DeFi Science: How does Uniswap work?
Author: Bisade Asolo
Link to original report:
https://www.mycryptopedia.com/
first level title
Uniswap is an Ethereum-based protocol designed to facilitate automated exchange transactions between ETH and ERC20 token digital assets. Uniswap is fully deployed on the chain. Any individual user can use this protocol as long as they have installed decentralized wallet software (currently supported wallets include MetaMask, WalletConnect, Coinbase Wallet, Fortmatic, and Portis). Uniswap can also be considered a DeFi project because it tries to use decentralized protocols to completely disintermediate the digital asset transaction process.
There are two types of smart contracts in Uniswap:
transaction contract
factory contract
These smart contracts are written in the Vyper smart contract programming language, and they are the core components of the Uniswap protocol to achieve various functions. A trading contract supports an ERC20 token, and each trading contract reserves a certain amount of ETH and the supported ERC20 token. This means that transactions executed in an ERC20 token-ETH trading contract are all based on the relative supply of ETH in this contract and the ERC20 token.
Through ETH as an intermediary, the transaction contract can also realize the direct transaction between one ERC20 token and another ERC20 token.
The factory contract can be used to deploy new trading contracts. Therefore, any ERC20 token that does not have a trading contract on Uniswap can use the factory contract to deploy a trading contract. Any Ethereum user can do this via the 'createExchange()' function. The factory contract plays the role of the "registration center" of the transaction contract in Uniswap. The factory contract can be used to find all the ERC20 tokens and transaction addresses that have been added to the Uniswap system. After a transaction contract is released, the factory contract will not perform operations such as background checks on the ERC20 tokens in the transaction contract. There is only a restriction that "a transaction contract only contains one ERC20 token". Therefore, users should only participate in the transactions of those ERC20 token projects that they trust.
Asset Liquidity on Uniswap
The design structure system of the Uniswap protocol is completely different from the transaction model in traditional digital asset exchanges. Most traditional exchanges match buyers and sellers of a digital asset by maintaining an "order book". Uniswap is completely different. It uses the liquidity of reserve funds to realize the exchange of digital assets on the agreement.
The reserves in the trading contract are provided by many "liquidity providers". These liquidity providers recharge the equivalent ETH and ERC20 tokens into this trading contract. The first liquidity provider who provides liquidity to this contract has the right to set the exchange rate between this ERC20 token and ETH. The first liquidity provider recharges the amount of ETH and the amount of ERC20 tokens that they think are equivalent to the transaction contract, and then the exchange rate can be set. And if the exchange rate set by the first liquidity provider is inconsistent with the larger market outside, then arbitrage traders will use bricks to smooth out these price differences and maintain an exchange rate consistent with the broader market. After that, all liquidity providers will use the exchange rate when they recharge as the basis for calculating the equivalent.
Uniswap also issues a “liquidity token,” which also complies with the ERC20 standard. This liquidity token represents the contribution of the liquidity provider to this trading contract. The logic behind Uniswap's restriction that "one trading contract only supports one ERC20 token" is to encourage liquidity providers to concentrate the liquidity they provide into the reserve fund of a trading contract. Uniswap issues liquidity tokens to track the ratio of the reserves contributed by each liquidity provider to the total reserves. The liquidity provider can choose to destroy the liquidity tokens it holds at any time, and then redeem the corresponding proportion of ETH and the ERC20 tokens from the trading contract.
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
text
Exchange rate = 45.33 BAT/ETH
The second transaction type on Uniswap: ERC20 ⇄ ERC20 transaction
Another type of transaction that can be performed on Uniswap is the exchange of an ERC20 token for another ERC20 token. Since ETH is regarded as the public trading pair of all ERC20 tokens, Uniswap uses ETH as an intermediary asset to realize the exchange transaction between ERC20 tokens and ERC20 tokens. For example, Uniswap can realize: convert BAT to ETH in one transaction contract, and then convert ETH to OMG in another transaction contract (for example, another ERC20 token), all of which occur in one transaction operation.
text
text
Uniswap charges fees for transactions that have occurred as follows:
ETH/ERC20 token transaction: 0.3% of ETH transaction amount
ERC20 token/ETH token transaction: 0.3% of ERC20 token transaction amount
ERC20/ERC20 transaction: 0.3% of the transaction volume of selling ERC20 tokens and 0.3% of the transaction volume of the intermediate medium ETH
Uniswap token exchange rate
The constant product formula used by Uniswap to determine the exchange rate of token transactions was originally derived from an article published by Vitalik Buterin in March 2018. As stated in this article, the transaction exchange rate of ERC20 tokens is calculated according to the following formula:
x * y = k
k represents an unchanging constant
x and y represent the available quantities of ETH and ERC20 tokens in a particular trading pair.
For Uniswap, it is the reserve amount of ETH and the liquidity pool of the ERC20 token in the transaction contract of the ERC20 token and ETH. In this formula, the exchange rate between the ERC20 token and ETH will always be at a certain point on the result curve of this formula.
This formula is part of the Uniswap protocol, and Vitalik Buterin uses the following diagram to describe it:
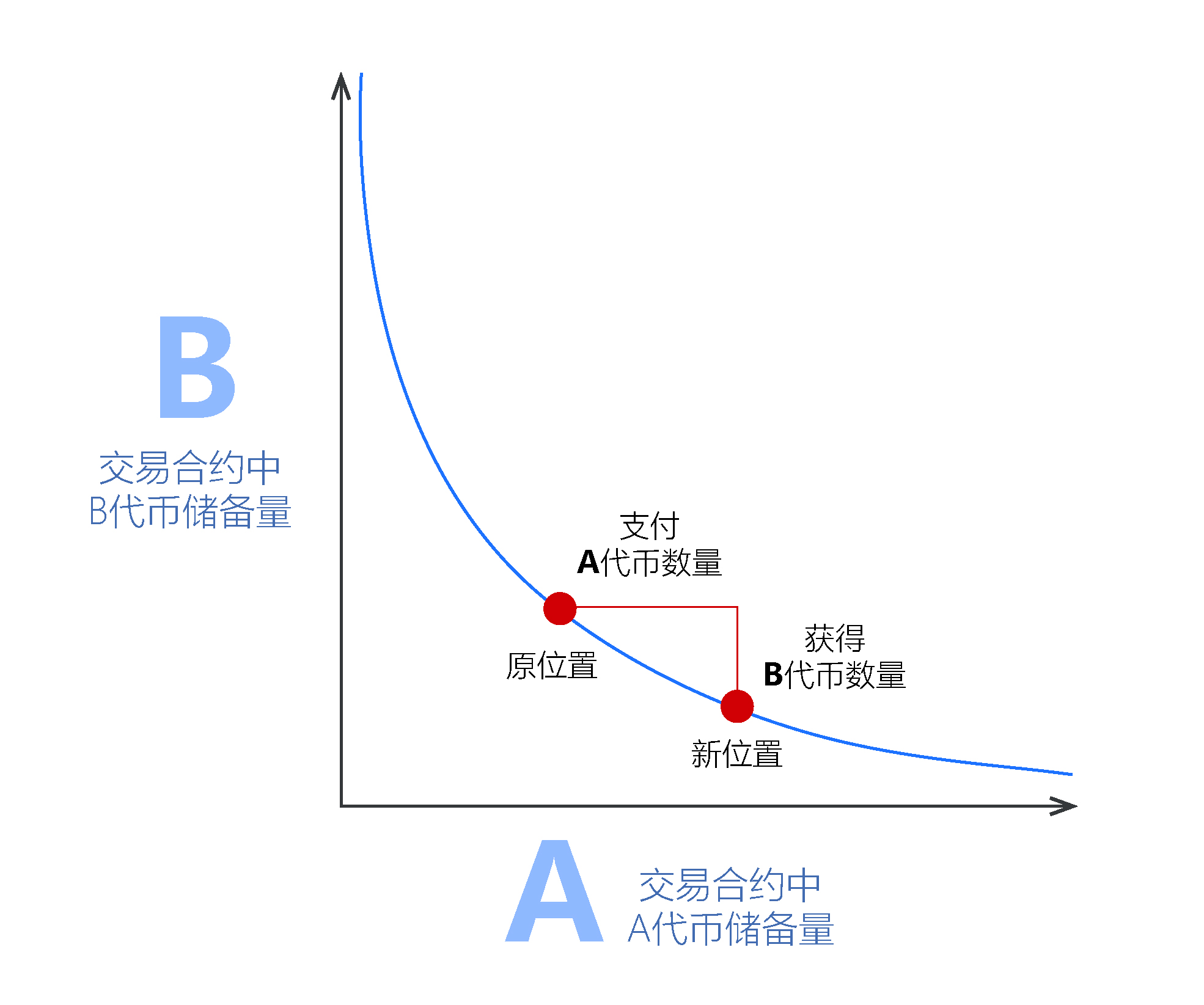
Using this formula, if we take the trading contract in Uniswap as an example, it means that the trading contract reserves x amount of A tokens and y amount of B tokens. This contract will always keep the product constant, that is, x * y yields the same value of k.
Anyone can buy or sell tokens by effectively changing the position of the market maker on the x*y curve.
The horizontal axis represents the quantity of A tokens sold, and the vertical axis represents the quantity of B tokens bought.
Assuming that token B is ETH, and token A is any ERC20 token, we can use the formula x * y = k to understand their functions:
If Alice decides to buy a large amount of A tokens, it will lead to a shortage of A tokens and an increase in the amount of ETH. Alice's purchase action causes the exchange rate to move to another point on the x * y = k curve.
The red dot will move to the left, that is, the price to buy A token becomes higher.
The relative supply of ETH and A token in the Uniswap trading contract can also be understood as the supply and demand relationship of A token, which determines the exchange rate between A token and ETH.
text
text
text
text
text
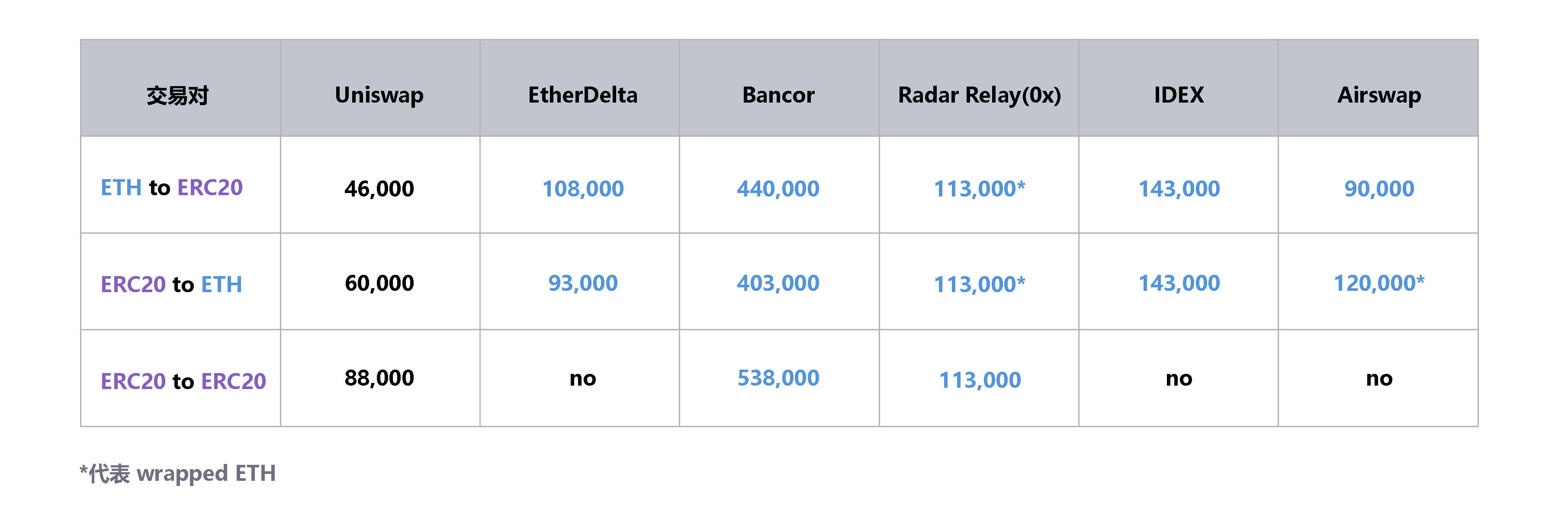
One of the advantages of using the Uniswap protocol for exchange transactions is that the Gas cost of transactions on Uniswap is very low compared to other decentralized exchanges. Gas consumption levels are shown in the table below, ERC20/ETH, ETH/ERC20, ERC20/ERC20 are much lower than Bancor and EtherDelta.
Saving Gas is just one of the advantages of the Uniswap protocol, and more advantages include:
Uniswap is decentralized, therefore, it does not depend on any third parties. Plus, it's free to access for any user. Compared with other digital asset trading platforms, the cost of trading on Uniswap is lower. Uniswap allows any user to create trading contracts for any ERC20 token.
Of course, Uniswap also has its limitations:
Uniswap does rely on arbitrage transactions to ensure that the transaction exchange rate is consistent with the market, which means that Uniswap relies on the transaction exchange rates of other exchanges to ensure its own exchange rate balance.
epilogue
epilogue
All in all, Uniswap makes digital asset trading more efficient. However, Uniswap is still in its infancy, and the most anticipated thing is its future development.



