Interpretation of PawnHouse: How the SMRA theory favored by the Nobel Prize is applied to NFT price discovery
2021 is a year for NFT to usher in explosive development, and market participants are paying more and more attention to NFT assets. However, due to the special attributes of NFT itself and the current development status of the industry, there are many problems behind the hot NFT market. Among them, the difficulty of pricing NFT and poor liquidity are very prominent, which has also become a bottleneck restricting the further development of the NFT field. In the links of NFT casting, issuance and trading circulation, a reasonable and reliable price discovery mechanism is an important support. At present, the products of the NFT track are still very scarce, and the development is seriously lagging behind.
Today, Odaily will introducePawnHousesecondary title
What is PawnHouse?
PawnHouse is an NFT pricing solution platform. Its current main products include an NFT mortgage lending platform and an upcoming Simultaneous Multi-Round Auction (SMRA) system. The transaction volume of its mortgage lending platform has exceeded 100 million U.S. dollars since its launch, and the upcoming Simultaneous Multi-Round Auction (SMRA) system aims to create an NFT decentralized oracle network. PawnHouse provides NFT mortgage lending and Synchronous Multi-Round Auction (SMRA) system to build NFT price corridors to obtain common value discovery, and is committed to price discovery and liquidity enhancement in the NFT market.
On October 28, PawnHouse announced the completion of a new round of financing of US$2 million. Investors include HG Ventures, Znoff Capital, Crypto Times, Chronos Ventures and other strategic partners. The funds will be used to strengthen the company’s NFT pricing infrastructure and improve the liquidity of the NFT market. At the same time, PawnHouse will continue to build its multi-chain and cross-ecosystem NFT architecture, and strengthen its operations and development in global markets such as Japan, South Korea, and Russia. On August 27, PawnHouse announced the completion of its first round of financing, with participation from Huobi Ventures, A&TC Capital, and Spark Digital Capital. The financing amount was not disclosed.
Price Discovery for NFTs: Understanding Private and Common Value
The current Fungible Tokens pricing mechanism comes from order book systems or matching engines such as AMMs. Buyers and sellers are brought together to freely place orders and quotes, forming a nearly perfectly competitive market. The bidding process is also the process of price discovery. The core of pricing is the relationship between supply and demand and the transmission of price information.
Obviously this method does not work for Non-fungible Tokens. Although there are many NFTs in total, each one is unique.
Auctions are a common method for NFT pricing and transactions, such as English auctions and Dutch auctions. Beeple's NFT work "Everydays: The First 5000 Days" was sold for $69.34 million at Christie's English auction.
Using these two auction methods as a solution for buying and selling individual NFTs is feasible. However, if only the final transaction price is used as a fundamental reference, it cannot capture the effective price space of this NFT and the range where most people are willing to bid. This is also one of the reasons for the high price and low frequency trading of NFT in reality.
In order to better discover NFT prices, PawnHouse introduces two concepts of "private value" and "common value". "Common value" was first proposed by economist Robert B. Wilson, and was applied in the theory of Simultaneous Multi-Round Auction (SMRA). PawnHouse believes that in the current NFT auction, the private value only reflects the value of the NFT to a special buyer, while the bidding range of most people reflects the "common value" of the NFT. In this price range, the NFT's The circulation efficiency is higher. For example, the final transaction price of Beeple's NFT works is 69.34 million US dollars. However, $69.34 million is just the private value of the Beeple piece to this particular buyer. In fact, the roughly $10,000 to $5 million price range was what most bidders offered throughout the auction. Therefore, the final transaction price should not be used as the main reference basis for ordinary users who may be interested in judging the price of Beeple's new works and other works on the market.
If a single auction transaction price is not enough to base a price on a particular NFT category, what is? The answer PawnHouse gives is: a lot of data and information generated by bidders with real motives. Offers from bidders who have no real motivation to participate in the transaction are meaningless. The data for the NFT price discovery mechanism therefore comes from a large number of bids that provide a highly dense price acceptance range. In addition, the authenticity of the bidder's motivation for bidding needs to be guaranteed. At the same time, the non-real motivation quotations here do not include heterogeneous quotations, because NFT objectively has differences in private value sense, so the typical FT oracle mechanism for punishing heterogeneous quotations does not apply to NFT.
PawnHouse's NFT Price Discovery Solution: Building a Price Corridor for NFT Assets
The biggest difference between the model designed by PawnHouse and ordinary NFT trading platforms is that the core or unique value of NFT is not measured by the final transaction price.
PawnHouse's goal is to capture all useful and valuable data and information from auctions happening on the platform throughout the auction process, especially in the Simultaneous Multi-Round Auction (SMRA) system (or possibly extract data from other platforms in the future as well) ), and use more open and timely information to encourage and strengthen bidding behavior, and build a "price corridor" for NFT assets through real and dense quotation ranges. All the information captured in the bidding will generate a certain type of common value of NFT, and PawnHouse uses the common value discovery mechanism as an oracle machine for NFT.
Currently, PawnHouse has designed three liquidity acquisition methods, and this process builds a "price corridor" of NFT assets through data recording, which promotes the price discovery of NFT assets. The three models are Mortgage Loan & PawnTickets Circulation, Limited-Time Bidding, and Simultaneous Multiple Round Auction (SMRA). Among them, the synchronous multi-round auction SMRA is the core.
1. Mortgage lending and PawnTickets circulation
The NFT mortgage contract is an NFT mortgage lending DeFi product that allows users to borrow or lend funds. Compared with other mortgage lending products, PawnHouse's contract innovation lies in the design of the automatic circulation and transfer link of PawnTicket, which increases the number of quotations during the loan period. During the quotation and transfer process of PawnTicket, a price corridor is gradually formed. Based on the information recorded on the chain, it provides sufficient and effective price information for trading decisions. In addition, to incentivize popularity, lenders who provide liquidity for mortgage assets and investors who participate in the circulation of PawnTickets can obtain token incentives.
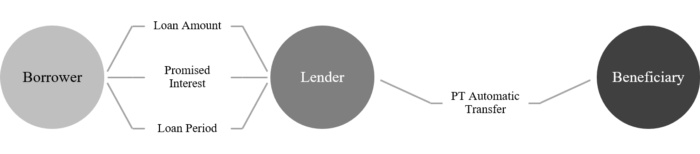
2. Time-limited auction
For defaulted PawnTickets that fail to repay on time, a time-limited auction will automatically start when it expires. This model is also suitable for holders who want to convert NFT into cash as soon as possible. These users can complete the disposal of assets by submitting time-limited bidding orders. This limited-time auction process also produced more price information.
3. Simultaneous Multi-Round Auction (SMRA)
Simultaneous Multi-Round Auction (SMRA) was proposed and designed by economists Paul R. Milgrom and Robert B. Wilson, who were jointly awarded the 2020 Nobel Prize in Economics for "the invention of a new auction format and improvements to auction theory" (Officially the Swedish Riksbank in memory of the Alfred Nobel Prize in Economics).
The US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) used SMRA for the first time in 1994 to conduct an auction of radio spectrum licenses. The auction sold 10 licenses in 47 rounds for $617 million and was covered by the New York Times in 1995. Voted "Greatest Auction in History". As a paradigm in multi-item auctions, SMRA has been emulated by many countries around the world. This auction mechanism has also been extended to the auction of public assets such as natural gas and electricity.
The special feature of the auction of radio spectrum licenses is that multiple licenses are auctioned at the same time. There is a substitution relationship and a complementary relationship between the licenses.
In SMRA's design, all licenses available for auction are auctioned simultaneously. The auction is conducted in multiple rounds. In each round, buyers may make separate sealed offers for one or more license plates. After each round of bidding, the auctioneer announces the highest bidding price for each license plate in that round, and the starting price of the next round of auctions will be increased by 5%-15% on the basis of the highest bidding price in the previous round. Buyers are required to bid for at least a certain percentage of the licenses in each round, otherwise they will be disqualified from bidding in future rounds. In this way, when there are no higher bids for all license plates, the entire auction ends, and each license plate is owned by the highest bidder.
The advantage of SMRA is that it solves the problem of substitution and complementarity between different auction items. Buyers can optimally choose the combination of auction items they want to buy according to the price in each round. Secondly, integrating the information behind the bidder’s quotation into the auction process can fully reveal the information and avoid the problem of “winner’s curse” (the bidder wins the product, but the bid is much higher than its true value) and the imbalance of information acquisition Problems (one with an information disadvantage will underbid or even withdraw from the auction due to uncertainty).
PawnHouse introduced SMRA into the NFT auction and designed the SMRA system. In the early stages of platform launch. In order to ensure that the duration of the auction is not too long, SMRA only needs 3 assets to start the auction. With the enrichment of the types of transactions on the platform, the NFT auctioned at the same time will be classified according to the dimensions of the underlying public chain, foundry platform, and foundry. At the same time, in the governance of DAO, the community will provide more classification standards suitable for DeFi. In addition, each round of bidding has a time limit and is executed in an automated manner on the chain.
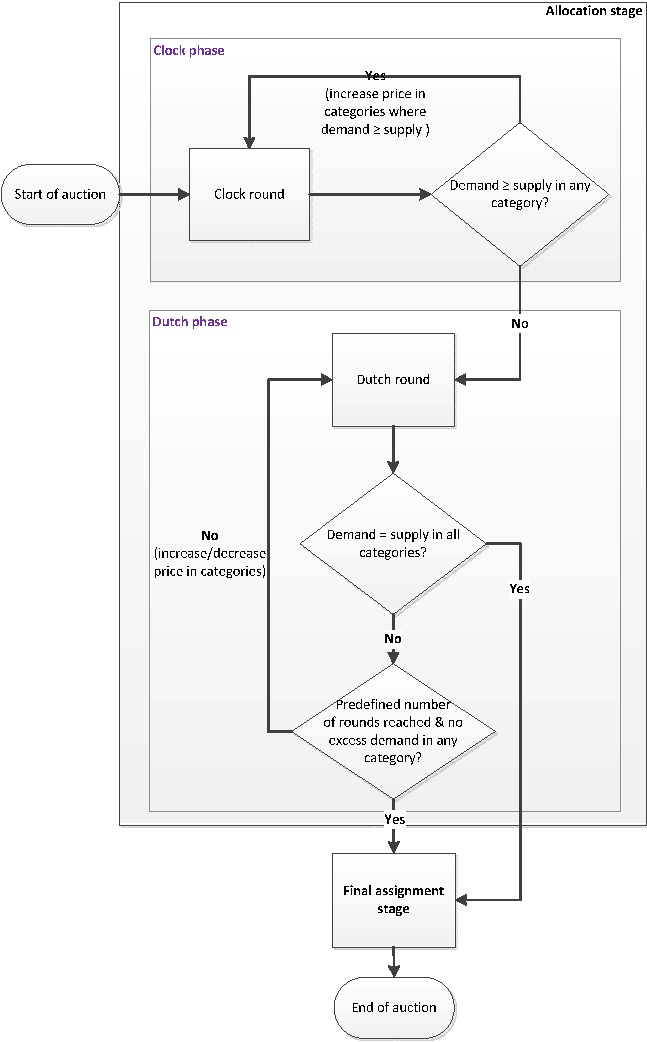
Building NFT decentralized oracle machine based on SMRA
asasNo one can accurately predict the price of markets and assets, but the more information you have, the better you can get the answers you need.
PawnHouse will collect as much quotation information from real investors as possible based on SMRA, build a decentralized NFT price oracle machine through price consensus, and use SMRA as an auction form for multi-asset sales. Implementation methods are optimized. As more users participate in the SMRA quoting system, PawnHouse will be able to collect more data to improve the accuracy of the price corridor.
The functions of the PawnHouse platform will be launched in three stages: the first stage is the launch of mortgage lending and liquidity mining, the second step is PawnTicket transfer and Staking mining, and finally the introduction of the SMRA system with reliable price corridors. These three phases are dedicated to developing NFT asset pricing tools through private and public value information.
token model
token model
PH is the native token of PawnHouse, and it is the certificate for users to participate in platform governance, profit distribution, token repurchase and other rules.
The total supply of PH tokens is 1 billion, of which 60% are used as mining incentives, including: liquidity mining and Staking mining. Among them, 24% will be supplied in the first year, 15% in the second year, 12% in the third year and 9% in total in the subsequent years.
The early team allocated 10%, unlocked half a year later, released 10% for the first time, and then released 90% within 3 years.
Financing allocation 15%.
Ecological incentive distribution 15%: 7% in the first year. 30% of them (21 million PH) will be unlocked after the project is launched, and 10% will be unlocked every time PawnHouse completes mortgage loan matching equivalent to 10 million US dollars. In the second year, 5% will be allocated, and PawnHouse will unlock 10% of it every time it completes USD 100 million USDT mortgage loan matching; in the third year, 3% will be allocated, and PawnHouse will unlock 10% of it every time it completes USD 200 million USDT mortgage loan matching . If the planned amount of the current year is fully unlocked before the end of the year, no new tokens will be added; if the matching mortgage loan amount of the year does not meet the full unlocking requirements, the remaining tokens will be directly destroyed.
epilogue
epilogue
The price discovery mechanism is a key part of the further development of the NFT ecosystem. If this key link is opened up, NFT trading, circulation and derivative financial applications will usher in substantial progress, and will also drive the development of NFT casting and project creation. PawnHouse provides a new way of thinking for NFT pricing. We also look forward to more NFT price discovery mechanisms in the market, and PawnHouse's scheme complements each other's strengths and jointly raises the ceiling of the NFT market.



