Original author: S Capital Research, published by Odaily with authorization
SCapital.fi is an anti-cyclical all-round blockchain investment fund. Its business covers bitcoin mining, venture capital in the primary market, and deeply participates in decentralized financial activities in the secondary market based on market/industry analysis.
Background
first level title
In traditional finance, fixed-rate loans are common, and commercial banks obtain lower financing costs through customer deposits. Borrowers obtain loans at higher financing costs in the form of mortgage assets to meet their needs for starting a business, housing loans, and car loans. In this mode, commercial banks take advantage of their brand and license monopoly to make borrowers pay higher financing costs and time costs in the loan application process. From the perspective of depositors, it is difficult for the income of deposits to outperform inflation. The risk management and control model of traditional finance leads to low overall efficiency."Billionaire investor Mark Cuban said of the growth of DeFi:"。
The basic benefit of DeFi is that it simplifies borrowing and lending for personal purposes, since borrowing money from banks is cumbersome
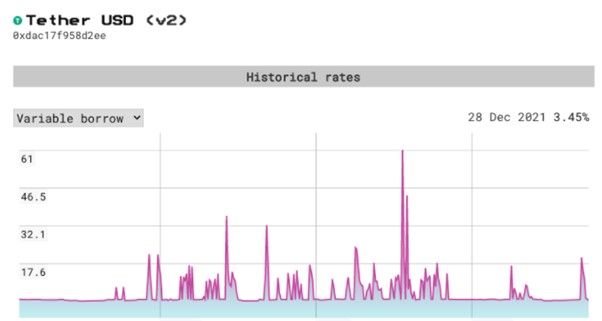
The current main mode of DeFi lending is a floating interest rate mechanism based on over-collateralization. The borrowing rate and deposit rate will fluctuate according to the needs of users. The more borrowable assets in the fund pool, the lower the general borrowing rate will be. The representative agreements for such products are Compound and AAVE. However, due to the high volatility of interest rates in DeFi, the risk of floating rate loans is high, making it impossible for cryptocurrency investors to manage funds in a predictable way for a long time. Taking AAVE as an example, from October 29 to 30, 2021, the USDT borrowing rate rose sharply from 3.73% to 61% within one day. From the perspective of the borrower, such a large fluctuation in floating interest rate is disastrous. Because borrowers often pledge high-quality assets in exchange for short-term liquidity when there is a lack of liquidity, they are usually unable to repay their debts in time when interest rates rise sharply, and can only bear unplanned high interest, or debt default discount auction mortgage Taste. From the perspective of the development of the DeFi Ecosystem, such high uncertainty in interest rates will inevitably hinder the development of the market on a larger scale, and the fixed-rate lending agreement can just fill this gap.
In fixed rate lending, the interest rate remains the same throughout the loan term. Since the interest rate is known to be pre-set, fixed-rate loans are less risky and can appeal to many broader, longer, and lower-risk use cases.
There are many ways to implement fixed interest rates, including basic fixed-rate lending agreements, principal-interest separation agreements, structured stratification (fixed-rate derivatives), and game-theoretic fixed-rate agreements. The first part will focus on the basic fixed rate lending agreement, dig out the basic mechanism of fixed rate realization, use cases, and comparative analysis.
first level title
Basic Fixed Rate Lending Agreement"A fundamental mechanism by which the underlying fixed-rate lending protocol achieves this goal is the". A bond is equivalent to a kind of IOU, on which the issuer will mark the interest payable before maturity, which can be used to buy a bond that is lower than the face value and does not need to pay interest. It is a zero-coupon bond. The logic is to use discounted bonds first. The person who sells and buys the bond will be repaid with the face value of the original price on the maturity date, and the price difference represents the interest, so a fixed interest rate acceptable to borrowers and depositors can be determined by balancing the supply and demand in the market . In the DeFi protocol, the zero-coupon bond model is usually to generate a property token with a bond function by collateralizing an asset. Users can trade, exchange, and build perpetual products for the bond token according to their needs. For short-term gains before the maturity date, representative projects include Notional Finance and Yield Protocol.
Notional Finance
Notional Finance is one of the first lending agreements on the Ethereum blockchain to provide fixed interest rate services, enabling cryptocurrency traders to deposit and lend digital assets at fixed interest rates, and the locked interest rates will not be fluctuated by market fluctuations.
Basic Mechanism
secondary title
fCash tokens are always created in pairs: assets and liabilities. Throughout the Notional system, assets and liabilities are always net zero. It is also well understood here that rights and obligations must be reciprocal.
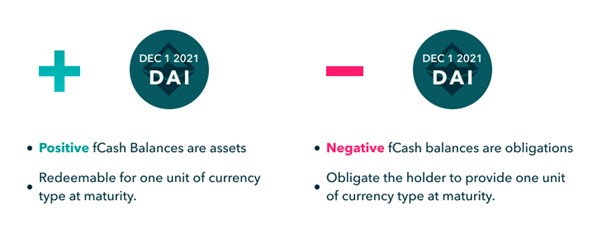
text
Quote Currency VS Settlement Currency
In Notional V2, the denomination currency of the fCash token is different from its settlement currency. fCash is denominated in basic tokens such as DAI or USDC, but it is settled in cTokens such as cDAI or cUSDC (cToken is the deposit certificate of Compound). For example, at maturity, 100 fDAI on December 1, 2021 cannot be directly redeemed for 100 DAI, but can be redeemed for cDAI worth 100 DAI, and then freely converted into DAI according to the user's wishes.
This is where the Notional ecosystem is cleverly designed. By separating the pricing currency from the settlement currency, cTokens (such as cDAI) are used to optimize Notional’s capital efficiency, while still enabling fixed-rate borrowing of basic tokens (such as DAI). This design has two main benefits.
From the depositor's point of view, since Notional's underlying asset is cToken, after the loan expires, the depositor will immediately stop earning fixed interest rates, and fCash will be automatically converted into Compound's cTokens to earn floating interest. In other words, this means that once a fixed-rate loan matures, even if it is not rolled over, it will start counting towards the variable cToken deposit rate.
text
settlement mechanism
At the maturity of the cash asset, Notional determines the number of cTokens equivalent to the denomination currency of the cash asset and converts the cash in the account into that amount of cTokens. For example, at expiration, 100 fDAI on December 1, 2021 will be converted to cDAI worth 100 DAI on December 1, 2021.
Mechanistically speaking, the settlement amount of cDAI is determined by the settlement exchange rate. The settlement rate is defined as the cDAI/DAI rate at maturity. The settlement rate is unknown before maturity, is set at maturity, and remains unchanged after maturity.
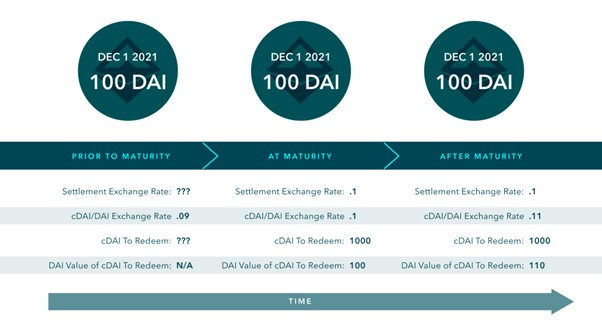
Here's how the value of 100 fDAI changes over time and with the cDAI/DAI exchange rate on December 1, 2021."cDAI to Redeem "have to be aware of is,"cDAI to Redeem "is set to the exact amount so that"cDAI to Redeem "The DAI value at maturity is equal to the face value of fCash. even though"cDAI to Redeem "The DAI value increases,
Remains unchanged after expiration. This reflects the fact that Notional's cash balances passively accrue cToken deposit rate yields.
After understanding the basic mechanism of Notional's underlying assets, let's dig deeper into how borrowers, depositors, and liquidity providers interact with the liquidity pool to achieve fixed-rate lending.
Liquidity Pool and nToken
However, it needs to be emphasized that since depositors and borrowers are unlikely to deposit and borrow at the same time, the counterparties of depositors and borrowers are Liquidity Pool, and these liquidity providers ensure that at any time Both cash and fCash are available to depositors or borrowers and receive transaction fees in return. Therefore, we need to first understand how the Liquidity Pool is established, because if there are no LPs injecting funds into the pool, there will be no fixed-rate lending.

Notional offers fCash transactions in its built-in AMM-enabled liquidity pool. Notional liquidity pools hold fCash and its settlement currency (e.g., cDai and fDai together).
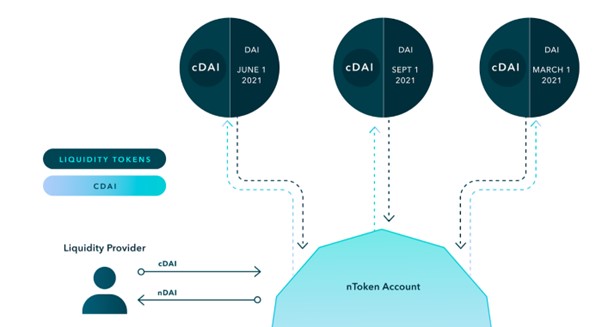
Liquidity providers provide cTokens for Notional's liquidity pool and get nTokens as certificates, which have no expiration date and can be redeemed at any time. nTokens are ERC-20 assets that represent Notional's share of the total liquidity of a specific currency. nTokens enable LPs to passively provide liquidity to all active liquidity pools of a specific currency simultaneously without interacting with the underlying liquidity pool in any way. The system will automatically distribute centralized liquidity to each pool, and the distribution ratio is determined by community governance to maximize the efficiency of capital use.
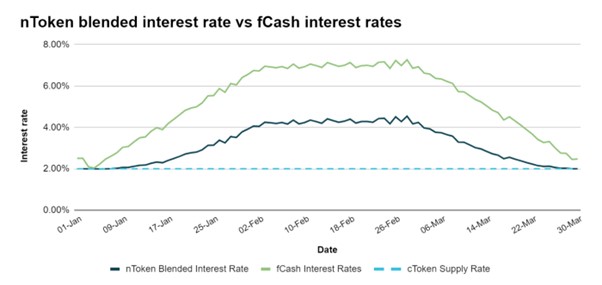
Part of the deposited cToken will be used to purchase fCash. Therefore, the liquidity pool is composed of cToken and fCash, and the mixed interest rate income of nToken will be between the deposit rate of fCash and Compound.
Although the returns obtained by liquidity providers are lower than the fCash interest rate, the purpose of LP is never to obtain fixed returns, so the protocol has the following ways to reward liquidity providers."Transaction fees generated for each deposit and borrow, fCash interest, base money market interest as a passive depositor of Compound, and rewards from the community governance token NOTE. The first three return sources are included"variable rate
In APY. Variable APY is usually maintained at around 0.5%, but there are extreme cases where negative values can appear. For example, when there is a lack of borrowers (a large number of depositors), LP becomes a borrower and needs to pay the interest due. A negative value means that the transaction fee plus Compound’s income is not enough to cover the interest generated by LP’s borrowing behavior. When there is a shortage of depositors (a large number of borrowers), LP becomes a depositor and will receive interest when it matures, thereby increasing the variable APY.
Initial Status
Let's illustrate with an example:
Scenario 1
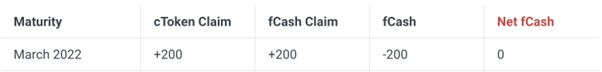
Assuming that the liquidity pool is in the initial state in March 2022, let's break down the nTokens into their underlying claims. For simplicity, assume that each nToken has a claim on 1 cToken and 1 fCash. At present, the lending behavior is maintained in a balanced state, and the net cash position of fCash is 0 at this time.
Scenario 2

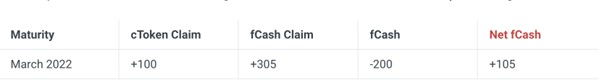
Consider the first user as the borrower, borrowing 100 cTokens from the March 2022 maturity date in exchange for 105 fCash. At this time, the liquidity pool cToken Claim drops to 100, and the fCash Claim increases to 305. So now nToken has a net cash position of +105 at the expiry date of March 2022. In other words, nToken (liquidity provider) is now a net depositor for this period and will receive interest when it expires.
The second user chooses to deposit 200 cTokens for the same term as the depositor in exchange for purchasing 208 fCash. At this time, the liquidity pool cToken Claim increased to 300, and the fCash Claim dropped to 97. So now nToken has a net cash position of -103 on its March 2022 expiry date. In other words, nTokens (liquidity providers) are now net borrowers for this term. The variable APY will be negative if the negative fCash expires with more interest than transaction fees plus Compound’s yield.
nToken's net cash position reflects the aggregate activity of all end users on Notional. When nToken has a large net cash position, it means that the activities of end users have been tilted in one direction. A large net cash position also affects the slippage users experience when redeeming their nTokens.
After understanding the basic operating mechanism of all the above liquidity pools and underlying assets, it will be easier to understand fixed-rate borrowing and deposits.
first level title
Fixed Rate Deposit Borrowing Facility
Depositors lock in an interest rate by purchasing discounted fCash, which represents the amount they are entitled to in the relevant base currency at maturity. Borrowers mint fCash with excess collateral, and sell fCash to obtain the base currency in exchange for the obligation to repay at a specific time in the future.
Fixed-rate deposit: The depositor pays Dai to the liquidity pool, and the system will automatically deposit the Dai into Compound in exchange for cDai, and then purchase the discounted zero-coupon bond fDai in the liquidity pool. The difference between the Dai paid by the depositor during the transaction and the fDai that can be obtained in its base currency when it matures is the fixed deposit interest obtained by the depositor.
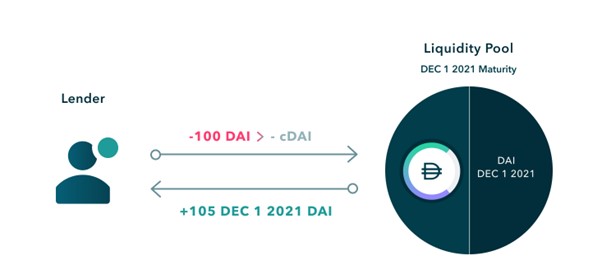

In the example below, a depositor wishes to lend 100 DAI to Notional at a fixed rate for one year. Depositors first convert their 100 DAI to cDAI, then deposit the cDAI into the Notional liquidity pool in exchange for 105 fDAI. When the loan matures on December 1, 2021, depositors can redeem their 105 fDAI for cDAI, and then convert the cDai into 105 DAI.
Fixed-rate loan: After over-mortgaging ETH, the borrower can mint a certain amount of fDai, which will be sold into cDai by the system, and finally retrieved from Compound to realize fixed-rate borrowing. The borrower receives during the transaction The difference between Dai and minted fDai is the fixed loan interest that the borrower needs to pay when it matures.

In the following example, the borrower first deposits an ETH into Notional:

Borrowers then mint a pair of fCash tokens on their chosen December 1, 2021 maturity date.
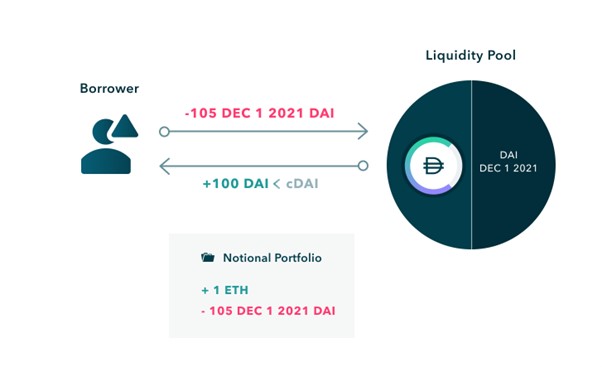
Borrowers can now sell positive fCash tokens into their liquidity pools in exchange for the base currency.

Liquidation
Now, the borrower obtains the loan by mortgaging the asset, as well as the obligation to repay the loan in the future (the collateral cannot be retrieved before the loan is returned). The difference between the repayment amount due and the borrowed amount is the fixed interest that the borrower needs to pay.
Roll over
When the price of collateral changes, the mortgage rate of the borrower also changes. For example, the minimum mortgage rate for borrowing USDC with ETH as collateral is 145%. If the mortgage rate falls below 145%, the borrower's collateral will start to be liquidated by the system. During liquidation, the liquidator buys part of the collateral of an account at a discount to the price of the oracle machine on the chain, and repays part of the debt of the account being liquidated. The liquidator can purchase at least 40% of the collateral of the account.
Notional AMM
If the borrower does not liquidate within the time limit, but fails to repay the debt owed to the agreement on the due date, the borrower will be forced to transfer automatically by a third party at a penalty interest rate. The penalty rate is currently set at 250 basis points (2.5%). For example, if the previous borrowing rate was 6%, the new rate will be 8.5% until the borrower repays the debt. The borrower can also roll over the debt to future maturities at the prevailing interest rate for that term. This means that the borrower can choose not to pay off the debt first, but roll over the debt to the nearest maturity date, and the borrower can repay the debt on the next maturity date.
Price of Zero Coupon Bond = Maturity Value / ( 1 + r)^n
The fCash designed by Notional is essentially a zero-coupon bond, and a very important feature of zero-coupon bonds is that the value will change over time:

As can be seen from the above formula, although the interest rate remains constant during the period, the price of the zero-coupon bond will also change over time. The closer to the maturity date, the closer the bond's price will be to the face value, and eventually the exchange rate between the two will tend to 1. From another point of view, if we use Uniswap's x×y=k as the AMM curve, if no one has any transactions during the period, the state of the fund pool remains unchanged, and the price of the zero-coupon bond will also remain unchanged. As the expiration date approaches, APY will show exponential growth, attracting people to arbitrage and causing liquidity providers to suffer impermanent losses.
Therefore, the AMM that does not consider the time variable is no longer effective in pricing fCash in the secondary market. We need a curve that can automatically change the quotation, so that the price of the zero-coupon bond is more sensitive to changes in time and interest rates from the beginning, and It can change according to market conditions. When the maturity date is approaching, the market price will continue to converge to the face value.
Notional AMM is composed of three variables - Scalar, Anchor, Liquidity fee
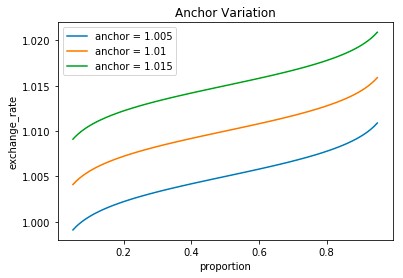
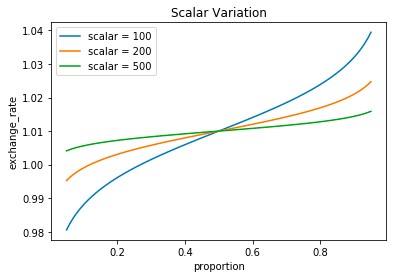
Scalar and Anchor allow changing the steepness of the curve and its position in the xy plane, respectively. The parameter Scalar represents the sensitivity of price to demand. As the maturity date approaches, the curve will become smoother, so that liquidity will be concentrated on the price riveted by the parameter Anchor. Increasing the Scalar value will flatten the curve, decreasing the Scalar value will make it steeper. This means that the larger the Scalar value, the less sensitive the curve is and the less slippage there will be on a given trade. Conversely, a smaller Scalar value will result in a more sensitive curve, and more slippage on a given trade. Changing the Anchor can move the curve up and down on the XY plane. The design concept of Anchor is that when the price does not change, Anchor can keep the interest rate constant and prevent time changes from affecting the interest rate.
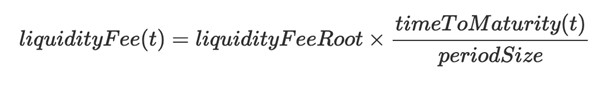
Therefore, we can get the pricing formula of Notional AMM by combining the above three parameters:

Yield Protocol
secondary title
Basic Mechanism
The basic mechanism of Yield is similar and different from Notional. Yield allows the borrower to mortgage an asset to mint fytokens. The fytokens here are equivalent to zero-coupon bonds, which do not pay interest themselves. The interest is determined by the difference between the face value of the token and the price paid. If it is used as the collateral of the borrowing position When the value is lower than the debt value * mortgage rate, the position will be auctioned and liquidated. Therefore, the entire Yield ecosystem revolves around fytokens, which serve as fixed interest rates for user loans in the form of zero-coupon bonds.
The fixed rate deposit and borrowing mechanisms are as follows:
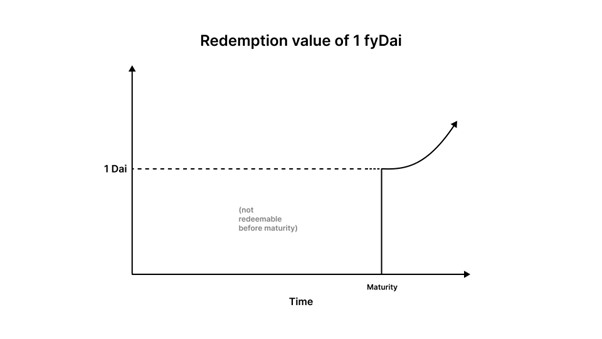
Fixed-rate deposits: Depositors now buy zero-coupon bonds fydai at a discount and redeem them after the maturity date to obtain fixed interest, where the difference between Dai and fDai is the interest. If the depositor does not redeem fydai at maturity, he will start earning Compound's cDai floating interest rate from fyDai until he decides to redeem it for Dai.
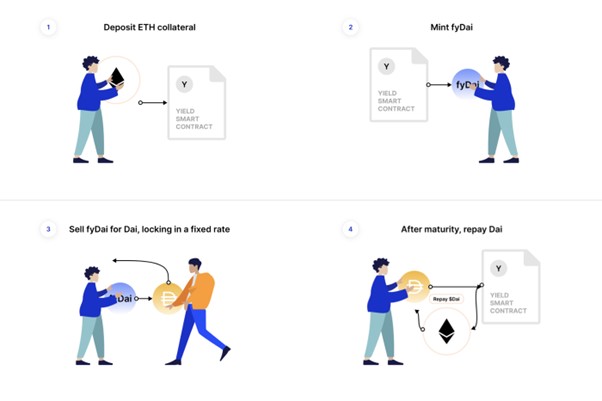
Fixed-rate borrowing: users first deposit collateral such as ETH to mint fyDai, and then sell it into Dai. Since fyDai is discounted, the amount of Dai they get will be reduced, and the difference between the two is the user's borrowing cost.
Liquidity Position Management
Yield Space(AMM)
Since each tranche of the zero-coupon bond has a different maturity date and price, trading in each tranche requires a separate liquidity pool. Currently, the term of the yield-per-tranche agreement is 6 months. In order to eliminate the need for liquidity providers to frequently adjust their positions, the liquidity will automatically roll to the latest period after expiration, so that liquidity providers can continue to earn fees without paying additional gas fees.
Like Notional’s fCash mentioned earlier, fyTokens can be traded using existing DEXs such as Uniswap, but the AMMs of these protocols are not optimized for fyTokens, ignoring the time variable that may cause arbitrage losses to the liquidity pool. Therefore, Yield protocol has innovated an AMM mechanism that considers time variables to support the pool's capital flow, aiming to realize effective transactions between fyTokens and its underlying assets. The automatic liquidity market maker agreement is called Yieldspace.
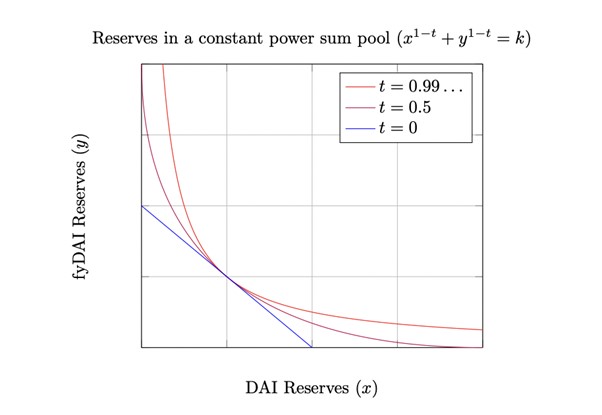
x^( 1 −t) + y^( 1 −t) = k
Where:
The Yield protocol adds a time variable constant power sum formula:
y represents the reserve of fyToken
x represents the reserve of the target token
When t=1, its formula is equivalent to the constant product formula used by uniswap, and when t=0, the constant power sum consensus is equivalent to the constant sum formula that provides tokens at a price of 1:1. The characteristic is that the marginal interest rate provided by the fund pool at any time = the interest rate of fyDai reserves and Dai minus 1.
r=y/x-1
text
Like other automated liquidity providers, users can choose to provide liquidity to the YieldSpace pool to earn fees on future trades. YieldSpace uses a custom fee model optimized for fyTokens. Instead of charging a percentage of the asset amount bought or sold, YieldSpace charges a fee that is a percentage of the interest rate and time to maturity. This fee model ensures that fees never result in unreasonable rates of interest paid by borrowers (fyToken sellers) and unreasonable amounts earned by lenders (fyToken buyers).
Notional Finance VS Yield Protocol
secondary title
data analysis
Notional Finance's current TVL is about US$60 million, much higher than Yield Protocol's US$8 million. A higher locked position means more market recognition, lower transaction slippage, and a more reasonable market interest rate level. Notional's cumulative lending activity amounted to $688 Million.
Mechanism angle
The significant difference between Notional Finance and Yield Protocol is that the underlying asset of the Notional ecosystem is cToken, which is the deposit certificate of Compound, and the liquidity pool for trading zero-interest tokens is fCash/cToken, so the funds stored in the liquidity pool Interest can be generated at any time, improving the efficiency of liquidity providers' fund use.
Yield uses its own improved version of the AMM called YieldSpace to manage slippage, while Notional uses a proprietary algorithm composed of dynamic sensitive curves to construct a zero-coupon bond liquidity pool price change through three parameters. Both mechanisms solve the following three problems to a certain extent.
1. As the maturity date approaches, the system will automatically adjust the price, keeping the interest rate unchanged even though no one is trading.
2. As the expiration date approaches, the price curve needs to become smoother, making changes in inventory less sensitive to price.
3. The handling fee cannot be charged at a fixed rate and needs to be reduced as the due date approaches."Both AMMs have their own advantages and disadvantages, and it is difficult to comprehensively judge which one performs better in controlling slippage and impermanent loss from a mechanism perspective. In Uniswap, as long as the price changes, there will be arbitrage transactions, while the arbitrage transactions in YieldSpace Pool will only occur when the interest rate changes, which can only reduce the LP’s suffering to a certain extent."。
impermanent loss
Notional's solution is to use three parameters to control the variables separately, but the disadvantage is that the parameters need to be adjusted frequently to achieve a constant interest rate, and there is a certain lag in the effect. Notional uses the last transaction rate to reflect the implied rate of the last executed transaction on the liquidity pool. The last deal rate can be manipulated for short periods of time (e.g. via flash loans) to display a rate that does not reflect the true or equilibrium rate of the liquidity pool at a particular time. Although in order to offset the drift of the implied interest rate, the Anchor parameter is used to ensure the consistency of the interest rate in the absence of any transaction, but the implied interest rate is frequently updated every time a transaction is generated.
Governance perspective
The Yield protocol believes in the three principles of decentralization, anti-censorship and security, so Yield does not have any governance tokens. Once the protocol is formulated, the developers will be removed. The Yield protocol runs automatically, and no one has management authority. And Notional has its own governance token NOTE. NOTE holders can propose, vote, and implement modifications to Notional system parameters and smart contracts. Each NOTE holder gets a voting right in each NOTE they hold . From a governance point of view, Notional’s development ceiling will be higher than Yield’s. The role of the underlying fixed-rate lending agreement is not simply to solve the problem of fixed-rate lending. The zero-coupon bonds involved will be combined with other derivative contracts in the future. Building a more versatile portfolio solution is driven by community member voting, decision-making and shared governance.
User Experience Perspective
At present, the loan period of Notional Finance is maintained at a period of 3 months, and the longest period is 1 year. The Yield Protocol is a half-year cycle. From the perspective of LP, both agreements support automatic extension upon expiration, and can continue to earn variable income, with little impact.
From the product interface, Notional Finance has a clear interest rate term structure (Term Structure), which is convenient for users to intuitively compare long-term interest rates and short-term interest rates and match their own needs to make investment decisions.


