万字研究:以太坊发展史、坎昆升级及生态现状
前言
为什么近期值得关注?
在比特币现货 ETF 通过以后,下一个叙事立马就转移到了以太坊为核心的叙事逻辑: 5 月份以太坊现货 ETF + 坎昆升级 + Restaking 等等。
以太坊发展规律初窥
Merge 以前的以太坊更像是一个创业公司的发展模式,PoW 赋予矿工区块奖励作为早期的营销手段,并不在意代币的价值,代币经济迅速通胀,优先级上,沉淀价值>用户体验。
Merge 的目的不是为了以太坊性能更好,而是为了降低生成区块链的消耗(PoW 转换成为 POS),用Web2.0 的做比喻比较像一条产业链的上游部分降本增效,为未来的可持续性发展做铺垫,代币经济也随着变成通缩,同时注重用户体验,将矿工的收益逐步转变成为质押收益,Gas fee 收益也有所降低。
坎昆升级对应的是 The surge 的部分,开始以用户体验第一位(例如提高交易速度、降低 Gas fee)。
未来的升级周期间隔会相对较短,以太坊某种意义上在上海升级以后,将 PoW 的共识改变成 PoS。进入了一个成熟期,虽然未来还有几次大升级,但是可以看出来核心目的是,专注于链上可扩展性、更简单的验证区块、更便宜、性能更强大而稳定。
一些思考
以太坊的发展是复杂而多元的,在学习整体发展路径的过程,有很多仍未解决的问题待思考。
Vitalik 在以太坊的发展过程中,有着非常强的引导作用。实际上如果从一个公司的角度来讲是,一个好的 CEO 带领公司冲锋陷阵,是一个非常好的发展方式,最后V神带动的所有以太坊生态的发展都会 Long ETH。
像 Arb、OP、ZKsync、Metis 等 Layer 2 ;Aave、Compound、Uniswap 等 Defi,等等很多天价估值的项目都依附于以太坊,并且能够成为一段时间的热门叙事,以太坊或多或少能够获得红利。
与其说是和微软、苹果类似,感觉最接近的应该是英伟达。AI 发展、VRAR、Web3.0、各种云、算力中心,啥前沿科技都绕不开算力,也就离不开英伟达。
Web 3.0 也有种类似的状态,任何发展都很难离开以太坊发展,以太坊叙事稍微安静了一段时间,结果兜兜转转因为坎昆升级和以太坊现货 etf,Layer 2、Eth 一起涨,包括更早期的 Defi Summer、NFT Summer 等等都会拉动以太坊的价格,而且半衰期长一点的项目都需要与以太坊有足够的接触。
很多想要脱离以太坊的,也基本上是抱着“以太坊杀手”的逻辑去思考的,之前讨论过的 TON,不拉踩以太坊,自己啥声音没有了。
以太坊的发展是很中心化的,以太坊本身这个链是很去中心化的;有些时候感觉以太坊在发展这一块儿的中心化程度和 Uniswap 的团队有一拼,没有 Aave、MakerDAO 等一些协议去中心化程度做的好。侧面也反映了,一个项目想要发展的好或许本质上还是得中心化。
或许有一天以太坊未来也能够发展到一个及其成熟的阶段,然后完全去中心化治理,但起码 Vitalik 只要还年轻,我就觉得那一天还遥遥无期。话说回来,以太坊也不过是一个才创业 11 年的公司,远远算不上成熟。
1. 大背景——以太坊历史简单回顾
1.1 History and Forks
以下内容框架引自:https://ethereum.org/zh/history,以及其他公开信息。更多具体内容请点击链接进行参考。
2013 ——第 0 阶段 以太坊诞生
白皮书发布,以太坊诞生
2013 年 11 月 27 日,Vitalik Buterin 发布《以太坊白皮书》
以太坊创始人维塔利克·布特林(Vitalik Buterin)发布以太坊的第一版白皮书,介绍了以太坊平台的代币系统;
摘要
白皮书定义了智能合约。其中首次提到了以太币的概念,白皮书中说明了以太币可以作为以太坊网络上的燃料费(Gas),用户进行转账交易、部署智能合约等活动时,需要支付一定的燃料费,部分燃料费会作为奖励,支付给区块验证者(也被称为矿工),如果交易的发起者支付的以太币不足,交易将不会执行,如果支付的以太币过剩,将会把剩余的部分返还给发起者的钱包。
2014 ——第 0.5 阶段 以太坊销售
以太坊销售
2014 年 7 月 22 日 00: 00: 00 +UTC
以太币的预售期为 42 天, 可以使用比特币进行购买。
摘要
初始汇率为 1 枚比特币可兑换 2000 枚以太币,这一汇率保持 14 天,然后汇率开始线性下降,直至下降为 1 枚比特币兑换 1337 枚以太币,这次代币销售于 2014 年 9 月 2 日结束,累计获得约 1800 万美元的销售额,易公出手 6000 多万以太币。完成购买之后,接收到的以太币需等到以太坊创世区块的推出才可以进行转账。
除了 6 千多万预售的 ETH,还有其他两笔分配。一笔分配给了参与以太坊早期开发的贡献者,另外一笔则分配给了长期的研究项目。这两笔 ETH 的数量均为预售 ETH 数量的 9.9% 。
也就是以太坊正式发行时,一共有 72002454.768 枚 ETH 分配完了。

图片来源:https://blog.ethereum.org/2014/07/22/launching-the-ether-sale
2015 ——第一阶段:Frontier
2015 年 3 月 3 日,在以太坊的官方博客中就宣布了四个重要阶段,根据该博客,当初 Vitalik 的一些思考逻辑如下:
Frontier(边境/前沿):Frontier 在发布过程中的主要用途是让采矿作业和以太币交易所运行,以便社区可以启动他们的采矿设备,并开始建立一个“实时”环境,人们可以在其中测试 DApp 并获取以太币来上传他们的将自己的软件引入以太坊。让以太坊在核心研发人员和审计师中完全稳定;
Homestead(家园):Frontier 像是内测版本,Homestead 是公测;
Metropolis(大都会):完整成熟的用户交互版本,追求用户体验;
Serenity(宁静):PoW 到 PoS
边境
2015 年 7 月 30 日 03: 26: 13 +UTC
摘要
边境是以太坊最初的版本,但在上面能做的事情很少。 该版本在奥利匹克测试阶段成功完成之后推出。 它面向的是技术用户,特别是开发者。 区块有 5, 000 单位的燃料限制。 此“解冻”期使矿工能够开始操作,并使早期采用者能够有足够的时间来安装客户端。
和很多 Web 3.0 项目的冷启动类似, “矿工”们在“边境”主网每挖掘一个区块,将收到 5 枚以太币的奖励。
边境解冻分叉
2015 年 9 月 7 日 09: 33: 09 +UTC
区块编号: 200, 000
以太币价格: $ 1.24
摘要
边境解冻分叉提高了每个区块 5, 000 单位燃料的限制,并将默认燃料价格设为 51 gwei。 这样便能进行交易 - 交易需要 21, 000 单位燃料。
为了确保未来硬分叉到权益证明,引入难度炸弹的概念。
难度炸弹,又名 TTD,全称为 Total Terminal Difficulty,即以往所有区块难度的总和。当全网积累的挖矿难度值达到 TTD 时,ETH 主网会启动“难度炸弹”。“难度炸弹”是进行以太坊难度调整的后门函数。以太坊的 PoW 出块时间并没有固定,而是根据全网算力大小对挖矿难度进行动态调整,通过这种方式把区块时间固定在一个大致的范围。难度炸弹的部署则是通过后门函数将挖矿难度调整到一个极大的值,使得没有矿工可以在该挖矿难度下生产区块,从而推动着矿工放弃 PoW。PoW-POS 的转换并没有设置一个固定的区块高度,而是规定 TTD 作为 Merge 发生的时刻,部分原因其实在于防止有人刻意破坏 Merge 的进程。
变相证明了以太坊很早就有了 PoW 到 PoS 的决心。
2016 ——第二阶段:Homestead
以太坊第一次硬分叉,在经历多次安全事件后,逐步完善智能合约的一些规范。
家园分叉
2016 年 3 月 14 日 06: 49: 53 +UTC
区块编号: 1, 150, 000
以太币价格: US$ 12.50
摘要
家园分叉, 优化了智能合约的创建过程。
DAO 分叉
2016 年 7 月 20 日 01: 20: 40 +UTC
区块编号: 1, 920, 000
以太币价格: US$ 12.54
摘要
这次分叉属于计划之外的一次被动分叉,源于一场以太坊上的攻击事件。
The DAO 是区块链公司 Slock.it 发起的一个众筹项目,旨在为项目提供一种社区资助的方式。社区用户通过将手中的 ETH 兑换成 DAO Token 来参与投票,如果众筹成功,就可以获得一部分利润奖励。该项目在 2016 年 4 月完成了一次为期 28 天的众筹,总共筹集超过 1200 万个 ETH,几乎占到当时以太坊数量的 14% 。然而就在 2 个月后,黑客利用 The DAO 代码里存在的漏洞从资金池里盗走了 360 万 ETH。
此操作是由以太坊社区投票决定的。 所有以太币持有者都能通过投票平台上的交易进行投票。 分叉的决定获得了 85% 以上的投票。通过分叉回滚,黑客盗走的 ETH 得以恢复。
此分叉将资金从有问题的合约转移到一个新合约,新合约只有一个功能:提款。 任何损失了资金的人都可以在他们的钱包中提取以太币,每 100 个 DAO 代币 1 个以太币。
一些矿工,因为那次 DAO 事件并不是协议中的缺陷而拒绝分叉。 它们之后组建了以太坊经典(ETC)。
橘子口哨分叉
2016 年 10 月 18 日 01: 19: 31 +UTC
区块编号: 2, 463, 000
以太币价格: US$ 12.50
摘要
橘子口哨分叉是对 2016 年 9 月 18 日以太坊网络遭受的拒绝服务 (DoS) 攻击导致交易处理出现严重延迟的问题进行优化;主要解决与作价低估的操作代码有关的紧急网络健康问题。
伪龙分叉——Spurious Dragon
2016 年 11 月 22 日 04: 15: 44 +UTC
区块编号: 2, 675, 000
以太币价格: US$ 9.84
摘要
伪龙分叉是对拒绝服务 (DoS) 网络攻击进一步优化,包括:
-调整操作码价格,以防网络将来再受攻击。
-启用区块链状态的“区块链减重”。
-增加重放攻击保护。
2017 ——第三阶段:Metropolis
Metropolis 的主要工作是修复以太坊网络中存在的一些问题、为引入 ZK-SNARKS 做准备。
在这个阶段发生的最具影响力的事件是区块奖励的两次减半:从 5 ETH 减少到 3 ETH 再到 2 ETH,算是 PoW 到 PoS 的一个过渡期。
这个阶段开始考虑用户体验,以及未来如何顺利从 PoW 到 PoS。
拜占庭升级
2017 年 10 月 16 日 05: 22: 11 +UTC
区块编号: 4, 370, 000
以太币价格:US$ 334.23
摘要
拜占庭分叉为引入 ZK-Snark 做铺垫,开始注重用户隐私和用户体验。
- 将区块挖矿奖励从 5 个以太币减少到 3 个以太币。
-将难度炸弹推迟一年。
-增加了调用其他合约而不更改状态的能力。
-增加了某些加密方法,以实现Layer 2 。
2019 ——第四阶段:Serenity(宁静)
以太坊逐渐成熟,共识由 PoW 转到 PoS,用户体验、安全性、区去中心化、可扩展性为以太坊最重要的发展方向。
君士坦丁堡分叉
2019 年 2 月 28 日 07: 52: 04 +UTC
区块编号: 7, 280, 000
以太币价格: US$ 136.29
摘要
将区块挖矿奖励从 3 个以太币减少到 2 个以太币。
2019 年 12 月 8 日 12: 25: 09 +UTC
区块编号: 9, 069, 000
以太币价格: US$ 151.06
摘要
-优化了以太坊虚拟机中特定操作的燃料成本。
-提高受到拒绝服务攻击后的复原能力。
-使基于“零知识简洁非交互式知识论证”和“零知识可扩容透明知识论证”的 Layer 2 解决方案具有更佳的性能。
-让合约能够引入更多创造性功能。
2020 缪尔冰川升级
2020 年 1 月 2 日 08: 30: 49 +UTC
区块编号: 9, 200, 000
以太币价格: US$ 127.18
摘要
缪尔冰川分叉使难度炸弹延迟。 增加工作量证明共识机制的区块难度可能会增加发送交易和使用去中心化应用程序的等待时间,从而降低以太坊的可用性。
部署质押存款合约
2020 年 10 月 14 日 09: 22: 52 +UTC
区块编号: 11, 052, 984
以太币价格: US$ 379.04
摘要
质押存款合约将质押引入以太坊生态系统。 虽然是一个主网合约,但它直接影响到信标链的发布时间线,而后者是以太坊升级的重要部分。
信标链创世块
2020 年 12 月 1 日 12: 00: 35 +UTC
信标链区块编号: 1
以太币价格: US$ 586.23
摘要
信标链需要 16384 个存储了 32 个质押以太币的帐户,以确保安全上线。 这发生于 2020 年 11 月 27 日,意味着信标链在 2020 年 12 月 1 日开始生产区块。
信标链扮演管理监督与验证区块链网络的角色。其中信标链是采用随机的方式来选择验证者,验证成功者将得到奖励,但若是存在恶意行为将会受到惩罚。
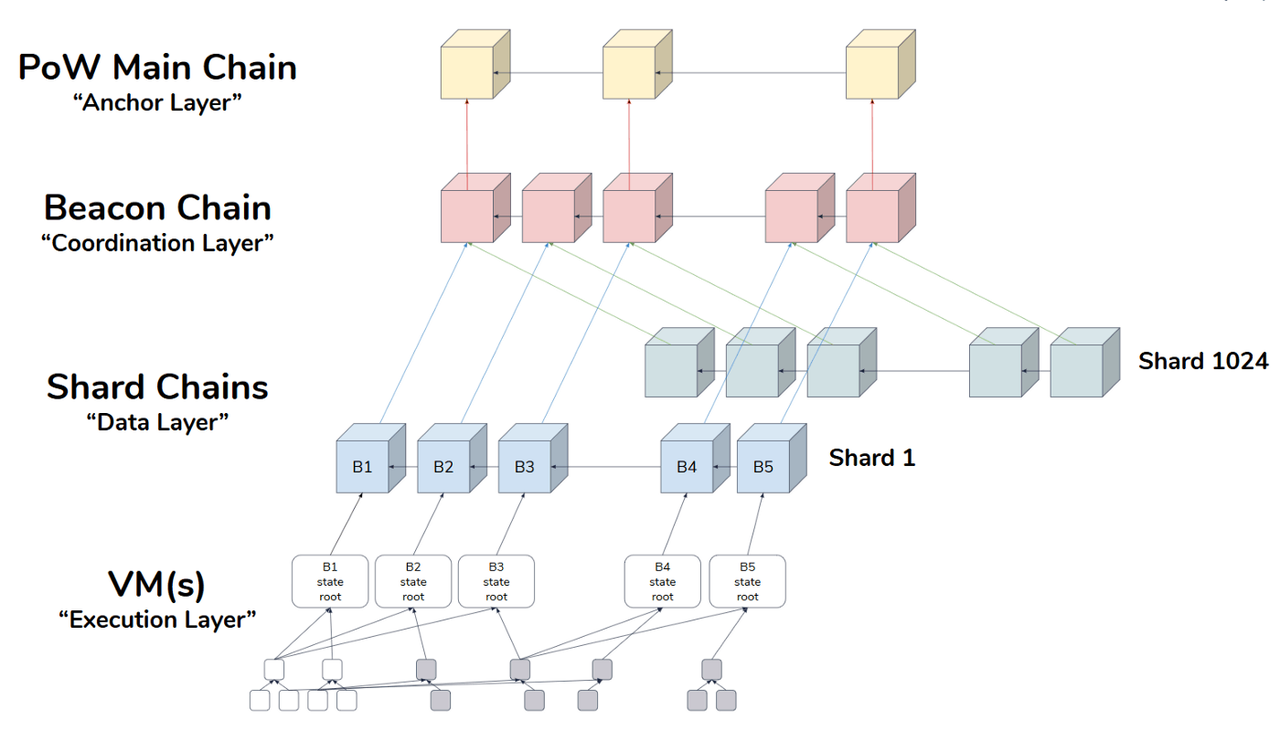
合并后,一个区块的时间单位将以槽和纪元的形式出现。每 12 秒创建一个槽,每个纪元包由 32 个槽组成。一个纪元是一个固定的时间段,核查员将在这个时间段结束时被重新分配。
要成为验证者并获得投票权,用户必须至少投入 32 个 ETH。
以太坊的规则是,对于每个纪元,验证者将被随机分配到 32 个委员会,确保每个委员会至少由 128 个验证者组成。系统使用随机算法 RANDAO 为每个时段分配 1 名验证者,并同时为这个时段随机选择一个委员会。这个验证者负责提出区块,而委员会负责验证和对提案进行投票。一旦投票通过,就会产生一个区块,提议者就会获得奖励;否则,不仅奖励无法获得,保证金也会被没收。同样的情况也适用于普通的核查员:如果正确地遵守规则,就可以得到奖励,而破坏者则会受到惩罚。一旦 32 个 ETH 的押金降至 16 个 ETH 以下,验证者的资格将终止。
2021
柏林升级
2021 年 4 月 15 日 10: 07: 03 +UTC
区块编号: 12, 244, 000
以太币价格: US$ 2, 454.00
摘要
柏林升级优化了某些以太坊虚拟机操作的燃料成本,并增加了对多种交易类型的支持。
伦敦升级
2021 年 8 月 5 日 12: 33: 42 +UTC
区块编号: 12, 965, 000
以太币价格: US$ 2, 621.00
摘要
伦敦升级引入了 EIP-1559 ,对交易费市场进行了改革。继续将难度炸弹延迟,直到 21 年 12 月 1 日启动。
天鹰座升级
2021 年 10 月 27 日 10: 56: 23 +UTC
时段编号: 74, 240
以太币价格: US$ 4, 024.00
摘要
天鹰座升级是计划的第一次信标链升级。 它增加了对“同步委员会”的支持—支持轻客户端,在向合并进展的过程中,增加了对验证者怠惰及可被罚没行为的惩罚。
箭形冰川升级
2021 年 12 月 9 日 07: 55: 23 +UTC
区块编号: 13, 773, 000
以太币价格: US$ 4, 111.00
摘要
难度炸弹推迟总共 10, 700, 000 个区块,直到 2022 年 6 月。
2022 灰色冰川升级
2022 年 6 月 30 日 10: 54: 04 +UTC
区块编号: 15, 050, 000
以太币价格: US$ 1, 069.00
摘要
灰色冰川网络升级将难度炸弹推迟了三个月。 这是此次升级中引入的唯一变更,本质上类似于箭形冰川和缪尔冰川升级。 拜占庭、君士坦丁堡和伦敦网络升级也做了类似的变更。
Bellatrix 升级
2022 年 9 月 6 日 11: 34: 47 +UTC
时段编号: 144, 896
以太币价格: US$ 1, 558.00
摘要
Bellatrix 升级是计划的第二次信标链升级,让信标链为合并做好准备。 它将验证者由于怠惰及进行了可被罚没的行为而受到的惩罚提高到其全部价值。 Bellatrix 升级还包括对分叉选择规则的更新,让信标链为合并以及从最后一个工作量证明区块过渡到第一个权益证明区块做好准备。 这包括让共识客户端意识到终端总难度 58750000000000000000000。
巴黎升级(合并)
2022 年 9 月 15 日 06: 42: 42 +UTC
区块编号: 15, 537, 394
以太币价格: US$ 1, 472.00
摘要
巴黎升级是由于工作量证明区块链超过了终端总难度 58750000000000000000000 而触发的。 这发生在 2022 年 9 月 15 日区块 15537393 上,并在下一个区块处触发了巴黎升级。 巴黎升级就是合并过渡,以太坊的主要功能结束了工作量证明挖矿算法及相关共识逻辑并启动了权益证明。 巴黎升级本身是对执行客户端的升级(相当于共识层上的 Bellatrix 升级),让执行客户端能够从与其连接的共识客户端接受指令。
2023 卡佩拉升级
2023 年 4 月 12 日 22: 27: 35 +UTC
时段编号: 194, 048
信标链区块编号: 6, 209, 536
以太币价格: US$ 1, 917.00
摘要
卡佩拉升级是共识层(信标链)的第三次重大升级,实现了质押提款。 卡佩拉与上海同步升级执行层并启用了质押提款功能。
这次共识层升级让未提供初始存款提款凭证的质押人能够提供提款凭证,从而实现提款。
该升级还提供了自动帐户扫描功能,可以持续处理验证者帐户的任何可用奖励支付或全额提款。
上海升级
2023 年 4 月 12 日 22: 27: 35 +UTC
区块编号: 17, 034, 870
以太币价格: US$ 1, 917.00
摘要
上海升级将质押提款引入执行层。 上海升级与卡佩拉升级同时进行,使区块能够接受提款操作,因此质押人可以将以太币从信标链提取到执行层。
1.2 为什么以太坊能够变成通缩模型?
PoW 更像是一个创业公司早期的营销手段,有稳定名曲的补贴(矿工挖矿的稳定收益),PoS 更像是股权,ETH 净发行量。
The Merge 显著改变了以太坊的货币政策。通过消除矿工奖励,转换成为质押奖励,它大幅削减了新的 ETH 代币发行量,这构成了每日 ETH 发行量下降了约 88.7% ,相当于总供应量的 0.52% 年化发行率,再由于 EIP-1559 下的 Gas 费被销毁,净发行量呈现通缩趋势。
有两个关键变动:
1.2.1 伦敦升级引进的 EIP-1559 :引用了费用燃烧机制
参考文章:燃料和费用
旧协议计算公式:Gas fee = Gas units (limit) * Gas price per unit
对于最简单的链上转账交易来说,不管链上有多么忙碌,**Gas limit 固定为 21, 000 。**所以,只要明确了 Gas price 和 Gas limit,就能够知道我们为这次交互花了多少 eth。其中 Gas price 将随着网络的拥堵而发生变化,Gas limit 保持不变。
假设 Alice 需要向 Bob 支付 1 个以太币。 在交易中,燃料限额为 21, 000 单位,燃料的价格是 200 gwei。
总费用为:Gas units (limit) * Gas price per unit,即 21, 000 * 200 = 4, 200, 000 gwei 或 0.0042 个以太币。
而为了能够更优先级,科学家可能一拍脑袋就设置了一个很高的 Gas fee,因此导致着用户体验是比较混乱,且难以预估。
新协议计算公式:Gas fee = (Base fee + Priority fee) × Gas limit,且下一区块 Base fee 的涨幅最多为 12.5%
其中 base fee 由协议设置会直接销毁,priority fee 是用户设置的支付给验证者的小费。
例如,假设 Jordan 要向 Taylor 支付 1 个以太币。 一笔以太币转账需要 21, 000 单位的燃料,基础费是 10 gwei。 Jordan 支付了 2 gwei 作为小费。
费用为 21, 000 * ( 10 + 2) = 252, 000 gwei(0.000252 个以太币)。
当 Jordan 转账时,将从 Jordan 帐户中扣除 1.000252 个以太币。 Taylor 的帐户增加 1.0000 个以太币。 验证者收到价值 0.000042 个以太币的小费。 0.00021 个以太币的 base fee 被销毁。
1.2.2 巴黎升级
先是君士坦丁堡硬分叉,挖矿奖励由原来的每区块奖励 3 个 ETH 降低为 2 个 ETH。然后,The merge 将 PoW 转变成为 PoS,挖矿奖励(160, 000 eth/天)直接消失,转变成为质押奖励(1, 600 eth/天),发行量骤减 99% 。
2022 年 9 月 15 日,巴黎升级后,以太坊正式开始通缩。
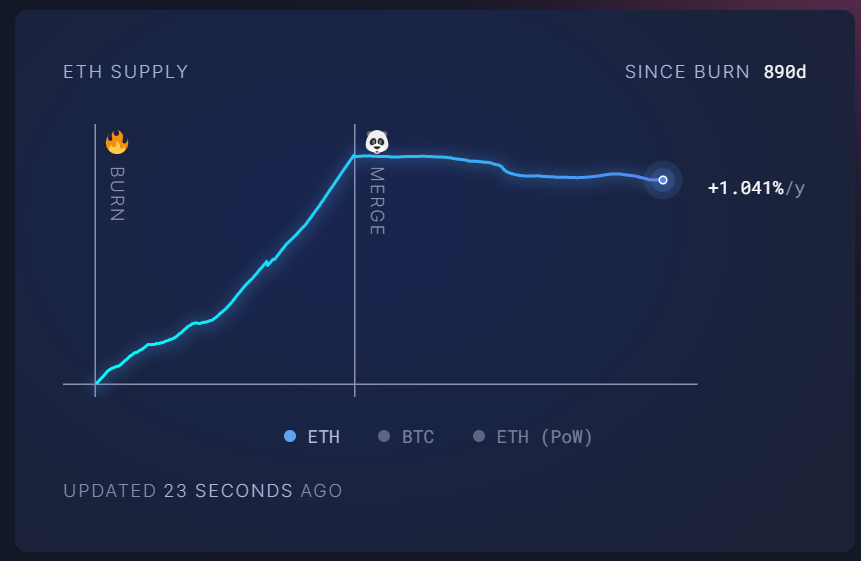
数据来源:https://ultrasound.money/
Merge以来总供应量已经煎炒超过 30 万枚以太币,每年销毁数量 981 k,增发数量 723 k,每年以 0.21% 的速度进行通缩。
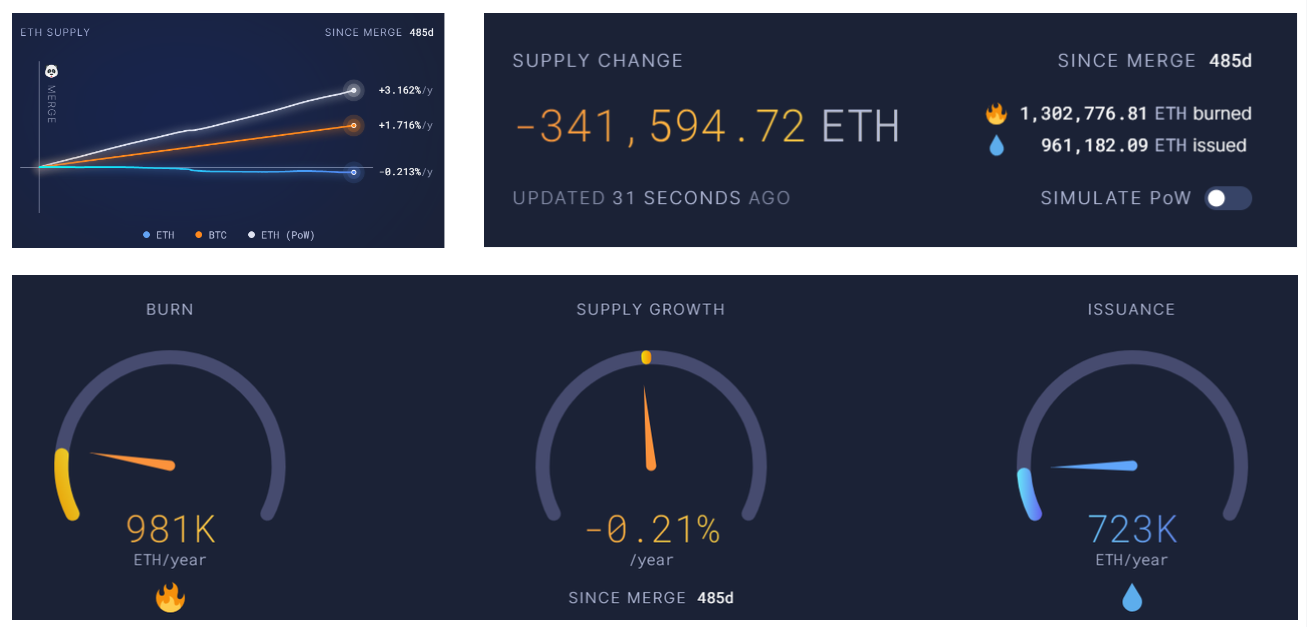
数据来源:https://ultrasound.money/
Merge以后以太坊解决了挖苦那个带来高能耗的问题,之后专注于性能问题和费用问题,Layer 2 在同时解决这两个问题,因此成为 Merge 后以太坊生态最受关注的赛道。
1.3 以太坊未来的升级路线
Vitalik Buterin 提出了以太坊线路图的愿景,根据对以太坊架构的影响,该路线图将升级分为几个类别。 这包括:
Merge:涉及从工作量证明转为权益证明的升级(已完成)
Surge:在 Rollups 上超过 100, 000 TPS
Scourge:涉及抗审查性、去中心化、LSD、和 MEV 风险的升级
Verge:涉及更轻松地验证区块的升级
Purge:涉及降低运营节点的计算成本和简化协议的升级
Splurge:其他
这些升级是并行的,也就是说哪个部分研发的快,可能就会先进行升级。
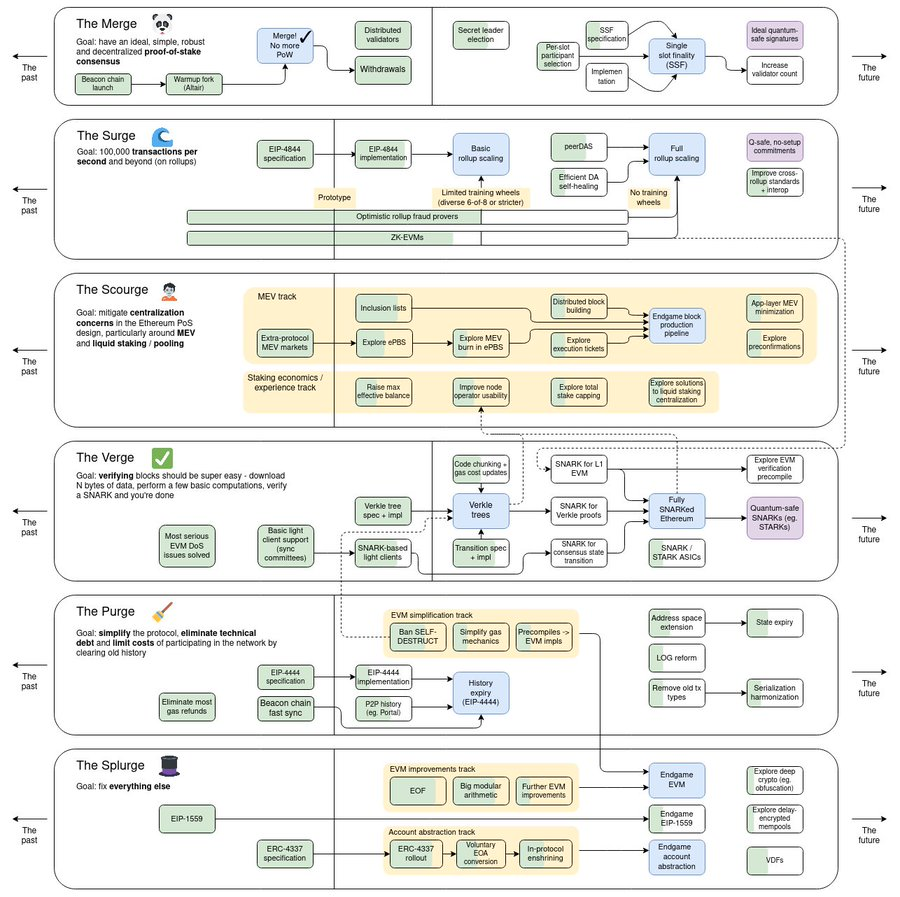
图片来源-V神推特:https://twitter.com/VitalikButerin/status/1741190491578810445
2. 什么是坎昆升级?落地哪些重要 EIP?
以太坊合并以后,最重要的事情就是提升性能 TPS,降低 Gas fee,让以太坊接近于一个完美的应用。
Vitalik 认为 Ethereum 达到什么样的 TPS 和 Gas Fee 才算一个合格的公链?
例如:TPS 达到 10 万+。VISA 平均 TPS 为 2000 ,峰值 4000+;Paypal 平均 TPS 为 200 ;支付宝繁忙期能达到 25 万。
本次以太坊升级被称为 Dencun 升级(Dencun+Cancun),其中 Cancun(坎昆,Devcon 举办城市)升级侧重于以太坊执行层(Execution Layer),Deneb 升级侧重于共识层(Consensus Layer)。
坎昆升级对应的是 The Surge 的部分,目标达到 10+TPS。
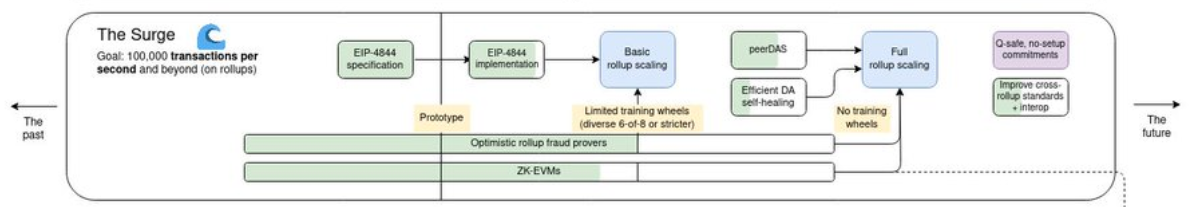
根据 Github 上显示坎昆升级要执行的是以下六个 EIP,我们在下一个部分会重点介绍一下。
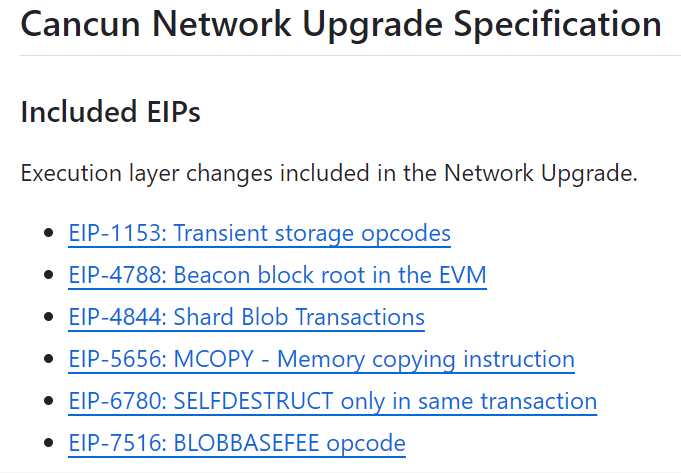
图片来源:https://github.com/ethereum/execution-specs/blob/master/network-upgrades/mainnet-upgrades/cancun.md
除了 Pro-Danksharding(EIP-4844),坎昆升级还包括 EIP-6780、EIP-1153、EIP-6475、EIP-4788 等改进提案。
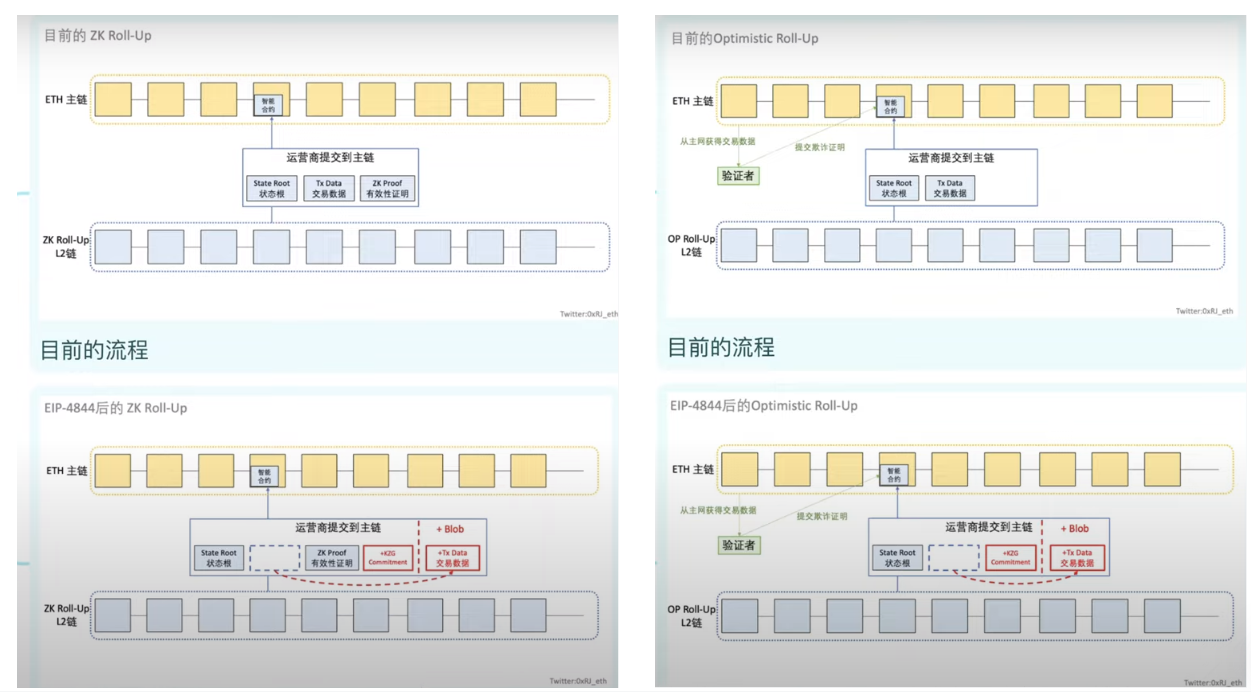
2.1 Proto-Danksharding——EIP 4844
坎昆升级最重要的一件事情就是引入 Proto-Danksharding 为以太坊完全分片扩容做过渡,提前将接近的技术引用。以太坊的最终目标是将主网分成 64 片从而达到 10 万+TPS。
Proto-Danksharding 提出的背景在于,虽然 Rollup 方案对比以太坊主链而言显著降低了交易费用,但还没有到足够低的理想程度。这是由于以太坊主链上提供数据可用性的 calldata 仍然占据较大的花费( 16 gas / byte)。在原先的设想中,以太坊提出在数据分片中提供每个区块 16 MB 的专用数据空间给 Rollup 使用,但距离数据分片的真正实施仍旧遥遥无期。
目前 Layer 2 回传到 Layer 1 的数据都存储在 Calldata 里,并永久将数据存储到执行层里。此外,为了安全,Calldata 为了防止网络资源滥用,每一步执行都需要 gas。
以太坊完成合并后,分出了共识层(负责 PoS 共识)和执行层(执行合约代码)。执行层的工作是执行 Calldata(可以认为是一种给交易类型)里面存储的数据。
可以将 Calldata 包含的内容分为两部分:
执行结果
交易数据——没有太多的用途,验证有效后就没有什么用,足够长的时间可以下载验证就行了,甚至不需要传到执行层——EIP-4844 就是为了解决交易数据的问题,这部分成为占了 Calldata 整个成本的 60% 以上。
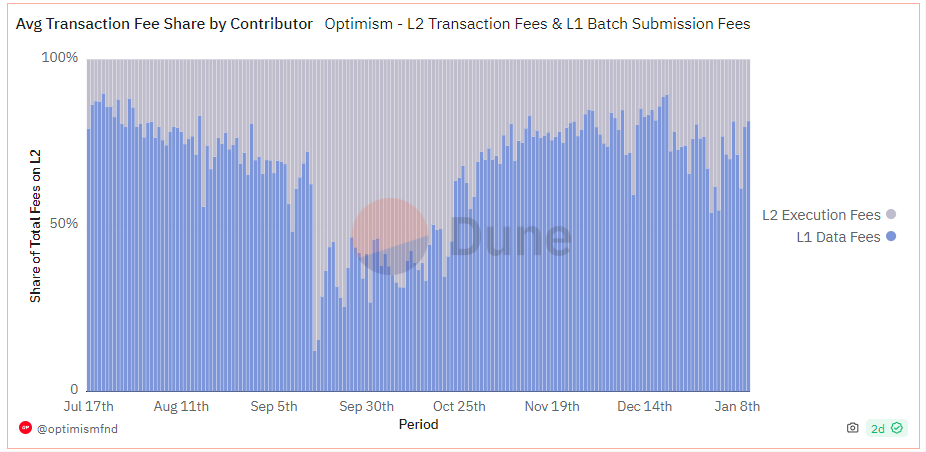
数据来源:https://dune.com/optimismfnd/optimism-l1-batch-submission-fees-security-costs
实际上,作为交易数据只有验证需求,没有执行需求,不需要传输到执行层来增加执行层负担,只存储在共识层的节点即可。
为此,EIP-4844 引入了一种新交易类型—Blob(Binary Large Objects,算是对交易类型进一步细分),比常规交易多携带一个数据包( 约 125 kb),只在共识层,类似于缓存包类似一个额外外挂数据库,为L2回传过来的数据单独设计一个数据类型 Blob,把它和 Layer 1 的 Calldata 分开。如此,Blob 数据只需要满足能在一定时间内被有需要的人访问验证即可,无需 Layer 1 执行层去全部执行,从而大大减轻 Layer 1 的负担。
Proto-Danksharding 所引进的每个 blob 大小为 128 KB,每个以太坊区块计划包含 3-6 个 blob(0.375 MB - 0.75 MB),未来逐步拓展至 64 个。
相比之下,目前以太坊每个区块可以容纳的数据大小不到 200 KB,引入 blob 后,以太坊区块可容纳的数据量将显著提高。
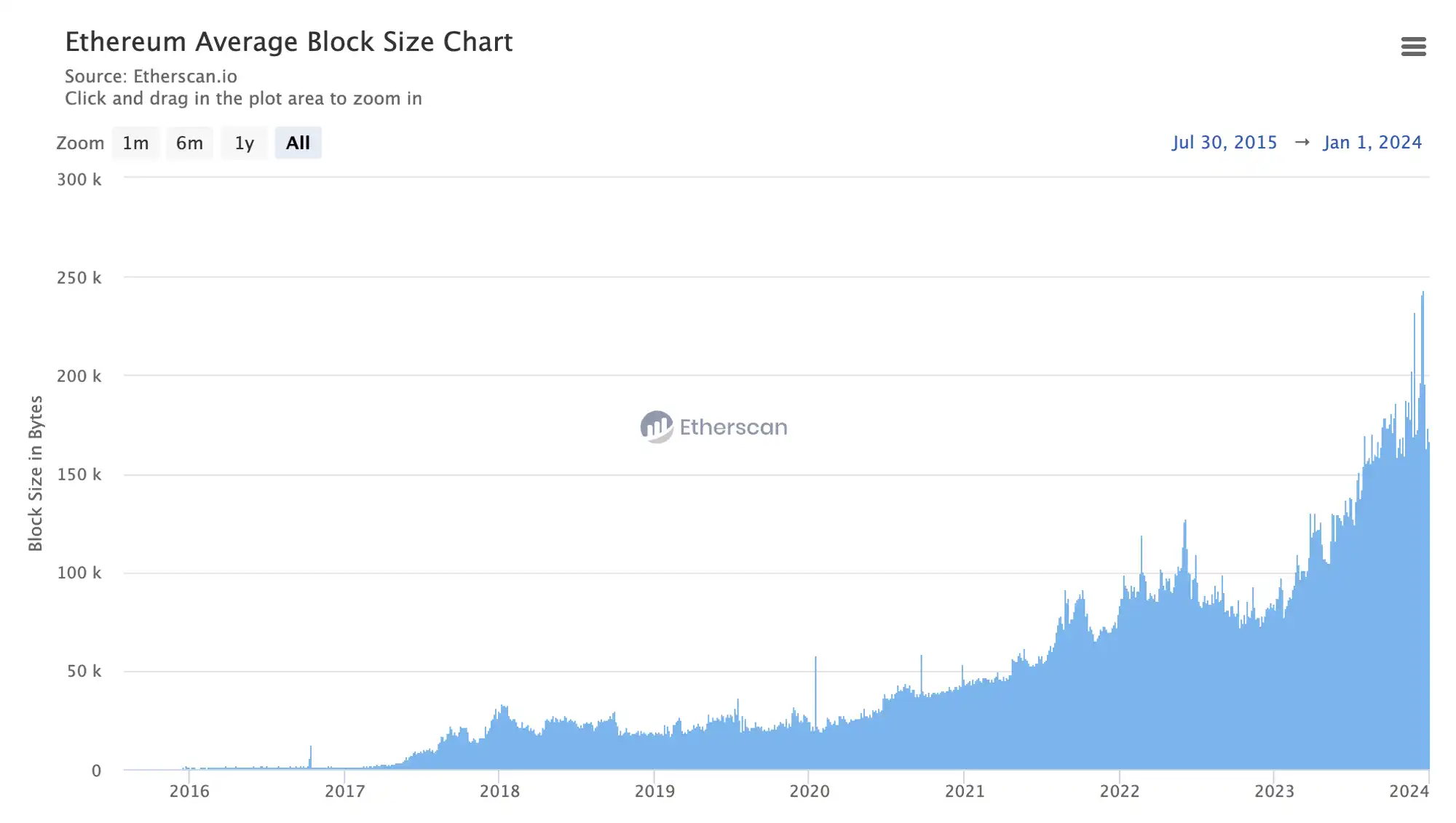
数据来源:https://etherscan.io/chart/blocksize
EIP-4844 是 Danksharding 的先行版本,旨在通过以太坊节点实现链下数据临时储存和检索,而 Layer 2 本身就是压缩链下数据,因此,有望使L2能够每个区块链携带更多数据的同时,交易费用降低 10-100 倍。
若 Dencun 升级后成功实现了一个区块外挂 3 个 blob 的平均目标,L2 的吞吐量将有接近 2 倍的提升。若最终实现了一个区块外挂 64 个 blob 的目标,L2 的吞吐量将有接近 40 倍的提升。
Proto-Danksharding 引入了 EIP-1559 ,进一步降低 blob 的费用
不同类型的 gas 应该有不同的基本费用和最大限制
blob 数据费用更便宜——Blob 不竞争区块空间,理论 gasfee 应该更低,天然便宜,进一步降低费用
如果想要看交易数据怎么办?
EIP-4844 还引入了 KZG (Kate-Zaverucha-Goldberg) 承诺⽅案,作为 blob 验证和证明⽣成过程的⼀部分。KZG 承诺是⼀种多项式承诺⽅案,使提交者能够使⽤一串短字符串来承诺多项式,支持验证者使⽤短字符串来确认所声明的承诺。简单来说,即 KZG 可以将大量数据的验证工作简化为对小型加密承诺的验证。
引入 Proto-Danksharding 前后对比。
2.2 其他
EIP-6780 提议修改 SELFDESTRUCT 操作码功能,为未来应用默克尔树做准备。后续通过应用默克尔树,以太坊存储效率将大大提升。
EIP-1153 通过添加瞬态存储操作码,可以让协议进行临时存储,从而节省网络 Gas 费。
EIP-6475 是 EIP-4844 的配套方案,通过引入 SSZ 编码交易类型,提供更佳可读性和紧凑序列化。
EIP-4788 旨在改善跨链桥和 Staking 池的结构。
3. 相关数据情况
3.1 Layer 2 数据情况
总 TVL
总 TVL 已经超过了$ 20 b
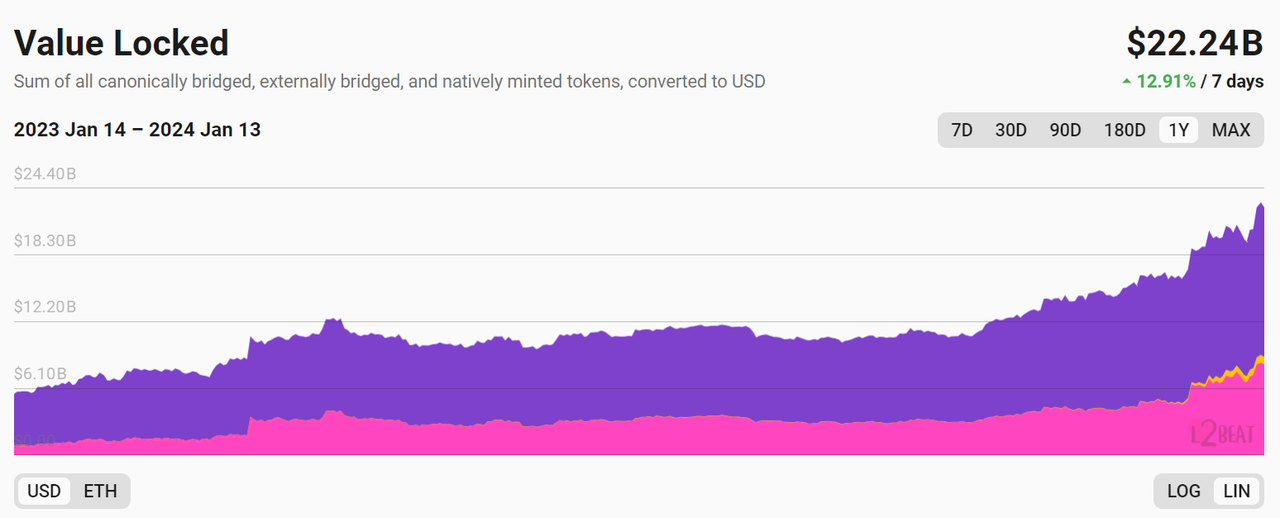
数据来源:https://l2 b eat.com/scaling/tvl
Layer 2 TVL 情况
固然 Vitalik 认为 ZK 是 Rollup 最终方案,其实际上 Arb+OP 以及其他 Op 系已经超过了 85% ,同时很多项目也在尝试 OP+ZK 的结合,不断迭代。
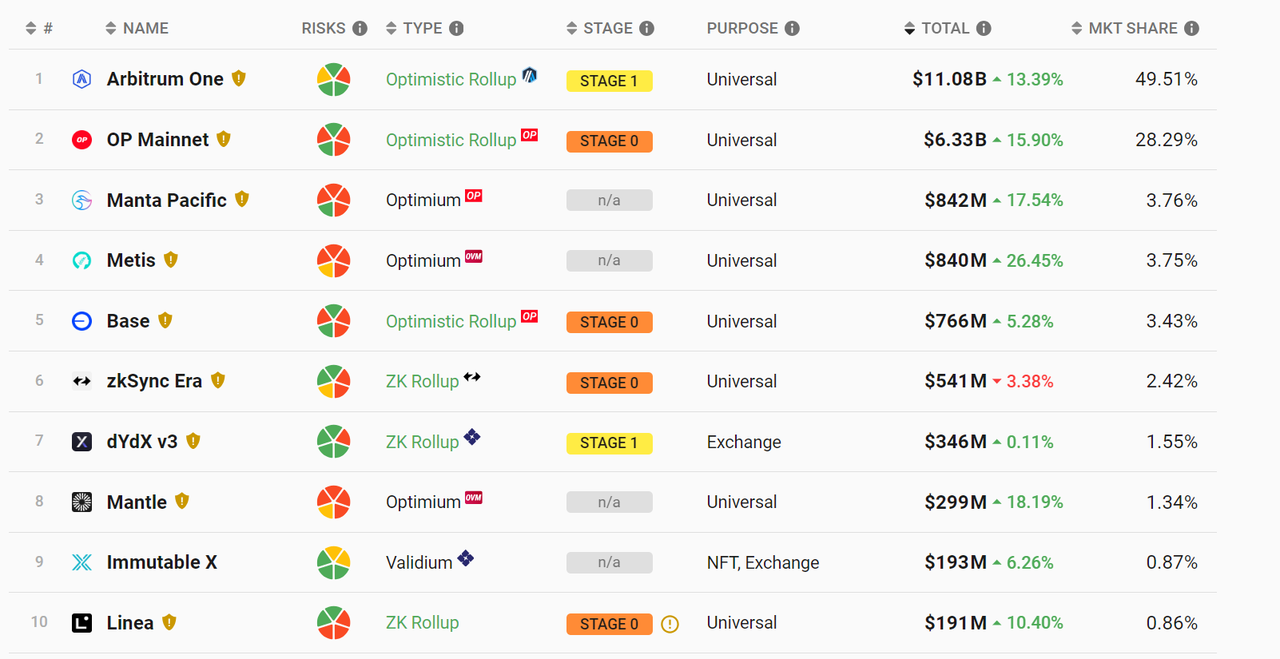
数据来源:https://l2 b eat.com/scaling/summary
Layer 2 Gas Fee 情况
单笔交易几块钱的手续费,或许对于早期接触web3.0 的 OG 来讲可能算是小数目,但是对于 Mass Adpotion 来说还是过于昂贵。
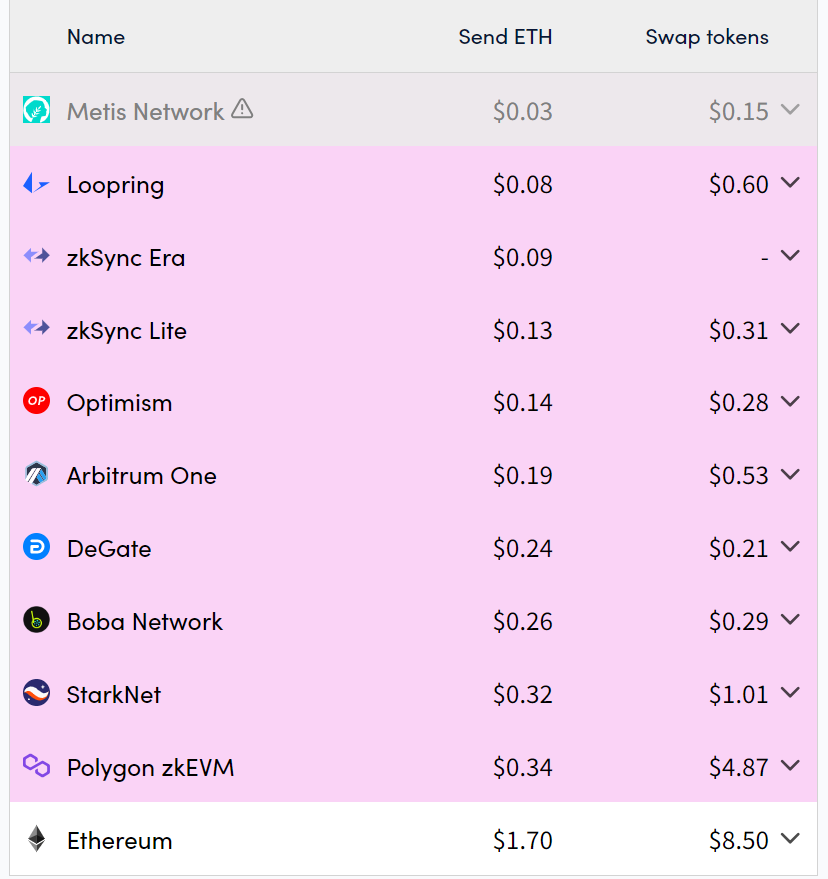
数据来源:https://l2 fees.info/
收入情况
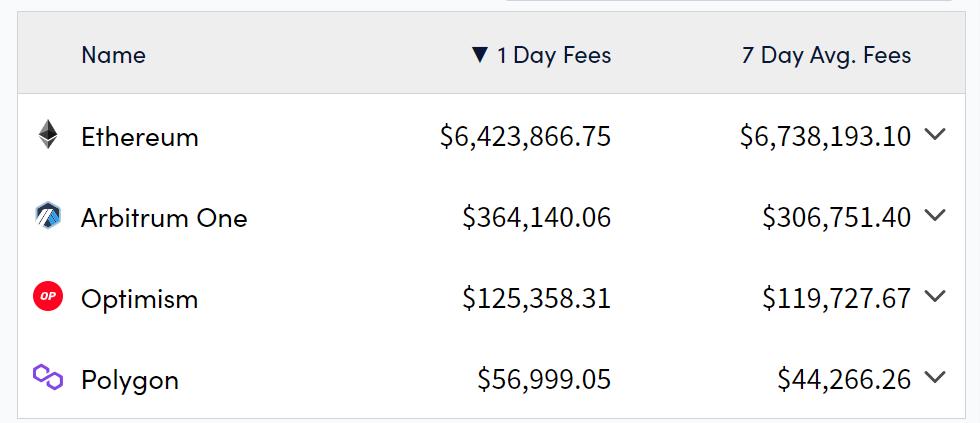
数据来源:https://cryptofees.info/,category选择 Layer 1、Layer 2 ,blockchain 选择图中四条公链
3.2 TPS
以太坊最早 TPS 为 108 ,理论上 Layer 2 的 TPS 是可以超过 10 万交易/秒的(TON),但是目前还没有这种级别的应用,也是一个比较担忧的地方。
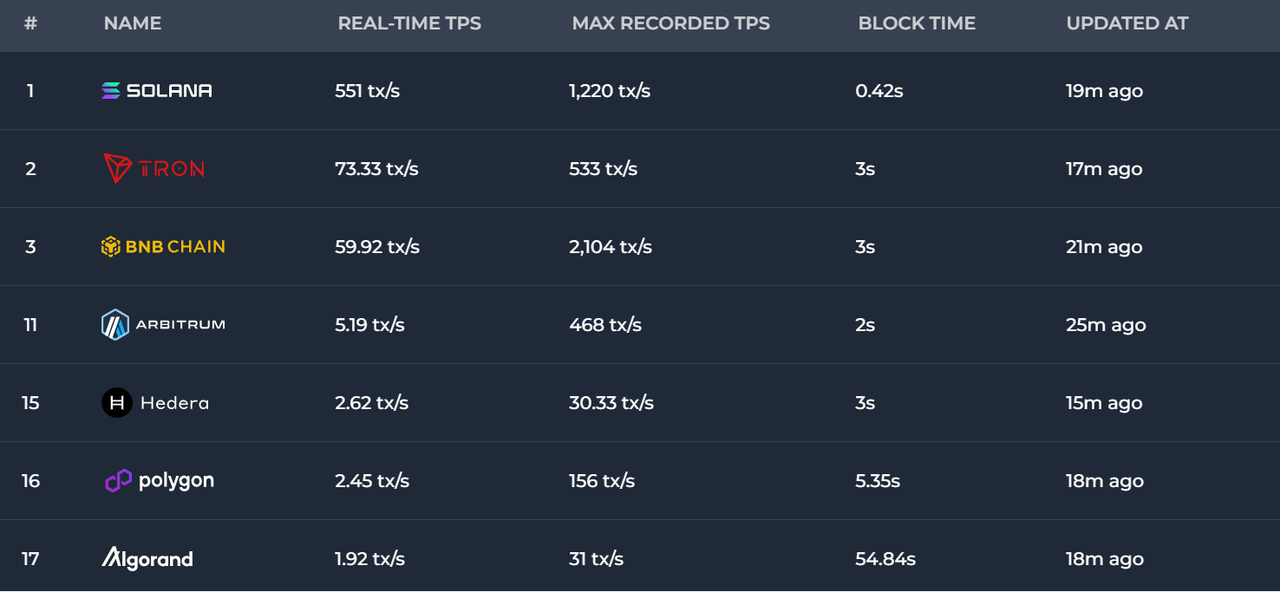
数据来源:https://chainspect.app/dashboard/tps
像 Layer 2 上的实时 TPS 目前最多的也不到 50 。
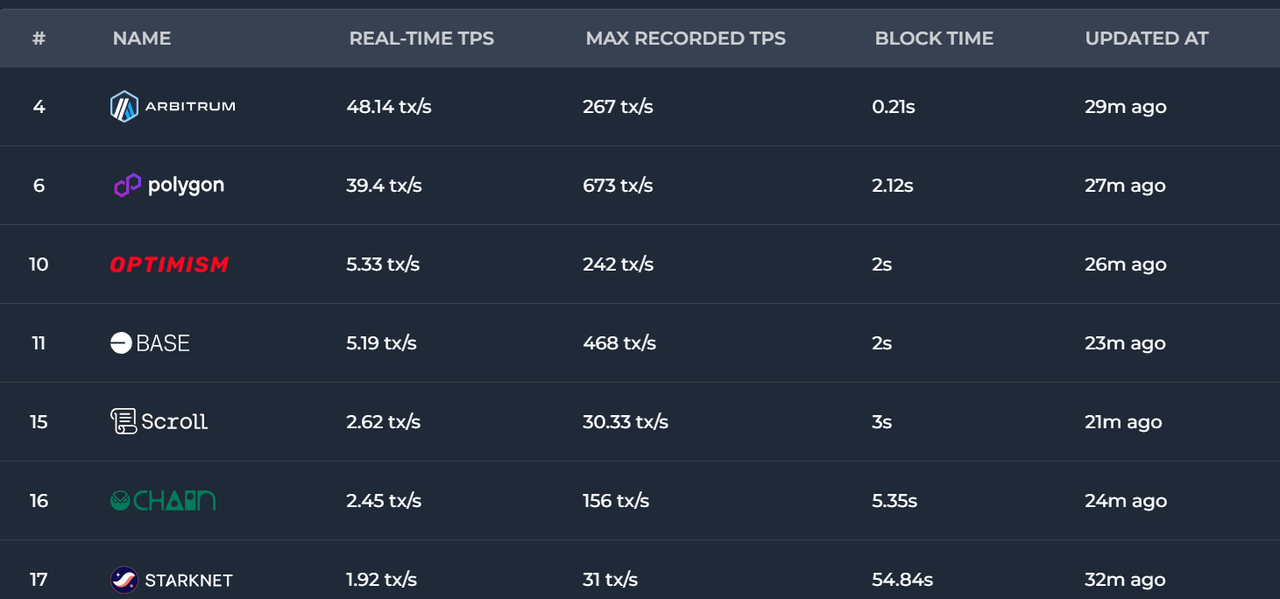
数据来源:https://chainspect.app/dashboard/tps?tag=layer_2
4. 仍待解决的问题
以太坊流动性由于多个不同的 Layer 2 而导致一定的割裂性?潜在方案为序列器共享、去中心化序列器等等
CM:A 链的钱不容易到 B 链,Layer 2 的概念就是一个服务层,Arb 以 Gmx 为首的衍生品为主,Layer 2 的市场偏小,一开始 Layer 2 的任务就是以太坊的业务细分到 Layer 2 。现在解决方案就是通过应用层解决。通过跨链应用来解决体验的问题,从链的角度必然会有资金割裂的现象,主要是安全性的问题。
DZ:最近好像 Layer 2 涨了不少?对 Layer 2 的预期炒起来了?一上 4844 能立马降低费用么?从而导致一些格局将发生变化,例如波场的 USDT 转到以太坊 Layer 2 上.
附录——知识科普
1. 网络升级和分叉
在以太坊协议的发展进程中,网络升级和分叉的意思相同,都是对以太坊协议进行更改,添加新的规则(EIP 形式),可以是计划内也可以是计划外。但是硬分叉的含义又有所不同,它是指这种网络更新不完全向后兼容,甚至可能会更改已部署合约的现有功能而使某些先前的交易无效。
2. EIP/ERC 介绍
主要参考来源:https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-1,即 EIP-1
2.1 EIP 分类
EIP 可以分为三个大类别:
Standards Track EIP(标准跟踪 EIP):这类 EIP 描述了影响大多数或所有以太坊实现的任何更改,或者影响使用以太坊的应用程序的互操作性的任何更改或添加。简单来说,就是任何会改变以太坊所有或者大多数实现细节的 EIP。它可以细分为以下几种:
Core(核心):指可能导致分叉的、需要对共识进行的修改(如 EIP-5、EIP-101 等),以及不一定是共识但可能与以太坊 “核心开发” 有关内容的更改;
Networking(网络):指围绕以太坊通信 dev p2p ( EIP-8 ) 和 Light Ethereum Subprotocol 的修改,以及对 Whisper 和 swarm 网络协议规范的拟议改进。
Interface(接口): 指对以太坊客户端 API/RPC 定义和标准的修改、调用方法称和合约 ABI 等语言级标准的改进。
ERC:指应用程序级标准和约定。它包括有 Token 标准、名称注册、URI 方案、账户抽象等。
Meta EIP(元提案 EIP):这类 EIP 围绕以太坊的流程(或流程中的事件)进行更改,包括有流程修改、用户指南、决策过程、开发环境及工具等的修改。因为这种修改需要社区用户一起遵守,因而需要达成社区共识。
Informational EIP(信息提案 EIP):这类 EIP 是非标准改进,不提出新功能,只提出设计问题和对以太坊社区通用指南或信息的意见,且不一定代表以太坊社区的共识或建议。
目前 EIP 存储库已经进行了 ERC 和 EIP 的分离。EIP-7329 提案提出将 ERC 规范从 EIP 存储库中拆分到新的存储库中,以便仅保留核心协议 EIP,因此,当前的 EIP 存储库是针对标准化以太坊本身以及基于其构建的协议,它以 EIP 的形式跟踪以太坊过去和正在进行的改进。而 ERC(Ethereum Request for Comment)存储库是针对标准化以太坊应用层,它以 ERC 的形式跟踪过去和正在进行的改进应用程序标准。ERC 里产生了不少我们熟知的 ERC-20、ERC-721、ERC-1155 等。
2.2 EIP 审核流程
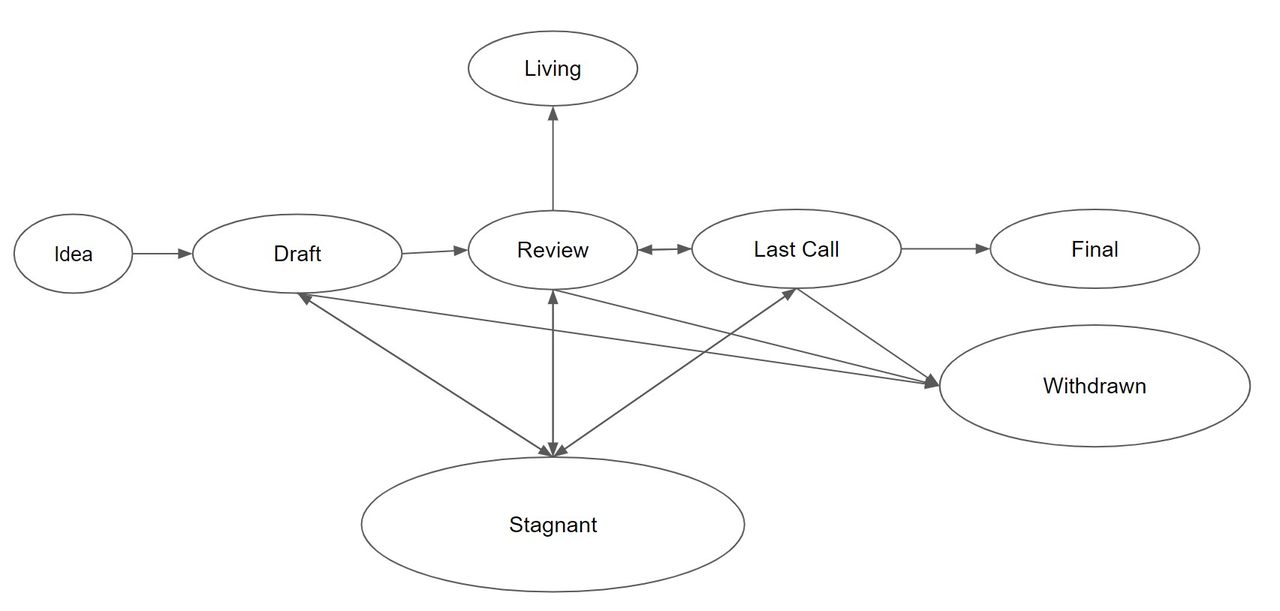
想法 Idea- 预草案的想法。EIP 存储库中不会对此进行跟踪。
草案 Draft- EIP 开发中的第一个正式跟踪阶段。当格式正确时,EIP 会被 EIP 编辑器合并到 EIP 存储库中。
审查 Review- EIP 作者将 EIP 标记为准备好并请求同行审查。
最后一次通话 Last Call- 这是转移到 之前 EIP 的最后审核窗口 Final。EIP 编辑将分配 Last Call 状态并设置审核结束日期 ( last-call-deadline),通常为 14 天后。
如果在此期间导致必要的规范性更改,EIP 将会恢复为 Review.
最终版 Final- 该 EIP 代表最终标准。最终 EIP 处于最终确定状态,仅应更新以更正勘误表并添加非规范性说明。
将 EIP 从上次调用转移到最终调用的 PR 不应包含除状态更新之外的任何更改。任何内容或编辑提议的更改都应与此状态更新 PR 分开并在其之前提交。
停滞 StagnantDraft- 处于或 Review 或 6 个月或更长时间不活动状态的任何 EIPLast Call 将移至 Stagnant。作者或 EIP 编辑者可以通过将 EIP 移回 Draft 或更早的状态来从该状态恢复。如果不复活,提案可能会永远保持这种状态。
EIP 作者会收到其 EIP 状态的任何算法更改的通知
撤回 Withdrawn- EIP 作者已撤回提议的 EIP。该状态具有最终性,不能再使用该 EIP 号复活。如果稍后继续实施该想法,则该想法将被视为新提案。
Living - EIP 的一种特殊状态,旨在不断更新且不会达到最终状态。其中最著名的是 EIP-1 。
参考文献
以太坊新分片方案 Danksharding 及 EIP-4844 万字研报:全新公链叙事已来?白话解读「区块链不可能三角」的变革…
了解定于 2024 年初进行的以太坊坎昆-德内布升级,以及它如何有望彻底改变区块链可扩展性和第 2 层解决方案。
Rollup 经济学:我们高估了 EIP-4844 对可扩展性的影响
我们用两种计算方法估算发现,EIP-4844 对于提高以太坊可扩展性的影响有限。
Vitalik:Danksharding 究竟是什么? - 深潮 TechFlow
Danksharding 是为以太坊提出的新分片设计,这种技术究竟能带来什么?
“以太坊 Layer 2 未来之争,百花齐放还是一枝独秀?” is published by Web3 CN.
深入了解以太坊的 Verkle 树 | HackerNoon
Verkle Tree 概念于 2018 年提出,Sin 7 Y 的这篇技术评论将展示 Verkle Tree 的原理。
IOSG Ventures:合并在即,详解以太坊最新技术路线-ODAILY
未来以太坊路线图的指向性是非常明显的——围绕服务 Rollup 而展开。
沃克尔树("Vector commitment"和"Merkle Trees"的组合)是一种数据结构,可用于升级以太坊节点,使其能够不再存储大量状态数据,同时不失去验证区块的能力。
gas 是以太坊区块链上交易和智能合约执行的燃料。它代表处理这些操作所需的计算工作,并以称为 gwei 的小面额以太币定价(1 gwei = 10 ^-9 ETH)。



