Everything you need to know about zkEVM (2)
TL,DR;
secondary title
Factors to evaluate a zkEVM project include: proof time, verification time, proof size, CRS, SRS, trusted settings, recursive support, cryptographic assumptions, quantum security, compatibility level.
Scroll has the shortest development time, but meets the equivalent standard of EVM; Polygon Hermez is the fastest open source, but uses new assembly code different from EVM "traditional", and there is neutral uncertainty; zkSync plans to launch the public network in 100 days, and the development progress is the fastest Fast; StarkNet insists on zkVM compatibility with limited prospects; Aztec has not yet completed Solidity language compatibility, and EVM compatibility is lagging behind; Loopring compatibility progress is nowhere in sight and has not yet been put on the agenda.This article belongs to the second article in the series "Understanding zkEVM in One Article".,The previous article introduced the basics of zkEVMThis article will take stock of the mainstream zkEVM general network in the industry
The importance of zkEVM is endlessly heard. Industry leaders represented by V God believe that in the medium and long term, with the improvement of ZK-SNARK technology (ZK algorithm), ZKR will win in all use cases. The zkEVM is a technology compatible with the ZKR project of Ethereum, and the zkEVM project is the ZKR project. This article refers to the ZKR project with zkEVM, which has been widely discussed on Twitter recently.
secondary title
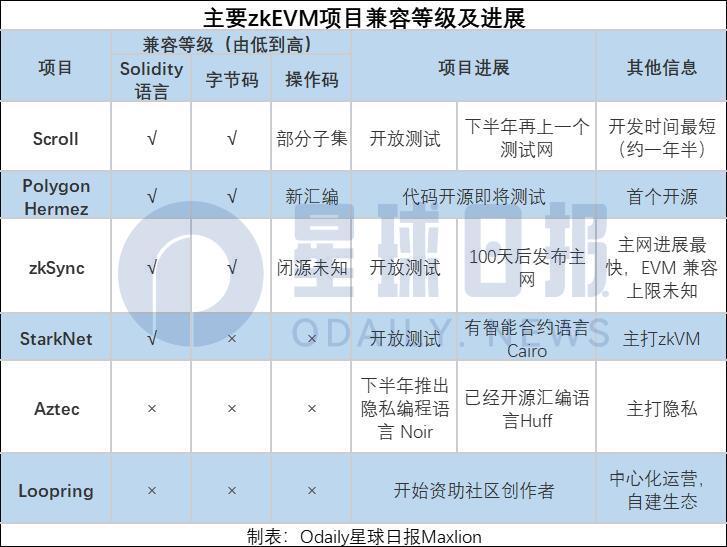
Evaluation factors of the zkEVM project
Before we start to take inventory of specific projects, we will inevitably ask a question - what are the factors to evaluate the zkEVM project?《FL Research | Incomplete Guide to ZK: Why ZK Matters? 》Fundamental Labs of CTH Group is inCommunity Proposal: A Benchmarking Framework for (Zero-Knowledge) Proof SystemsThis ZK research report proposes ten factors for evaluating the ZK project, which are: proof time, verification time, proof size, CRS, SRS, trusted settings, recursive support, cryptographic assumptions, quantum security, and compatibility level. This study also refers to the
"The basic framework of the zero-knowledge proof system proposed in this paper.This article mainly reviews the zkEVM project from two aspects: project introduction and EVM compatibility progress, including Scroll, Polygon Hermez, zkSync, StarkNet, Aztec, and Loopring.
secondary title

Scroll: a dark horse in the industry
The goal of Scroll is to be fully compatible with EVM, so that smart contracts on Ethereum can be copied directly to Scroll, and compatible with Ethereum infrastructure without modifying the code.《Introducing Scroll, a new layer2 solution》Scroll Lianchuang Ye Zhang first proposed on the Ethereum research forum ETH Research in March 21
Initially introduced the technical principle and future route of Scroll as a new Layer2 solution.
According to official sources, Scroll has been working with the Ethereum Foundation PSE (Privacy and Scaling Explorations) group for more than a year.
In terms of financing, on April 22 this year, Scroll completed a US$30 million Series A financing, led by Polychain Capital, and participated by Bain Capital Crypto, Robot Ventures, and Geometry DAO. Ying Tong and Carlos Aria of the Ethereum Foundation, as well as members of the Ethereum community also participated in the round. Founder Peng said the project had previously raised about $3 million from angel investors.
On July 20, because of the official announcement of the zkEVM testnet with Polygon Hermez and zkSync, there was a lot of debate on Twitter about "who is the first zkEVM".Ye Zhang on Twitter。
Think Scroll is a little different from Polygon Hermez
 Both Scroll and Polygon Hermez have made great progress in proving native EVM bytecode execution. But the implementation is very different. In short, Scroll is closer to Ethereum's implementation, Polygon Hermez uses a new set of assembly code to express each opcode, and then proves the execution of the new assembly on their own defined state machine. Therefore, they can also achieve "bytecode level" compatibility, but the behavior may be different from EVM, Polygon Hermez's scheme is simpler and may be more efficient, and there may be some unknown situations.
Both Scroll and Polygon Hermez have made great progress in proving native EVM bytecode execution. But the implementation is very different. In short, Scroll is closer to Ethereum's implementation, Polygon Hermez uses a new set of assembly code to express each opcode, and then proves the execution of the new assembly on their own defined state machine. Therefore, they can also achieve "bytecode level" compatibility, but the behavior may be different from EVM, Polygon Hermez's scheme is simpler and may be more efficient, and there may be some unknown situations.
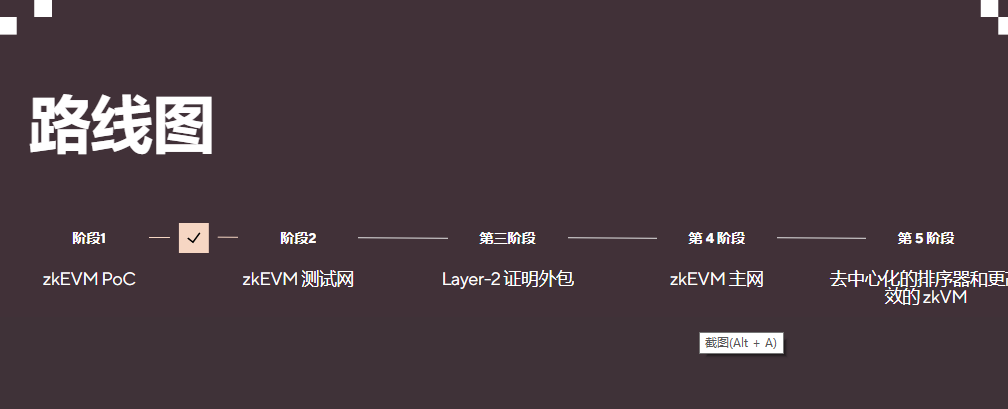
It is planned to launch a test network again in the second half of the year, which is open to all the public. The functions include: allowing developers to deploy smart contracts; allowing anyone to run archived Scroll nodes; generating and aggregating more zkEVM proofs verified on the chain; According to official documents, Scroll has implemented bytecode compatible EVM and a subset of EVM opcodes.
secondary title
 Polygon Hermez: the fastest open sourceJuly 20 Polygon HermezOfficial announcement
Polygon Hermez: the fastest open sourceJuly 20 Polygon HermezOfficial announcement
And open source the first EVM equivalent ZK L2 (ZKR).
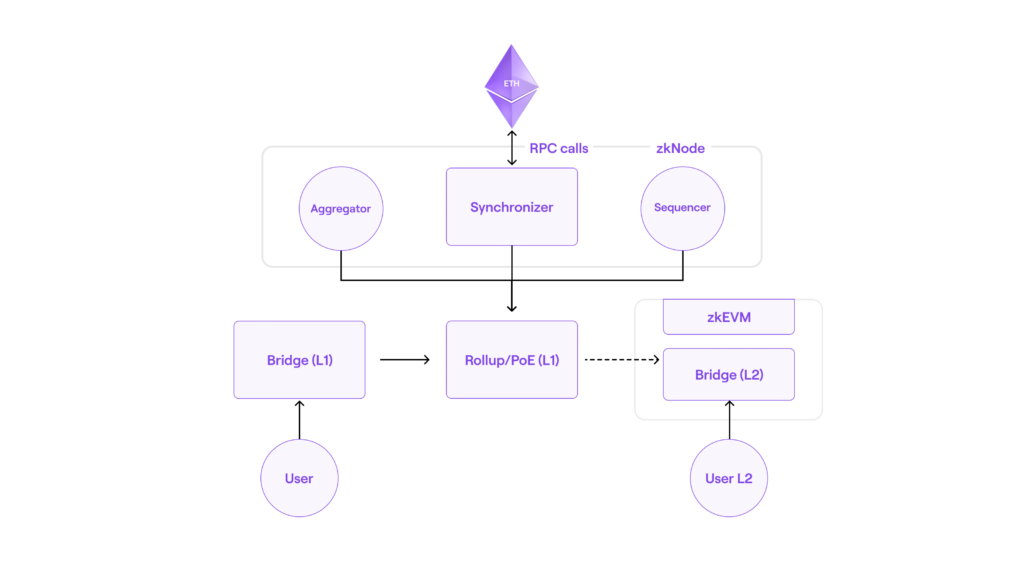
But unlike other projects, the Polygon Hermez project is not independently developed by Polygon, but acquired and merged by Polygon through the acquisition and merger of a ZKR project called Hermez. According to Coindesk, on August 13, 2021, the Hermez team and project were acquired by Polygon for $250 million. Hermez was incorporated into the Polygon ecosystem under the name Polygon Hermez, and the two networks were merged. This is also the first time a blockchain network has been fully merged into another blockchain network.
Regarding Polygon Hermez's EVM implementation, Ye Zhang tweeted, "Polygon expresses each opcode using a new set of assembly code, the human-readable bytecode translation, which allows code to behave on the EVM Different, "bytecode level" compatibility can be achieved, but the behavior may be different from EVM, Polygon Hermez's solution is simpler and may be more efficient, and there may be some unknown situations."The code is currently open source (。open source link)It achieves EVM equivalence, and after opening the testnet, developers can seamlessly deploy any Ethereum smart contract to Polygon Hermez. The plan is to launch a public testnet in the second half of the year.
secondary title

zkSync: an industry veteran
zkSync has raised a total of US$58 million. Placeholder, 1kx, and Dragonfly Capital participated in 3 rounds of financing, and Union Square Ventures and a16z participated in 2 rounds.
zkSync is a user-centric, trust-free layer-2 protocol started by MatterLabs in 2019. It uses ZKP as the core technology and focuses on security, user experience and developer experience. The project leans towards incremental protocol development, that is, introducing features one by one sequentially, bringing the most tangible value to users at each step. They start with the basics (security), initially focusing on the fundamentals of scalability (token transfers), then programmability (smart contracts), and finally privacy.
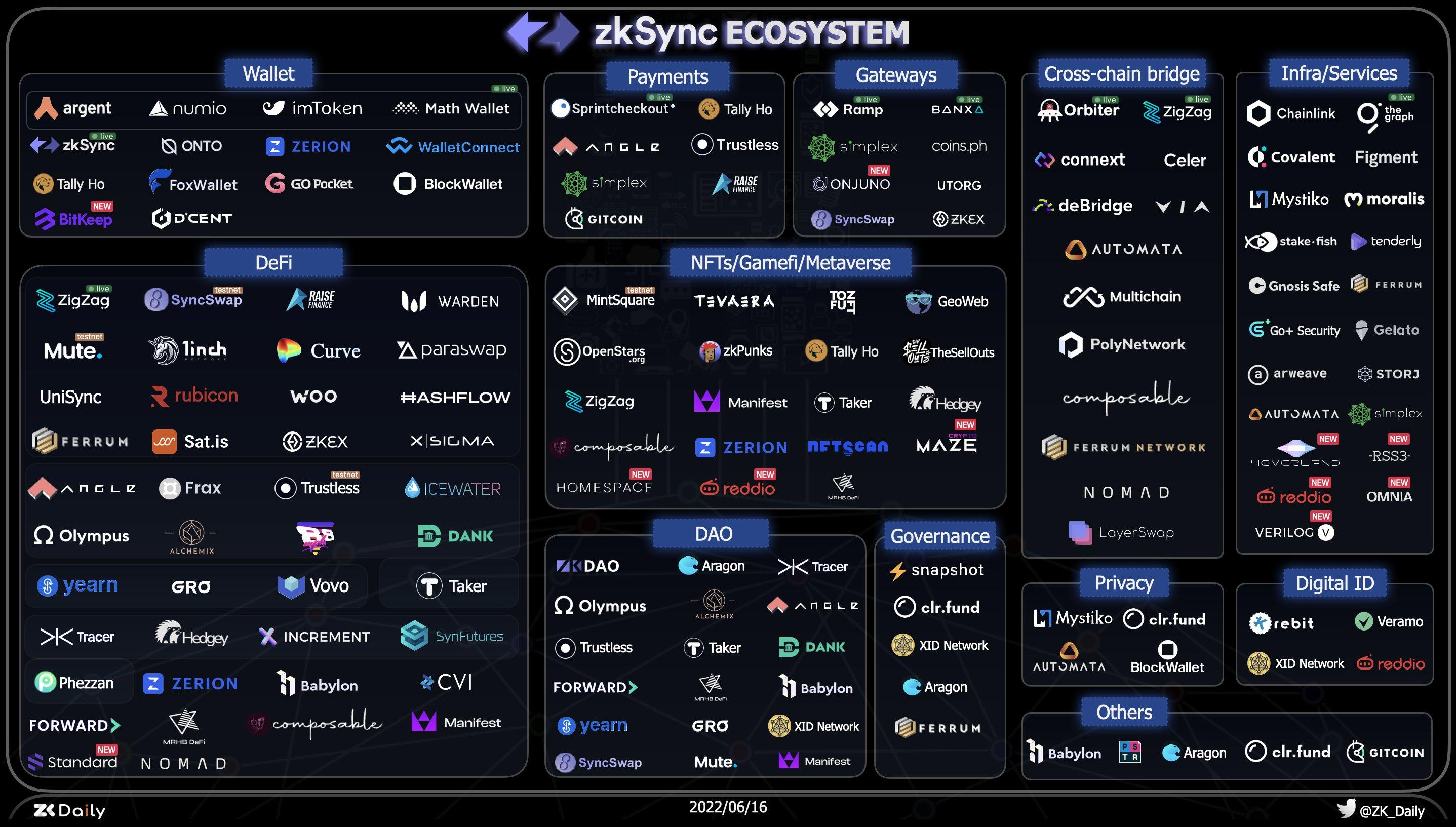
Key features of zkSync include: extremely low transaction fees, cryptographic security, user control, and permissionless smart contracts.
At present, a rich ecology has been established on zkSync, and zkSync is also one of the main donation methods on Gitcoin.According to the official announcement, zkSync has completed the translation/translator development of the Ethereum Solidity language and the zkSync development language Zinc; and achieved compatibility at the EVM bytecode level.
zkSync has opened the test network, and plans to release the zkSync public network in November (originally scheduled to be released in 2023), with the fastest development progress among all zkEVM projects.
secondary title
StarkNet: Focus on ZK
StarkNet is a permissionless decentralized Validity-Rollup (also known as "ZK-Rollup"). It operates as an L2 network on Ethereum, enabling any dApp to achieve infinite scale of its computations without compromising Ethereum's composability and security, as StarkNet is built on the most secure and scalable cryptographic proof system above STARK.
So far, StarkWare (the team behind StarkNet) has completed 6 rounds of financing, totaling $273 million. Especially in the latest round of financing, the financing amount reached 100 million US dollars, which directly quadrupled its valuation to 8 billion, which is the highest valuation among all L2 projects. Vitalik is their seed round investor. In addition, the list of investors also includes Paradigm, Sequoia Capital, Pantera Capital, Founders Fund and other rounds of investors.

StarkWare is mainly composed of the world's top cryptographers, such as Eli Ben-Sasson, who jointly invented the two most mainstream zero-knowledge proof systems ZK-SNARKs and ZK-STARK; Alessandro Chiesa, who is also the co-inventor of ZK-SNARKs, Co-founder of Zcash. ZK-SNARKs and ZK-STARK are used in the zero-knowledge proof systems built by several industry leading zkEVM projects, including zkSync, Scroll, and Hermez.
In the last year and the first half of this year, StarkWare created a scaling as a service (scaling as a service) business model by providing the expansion technology solution StarkEx, established an application-specific network, and served the industry's top customers dYdX, Sorare, ImmutableX, DeversiFi, etc. At present, with the continuous improvement of StarkNet network infrastructure, StarkNet has gradually shifted its business focus to the general network.
In terms of progress, regarding the development language, the proprietary Cairo language on the StarkNet network has a very prominent advantage: in addition to supporting the zero-knowledge proof system, it also reduces the execution of the program to several sets of polynomial equations, specifically writing provable programs. These features enable Cairo developers to abstract business logic from smart contracts into an off-chain execution environment, support the writing of apps that are costly and re-executable, while retaining the security and settlement guarantees of Ethereum, without being affected by Gas and Layer1 limits.Regarding tokens and governance, StarkNet proposesDecentralized Governance ProposalIt is also planned to issue coins in the second half of the year to promote the decentralized operation of the second-tier nodes. For relevant information, please refer to it.。
"How StarkNet Issuing Tokens Changes the L2 Industry Pattern"
Since StarkNet focuses on zkVM, from the perspective of virtual machines, StarkNet does not belong to the zkEVM project, but from the perspective of EVM compatibility, StarkNet's compatibility level for EVM stays at the translation/translator of Solidity and Cairo languages. Due to the complexity and contradiction of being compatible with EVM, it is expected that StarkNet will not make any progress in EVM compatibility in the future.
Before the appearance of Scroll and Polygon Hermez, zkSync and StarkNet were the only two zkEVM networks with high hopes. The key difference is that zkSync is committed to equivalent EVM, allowing applications, assets, and users on Ethereum to migrate seamlessly to zkSync. The goal of StarkNet is not to achieve EVM equivalence, but to develop the potential of ZK technology, and to create a decentralized network foundation for future innovative applications through almost unlimited performance expansion.
"zkSync vs. StarkWare - What is the difference between the top two ZK Rollups? 》——Tokeninsight
《zkSync vs. Starkware》——Yilun Zhang
secondary title

Aztec: Focus on Privacy
Founded in 2017, Aztec started out as an institutional financing platform on the blockchain.
On September 15, 2019, A.Capital, Coinbase, and Libertus Capital participated in its round of investment.
image description
Image Source:
In terms of progress, on July 7, Aztec launched the private DeFi Aztec Connect on the main network, a set of privacy development tools including bridging contracts and SDKs, to support users in using private DeFi applications on Ethereum.

image descriptionhttps://medium.com/aztec-protocolPicture from:
(Aztec architecture)
According to the official, Aztec is expected to launch Aztec 3 and the privacy programming language Noir in the second half of the year. There is no plan for the Solidity translator, and there is no virtual machine compatible with Ethereum. The progress of EVM compatibility is lagging behind other projects.
secondary title

Loopring: self-built ecology
Loopring is the first ZKR based on Ethereum that focuses on DeFi applications. Unlike other L2 (rollup) that have established themselves as incubation platforms, Loopring focuses on building its own products and functions on the second layer.
In terms of financing, Loopring raised $45 million through ICO in 2017.
Unlike other public networks, external developers cannot build their own general protocols or products on Loopring, they can only call loopring's API. And because Loorping focuses on building products by itself, the Loopring protocol is not just a network, it is a collective, which consists of the following four parts:
The Loopring protocol, is an open-source Ethereum zkRollup (ZKR) protocol - Layer 2 for secure scaling exchanges and payments.
Loopring repeater, is a closed-source zkRollup repeater - performs all off-chain duties for zkRollup rolling (L1-like nodes and L2 sorters).
Loopring Wallet, an Ethereum smart contract wallet - a mobile wallet app with social recovery, other security features, and built-in Loopring L2.
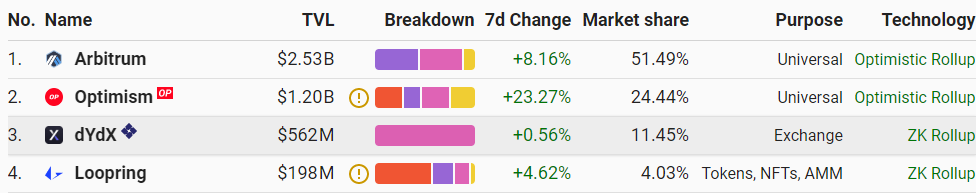
image description
Data source: https://l2beat.com/
Loopring's TVL ranks fourth among all L2 projects and ranks second among ZKRs.
But as of the date of writing, inOfficial websiteOfficial website



