This article clarifies the debate on the definition of NFT in the course of historical development
Original compilation: Aididiao
Original compilation: Aididiao
The three-letter acronym NFT is believed to be familiar to most people, but even experienced players in the encryption industry cannot give a clear definition of NFT. Everyone may know that the abbreviation of NFT is "Non-Fungible Token", that is, non-homogeneous tokens, but what it really means, there are actually many controversies and discussions. For example, is NFT just a data credential? Is it a real work of art? What is the meaning of non-homogenization? What is a token...
In fact, digital art already existed before NFT became popular. Early digital art usually represents some pioneering achievements of creators, so it has a certain collection value. So early digital art is NFT?
This article will discuss the debate over the definition of NFT and the meaning of "non-fungible" and "token" in the course of historical development. Before getting into the topic, first understand what unique functions NFT has.
Significance of NFTs
What changes does NFT bring to the field of digital art?
Digital art existed before NFTs, and even encrypted artwork predated NFTs for a while. But they've never attracted as many collectors as NFTs.
image description
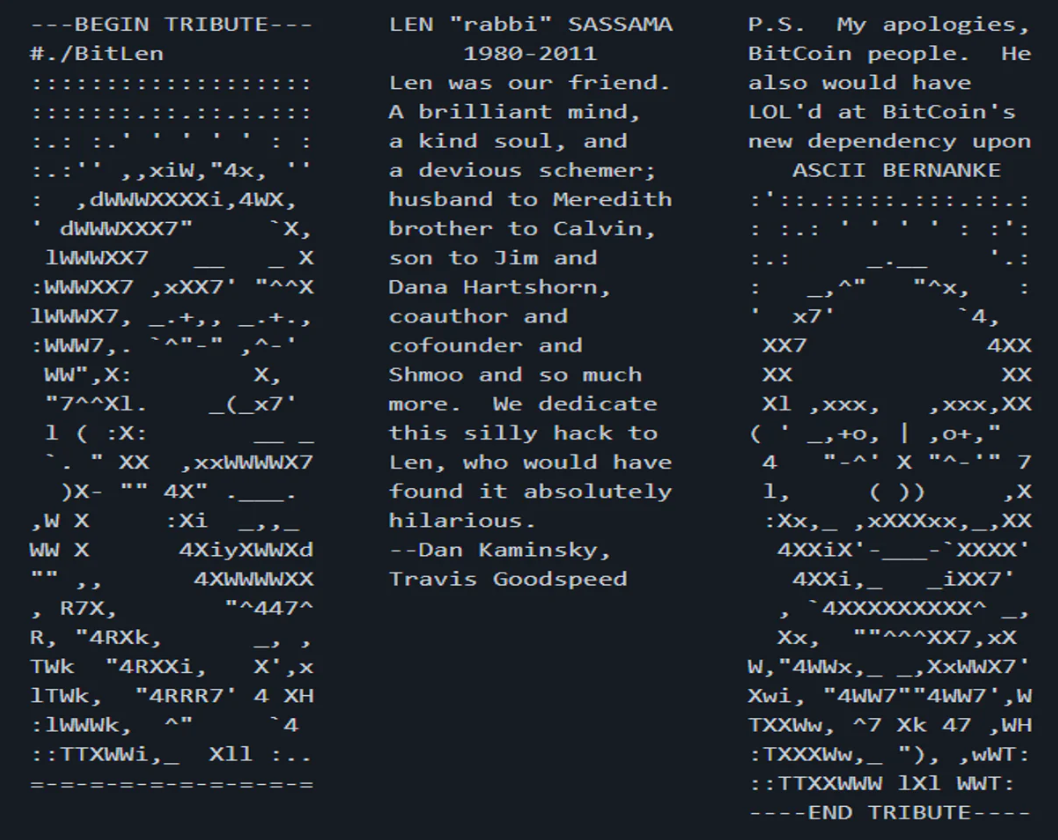
BitLen ASCII
"BitLen ASCII" is a memorable work of art in the history of the blockchain, which remains permanently on the blockchain for all to see. But let's go back to the original question: Why are NFTs more popular than early encrypted artwork?
Image Source
"Token" is an abstract term that doesn't actually exist, just a shorthand way of calling a code that identifies an ownable asset. Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, satisfy the innate human desire to own something unique, but the definition of "non-fungible" is widely divided.
Discussion on "non-homogeneity"
semi-homogenization
In some Discord server chats, people will object to calling some famous digital art NFT, such as Rare Pepes, Curio Cards or JakNFT, etc., because they are semi-homogeneous. Different versions of the same digital art token can be exchanged equally without any loss of value, but they are different from fully fungible tokens because they are irreplaceable in different digital art collections.
Undoubtedly, these can be called decentralized digital collections, but if we want to call it NFT, then we must give NFT a clear interpretation, that is, what unique significance NFT has for artists and collectors.
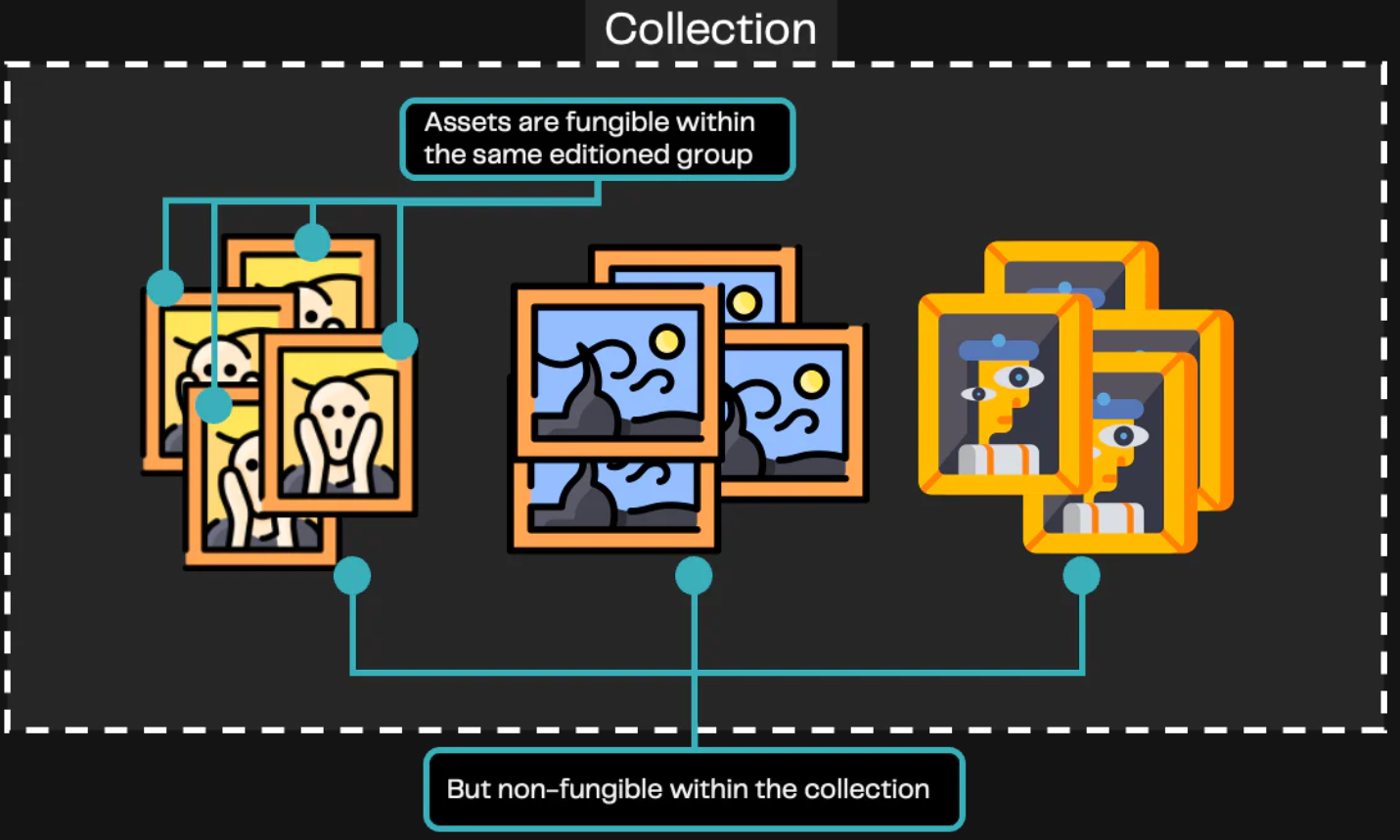
Homogenization
Fungible tokens are fungible with each other, and some are created for completely fungible purposes, e.g. most investors trade crypto assets that are fungible. On the other hand, some homogeneous tokens still have certain collection value and exist on the decentralized network. Homogeneous tokens with collection value will also claim to be NFT, but they have been opposed by doubters. So the question becomes what is "collection value"? We try to understand it from the point of view of some collectors.
Rare assets have collection value. Assets may have certain characteristics when they are issued and become scarce, or they may symbolize a certain milestone event on the timeline. For example, in 2014 Dogeparty issued JOLLYROGER, which is a Dogeparty token with an image attached to it. Although each token is fungible in JOLLYROGER, since it is issued with an image, it is JOLLYROGERIt has collection value in the process of creation. famous crypto artist Rhea Myers Created in 2014MYSOULConcept artwork, MYSOUL Although there is no attached image, it is possessable and tradable making it collectible. Also the XCPinata asset on Counterparty has artistic value, and while the actual image was attached at a later date, the original creative intent makes it an important collectible.
There are some encrypted assets that did not have unique collectible value when they were created, but now retroactively have special commemorative value, such as the first Counterparty token in 2014TEST, and the supply is only 400. Because the initial release of TESR led to the rise of the encrypted art movement (Rare Pepes), and the scarcity of TESR itself, it now appears that it has certain collectible value.
Are bitcoins mined in early blocks collectible? They have no image and are not scarce, the only thing that makes them different is the UTXO mechanism that defines where each blockchain transaction starts and ends. It is precisely because of this traceability and uniqueness that the bitcoins mined in the early days have collection value. Created by Casey Rodarmorordinalsimage description
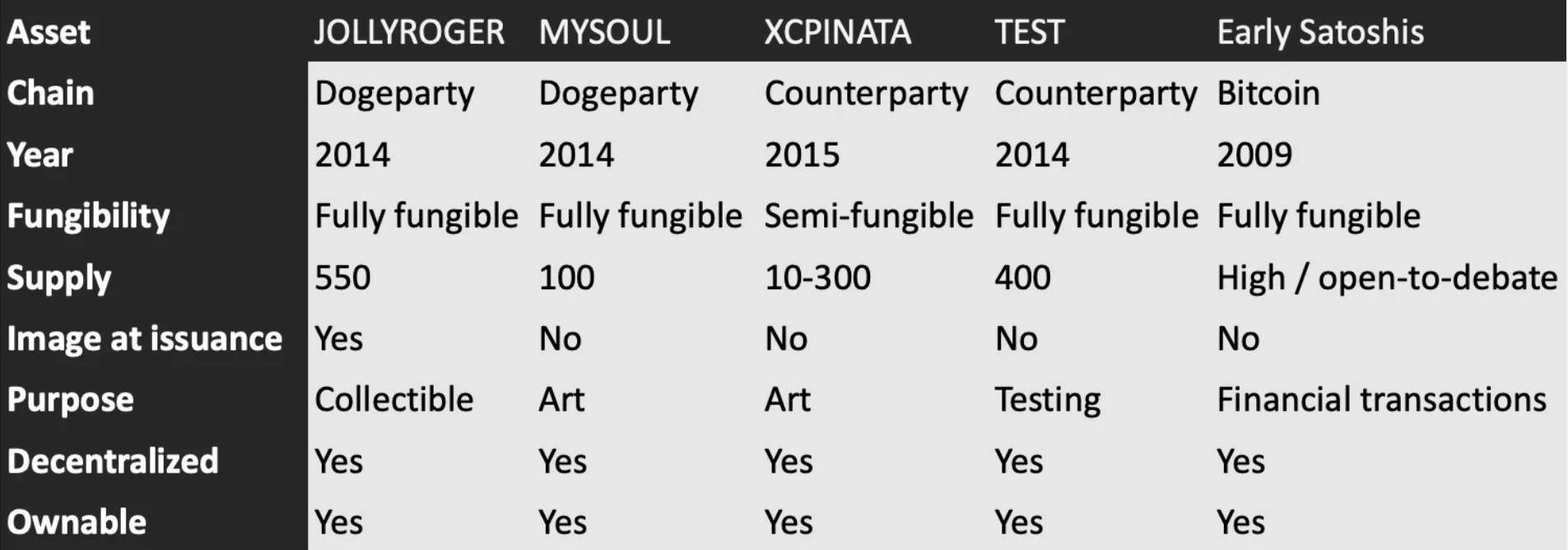
Some semi-fungible and fungible tokens with collectible value
Namecoin NFT
The debate over Namecoin NFTs has centered on the ownership of the "token".
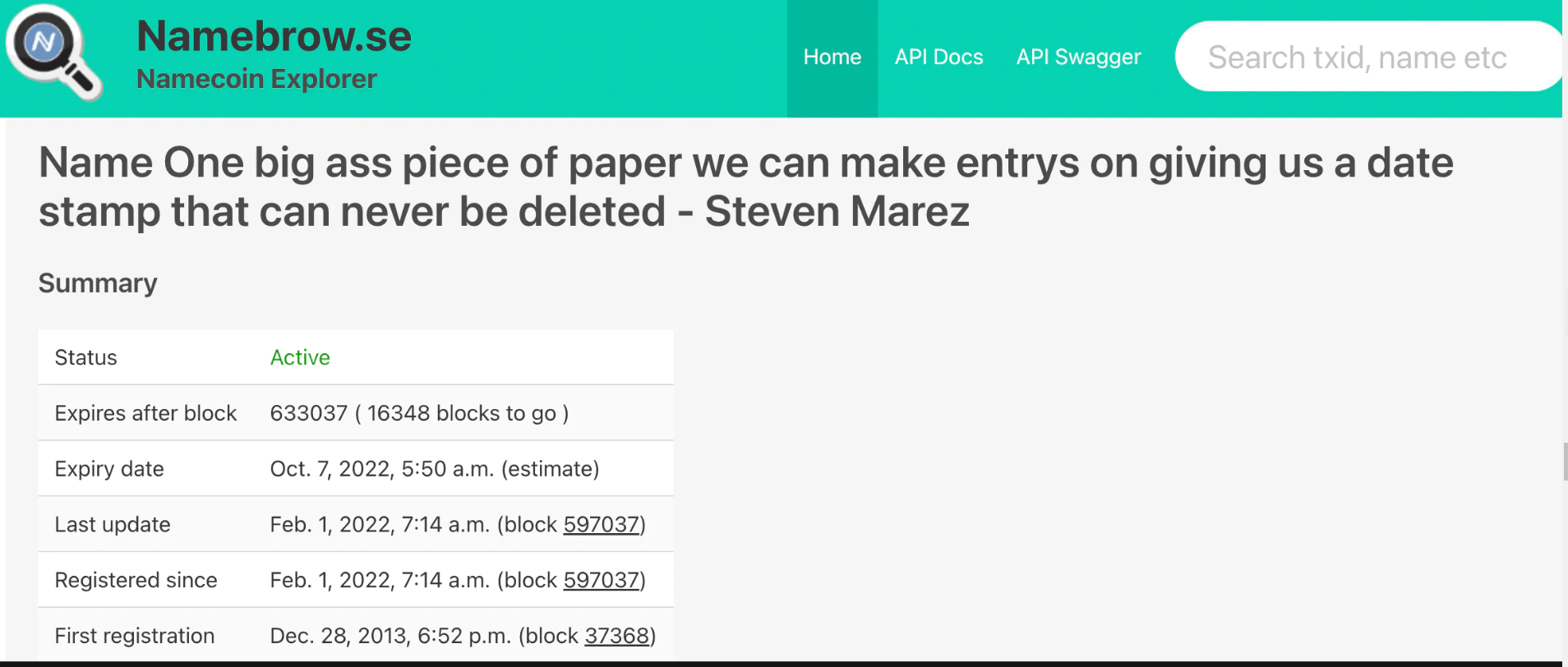
The earliest NFT is the Namecoin NFT. The domain name whose text content is "d/bitcoin" minted on April 21, 2011 became the first NFT. There is no concrete debate that Namecoin assets are non-fungible, ownable, transferable tokens. Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin mentioned Namecoin NFT on the first page of the Ethereum white paper. He used "non-fungible assets" in the white paper, and the term NFT officially appeared in 2017.
Namecoin NFT is the first NFT to be largely accepted, and more controversial is the setting of the expiration time: if the owner does not renew their domain name in time, it will expire after nine months.
Some argue that if holders have to renew their domains, it is more like a lease than a true transfer of ownership, defeating the original purpose of Web3.
This view is wrong because Namecoin NFTs provide holders with full ownership. Unlike renting, the decision to continue ownership is entirely up to the owner. The update is mainly for the maintenance of the network, which requires a very low fee paid to the miners, more like an infrastructure tax. As of this writing, 50-year renewals cost about $1.
The bigger problem about Namecoin NFT is the traceability issue. After the Namecoin NFT expires, it can be re-registered, so there will be a problem of changing the holder.
Technical Discussion on Namecoin NFT Traceability
What happens to Namecoin domains when domain ownership expires and is re-registered after a period of time?
When a domain name is registered for the first time, there will be a specific identifier UTXO, and the transaction history data of the domain name can be queried through the specific UTXO. UTXO is a special token, and this paper calls this special identifier "colored coin". When the domain name expires, the "colored coin" cannot be used, that is, it will be "burned". When the domain name is re-registered later, a new UTXO will be generated, which means that when the domain name expires, the unique identifier of the domain name will not be recognized. The domain name is unique, and all updates and transactions will be saved on the chain.
Editor's note: UTXO is a protocol for distributing bits of cryptocurrency data, which allows users to track and query ownership transactions of cryptocurrencies. A "colored coin" roughly describes a class of methods for representing and managing real-world assets on the Bitcoin blockchain, where the issuer of the asset promises that it can be redeemed for certain goods and services, thereby attaching displayed world value to the token superior.
image description
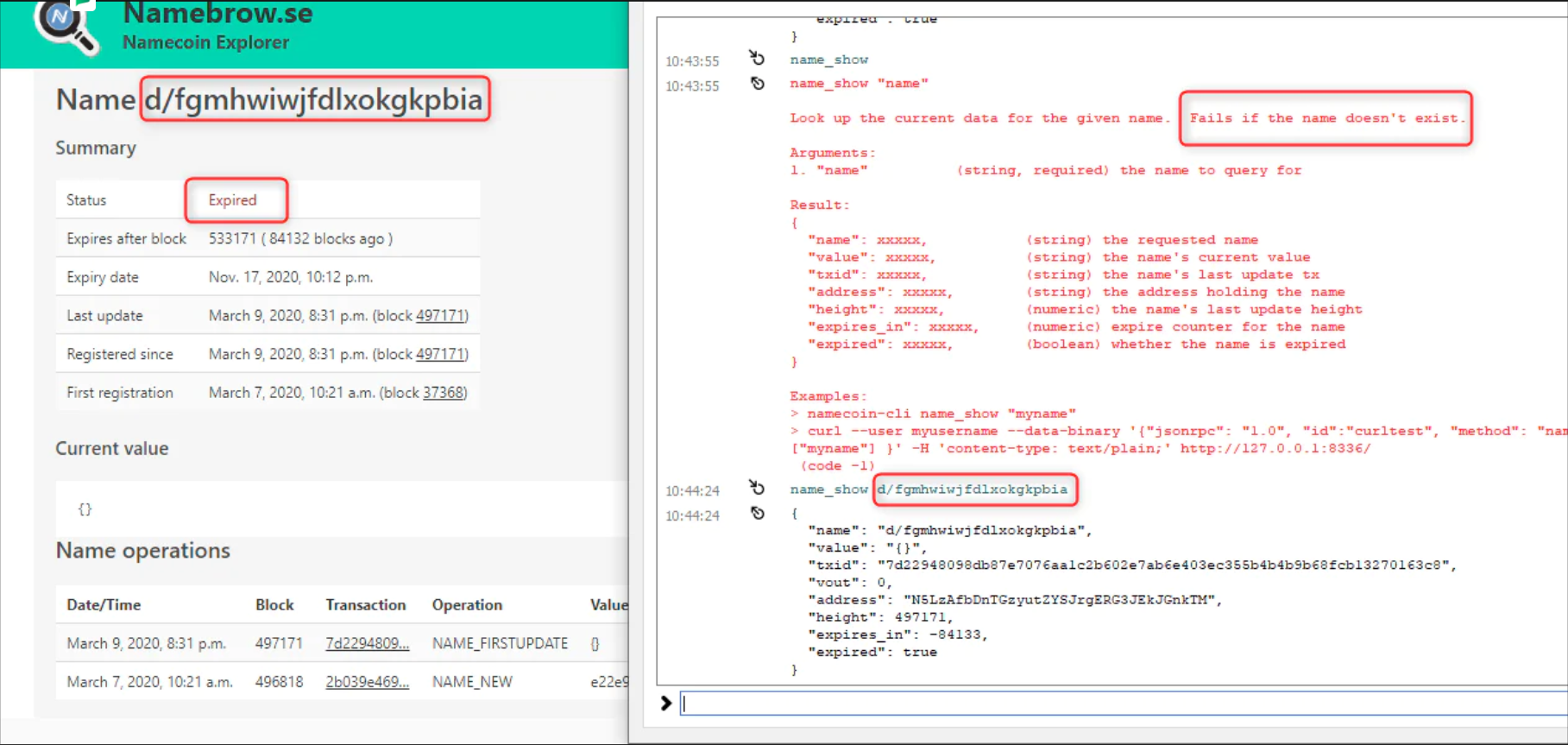
name_show function
In fact, the expired domain name can still work normally. When returning the local state name_show, it will indicate that it is in an expired state. If the resolver is reset, the domain name can still work. Also expired "id/" names in domain names can still be used as login names.
Another built-in RCP method is name_history, this function can extract all the original data and history of the domain name, this function shows that the domain name has traceability from the beginning of design.
Explanation of "token"
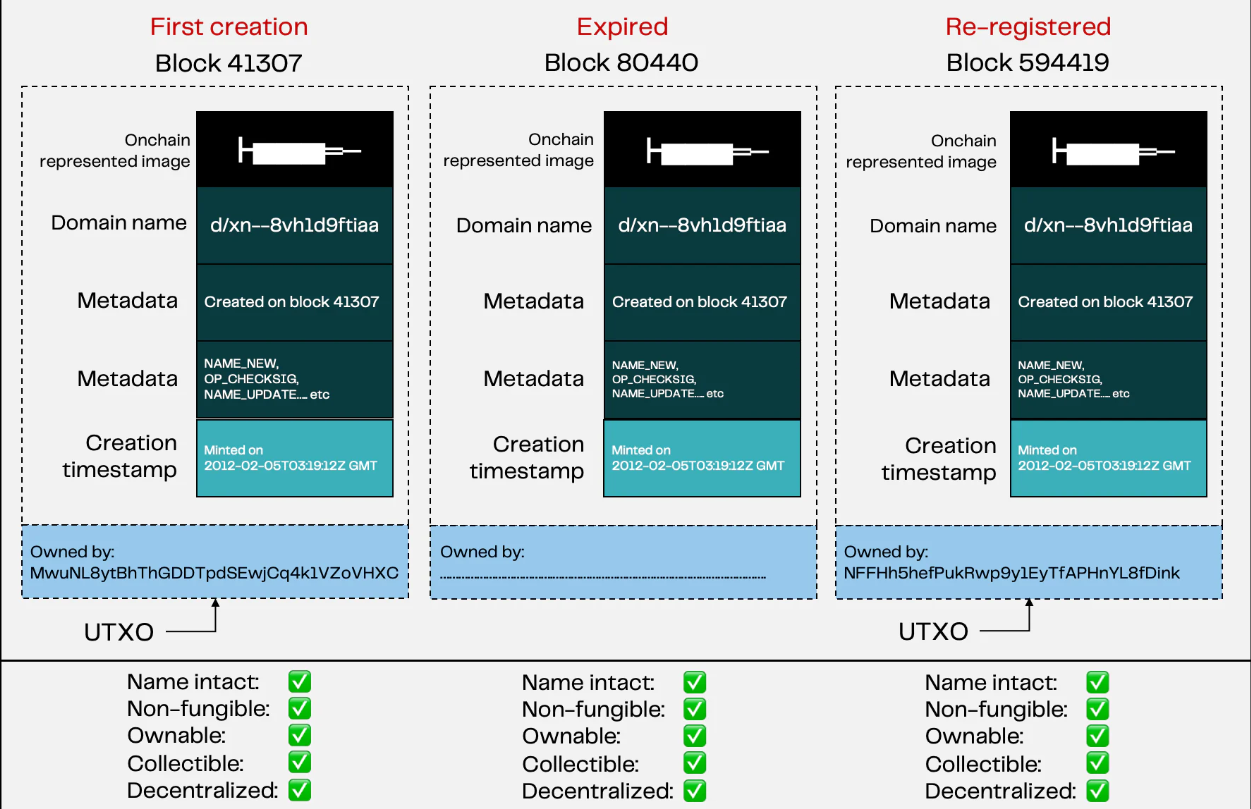
Explanation 1: A "token" is a "colored coin", which is represented by a domain name with a unique identifier. When re-registering after the domain name expires, a new "colored coin" will be allocated to form a new asset.
Explanation 2: "Token" itself is a domain name, which is a uniquely identifiable asset. Namecoin is designed with domain names as the primary unique identifier. When a domain name expires, the domain name's data is still stored on the chain and is still traceable.
Explanation 3: A "token" is a "colored coin", which is an encrypted representation of a domain name. When the domain name is re-registered, the new "colored coin" becomes a new NFT, but it still represents the asset value before being re-registered, that is to say, only the ownership of the "colored coin" changes before and after registration, and the represented assets The value has not changed.
cryptocurrency
cryptocurrency
encrypted assets
Off-chain assets (applicable when referencing real-world assets, eg: Twitter Eggs, Blockheads, Quantum, etc. Not used for Punycodes, Damselfly, Identities, Bit Domains)
For collectors and decentralization enthusiasts, it is important to own collectible assets in a decentralized manner. Even historical data on expired Namecoin domains still exists on the decentralized blockchain. This data can be owned in a decentralized manner, so it is still called a decentralized collection.
The above has been discussed from the perspective of technical principles, and then began to consider ethical, philosophical and legal perspectives. These perspectives are somewhat subjective, but they are worth learning.
Ethical and Philosophical Discussions on the Origin of Namecoin NFT
The bull market in the encryption market triggered by NFT in 2021 has convinced many Web3 participants that the decentralization and traceability of the blockchain will bring about a paradigm shift in ownership. Holders of this view support CC0 (no rights reserved) and care less about real world arguments or even the law.
Editor's note: CC0 makes scientists, educators, technology plus, and other copyrighted or database-protected content fully open source so that others can freely use and add to it, unrestricted by copyright laws.
Critics of this view argue that blockchains can bring a lot of value to creators and collectors, but physics, ethics, and universal truths cannot be ignored.
Image Source
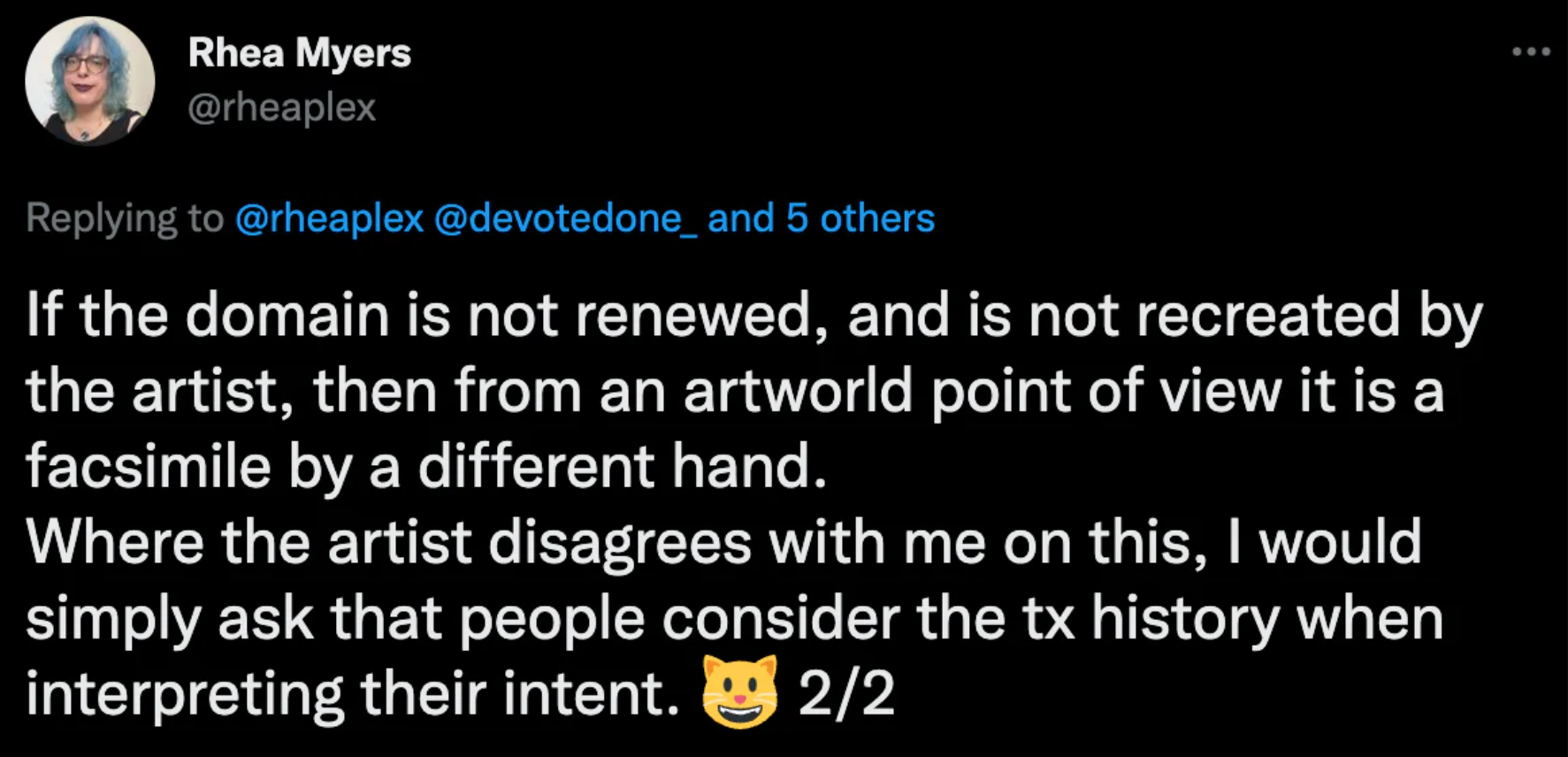
If a work of art is created by a creator on Namecoin and re-registered by the same creator after expiration, there is no change or transfer of ownership in the philosophical sense. But if it is re-registered by others after the expiration, there is a lot of controversy.
Explanation 1: In a philosophical sense, after an artist creates a work, others cannot claim to be the creator after re-registering; from this perspective, it is immoral to steal other people's works and sell them.
Explanation 2: Namecoin offers 100% ownership, and it is up to the owner whether to extend ownership. In a philosophical sense, if an artist does not renew their ownership, it is a decision to make their work public and anyone can claim it. If later holders increase their recognition through marketing, it is ethical to profit financially from it.
The situation is further complicated when the artwork is linked to an external server over which the original creator has control. We take off-chain information into account, so what exactly is an artwork? Whether it is one or all of the off-chain files, the domain name attached to the link, or the "colored coin" corresponding to the domain name is debatable.
Traceability for ethical reasons
Recently, the Punycodes community discovered the original creator of 966 Punycodes, and the Punycodes DAO immediately invited haluciphile to become a member of the DAO, and presented multiple Punycodes. The Punycodes DAO also promises to distribute a portion of the royalties from the vault contracts on Ethereum to the haluciphile. Then Punycodes announced an announcement: If the original creator of Punycode proves their identity through the wallet verification message process, the Punycodes DAO promises to do its best to ensure that the original creator gets value, such as token assets and royalties.
Collectible Value Fundamentals and Indicators
Timestamp: Immutable objective data on the blockchain.
Scarcity: The number of assets in a collection or version.
Creativity: Artistic and Conceptual Intention.
Technological achievements: Technological innovations that drive the development of NFT.
in conclusion
in conclusion
Original link



