In-depth Analysis of Trustless Bridge: Solving the Interoperability Crisis and Optimizing the Utilization Efficiency of Liquidity
Author: Hakeen|W3.Hitchhiker
Edited by: Marina|W3.Hitchhiker
Revision: Evelyn | W3. Hitchhiker

With the advent of the multi-chain era, the requirements for interoperability of blockchain networks are getting higher and higher. Starting from 2021, cross-chain bridges will show explosive growth. The cross-chain bridge can transmit "information", the information here is not only assets, but also includes smart contract calls, identity proofs, and state interactions. As of the end of April 2022, more than 65 cross-chain bridges have emerged in the encryption world.
The cross-chain bridge can well solve the problem of insufficient liquidity. In addition to playing an important role in asset extradition, the cross-chain bridge can also solve the problem of insufficient performance of the underlying public chain. Like the current Ethereum Layer 2, it can help transfer the transaction throughput from the first layer to the off-chain system. The whole process is realized through the bridge. Keep funds and release a layer of huge trading volume pressure. But such a bridge also has certain disadvantages. As a blockchain network independent of the main chain, most of them only focus on their own security model, so they have a certain degree of security risk.
**The ideal cross-chain bridge, under the premise of ensuring a highly transparent and tamper-free cross-chain environment, can not only meet the interaction of assets and other information, but also have extremely high security guarantees, achieving higher performance and compatibility with all public chains Consensus on categories such as protocols, applications, and transactions. **Developed in this way, the "middleware" role of the cross-chain bridge can be recognized by the market and used more frequently, and the development of the industry can also enter the era of indiscriminate cross-chain interaction.
This article will mainly start from the security of asset cross-chain bridges, according towho is verifying the systemClassify and select three recently popular Trustless cross-chain bridges, and summarize the advantages and disadvantages from their respective operating principles, teams, investment and financing, and costs.
1. Classification of cross-chain bridges
Safe and fast has always been the top priority of cross-chain bridges. Since the Layer 2 cross-chain bridges on the market are mainly built on Ethereum, if we put funds on Layer 2, then the funds are still protected by Ethereum verifiers; if we transfer the assets on Arbitrum through the cross-chain bridge When it comes to Optimism, Arbitrum and Optimism themselves are also secured by Ethereum. The validator is on Ethereum, and the strong consensus foundation of Ethereum provides extremely high security, but the bridge protocol uses a set of external validators, and the funds are no longer protected by Ethereum, but by the validators of the bridge. According to the barrel principle, it is the most vulnerable part that determines the safety.
Therefore, according to who is verifying the system, we can divide it into the following three categories:
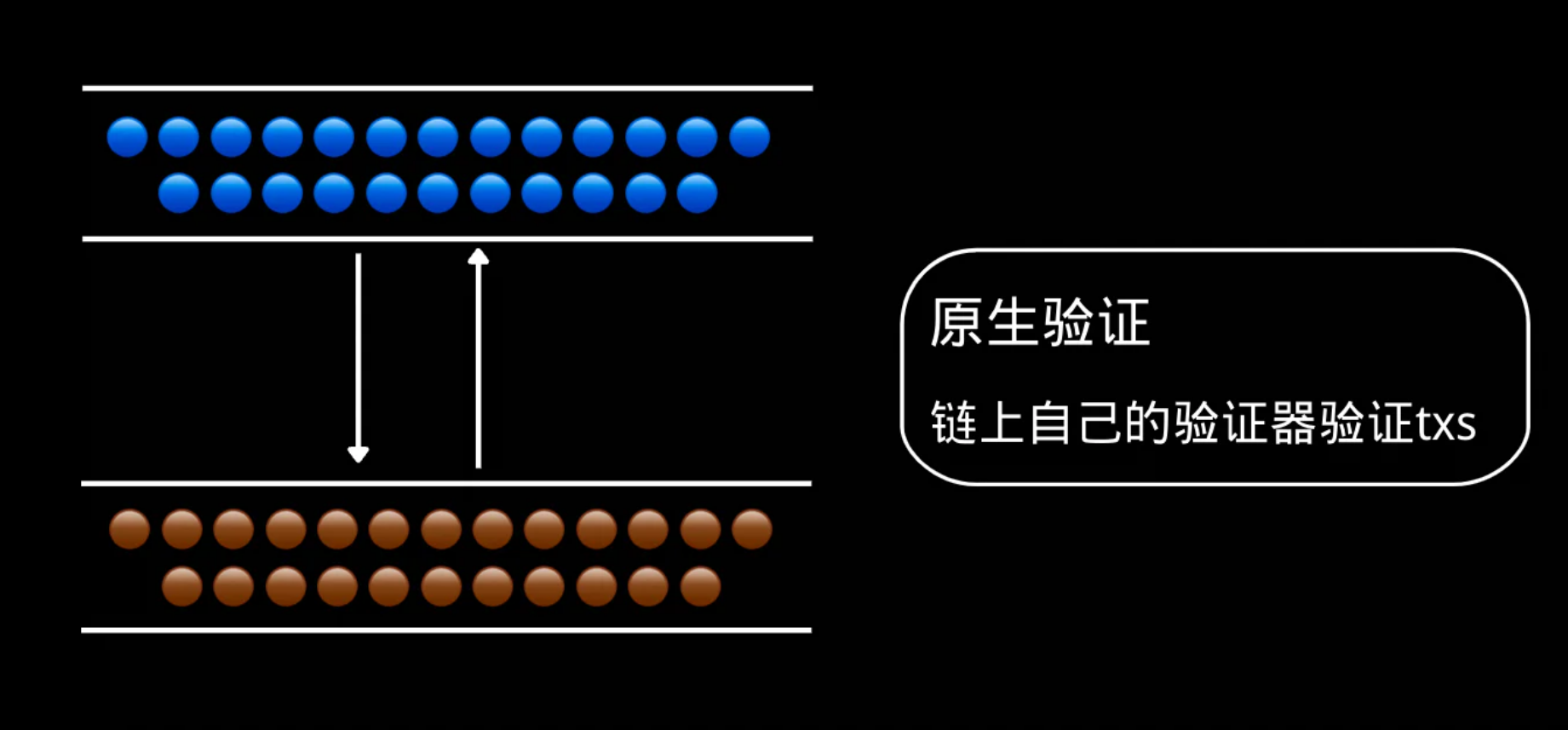
1. Original authentication
It does this by running a light client of the source chain in the virtual machine of the target chain.
Such as IBC, BTC Relay, Near Rainbow Bridge, Polkadot SnowBridge, LayerZero, Movr, Optics, Gravity Bridge, etc.
2. External verification
This type of verification method has one or a group of verifiers, and the verifier needs to monitor the specific address of the source chain. Users send assets to a specific address on the source chain to lock them, and third-party verifiers will verify the information and need to reach a consensus. When the consensus is reached, corresponding assets will be generated on the target chain.
This type of cross-chain bridge includes Synapse, Thorchain, Anyswap, PolyNetwork, WBTC, WormHole, Qredo, Ronin, etc.
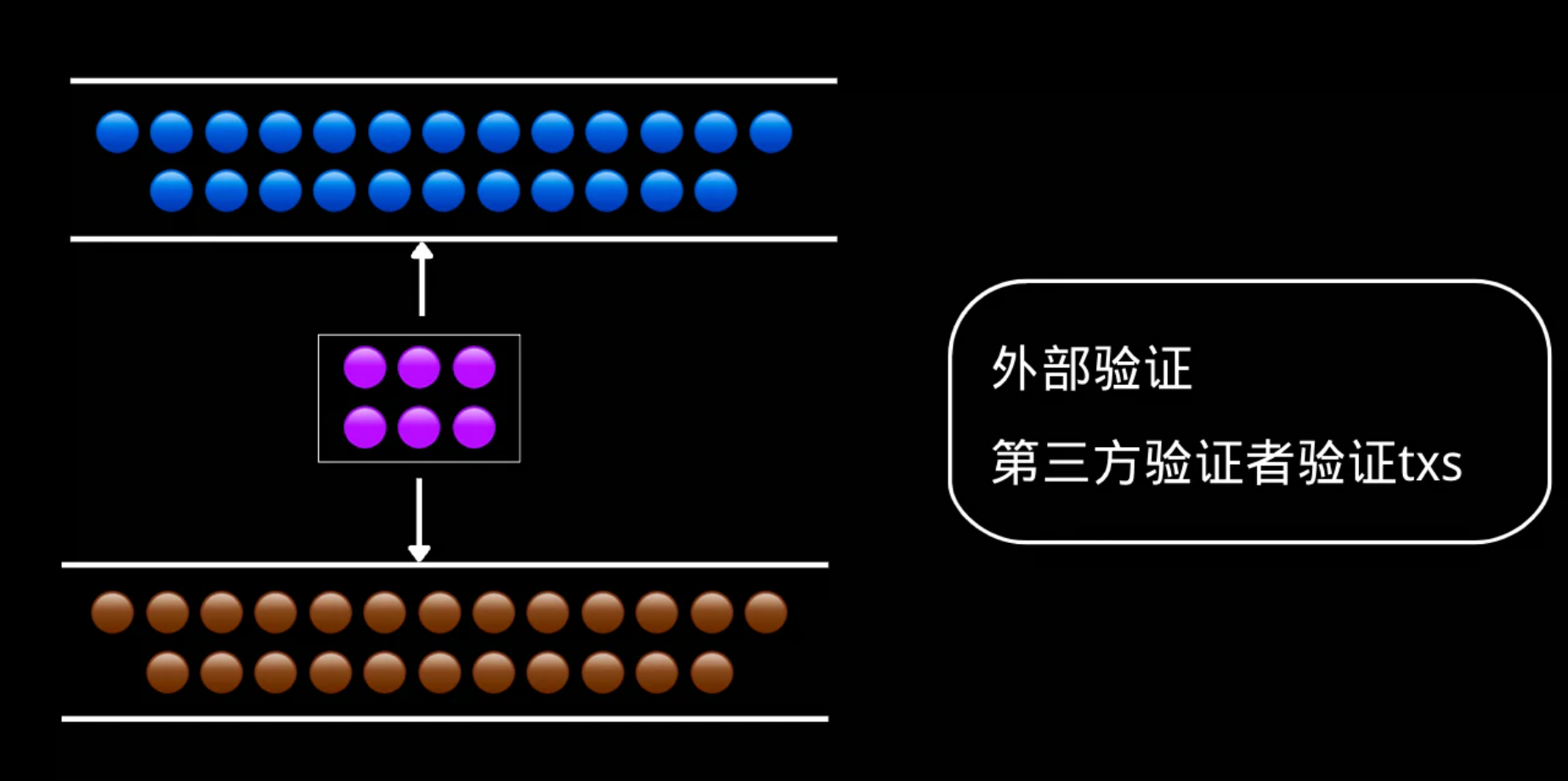
There are two main types of validators of this type:
one isHas a managed principal.The transferred assets are kept by the custodian, which requires full trust in the custodian. This model depends entirely on the credibility of the bridge operator itself. Essentially, they can take away users' native assets and make cross-chain assets lose value. For example, if the custodian of wBTC takes away all the BTC backing the value of wBTC, then wBTC will become worthless, although this probability is very small.
the other isA set of validators.In order to become a validator, they need to bond assets to prevent evil. Binding assets can also be divided into two categories. One is to bind the corresponding cross-chain assets. For example, in order to realize the cross-chain of BTC or ETH, the verifier needs to bind BTC or ETH. The other type is token assets bound to their own protocols. For example, Thorchain is bound to RUNE, and Synapse also plans to bind its own token SYN in the future to ensure the security of its chain. In this model, bridge participants have the opportunity to steal users' funds, but due to the existence of the "game" mechanism (that is, pledge their own funds, and the penalty mechanism for stealing funds), they should not do so.
mentioned belowThe local verification protocol turns the complex multi-party verification problem into a set of simpler two-party interactions where each party only verifies the counterparty, a model that works as long as the two parties are economically adversarial - i.e. two parties cannot collude to gain access to funds in the chain.
3. Local authentication
Local verification is a partial verification mode and a peer-to-peer liquidity network. Each node is a "router" itself, and what the router provides is the original asset of the target chain, not the derivative asset. Additionally, routers cannot withdraw user funds through locking and dispute resolution mechanisms.
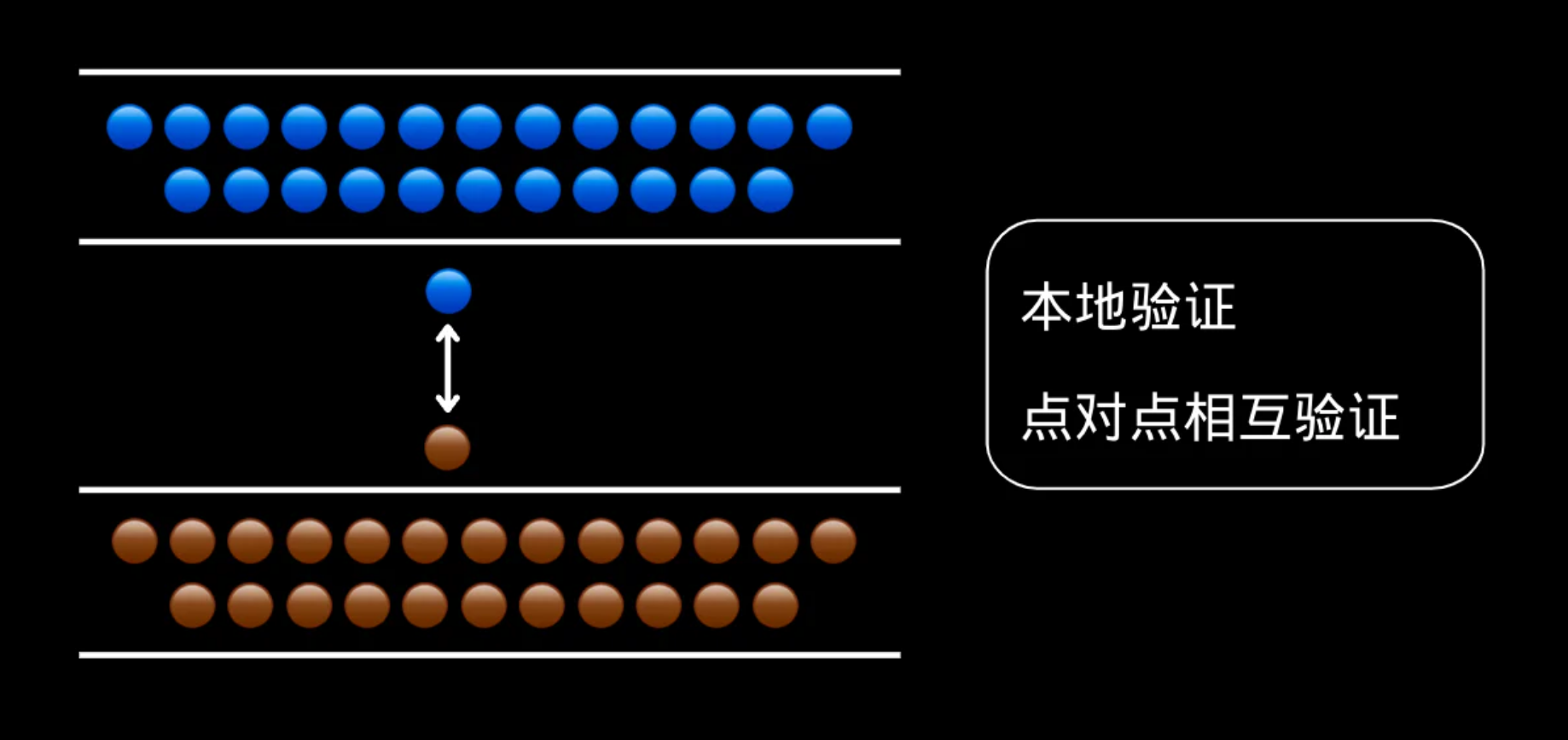
image description
4. Summary
4. Summary
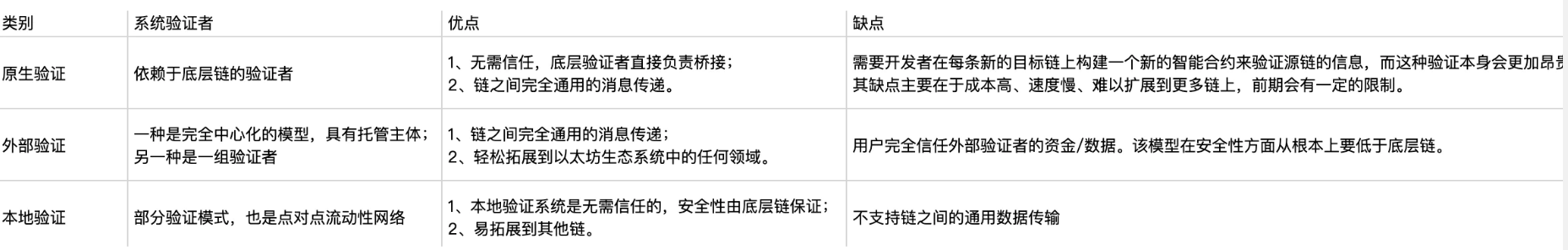
**External verification mode to build a cross-chain bridge has the advantages of faster speed, lower cost, universal data transmission, easier multi-chain connection, and better user experience, but the potential disadvantage of this model is its security. **Due to the introduction of the role of external actors, the user's security is not only dependent on the security of the source chain or target chain, but also limited by the security of the bridge. In the process of transferring assets across chains, if the bridge is not secure, the assets are at risk.
**Native verification mode is a cross-chain bridge that does not require trust. It does not have the potential security trade-offs of third-party verifiers, and can transmit various general data. The security of the cross-chain bridge is related to the security of the blockchain itself. The financial security of users is not affected by the bridge itself. If there is a security problem, it is also a problem with the chain itself. At the same time, there is no need to pledge assets (more efficient funds). **But the model still lacks enough activity and multi-chain connection. Between any two chains, developers need to develop and deploy new light-client smart contracts on the source and target chains. also,It also has the disadvantages of being slower and more expensive.
**Local authentication mode uses mobile network mode. It uses local validation and does not require global validation, so it is faster and less expensive. ** Relatively speaking, its capital efficiency is higher than that of the external verification model and lower than that of the native verification model. At the same time, the throughput of the peer-to-peer liquidity network is also greater. Of course, it also has shortcomings.It has limitations in information transmission and cannot achieve universal information transmission.
2. Development trend
Different models of cross-chain bridges have different trade-offs. Therefore, at different stages, according to the different needs of users for speed, cost, versatility, security, etc., different models of cross-chain bridges may achieve different effects at different stages.In the early days, the external verification mode and the local verification mode may gain faster development speed because of the empirical advantages in cost and speed. With people's emphasis on security and the development of technology, the native verification model may also develop gradually in the later stage.
Over time, some cross-chain bridges will gradually gain the upper hand and become the main players in the cross-chain bridge market. With the continuous in-depth development of Layer 2, cross-chain bridges will become an important part of the future multi-chain era.
3. List several cross-chain bridges
1、Hop protocol
image description
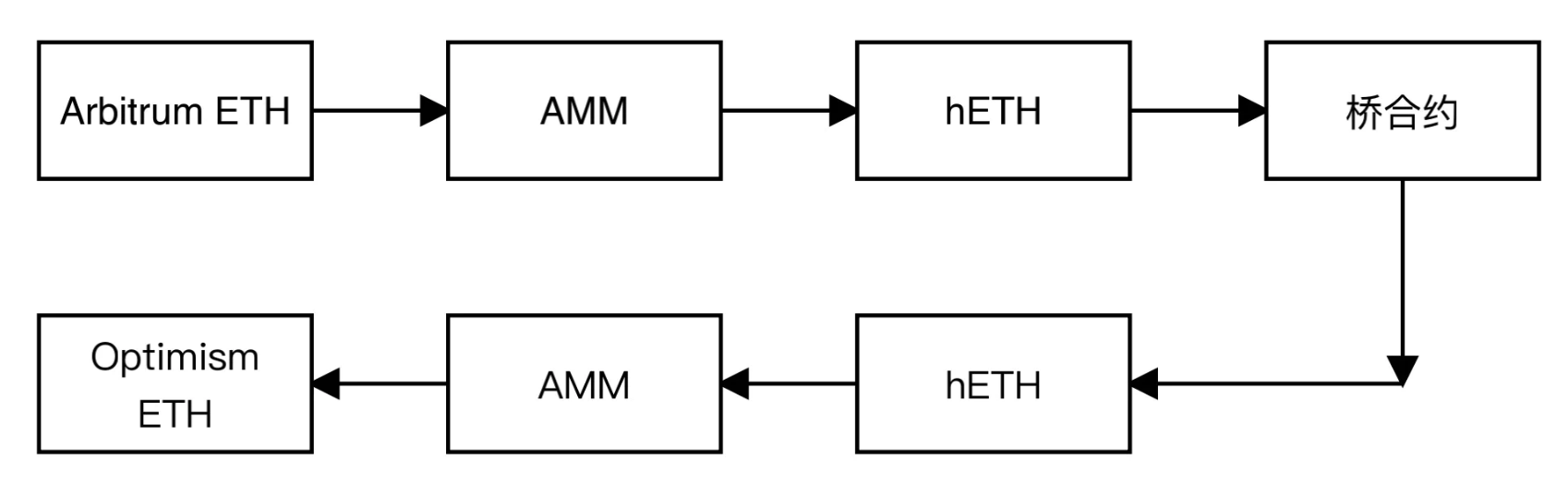
roll up and roll up transfer
The ETH officially minted by Arbitrum is transferred to hETH through the AMM, then the hETH on the Arbitrum chain is locked through the bridge contract, hETH is minted on another bridge, and then converted into ETH officially minted by the Op through the AMM deployed on the Op.
image description
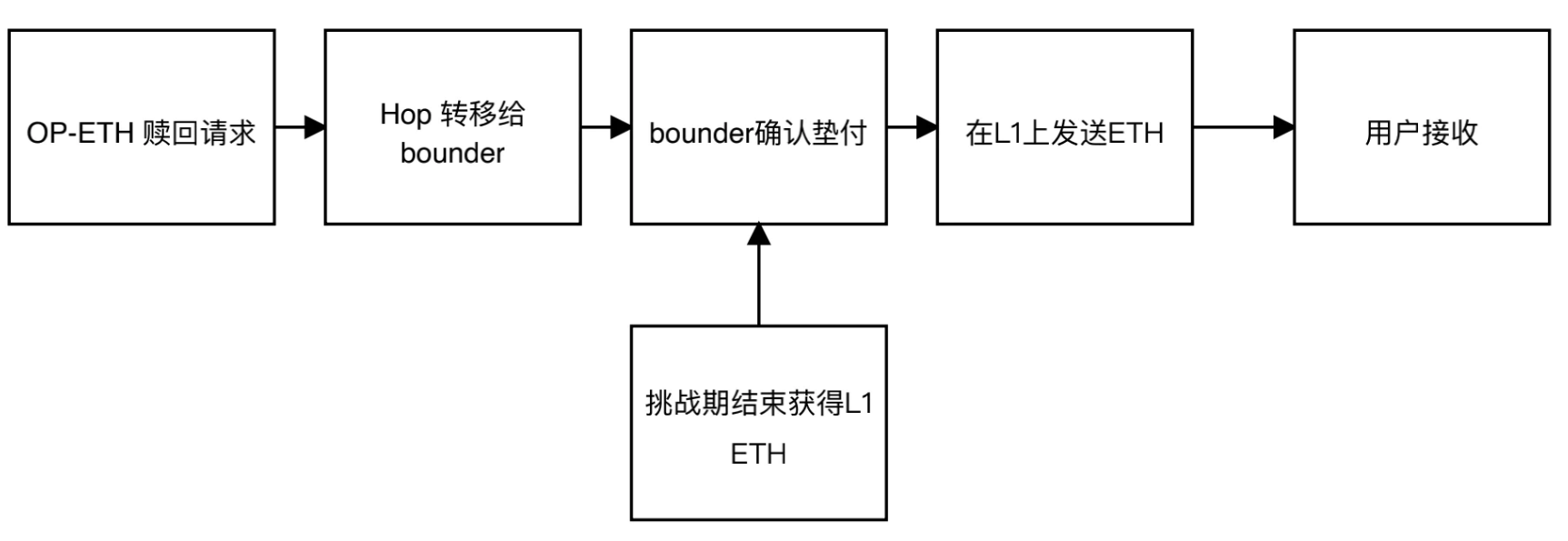
roll up and L1 transfer
The user sends a request to redeem ETH from the Op chain through the Hop protocol, and the Hop protocol informs Bounder, Bounder confirms the advance asset, sends ETH to the user on Layer 1, the user receives it immediately, and the challenge period ends, and Bounder obtains the ETH withdrawn from Layer 1.
At this time, it is necessary to interact with Layer 1. Because of the competition, Bounder needs to pay the gas fee by itself. In order to reduce the cost, it will mix multiple transactions into one transaction, so the time required to complete the interaction is uncertain.
The Hop protocol has three important roles:
AMM:As an automated market maker, it provides liquidity for different cross-chains.
Bridge contracts:Responsible for network transfers and providing liquidity.
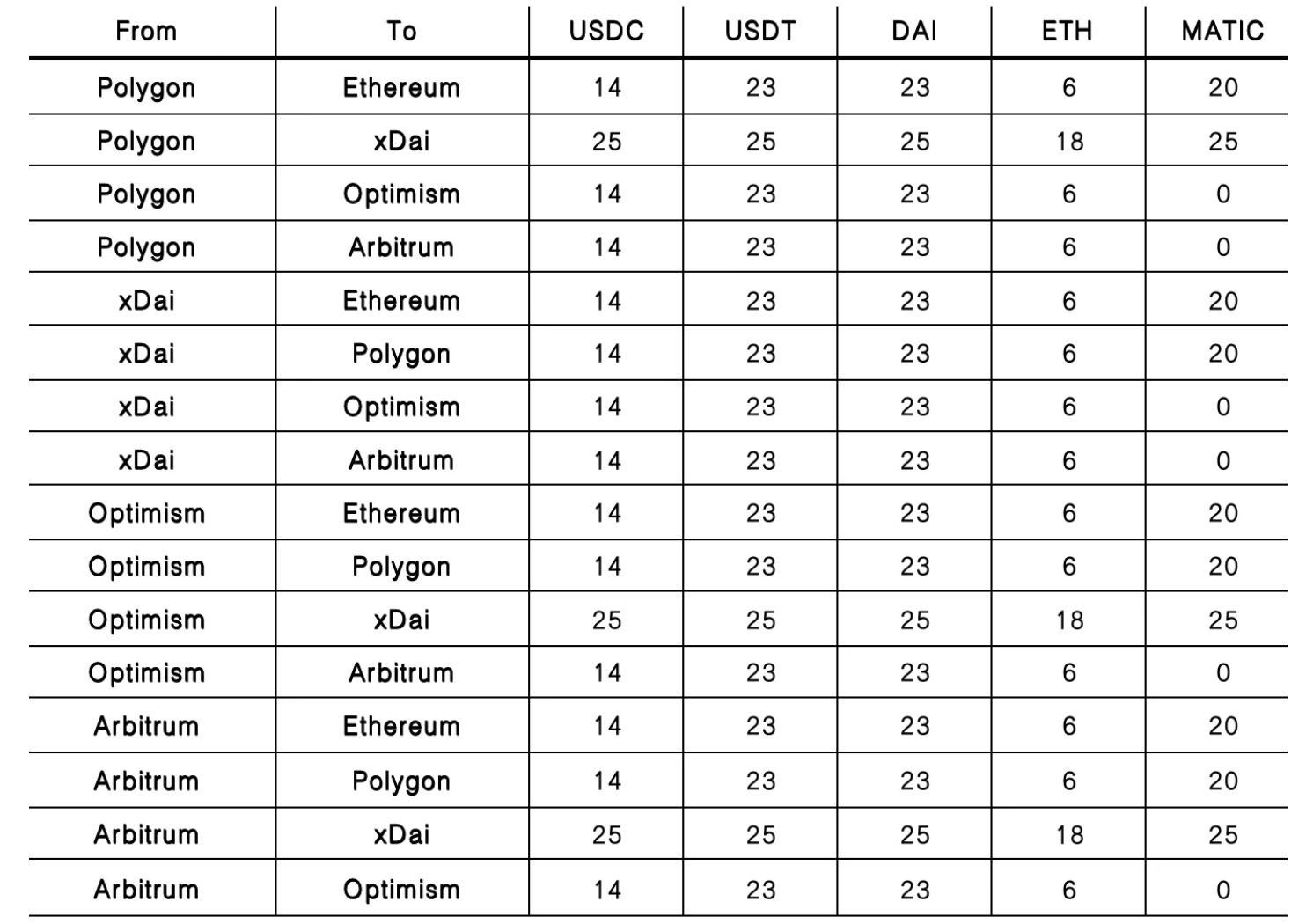
Bounder:cost
cost
Team situation
Team situation
Shane Fontaine: Ethereum developer, co-founder of Authereum, and organizer of Ethereum meetups in the Los Angeles area. He was the chief cryptographic developer of CoinCircle, participated in the development of Level K, and served as a technical consultant for UNIKOIN and Synapse Capital. Many smart contract codes are written in the Solidity language.
Lito Coen: Founder of Crypto Testers, also responsible for business growth at Hop Protocol. He has invested in more than ten projects in the Web3 field. Previously, he was the Business Development Manager at SatoshiPay.
Christopher WhinfreyInvestment and Financing
Investment and Financing
The financing information is unknown, and currently only disclosed investors include 1confirmation, 6th man ventures, infinite capital, etc.
2、Connext
Connext Network: - Making Blockchains Composable
Operating principle
Auction: Users are paired with liquidity providers who provide liquidity for transfers, lock your DAI on Op, and provide DAI on Arbitrum.
Preparation: At this stage, two parties lock funds for transfer - the user on the sending chain and the router on the receiving chain.
Fulfillment: In this phase, both parties unlock funds for transfer. Users provide a signature to unlock their funds on the receiving chain, and liquidity providers use the same signature to unlock funds on the sending chain.
specific process
The sender broadcasts the transaction request to the NATS message network
The router listens to the network, quotes, and the network automatically selects a low-cost router
The sender is paired with the router
The sender sends asset and quotation information to the nxtp contract, and the contract broadcasts a signal that the transaction is ready to complete
Router sends transfer preparation to nxtp
The sender sends the information and signature required for the appropriation to the relayer, and the relayer assists in sending the appropriation transaction to the nxtp contract of the receiver chain
The router obtains a local signature from the nxtp contract, and the router allocates funds to the address
user obtains assets in another chain and signs
The router obtains the signature message and obtains the advance assets from the nxtp contract of the sender chain
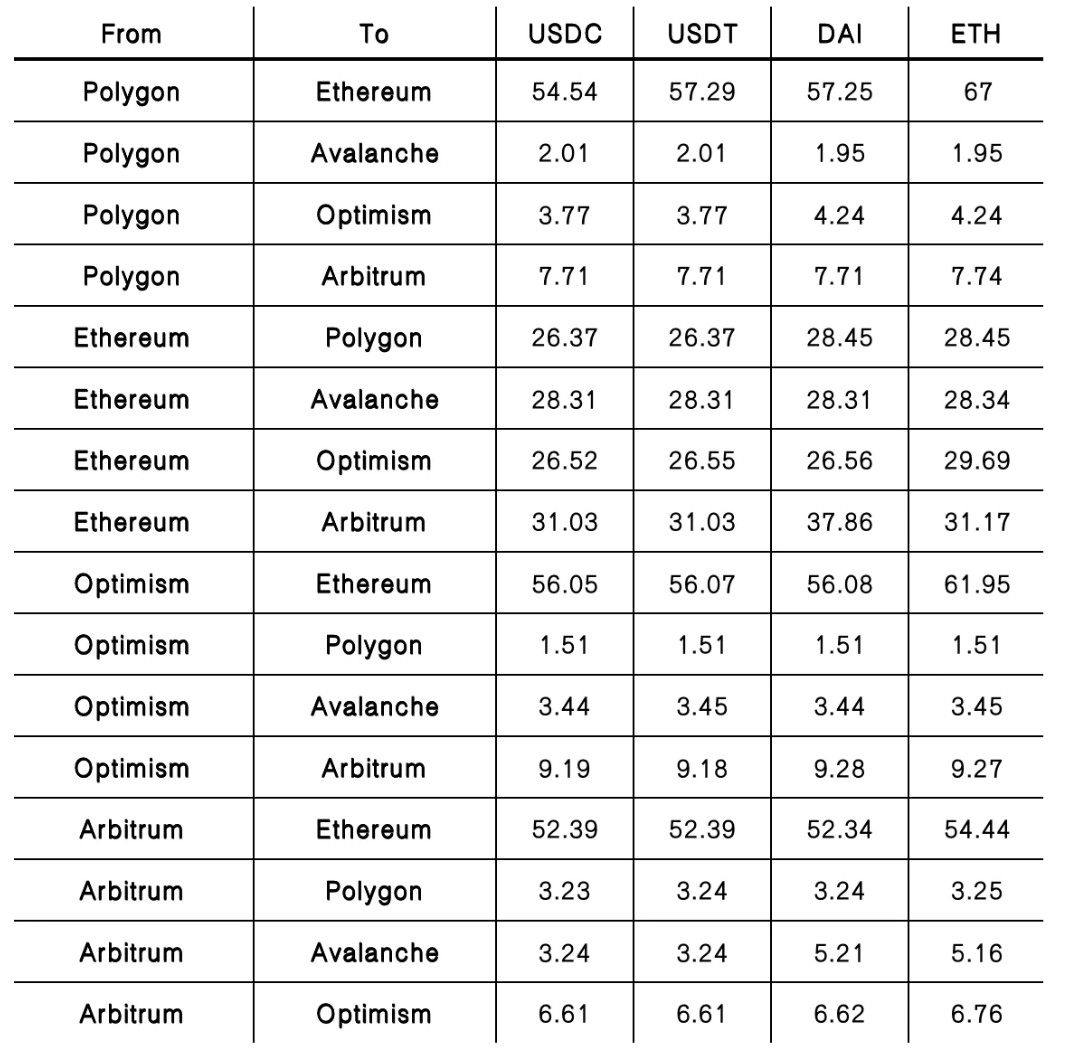
operating costs
team
team
Arjun Bhuptani: Founder, Co-Founder of Moloch dao, Colgate University (Noble Liberal Arts College).
Layne Haber: COO, UCLA, CEO of two startups.
Rahul SethuramInvestment and Financing
Investment and Financing
The total financing is 15.7 million US dollars, and the A round of financing has been completed.
Investors include: #Hashed, Ethereum foundation, Consensys, 1kx, OK ventures, huobi ventures, coinbase ventures, polychain, jinglan wang (optimism), Sandeep Nailwal (polygon)
3、Nomad
Operating principle
Drawing inspiration and experience from the Optimism team, Nomad itself is an implementation and extension of Optimistic Interchain Communication. The security guarantee of the system is that any participant can publish all fraud proofs, and all participants have a window to react to any fraudulent behavior.
Nomad forms the base layer of a cross-chain communication network capable of sending general-purpose messages with higher generality but with a 30-minute latency.
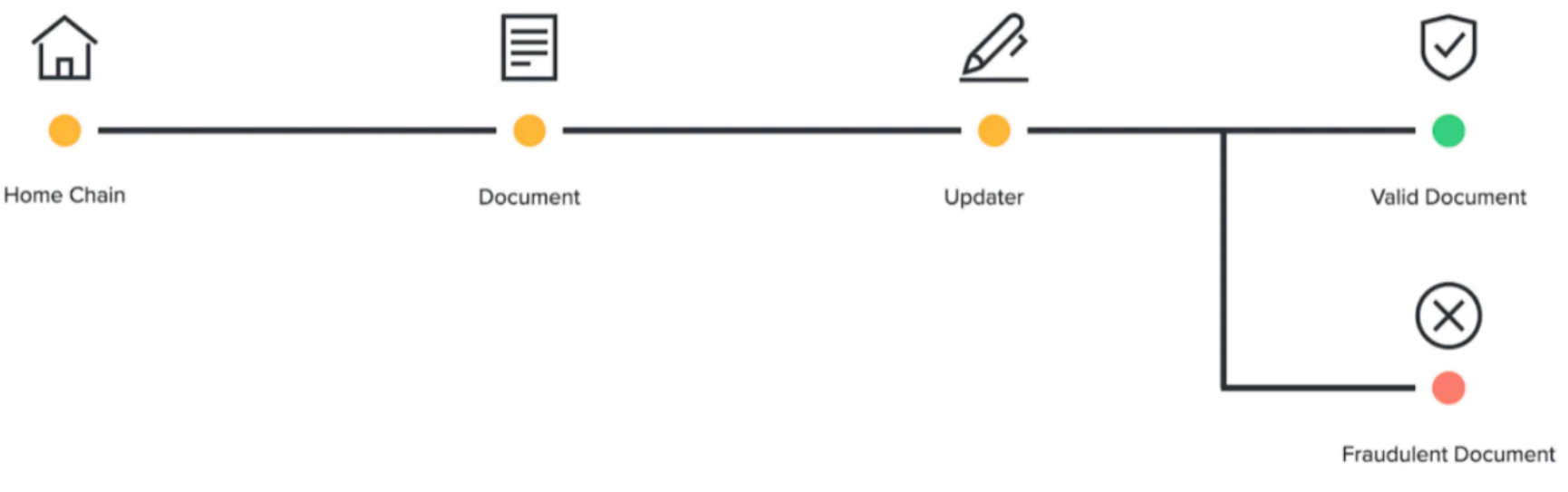
The sending chain (home chain) generates a series of messages (document), which are signed by the signing notary (updater). If the notary presents a fake copy, a penalty is broadcast and all clients know it is malicious and access to their account can be blocked.
Nomad uses optimistic proofs as a prototype, sending some data proofs, accepting them as valid after a timer elapses, and introducing challengers to submit fraud proofs.
Nomad spans multiple chains. The sending chain is the source of messages, and messages are committed into the merkle tree ("message tree"). The root of this tree is notarized by the updater and relayed to the receiving chain via the relayer in an "update". Updates are signed by the updater. They commit to the previous root and a new root. Any chain can maintain a "replica" contract that contains knowledge of the updater and the current root. Signed updates are held by replicas and accepted after a timeout.
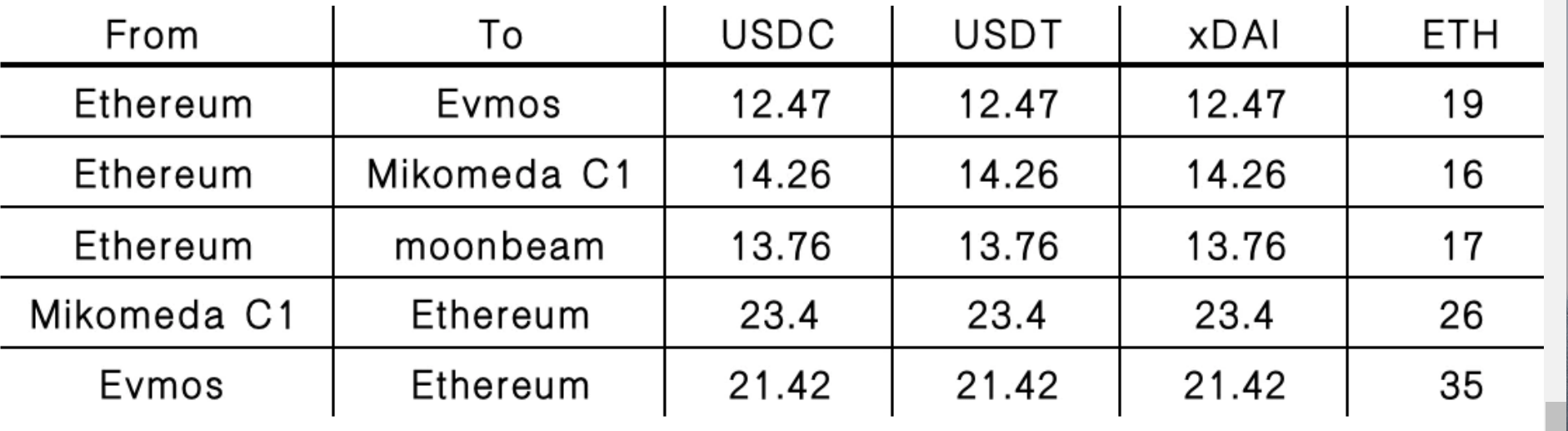
cost
cost
team
team
Investment and Financing
Investment and Financing
The seed round of financing is 22.4 million US dollars, led by polychain capital, and the remaining investors include the graph, celestia, amber group, mina, circle, avalanche, 1kx, polkadot, A&T capital, coinbase and other 27 investors.
Nomad integration with Connext
The advantage of Connext is that it realizes cross-chain and L2 Trustless sending value and calling contracts, but the disadvantage is that it does not allow fully general communication, but its latency is indeed much lower. Rely on Nomad high security, absorb Nomad trust/risk.
Leveraging Connext's low-latency liquidity pools allows end users to complete transfers in minutes, rather than delays of more than 30 minutes. According to the official Connext report, whales and institutions will take 35 minutes longer to complete Nomad's bridge time.
Connext and Nomad are a combination of low-latency liquidity + security. With the growth of Connext liquidity, the adoption of Nomad may gradually favor institutional capital or large capital volume in the future.
4. Summary
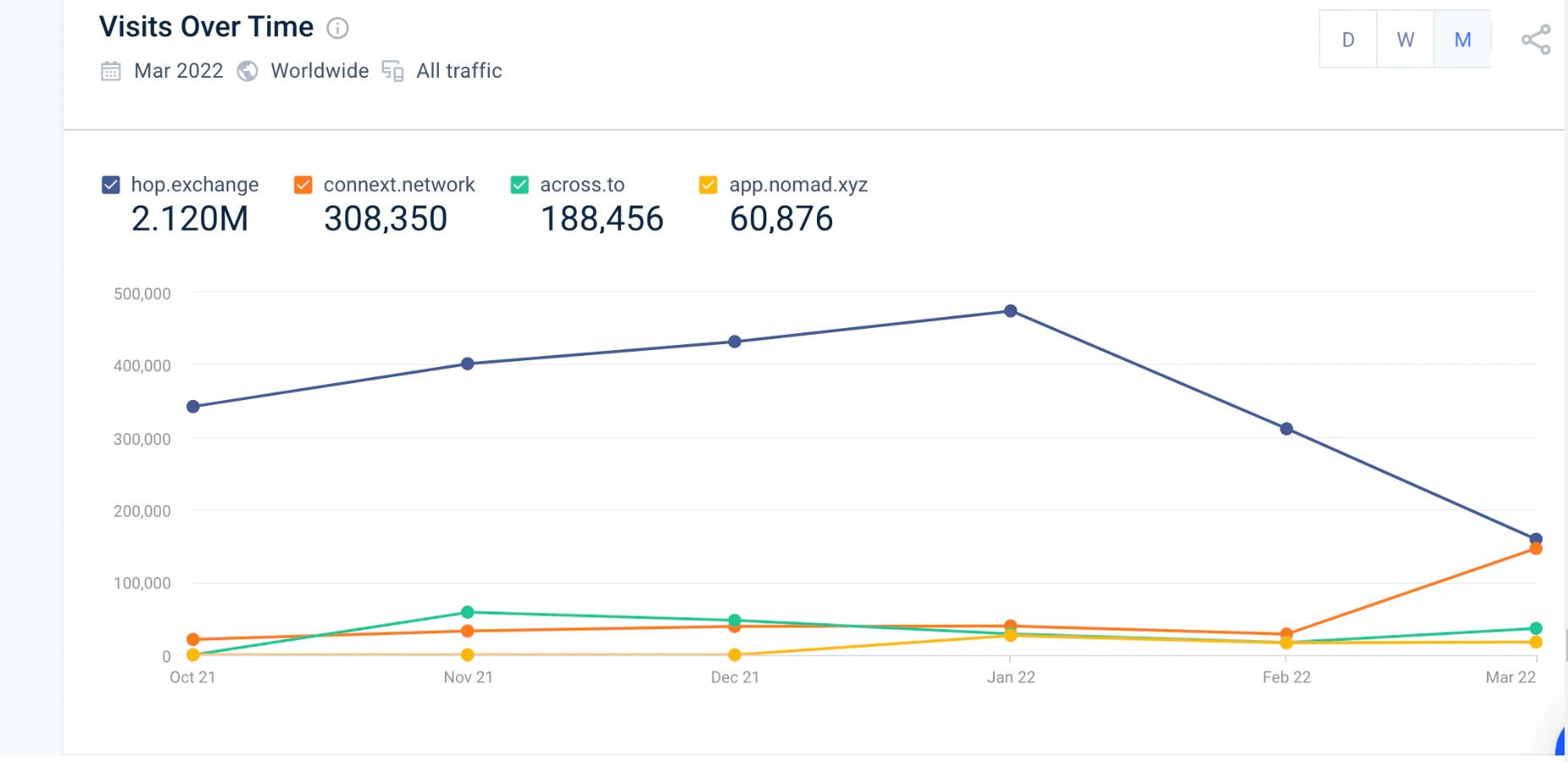
From the perspective of off-site popularity, Hop bridge is still the best. The popularity caused by the integration of Connext and Nomad has gradually increased the public's attention to it.
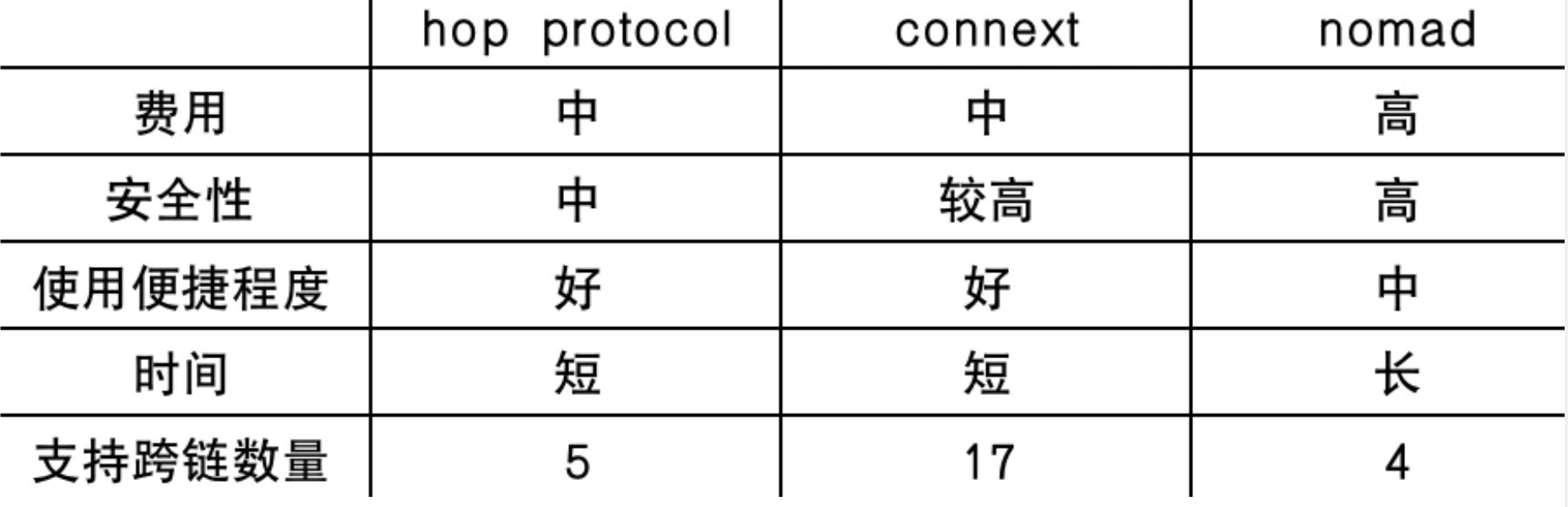
Taken together, Nomad is an ideal protocol for more general cross-chain operations due to its higher security and higher fraud costs. These operations are usually performed by DAOs or other organizations rather than end users, so the corresponding The use and cross-chain time are not so convenient and fast; however, the integration with Connext can make up for some of the problems.

If we look back at the hacks that have occurred in recent months:

At present, almost all of the largest blockchain hacking attacks come from cross-chain bridges, such as Ronin Network’s $624 million, Poly Network’s $611 million, Wormhole’s $326 million... These attacks remind us that no matter what users think, Decentralization is a real security necessity for high value applications.
local authenticationlocal authenticationIt is currently a better solution overall.
Of course, the cross-chain bridge should not be limited to the cross-chain of assets. Message and contract calls, data interaction, and state interaction are all application directions of the cross-chain bridge. The rigid demand for diversified cross-chains creates unlimited future potential for the entire track.



