy, and many funds cannot be withdrawn. This increases the threshold for future institutions to enter the encryption field.
In order to deal with the above risks, each market maker will have a certain strategy, for example, in an extremely volatile market, they are more inclined to withdraw. Or use a risk hedging strategy to preserve the value of the position, and transfer the risk to the asset based on the inventory model and information model.
secondary title
3.3 On-chain and off-chain risks
Off-chain risks are generally transaction risks, such as the integrity of historical data, flaws in strategy model design, system failure, lack of risk control, overfitting, and transaction cost sensitivity risks.
Pricing risk: It determines whether the market maker can provide an attractive price, and whether the pricing is correct or not is directly related to the profit and loss of the market maker.
Inventory risk with huge fluctuations in asset prices: If the price of the underlying asset develops in a unilateral direction, for example, in an upward trend, if the sell order is completed and the buy order is not executed, you will bear the risk of an increase in the selling price. In a downtrend, if the sell order is not fully completed after the buy order is completed, you will bear the risk of the purchase price falling.
Trading platform risk: There are also many types of trading platform risks.
The frequency and quantity of buying and selling orders are random, which may cause the risk that the buying order has not been fully completed after the selling order is completed.
API risk: This includes internal leak issues, API outages, etc.
The source of risk in the encryption market is not only the risk brought by off-chain transactions, but more possible risks come from the chain. First of all, if there are loopholes in the smart contract of the market-making token and it is attacked by hackers, it will cause losses to the stock assets of the market maker. Secondly, encrypted market makers may need to participate in on-chain protocols, DeFi applications, etc. to provide liquidity, and all risks on the chain will be transmitted to every participant. For example, there is a fork in the public chain where the protocol is located or the speed of transactions on the chain slows down.
secondary title
3.4 Risk Management
In order to control the above possible risks, the market maker will also set strict strategies and disciplines.
Focus on deal quality over quantity
Although market makers can obtain certain commissions by providing liquidity for exchanges, excessive trading often wastes more time and money. Therefore, the key to effective trading is to choose the quality of transactions rather than the quantity of transactions. This is reflected in three aspects: (1) choose a good asset target; (2) choose a reputable exchange; (3) analyze the market and determine an appropriate trading strategy.
Build a good cooperative relationship
Market makers need to establish good cooperative relationships with exchanges, project parties, investors, etc. to obtain more information and support and reduce their own risks.
strict discipline
This includes exit mechanisms and not using excessive leverage. Market makers need to control their own risk exposure and diversify risks as much as possible.
Inventory Risk Management
Maintain a proper position of inventory in continuous buying and selling. Inventory risk and its management promote the trading enthusiasm of market makers and are also the main reason for certain impact on market prices.
Use price change leverage to enable inventory to meet its continuous transaction and cost reduction requirements.
monitor the market
Market makers need to constantly monitor changes in market liquidity, including market depth, trading volume, transaction counterparty and other indicators, and adjust their quotation strategies in a timely manner to ensure that there is sufficient liquidity support in the market.
4. Typical case analysis of encrypted market makers
In recent years, with the continuous development of the cryptocurrency market, crypto market maker companies have gradually emerged. These companies are committed to providing services such as liquidity management, price discovery and transaction matching to meet the growing demand for cryptocurrency trading. At present, many professional crypto market maker companies have emerged around the world. They use various efficient technologies and strategies to provide market participants with diversified trading services, and promote the further development and maturity of the cryptocurrency market. Since the encryption market still has a big gap with traditional finance, it is easier for market makers to form a monopoly, and the liquidity of cryptocurrencies is dominated by several large market makers. This includes Jump, Wintermute, Amber Group, B2C 2, DRW Trading.
secondary title
Alameda Research was founded in 2018 and is headquartered in California, USA. The company was founded by mathematician Samuel Bankman-Fried. Samuel Bankman-Fried worked at Jane Street, where he gained extensive quantitative trading experience. In addition to market making and quantitative trading in the crypto market, the company has also developed some cryptocurrency trading tools and infrastructure, such as the crypto exchange FTX and the crypto trading protocol Serum on the Solana blockchain.
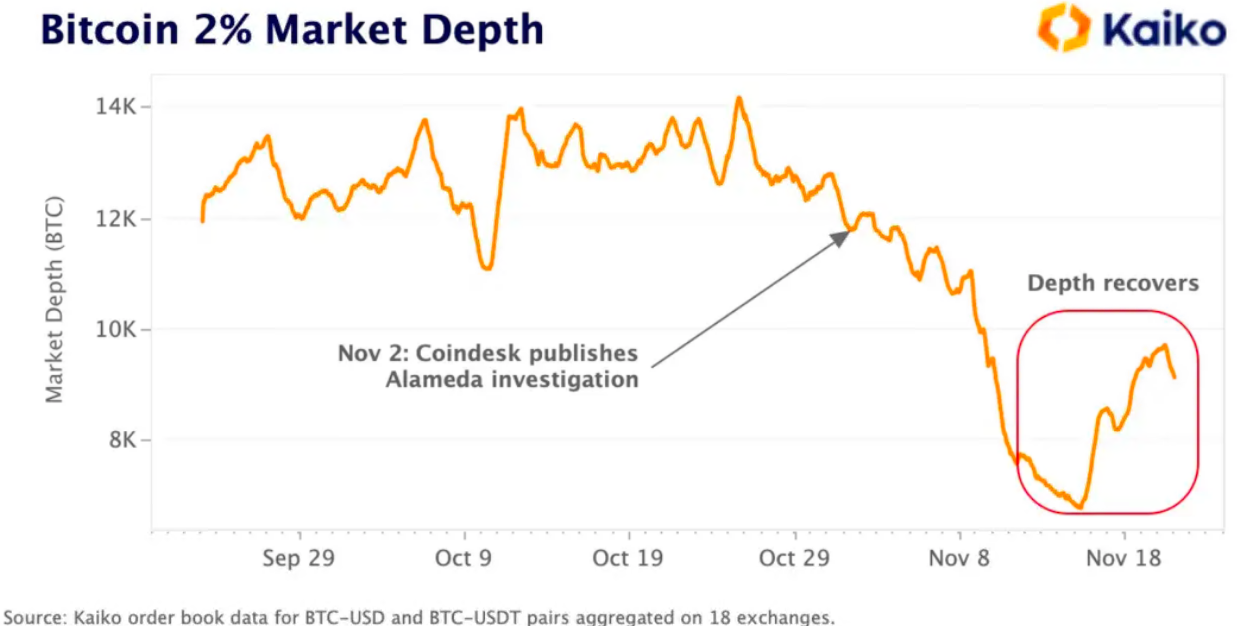
image description
Figure 6. Kaiko BTC exchange liquidity
secondary title
4.2 Wintermute and DeFi hacking incidents
CEO: Evgeny Gaevoy, who was previously in charge of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) for the European market at Optiver;
CTO: Valentine Samko, who worked as a software engineer at trading firms and banks, including Barclays and JPMorgan.
image description
In addition to its business in the cryptocurrency market, Wintermute Trading is actively involved in promoting the development and regulation of the cryptocurrency market. The company is a member of the London Digital Asset Exchange Association (LSTA) and a member of the Association of Digital Asset Dealers (ADAM). In February 2021, Wintermute announced the completion of a $25 million financing round, with investors including Lightspeed Venture Partners and Pantera Capital, among others. But Wintermute's 2022 revenue will be around $300 million, down from $1 billion in 2021, thanks to the bear market and hacking.
4.3 GSR Market
secondary title
Features:
GSR Markets is fundamentally an algorithmic digital trading company belonging to Hong Kong. It leverages its software to provide liquidity for order execution solutions for several digital asset classes. The company deploys multiple trading models, integrates with more than 30 liquidity pools, and its trading fees are relatively low in the market.
Features:
First-class leadership and a strong team of technical and financial practitioners from world-class financial institutions.
Its proprietary trading technology can be modified according to trading needs. Its sales and aggregation strategies are adjusted for real-time liquidity and volatility, allowing investors to truly get the best prices.
Recently, GSR has frequently cooperated with various project parties. Including Stargate, Stargate will provide GSR with European options on 8 million STGs, provided that the average STG price exceeds $1.15 after 24 months. After the proposal passed, STG surged 36.2% in the past 14 days.
first level title
5. Decentralized Market Maker
Anyone who participates in market making on the chain can become a decentralized market maker. There are three forms: (1) Liquidity providers participating in the decentralized exchange DEX, also known as mining, have a low threshold and anyone can Can participate, provide liquidity of trading pairs, and get certain rewards; (2) Participate in the decentralized derivatives market, similar to the dydx model; (3) Some DeFi protocols that specialize in market making, such as Elixir, these protocols have become CLOB And the liquidity allocation tool of the AMM model.
DEX generally adopts the automatic market maker algorithm AMM, and anyone can become a market maker. It uses an automated algorithm to balance the supply and demand of tokens in the trading pool. AMMs work by allowing liquidity providers to deposit tokens (usually equal amounts) into a liquidity pool. Then, the price of the tokens in the liquidity pool follows a formula, such as the constant product market maker algorithm x*y = k, where x and y are the number of two tokens in the pool, and k is a constant. This results in the proportion of tokens in the pool determining the price, ensuring that regardless of the transaction size, the pool can always provide liquidity, and that the amount of slippage is determined by the transaction size compared to the pool size. As the price in the liquidity pool deviates from the global market price, arbitrageurs will come in and push the price back to the global market price. Various protocols iterate on this basic AMM model or introduce new ones, such as Curve, Balancer, Uniswap V3, etc. providing improved performance and extending to derivatives.



