Cobo: Review of the major DeFi security events in 2022
Original post by Max Cobo Security Director
Original source: Cobo Global
Invited by Moledao, Cobo Security Director Max recently shared a DeFi security lesson for community members via the Internet. Max reviewed the major security incidents encountered by the Web3 industry in the past year or so, and focused on the reasons for these security incidents and how to avoid them. He also summarized the security vulnerabilities and preventive measures of common smart contracts. Some security suggestions are given. Here, we divide the content shared by Max into two releases for collection by DeFi enthusiasts.
According to SlowMist statistics, in 2022 there will be300 Multiple blockchain security incidents involving a total amount of$4.3 billion。
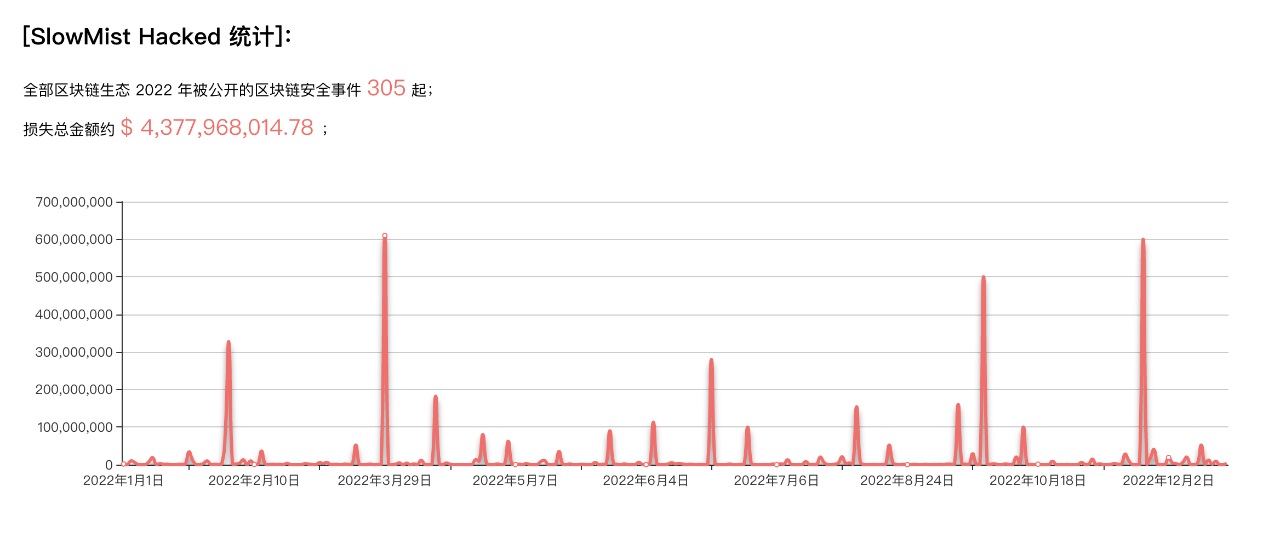
secondary title
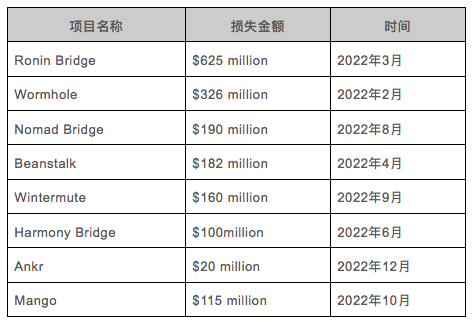
Ronin Bridge
Event review:
On March 23, 2022, the NFT game Axie Infinity sidechain Ronin Network stated that it had earlier discovered that Sky Mavis's Ronin validator node and Axie DAO validator node had been compromised, resulting in the bridging of 173,600 tokens in two transactions. ETH (currently worth over $590 million) and 25.5 million USD.
The U.S. Treasury Department said the North Korean hacking group Lazarus was linked to the $625 million hack of the AxieInfinity Ronin Network.
According to people familiar with the matter quoted by the media, the hacker contacted an employee of Sky Mavis, the developer of Axie Infinity, through LinkedIn, and told him that he was hired with a high salary after several rounds of interviews. The employee then downloaded the fake "Offer" letter presented as a PDF document, causing hacking software to infiltrate Ronin's systems, thereby hacking and taking over four of the nine validators on the Ronin network, short of one validator being unable to fully control. Subsequently, hackers took control of Axie DAO, which had not been revoked, to achieve the final intrusion.
The North Korean hacker group has existed for a long time. When Web3 technology was not yet popular, there were many news reports that some banks or large commercial institutions were hacked. Now, more and more traditional hacker groups, as well as some state-level forces, have evolved from stealing data and credit card information in the past to attacking blockchain projects and directly gaining actual benefits.
The attack method of this incident is very typical. In the traditional security field, it is called APT, which stands for Advanced Persistent Threat. Once the hacker group determines the target, it will use social engineering and other methods to first control a computer in the target organization as a springboard for further penetration and finally achieve the purpose of attack.
secondary title
Wormhole
Event review:
According to Wormhole’s report on the incident, the Wormhole’s vulnerability in this incident is specifically that there is an error in the signature verification code of the core Wormhole contract on the Solana side, which allows attackers to forge messages from the “guardian” to mint Wormhole-wrapped ETH. Lost about 120,000 ETH.
Jump Crypto invests 120,000 Ethereum to make up for the stolen loss of Wormhole, a cross-chain bridge, and supports the continued development of Wormhole
secondary title
Nomad Bridge
Event review:
The cross-chain interoperability protocol Nomad Bridge was hacked because the trusted root of the Nomad Bridge Replica contract was set to 0x 0 during initialization, and the old root was not invalidated when the trusted root was modified, which led to the attacker being able to construct Arbitrary messages were used to steal funds from the bridge, and the attackers were able to extract over $190 million in value from the attack.
The hacker took advantage of this vulnerability to find a valid transaction and repeatedly send the structured transaction data to extract the locked funds of the cross-chain bridge, resulting in almost all the locked funds on Nomad being stolen.
PeckShield monitoring shows that in the Nomad attack, about 41 addresses made a profit of about 152 million U.S. dollars (accounting for 80%), including about 7 MEV robots (about 7.1 million U.S. dollars), Rari Capital hackers (about 3.4 million U.S. dollars) USD) and 6 white-hat hackers (approximately USD 8.2 million), about 10% of the ENS domain name addresses made a profit of USD 6.1 million.
The Nomad Bridge event is very typical, essentially because there are some problems in its settings during initialization. If a hacker finds a batch of once-valid transactions and re-broadcasts them, the funds involved in that valid transaction will be lost again. Execute and return the proceeds to the hacker. In the entire Ethereum ecosystem, there are many participants. In addition to project parties and participants, there are also many MEV robots. In this case, when the automated robot discovers the attack transaction, no matter who broadcasts it, the person who broadcasts it will get benefits. As long as the gas fee can be covered, everyone will broadcast more, so the whole incident has become a money-grabbing incident. There are many addresses involved in this incident. Although the project party found some addresses of ENS and some white-hat hackers afterwards and recovered some of the funds, most of the funds were not recovered. If a hacker uses a very clean device and a very clean address, it will be difficult to find out who is behind it from the perspective of some data associations.
secondary title
Beanstalk
Event review:
Beanstalk Farms, an algorithmic stablecoin project based on Ethereum, lost about $182 million in this flash loan attack. The specific assets include 79238241 BEAN 3 CRV-f, 1637956 BEANLUSD-f, 36084584 BEAN and 0.54 UNI- V2_WETH_BEAN. The attacker earned more than $80 million, including about 24,830 Ethereum and 36 million BEAN.
The main reason for this attack is that there is no time interval between the two stages of voting and execution of the proposal, so that the attacker can directly execute the malicious proposal without community review after the voting is completed.
Attack process:
Purchase tokens one day in advance and pledge to obtain proposal qualifications, and create malicious proposal contracts;
Obtain a large number of tokens to vote on malicious contracts through flash loans;
Malicious contract execution completes arbitrage.
Beanstalk is also a typical case. The hackers did not use any vulnerabilities, but only used a mechanism of the project. The mechanism of this project is that anyone can submit a proposal after mortgaging tokens, and the proposal is also a contract. The attacker bought a certain amount of tokens the day before the attack, and then submitted a malicious proposal. The proposal can be voted on after 24 hours. There is no time window and no time lock after the vote is completed, and the vote is passed. , it can be executed immediately.
secondary title
Wintermute
Event review:
On the morning of September 21, 2022, Evgeny Gaevoy announced the progress of the theft incident on Twitter, saying that Wintermute had indeed used Profanity and an internal tool to create wallet addresses in June. The reason for this is to optimize the handling fee, not just to create a good name, and said that after learning of the vulnerability in Profanity last week, Wintermute accelerated the deprecation of the old key. But due to an internal (human) error, the wrong function was called, so Wintermute did not remove the signature and execution of the infected address.
We can see that there are eight 0 numbers in front of many online addresses. The more 0s in the Ethereum address, the lower the handling fee. Therefore, many MEV bots and project parties prefer to use them, especially some relatively high-priced ones. frequently operated.
Wintermute is a market maker. At that time, they sent a lot of tokens to a contract, and used the smart number generation program to generate the contract address. The owner of this contract is also a good name. Unfortunately, the private key of the owner's good name was forcibly calculated, and all the money in the contract was directly transferred away.
secondary title
Harmony Bridge
Event review:
The Horizon cross-chain bridge lost more than $100 million, including more than 13,000 Ethereum and 5,000 BNB.
According to the founder of Harmony, the Horizon attack was caused by the leakage of the private key.
A suspected North Korean hacking group known as the Lazarus Group is believed to be behind the theft of $100 million on Harmony cross-chain bridge Horizon, according to a new analysis by blockchain research firm Elliptic, Bloomberg reported. Elliptic's analysis highlights key factors in the hack that point to the Lazarus Group, including programmatic money laundering that was automatically deposited into Tornado.Cash to simulate the Ronin Bridge incident, and the timing of the theft.
secondary title
Ankr
Event review:
Ankr: Deployer update contract.
Ankr: Deployer transferred BNB to Ankr Exploiter.
Ankr Exploiter is minted through the minting method of the updated contract.
10 trillion pieces of aBNBc were minted out of thin air. Hacker A exchanged aBNBc for 5 million USDC through PancakeSwap, which emptied the transaction pool and caused aBNBc to almost return to zero. Hacker A subsequently transferred the currency to Ethereum and transferred it to Tornado Cash.
About half an hour after hacker A minted coins, aBNBc plummeted, creating an arbitrage opportunity. Arbitrageur B used the 6-hour average overtime weight setting of the oracle machine of the lending agreement Helio, and used the price difference between aBNBc in the market and in the Helio system to set its Swapped into hBNB, and pledged hBNB out of the stablecoin HAY, and exchanged it into BNB and USDC. A total of more than 17 million US dollars equivalent of stablecoins and BNB were withdrawn, which basically emptied HAY's trading pair pool.
Ankr will transfer funds from the $15 million recovery fund to purchase additional HAY to compensate victims of the attack
The overall loss of Ankr is not big, let's talk about it individually. Because many DeFi projects are now Lego building blocks, A depends on B, B depends on C, and various assemblies, then when there is a problem in one link in the chain, all upstream and downstream in the entire chain may be affected.

secondary title
Mango
Event review:
The hacker used two accounts with a total of 10 million USDT initial funds.
In the first step, the hacker transfers USD 5 million to addresses A and B of the Mango trading platform respectively.
In the second step, the hacker uses the MNGO perpetual contract short-selling platform Token MNGO on Mango through the A address, the opening price is 0.0382 US dollars, and the short position is 483 million; at the same time, the hacker is long MNGO at the B address, and the opening price is 0.0382 US dollars, 483 million long positions. (The reason for both long and short openings is that the Mango platform is not deep enough. If you don’t compete with yourself, it is difficult to open such a high position)
In the third step, the hacker turns around and pulls up the spot price of MNGO on multiple platforms (FTX, Ascendex), causing the price to increase by 5-10 times. The price of MNGO on the Mango platform rose from US$0.0382 to a maximum of US$0.91.
In the fourth step, the hacker's long position profit is 483 million * ($0.91 - $0.0382) = $420 million, and the hacker then uses the net assets of the account to borrow from Mango. Fortunately, the platform lacked liquidity, and the hackers ended up only lending nearly $115 million in funds.
After the attack, the hacker released a new proposal, expressing the hope that the government will use treasury funds ($70 million) to repay the bad debts of the agreement. It is understood that the current treasury funds are approximately US$144 million, including MNGO Token worth US$88.5 million and USDC worth nearly US$60 million. The hackers said that if officials agree to the plan, some of the stolen funds will be returned, while hoping that there will be no criminal investigation or freezing of funds. "If this proposal is passed, I will send the MSOL, SOL and MNGO in this account to the address announced by the Mango team. The Mango treasury will be used to cover the remaining bad debts in the agreement, and all users with bad debts will be fully compensated.... ..once the Tokens are returned as described above, there will be no criminal investigations or freezing of funds.”
According to CoinDesk, the Mango attacker Avraham Eisenberg, who was previously identified, was arrested in Puerto Rico on December 26, 2022. Avraham Eisenberg faces charges of commodity fraud and commodity manipulation, which may be punished by fines and imprisonment.
The event of Mango can be defined as a security incident or an arbitrage behavior, because the problem is not a security vulnerability, but a business model vulnerability. Its trading categories include currencies with high market value such as BTC and ETH, as well as small currencies such as MNGO. When the liquidity of this small currency is insufficient in a bear market, it is possible to pull up the price of the currency with a small amount of money , This kind of currency price manipulation makes the position management of the perpetual contract platform very difficult.
Therefore, as a project party, we must fully consider various scenarios, and when testing, we must include all scenarios that exceed expectations in the test cases.
Original link



