Understanding Web3 Identity in One Article: Blockchain, Identity Proof, and Oracles

Web3smart contractsmart contractApplications (i.e. dApps). This has led to utility, governance and asset-backed tokens, and dApps can use, trade, borrow and earn tokens in various business and social application scenarios.
Web3 brings many benefits to society, lowering the capital threshold, improving application transparency and encryption security, and providing permissionless financial services to the masses. While Web3 has achieved such success, it faces the risk of hyper-financialization. Once hyper-financialization occurs, those with the deepest pockets will have disproportionate influence over core areas such as ecological development, governance, and culture. Currently, Web3 users know nothing about each other other than each other's on-chain addresses.
In order to unlock more innovative application scenarios, Web3 needs to establish a technology stack to operate based on the user's economic and social attributes. In this way, on-chain relationships are not limited to transactions, but can be extended to various dimensions such as personal relationships, culture, reputation, identity, and trust.
Integrating social capital into Web3 requires the creation of an identity layer on the chain to expand the use of addresses on the chain, not only to display account balances, but also to include various information such as user characteristics, social relationships, and reputation. Combining these identity information together, Web3 users can have a "soul". E. Glen Weyl, Puja Ohlhaver and Vitalik Buterin in the titled“Decentralized Society: Finding Web3’s Soul”This concept is elaborated in the research paper of .
first level title
Why is Web3 creating an identity layer?
trust minimizationtrust minimization, the process can be almost 100% guaranteed to proceed as the participants expected. The reason why the blockchain adopts decentralization, economic incentives and encryption technology is to minimize trust and ensure the accuracy, timeliness, manipulation resistance and non-tampering for users. Execute code and store data in a trust-minimized way on the blockchain, which is also known as "image description”。
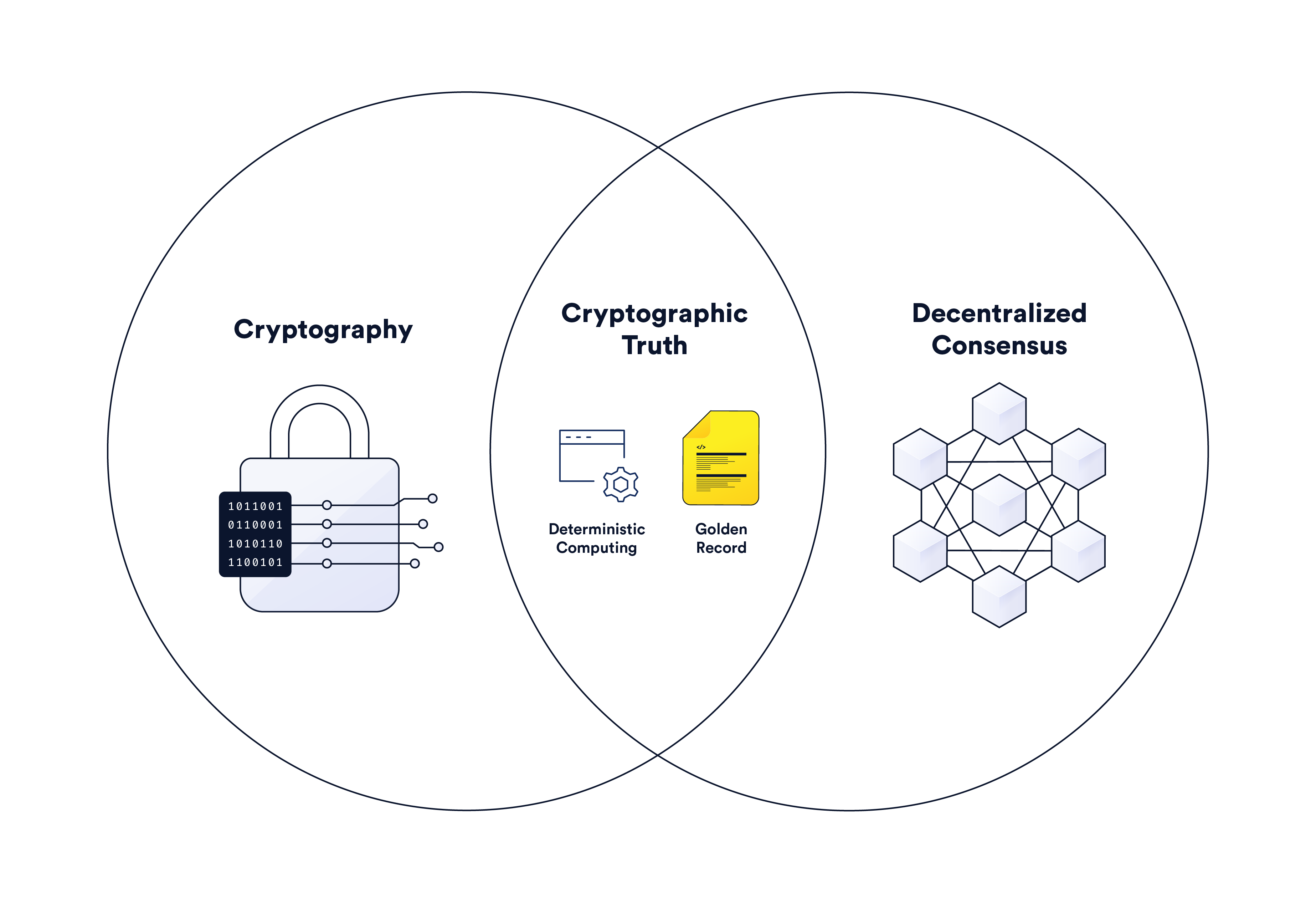
Encrypted fact combines encryption technology and decentralized consensus to reach consensus in a distributed network, create a unified record, and perform calculations for applications in a deterministic manner.
Cryptofacts are primarily created based on game theory, which encourages rational behavior by the majority of nodes in a decentralized network by incentivizing correct behavior with rewards and punishing wrong behavior. For example, most blockchain game theories assume that if the network is completely transparent, decentralized, and economically incentivized, it will be difficult for attackers to succeed because they must pay a certain economic cost to launch an attack (for example, computing resources are required in a PoW network). , Pledge tokens are required in the PoS network). The ultimate goal of this game mechanism is to create deterministic software, that is, an input x will always output an outcome y.
The problem, however, is that financial incentives alone are simply not enough to create the framework for end-users to engage in social and economic activities. First of all, in some application scenarios, the penalty mechanism established to achieve trust minimization may be too strict for users, and the penalty is greater than the reward, so the gain outweighs the loss. What if I get fined due to accident or misunderstanding? In many application scenarios, users do not want to be affected by economic factors, or at least do not want to take the risk of staking a large amount of assets in the interaction (such as governance, public goods and social clubs).
Web3 protocols may also face many other challenges, such as legal compliance, verifying off-chain behavior, or resolving disputes. This is especially true for protocols where users are pseudo-anonymous. While pseudo-anonymity is a valuable feature in some application scenarios (for example, to defend against the risk of manipulation), for many applications, certain personal information of the end user must be known in order to function properly.
Therefore, we urgently need to create an identity layer on the chain for Web3, which can prove the user's social identity to the blockchain application while protecting the privacy of the user's reputation, KYC/AML, characteristics and other personalized data, and retain the block to a certain extent or completely The feature of chain trust minimization. Identity solutions can help users and applications understand information other than user account balances and transaction history, and conduct on-chain interactions based on various types of social information.
first level title
Underlying Technology of Web3 Identity Solutions
To better understand identity information, let's first look at the following three types of identity information:
official status -Refers to an individual's officially recognized or legally recognized achievements and facts in a jurisdiction.
social status -Refers to an unofficial attribute, achievement, or claim that an individual receives from another person.
self-identity-Refers to an attribute, achievement, or claim that an individual creates for himself or herself.
How these three types of identity information are applied to the Web3 field depends on the specific value orientation and business needs of developers, users, or decentralized communities. For example, some companies may prefer official private identity information due to their own operating mechanism. Some Web3 native applications may be more inclined to transparent social identity solutions, and the decentralized community can verify the information of users on the chain through consensus. Each type of identity information has its own advantages and disadvantages, which need to be fully considered before adopting.
secondary title
blockchain
blockchainIt is a public database. Technically speaking, the data stored by users cannot be tampered with. Anyone in the world can access these data and can be easily applied to various scenarios. However, storing raw personally identifiable information (PII) on public chains may lead to serious privacy concerns because public chains are open and transparent in nature.
secondary title
Proof of Identity: Identity Information and Proof
Proof of identity refers to a claim about a person's qualifications, achievements, characteristics, or any background information. Identity solutions use proofs to verify that an individual is qualified to perform certain actions, such as driving a car only with a driver's license, or practicing in a certain profession with relevant professional certification.
The fundamental purpose of Web3 is to establish digital relationships, so the key to developing Web3 identity solutions is to have access to digital proofs. The two most common features of Web3 identities are verifiable credentials and decentralized identities (DIDs). A verifiable proof of identity is an immutable statement about a user's identity, cryptographically signed by the issuer. The verifier (verifier) can verify this identity certificate through DID, such as using the public-private key pair on the blockchain to verify that the hashed identity certificate belongs to a certain user.
Alternatively, identity data or proofs can be turned into tokens. for example,Soul Binding Token (SBT)It is a non-transferable non-homogeneous token (NFT), representing the promise, qualification, membership, affiliation or statement of the token owner. SBTs can be issued by one user to another, or by an institution. In addition, users can also send to themselves. SBT contains a variety of information, which can be a degree certificate issued by a university, or a statement that the user wishes to be publicly accountable. SBT is non-transferable, so it is a very reliable unique identity for addresses on the chain, but they are transparent in nature, so it is difficult to use in scenarios where privacy is required.POAPsAnother type of tokenized identity solution, event organizers can issue NFTs to participants to prove their participation in the event.
secondary title
Oracle
OracleUser identity information originally stored or generated off-chain can be verified and uploaded to the chain. Oracles can transfer raw data directly from off-chain APIs, or transfer data between different blockchains. Before the oracle machine transmits data to the chain and triggers execution on the chain (Note: For example, triggering the minting of tokens on the chain based on certain personal identity data stored off the chain), operations can also be performed on the original data.
first level title
Web3 Identity Solution Empowers New Application Scenarios
secondary title
Legal Identification - "You Are Someone"
Identity information such as legal name, date of birth, and place of residence are very important if the company or project needs to comply with the regulatory requirements of a certain jurisdiction, or follow up with users after contract disputes.
Proving a person's legal identity can be done in several ways. One way this is done is when an official identity issuer, such as a government or a bank, issues a verifiable identity. The problem with this, though, is that most ID issuers currently don't want to build verifiable ID systems from scratch, nor can they afford to invest in new technology to improve existing IT systems.
Therefore, a more practical approach is to useDECO. DECO is a privacy-preserving oracle protocol currently in development. It uses zero-knowledge proof technology, allowing users to prove data about their identity to the application, while not disclosing personal privacy data to the public or even the oracle. DECO can be connected to existing APIs, even if end-user authentication is required, there is no need for any modification by the API data provider.
Burratasecondary title
Social identity proof - "you have an online account"
Many applications will want to leverage already created social identities (such as Facebook and Twitter) in Web3 related services. Therefore, in order to interact with other users of the Web3 platform, users must first verify the Web2 social identity associated with their Web3 address for security reasons.
PhotoChromicsecondary title
Proof of Creation - "You Created Something"
Many application scenarios do not require KYC, but need to prove the source of a statement or artwork. By tracing the creator of a text or item, users can attest to the authenticity of their artistic creation or luxury item, as well as verify the authenticity of a video or claim.
One way to establish a proof-of-creation mechanism is to issue SBTs. As described in the paper "Decentralized Society: Finding Web3's Soul", an artist can issue an NFT from his own soul (address), and others can verify that this NFT is indeed from the artist. The artist can also issue a statement, which is the SBT associated with a certain NFT and stored in his "soul" address, to prove that the NFT belongs to a certain series and the scarcity of the NFT. In addition, photographers can also publish photos and videos related to SBT to avoid forgery of works. A social critic can also issue SBTs associated with a certain statement (note: the statement can be about finance, politics, or any other hot topic) and build a personal reputation system based on the accuracy and ethics of his past comments.
secondary title
Proof of Funds - "How much money do you have"
Another important thing is to prove how much assets someone owns, which cannot be done by blockchain alone, because assets may be stored off-chain or on other blockchains. In financial transactions, proof of funds is very important for assessing risk, because the more funds a counterparty has, the more reliable it is usually.
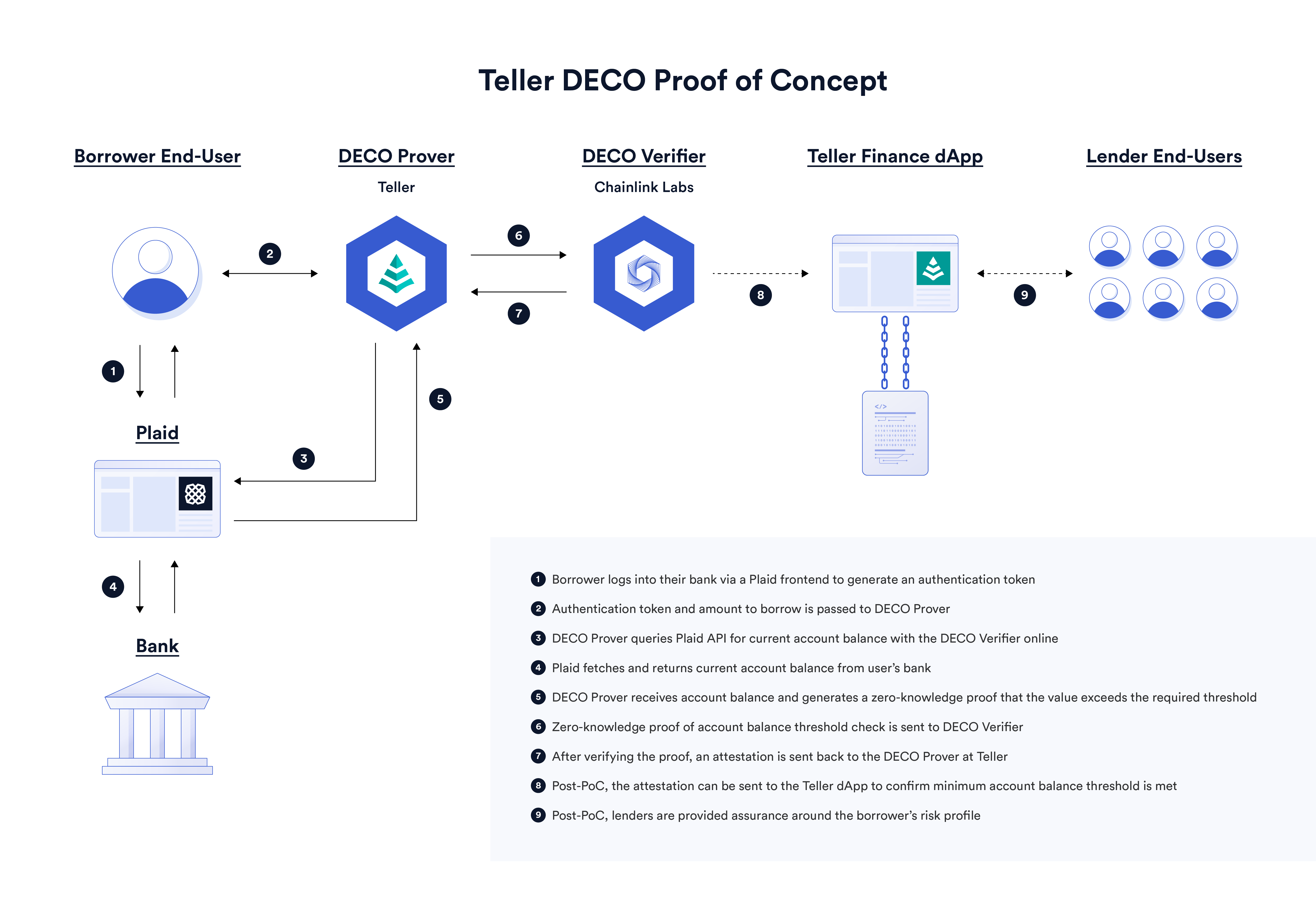
Telleris a DiFi protocol that provides a market for digital asset lending and supports low-collateralization loans. Teller adopted the DECO protocol in a proof-of-concept project, proving that a user’s asset balance in an off-chain bank account exceeds a dynamic minimum threshold required for a loan. If a user's account balance exceeds a minimum threshold, then they are less risky as a lender, and therefore the collateral terms of the loan are significantly lower. For example, if a lender needs to loan $5,000, it must prove that the bank account has a balance of at least $5,000 in order to prove its repayment ability.
For more details, check out the blog postimage description
secondary title
Proof of Social Reputation - How Much Social Reputation Do You Have
Social reputation is an emerging field of identity segmentation, which refers to the use of decentralized communities to verify certain actions or characteristics of users. Social reputation can also be extracted from a user's on-chain transaction history or SBT.
For example, if the user's on-chain transaction history can prove that he has a good repayment record, the lending agreement can lower the user's mortgage threshold. Weyl, Ohlhaver, and Buterin mentioned in the paper that users can pledge SBT (ie reputation) to obtain better loan terms. Once the loan is repaid, the SBT will be destroyed or exchanged for a new SBT, representing that the user has repaid the loan. If the loan is overdue, an SBT will be automatically issued to represent the user's default, which is a bit like a bad review. However, it is worth mentioning that if you can freely post negative comments on SBT without any permission, it may cause some problems, such as the disclosure of personal information, cyberbullying or content manipulation.
secondary title
Proof of Personality - "Who You Are"
If the application can know the key information of the user, that is: whether the user is a bot or a real human being that cannot be copied, the functionality can be greatly improved. A non-transferable and non-reusable proof of personality can be effectively used in various applications as long as it can protect the privacy of the user's personal data. For example, social media platforms can use proof of personality to prevent bots from sending spam or malicious links to users, and to prevent false social consensus through Sybil attacks.
secondary title
text
If the application can prove that the user has interacted with an object in a certain way, it will have the potential to realize various innovative application scenarios. Proof of interaction is especially useful in marketing campaigns, where users are financially incentivized to perform certain actions in order to earn rewards. Some interactions will even trigger the issuance of SBT, such as donating to charity or providing community services, you can get SBT for social welfare. In addition, this trigger mode is also suitable for recurring operations, such as in the x-to-earn application, each interaction can trigger an airdrop.
Cliquefirst level title
The Next Evolution of Web3
There is no doubt that identity is a key link in the expansion of Web3 applications and services. However, it is very difficult to realize identity proof on the blockchain. We need to protect user privacy, prevent fraud during the process of issuing identity proof, and also need to strike a balance between data immutability and proof efficiency. Although difficult, Web3 identity can indeed bring unprecedented value to users, allowing users to share only the information they want to share with applications. Users can even prove their identity information without revealing their privacy, which can be achieved through DECO technology.
It is through these technological innovations that social capital will become an indispensable part of the chain, preventing Web3 from falling into the vortex of excessive financialization, and realizing a series of innovative application scenarios, attracting enterprises and mature institutions to Web3. Ultimately, identity solutions will minimize trust in Web3, integrate into our daily lives, and better protect the privacy, transparency, and ownership of sensitive data for users.



