Original author:WEIWEI
Original author:
2020 is a big year for the development of the blockchain. In this year, Uniswap, the king of Defi, rose and led the entire Ethereum ecosystem to prosperity. It was hailed as the summer of DeFi by blockchain practitioners.
What followed was the congestion of the Ethereum main network, and the soaring GAS fees caused by the congestion made it difficult for ordinary users to participate in this prosperous world. Therefore, blockchain practitioners turned their attention to Ethereum's Rollup expansion plan and new public chain. Both Rollup and the new public chain need to communicate between chains to complete the transmission of assets or data on different chains. The cross-chain bridge has become an indispensable part of the multi-chain ecology. However, from 2021 to 2022, well-known cross-chain projects such as Ronin Network, Horizon, BNB Chain, Wormhole, and Nomad have all had hacking incidents, and huge amounts of assets have been stolen. This series of cross-chain bridge hacking incidents tells us that the current cross-chain bridge is far from mature. There is still a long way to go to meet the market's expectations for cross-chain bridges and meet the needs of users.
1. Cross-chain logic shifts from decentralization to trustlessness
Decentralized cross-chain
With the development of cross-chain technology, there are mainly two aspects of progress. The first is inter-chain communication, which belongs to the expansion of cross-chain assets. The technology is relatively simple, but it can achieve extensive multi-chain interoperability. The second is to realize decentralized cross-chain. Typical solutions include MPC, Oracle Systems, PoS/PoA, multi-signature and TEE, etc. These solutions transfer the single-point trust problem to multi-point trust to form a decentralized network. A decentralized network is used to eliminate single-point risks. In the later stage of development, many cross-chain projects use a chain to achieve further decentralization. It can be simply described as from a single point of trust to a multi-point network of trust, and finally develops into a decentralized chain of trust. However, this scheme always needs to trust the relayer, which means increased security risks.
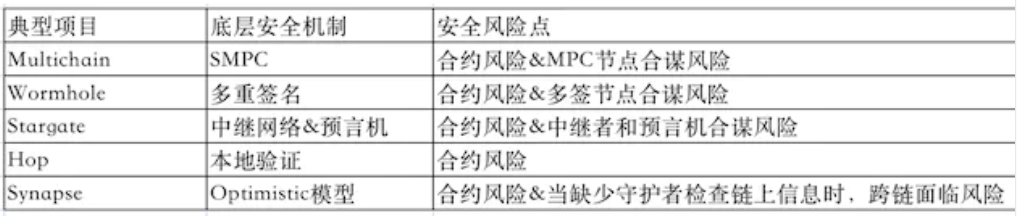
image description
Typical cross-chain project security mechanism and main risk sources
From the above table, it can be found that most of the current mainstream cross-chain solutions use the mechanism of trusting the third-party network, and the third-party network nodes may have the risk of collusion, and the locally verified Hop currently only supports Ethereum and L2, L2 and L2. Although there is no risk of collusion in local verification, it has weak versatility and is not suitable for general inter-chain communication. As a medium for users to interact with multiple chains, the best way is to trustless (Trustless), use the light client on the chain to verify cross-chain messages, and realize code as law without relying on honest nodes.
Trustless cross-chain
Typical Cefi scenarios such as banking, insurance, trust, and securities are different from DeFi scenarios. Various institutions in these systems face strong supervision from government agencies. This centralized supervision experience continues to develop with the birth of the financial system , is relatively safe. On the contrary, the current cross-chain protocol faces little supervision while carrying out global business, which is also one of the important reasons for the frequent occurrence of cross-chain bridge security incidents. As a blockchain project, its core narrative logic is decentralization. Naturally, centralized supervision is not recognized by the industry.
How to ensure the security of inter-chain communication without the supervision of a centralized institution is a problem faced by the cross-chain industry. The author believes that the best way to solve this problem is to realize trustless cross-chain while being permissionless, highly scalable, and easy to integrate. Only in this way will no new security risks be introduced. Users only need to trust the source chain consensus and target chain consensus during the multi-chain interaction process to complete secure inter-chain communication. The introduction of zero-knowledge proof (Zero-knowledge Proof, ZKP) technology into the cross-chain bridge scenario can perfectly realize trustless inter-chain communication, and zkRouter was born in this scenario. It has the following characteristics:
1. Do not introduce trust assumptions
The correctness of cross-chain messages is guaranteed by ZKP, and no external trust assumptions are introduced. On the premise of the security of the external public chain and the underlying consensus, as long as there is an honest node in the relay network, the security of the zkRouter cross-chain can be guaranteed. Code is law, which allows Dapps to use zkRouter as a tool for inter-chain communication without any worries.
2. No license
In order to allow more Dapps to use zkRouter, zkRouter is designed to be authorization-free, and Dapps can access zkRouter services by themselves. At the same time, zkRouter will be equipped with sufficient technical documents and integration middleware, so that Dapps can easily complete the integration.
High scalability is reflected in the fact that zkRouter is suitable for inter-chain communication between heterogeneous chains. Dapps can use zkRouter for inter-chain communication according to their own needs.
first level title
2. zkRouter - trustless inter-chain communication
The principle of cross-chain has been explained in detail in the article "How zkRouter achieves safe cross-chain", so I won't go into details here. ZKP cross-chain is one of the original cross-chain methods. The specific implementation method is very dependent on the source chain consensus, so expanding to multiple chains requires a large workload.<-->zkRouter is live on Ethereum
A two-way test cross-chain bridge between Fantom. Here, compare the Dashboard of the zkRouter website to explain the main participants and cross-chain process of ZK cross-chain.
The main participants of zkRouter in the entire cross-chain process are:1. Certifier:
The prover needs to synchronize the source chain state ZKP and the Merkle tree transaction path proof.** 2. Verifier:
**The verifier is a light client on the chain, verifying the ZK proof and the transaction Merkle tree path proof.3. User:
image description
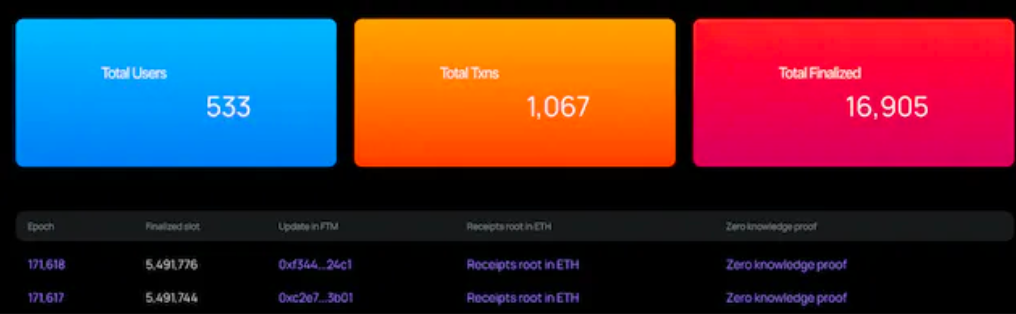
zkRouter Dashboard
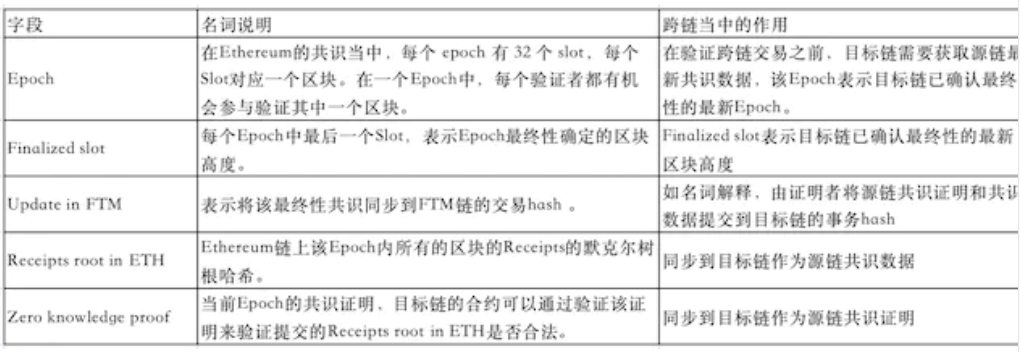
image description
zkRouter Dashboard Field Explanation
To maintain the operation of the ZK cross-chain bridge, the source chain consensus must be synchronized to the target chain. The consensus synchronization process is as follows:
** 1.** The prover will hash the Merkle root hash of the Receipts of all blocks in each Epoch that confirms the finality (current source chain consensus, including the LOG information of all transactions in the Epoch ) to the target chain and provide the corresponding ZKP proof.
** 2.** The target chain light client will verify the latest source chain consensus based on the historical source chain status and ZKP proof.On the basis that the target chain maintains the consensus state of the source chain, users can use cross-chain services.
Specific cross-chain process:
1. The user initiates a cross-chain transaction;
2. Wait for the transaction to be finalized;
3. The prover synchronizes information such as the source chain transaction Merkle query path to the target chain;
4. The target chain light client verifies whether the transaction information is included in the current source chain consensus;
The prover cannot construct a verifiable ZKP without tampering with the data. At the same time, the receiver can independently verify the authenticity of the received content based on ZKP. This means that the generation and transfer of ZKP will not have any impact on trust, thus realizing the transfer of consensus in a trustless manner. Trustless is also reflected in the fact that anyone in the real world can complete the generation and delivery of ZKP for zkRouter. Even if these nodes come from the project side of the application built with zkRouter, zkRouter can still work safely and credibly. For these reasons, zkRouter delegates both tasks to Relyaer. The Relayer can only work truthfully, generate a valid ZKP and pass it to the target chain accurately, or not work, and there will be no possibility of doing evil. Therefore, zkRouter can accept anyone to become a Relayer, and incentivize effective work in a Tokenomic way. Among the many relayers, only one relayer can guarantee the effective operation of zkRouter.
first level title
3. The multi-chain layout of Multichain
Starting from the prosperity and development of the multi-chain ecology in 2021, Multichain was the first to use MPC technology to build a cross-chain bridge and gained a leading market position. Today, more than 1,000 Dapps have implemented multi-chain deployment through Multichain, connecting 89 public chain ecosystems, covering more than 900,000 users, and already have a huge ecosystem. The multi-chain layout has achieved initial results.
But as mentioned at the beginning of the article, trustless cross-chain can eliminate the doubts of Dapps and users, and is the right way to open future inter-chain communication. The cross-chain solution based on MPC technology cannot meet the needs of all users for cross-chain bridges. To better serve all cross-chain applications, zkRouter will be a more effective choice.
In the 2023 Hong Kong Web3 Carnival Forum, Zhang Guojun, Deputy Secretary of the Hong Kong Department of Justice delivered a speech, announcing the launch of the Hong Kong Web3 Hub Ecological Fund, through this compliant platform to encourage more companies to settle in Hong Kong and promote the development of the web3 industry. As the co-sponsor of the Web3 Hub Ecological Fund, Multichain can use this platform to attract more ecological projects and grow itself.
By the beginning of 2022, Multichain will mainly build products such as Router and Bridge around asset cross-chain. With the individualization of inter-chain communication needs, pure asset cross-chain cannot meet the needs of Dapps and users. anyCall came into being, and anyCall can complete general message Cross-chain, at the same time has the characteristics of no permission, high scalability, and easy integration. It is suitable for multi-chain Dapps and will become the main support for Multichain to expand its larger ecology in the future.
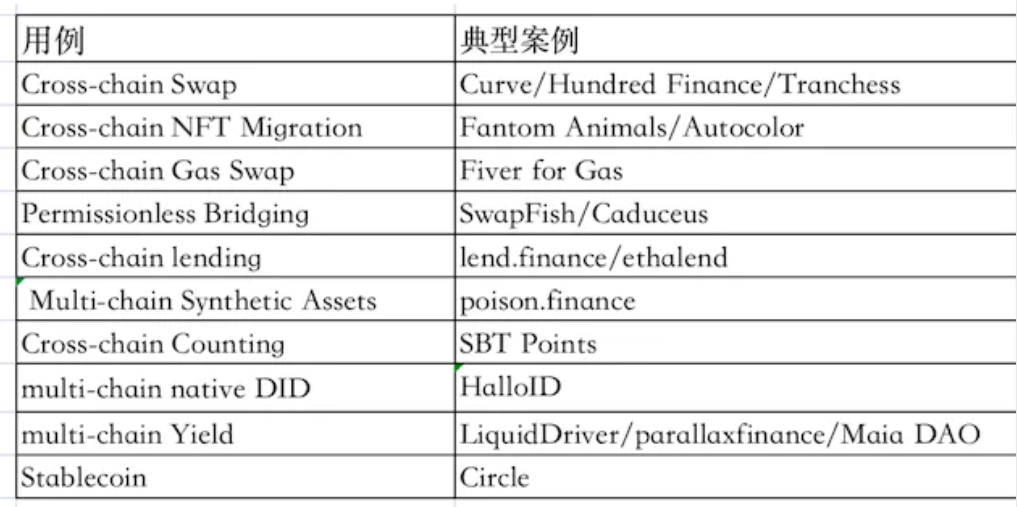
image description
anyCall typical use case
Some of the above use cases are conventional multi-chain use cases, and the application scenarios of anyCall are far more than these. Of course, as a general inter-chain communication protocol, the combinability and innovative use of it are not determined by anyCall, but rely on multiple The development and innovation of the chain ecology itself. What are the more novel use cases for inter-chain communication in the future? I believe the market will give the answer.
zkRouter empowers anyCall with unlimited possibilities
Nowadays, the multi-chain development situation is good. At present, there are hundreds of L1 public chains (bottom chains), and dozens of L2 public chains. The L3 public chain is on the way. These blockchains are all developed based on different needs, and the public chain ecology is also very different. Multi-chain Dapps were born in this scenario. For multi-chain Dapps, in order to maintain a unified state in a multi-chain environment, it is necessary to rely on inter-chain communication. Trust assumptions are generally required in current inter-chain communication relay schemes, which limits the development of inter-chain communication.



