Understand Chainlink's cross-chain compatibility solution in one article

smart contractThe ecology is developing in the direction of multi-chain,blockchainThe application is no longer limited to a certain network, but across various decentralized ledgers, forming an ecology together. Each of these blockchains has its own unique value proposition and technical characteristics. Various blockchain and L2 solutions have different consensus algorithms, security models, programming languages, and hardware requirements. This gives developers and users more options, and they have the flexibility to choose what works best for themSmart Contract Use CasesSmart Contract Use Cases
However, one thing that all blockchains and L2 networks have in common is the inability to directly access the outside world, a problem that is often referred to as "The oracle problem". To solve this problem requires a method called "OracleOracle
"Infrastructure, it can securely and reliably connect to external data and off-chain computing resources for blockchain and smart contract applications on the chain.Chainlink is compatible with all blockchainsThe decentralized oracle network development framework can provide developers with a secure oracle infrastructure for development in any desired blockchain networkHybrid Smart Contract, and ultimately promote the development of multi-chain ecology. The Chainlink oracle network has secured tens of billions of dollars in value for many top blockchain networks, including Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, xDai, Heco, Avalanche, Fantom, Arbitrum, Harmony, Optimism, and Solana Devnet et al. everyone can inChainlink DocumentationChainlink Documentation
View the oracle network running on each blockchain in .The reason why Chainlink can provide native services for so many blockchain networks is due to the strong development team in the Chainlink ecosystem. These teams have gainedChainlink Community Incentive Program
However, different oracle networks employ different mechanisms to ensure compatibility. This article will explore the key security considerations that oracles need to consider when ensuring compatibility with blockchains, the unique way Chainlink achieves compatibility, and how this model will facilitate the development of the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP).
first level title
The decentralized oracle network provides smart contracts with the required data input and computing resources to generate expected results, so it can be said that it directly guarantees the effective execution of smart contracts. If the data is entered incorrectly or if the data is not available, the user's smart contract will not execute as expected and may result in the loss of the user's funds. Therefore, the compatibility scheme of the oracle machine network must be designed carefully and carefully, and must not sacrifice security, speed or usability, because these are the core values of hybrid smart contracts.
secondary title
One way to ensure oracle compatibility is to run the oracle network on only one blockchain, and then use relay layers to bridge data to other chains. In theory, this mechanism can indeed transmit oracle reports for smart contracts on various blockchains, but it has serious loopholes.
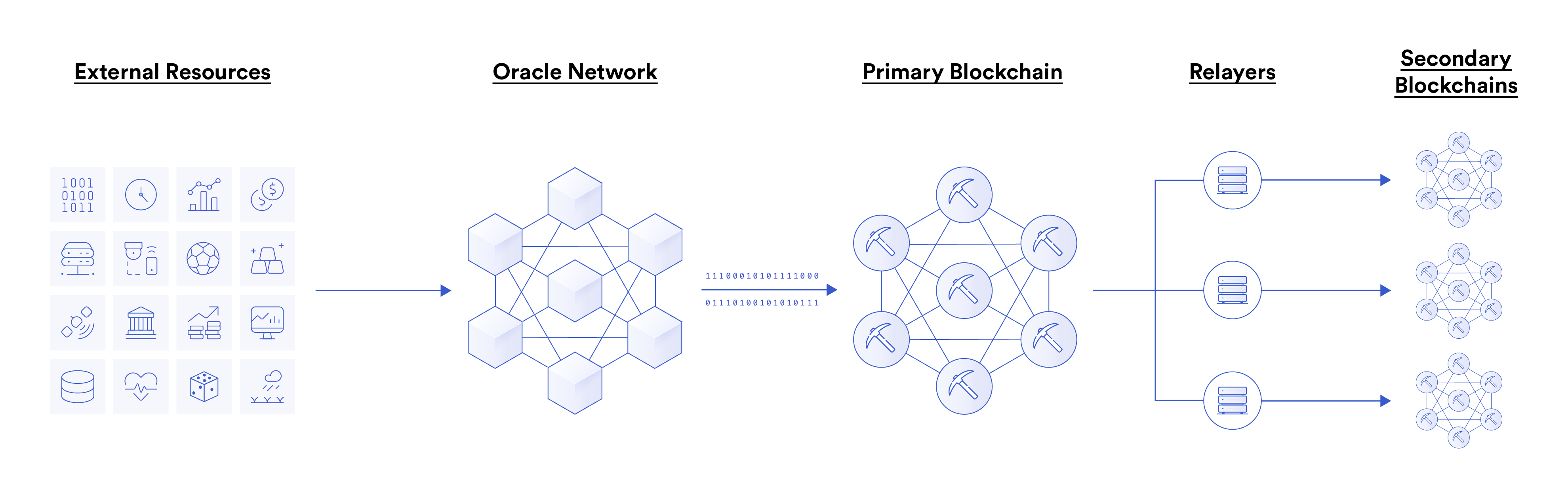
image description
Security loopholes in some oracle compatible solutions
First, in this mode, oracle nodes can only transmit data directly to one blockchain. This means that the update frequency and cost of oracles on all other blockchains will be limited by the speed and throughput of the main chain. There will be a bottleneck here. Even if a higher throughput and lower cost L1 or L2 blockchain network is deployed, oracle updates will still be limited by the main chain because data needs to be bridged from the main chain. This will lead to higher costs for users, and the update frequency of the oracle will be lower than that of running directly on the blockchain.
Second, using a relay layer can exacerbate latency, as users not only need to wait for data to be transmitted to the main chain first, but also for data to be bridged from the main chain to the second blockchain or L2 blockchain where the smart contract resides. When the market fluctuates greatly or the blockchain network is congested, the data transmitted to the smart contract will be seriously lagged, and this may eventually lead to the risk of insufficient collateralization of the agreement.
Finally, bridging oracle reports from one blockchain to another leads to serious dependency issues. Users must not only trust the blockchain that gets data directly from the oracle, but also the relay layer that transmits the data to other blockchains, because these two links are critical for the entire mechanism to work properly. In this mode, there are too many links involving user trust, which will expand the attack surface of user smart contracts.
secondary title
Chainlink’s approach to oracle compatibility is fundamentally different from the relay model mentioned above. The Chainlink oracle network does not only transmit data to one blockchain network and bridge the data to other chains; it transmits data directly to all blockchains and L2 networks, and the whole process does not depend on any other blockchain network or relay node. This means that the Chainlink oracle network can run directly on each blockchain, provide native oracle services for the blockchain, and access external data and off-chain computing resources.
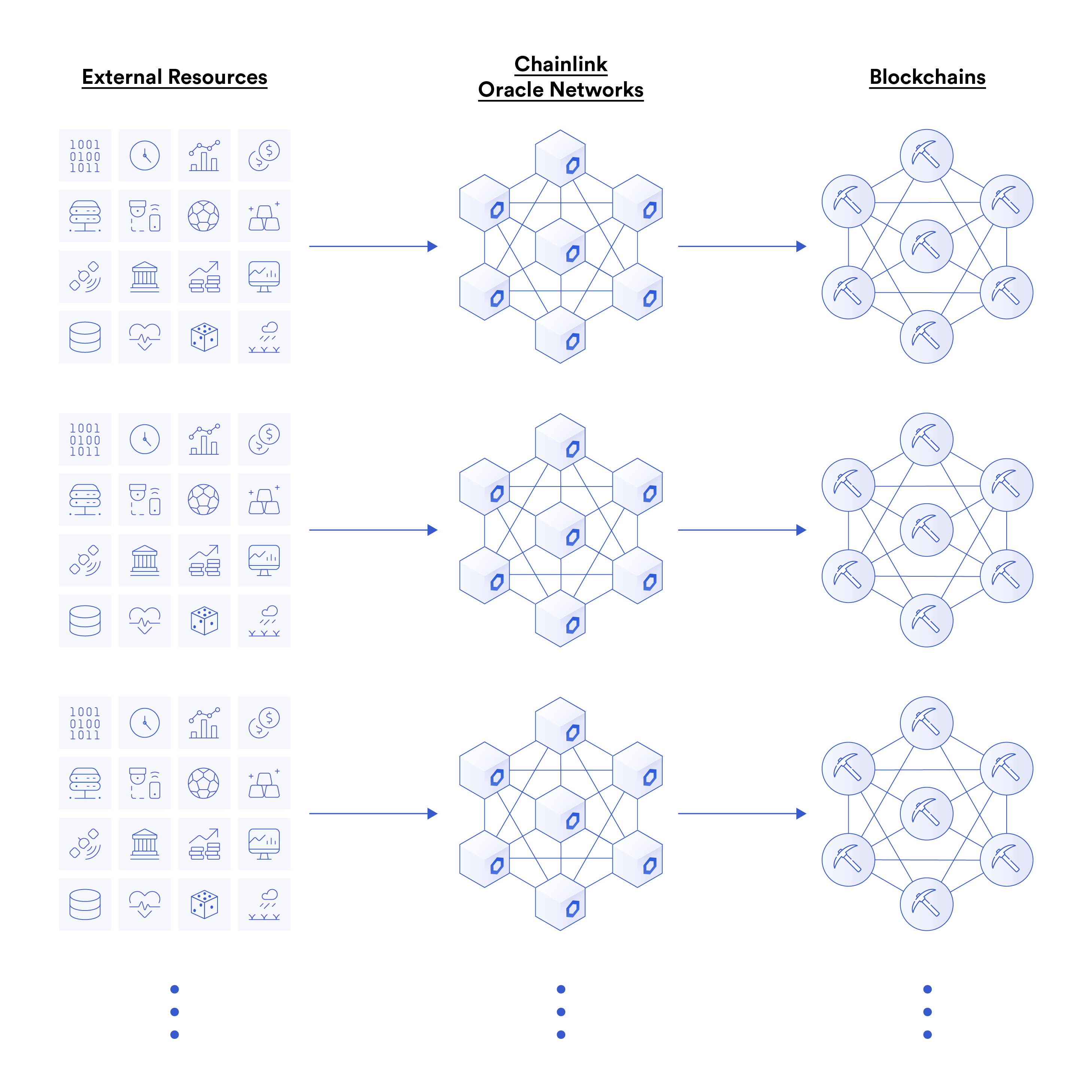
image description
The Chainlink oracle network provides native oracle services directly to any blockchain network
As a result, the Chainlink oracle network can keep pace with any blockchain or L2 network in speed and cost, and blockchains with higher throughput and lower costs can enjoy more frequent and low-cost oracle updates. For example, the Chainlink oracle network on Polygon can update data frequently. In contrast, bridging data from a low-throughput/high-cost blockchain simply cannot achieve such a high update frequency.
In addition, since the on-chain oracle network does not rely on any external blockchain, it can better guarantee the timeliness of oracle updates for users, even if other blockchains experience downtime, it will not be affected. This model reduces the attack surface and oracle update latency, and smart contracts have the flexibility to choose the blockchain that best suits their needs for deployment. For example, the Chainlink oracle network on Ethereum does not rely on the security or liveness of a high-throughput blockchain, thus guaranteeing the accuracy of oracle reports.
We work closely with the development teams of various blockchains and L2 networks to deeply integrate Chainlink oracles into each chain, and ensure the long-term reliability of the blockchain and meet the needs of the developer ecosystem. Without sacrificing security, speed and reliability at all, the Chainlink network provides a series of decentralized oracle networks compatible with all blockchains for the multi-chain ecosystem, which are natively integrated into each blockchain, providing On-chain hybrid smart contracts provide services. In addition, Chainlink will continue to integrate into more blockchain networks to provide more support for smart contract ecosystem developers.
first level title
Use CCIP to achieve interoperability of multi-chain ecology
developer useCross-chain Interoperability ProtocolCross-chain Interoperability Protocol
(Note: The abbreviation is CCIP, which is a global open source standard for cross-chain message transmission), and a secure off-chain infrastructure will be obtained to create a truly secure cross-chain application and token bridge. CCIP will utilize Chainlink's existing oracle nodes, which are highly secure and resistant to sybil attacks, and are compatible with all blockchains. Currently, tens of billions of dollars have been guaranteed for DeFi applications in various blockchain networks. dollar value. Developers use CCIP general standards to create various secure cross-chain bridges, completely avoid the risk of centralization, and provide users with seamless interoperability solutions.Smart Contract Summit #1Watch Chainlink co-founder Sergey Nazarov at
We will launch an innovative risk control mechanism called "Anti-Fraud Network" to further enhance the security of CCIP standards. The anti-fraud network consists of a decentralized oracle network with an independent node committee whose sole purpose is to monitor malicious behavior in CCIP services and the activity of the blockchain network. With this layer of verification, an emergency shutdown of the network can be triggered automatically, protecting users from black swan events.
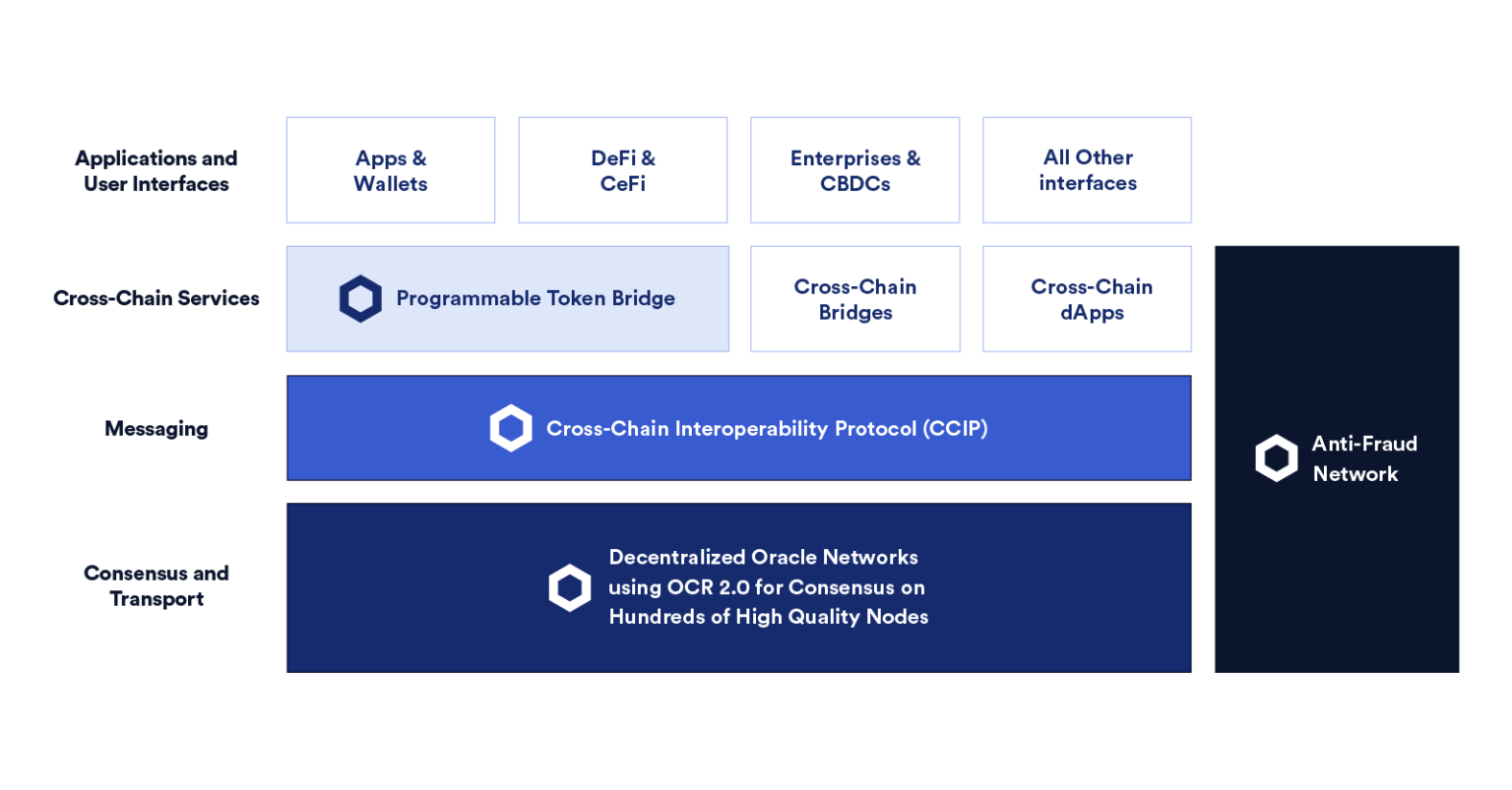
image description
CCIP has a multi-layer technology stack, including Chainlink oracle nodes that can be compatible with any blockchain.
At present, Chainlink has been integrated into more than 100 blockchain networks and has been released on many mainnets, so it is the most ideal infrastructure, which can be used as a neutral protocol for cross-chain communication between all blockchains and L2 networks . As Chainlink oracles continue to cover more and more blockchains, developers can also access a wealth of decentralized services to create increasingly advanced hybrid smart contract applications.docs.chain.linkCheck out the developer documentation. To discuss integration related matters, pleaseContact a Chainlink Expert。



