Security Special Issue 05|OKX Web3 & BlockSec: @All Whales, the Latest Risk Hedging Strategy in the DeFi World
Introduction: OKX Web3 Wallet has specially planned the "Security Special Issue" column to provide special answers to different types of on-chain security issues. Through the most real cases happening around users, in collaboration with experts or institutions in the security field, dual sharing and answers from different perspectives are conducted, so as to sort out and summarize the rules of safe transactions from the shallow to the deep, aiming to strengthen user security education while helping users learn to protect their private keys and wallet asset security from themselves.
The biggest charm of the DeFi world is that everyone has the potential to become a "whale"
But even the "giant whale" cannot be arrogant. Although it eats meat, it also has its "beaten" moments.
So, when playing on the chain, safety comes first
Otherwise, you have to start from scratch again~
This is the 5th special issue of Security. We invite blockchain security pioneer BlockSec and OKX Web3 wallet security team to share a DeFi risk avoidance strategy from the perspective of practical guide for all users and project owners who are about to become or have become "whales". For example, how to read audit reports, common indicators and parameters for preliminary assessment of DeFi project risks, how project owners or whale users can build monitoring perception capabilities, DeFi security protection rules, etc. Don't miss it!

BlockSec Security Team: BlockSec is the world's leading "full-stack" blockchain security service provider. The company currently serves more than 300 customers, including well-known project parties such as MetaMask, Compound, Uniswap Foundation, Forta, PancakeSwap, Puffer, etc., and has recovered more than US$20 million in financial losses through white hat rescue.
BlockSec CEO & Co-Founder Zhou Yajin is a professor of computer science at Zhejiang University and one of the most influential scholars in the world selected by Aminer. He has published more than 50 top papers and received more than 10,000 citations. CTO & Co-Founder Wu Lei is a professor of computer science at Zhejiang University and the former co-founder of Paidun. He led the team to discover dozens of zero-day vulnerabilities in many well-known projects. Product Director Raymond was responsible for security products at Tencent and 360.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: Hello everyone, I am very happy to share this. The OKX Web3 Security team is mainly responsible for the construction of various security capabilities of OKX in the Web3 field, such as smart contract security audits, wallet security capability construction, on-chain project security monitoring, etc., providing users with multiple protection services such as product security, fund security, and transaction security, and contributing to maintaining the entire blockchain security ecosystem.
Q1: Share some real DeFi risk cases encountered by users
BlockSec Security Team: DeFi has attracted many large investors because of the relatively stable high returns it brings to assets. In order to increase liquidity, many project owners will also actively invite large investors to join. For example, we often see news reports that some large investors deposit huge amounts of assets into DeFi. Of course, in addition to obtaining stable returns, these whales will also face some risks when participating in DeFi projects. Next, we share some DeFi risk cases that have been made public in the industry:
Case 1: In the PolyNetwork security incident in 2022, a total of more than $600 million in assets were attacked. It is rumored that Shenyu also had $100 million in it. Although the attacker later paid back the money and the incident was successfully resolved, Shenyu also announced that it would build a monument on the chain to commemorate the incident, but the process must have been very painful. Although a small number of security incidents have achieved good results, most security incidents are not so lucky.
Case 2: The well-known DEX SushiSwap was attacked in 2023, and the big investor 0x Sifu lost more than 3.3 million US dollars. His loss alone accounted for about 90% of the total loss.
Case 3: In the Prisma security incident in March this year, the total loss was $14 million, which came from 17 wallet addresses, with an average loss of $820,000 per wallet, but the losses of four users accounted for 80%. Most of these stolen assets have not been recovered.
In the final analysis, DeFi, especially the mainnet DeFi, because Gas Fee cannot be ignored, only when assets reach a certain scale can they really get benefits (except airdrop rewards). Therefore, the main TVL of DeFi projects is generally contributed by whales. In some projects, even 2% of whales contribute 80% of TVL. When security incidents occur, these whales will inevitably bear most of the losses. "You can't just see the whales eating meat, they also get beaten up."
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: With the prosperity and development of the on-chain world, the number of DeFi risk cases encountered by users is also increasing day by day. On-chain security is always the most basic and important need of users.
Case 1: PlayDapp privileged account private key leakage incident. From February 9 to 12, 2024, the Ethereum-based PlayDapp gaming platform was attacked due to private key leakage. The attacker minted and stole 1.79 billion PLA tokens without authorization, resulting in a loss of approximately $32.35 million. The attacker added a new minter to the PLA token, minted a large amount of PLA, and dispersed it to multiple on-chain addresses and exchanges.
Case 2: Hedgey Finance attack. On April 19, 2024, Hedgey Finance suffered a major security vulnerability on Ethereum and Arbitrum, resulting in a loss of approximately $44.7 million. The attacker exploited the lack of user input validation in the contract to gain authorization to the vulnerable contract, thereby stealing assets from the contract.
Q2: Can you summarize the main types of risks in the current DeFi field?
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: Based on real cases, we have sorted out the four common types of risks in the current DeFi field
Category 1: Phishing attacks. Phishing attacks are a common type of cyberattack that tricks victims into providing sensitive information such as private keys, passwords, or other personal data by disguising as a legitimate entity or individual. In the DeFi field, phishing attacks are usually carried out in the following ways:
1) Fake websites: Attackers create phishing websites similar to real DeFi projects to trick users into signing authorization or transfer transactions.
2) Social engineering attacks: On Twitter, attackers use high-imitation accounts or hijack the project’s Twitter or Discord accounts to post fake promotional activities or airdrop information (actually phishing links) to carry out phishing attacks on users.
3) Malicious smart contracts: Attackers publish seemingly attractive smart contracts or DeFi projects to trick users into authorizing their access rights and stealing funds.
The second category: Rugpull. Rugpull is a unique scam in the DeFi field, which refers to the project developers suddenly withdrawing funds and disappearing after attracting a large amount of investment, resulting in all investors' funds being swept away. Rugpull usually occurs in decentralized exchanges (DEX) and liquidity mining projects. The main manifestations include:
1) Liquidity withdrawal: Developers provide a large amount of liquidity in the liquidity pool to attract user investment, and then suddenly withdraw all liquidity, causing the token price to plummet and investors to suffer heavy losses.
2) Fake projects: Developers create a seemingly legitimate DeFi project and lure users into investing through false promises and high returns, but in fact there are no actual products or services.
3) Changing contract permissions: Developers can use backdoors or permissions in smart contracts to change the rules of the contract or withdraw funds at any time.
The third category: smart contract vulnerabilities. Smart contracts are automatically executed codes that run on the blockchain and cannot be changed once deployed. If there are vulnerabilities in smart contracts, it will lead to serious security issues. Common smart contract vulnerabilities include:
1) Reentrancy vulnerability: The attacker repeatedly calls the vulnerable contract before the last call is completed, causing problems in the internal state of the contract.
2) Logical errors: Logical errors in contract design or implementation that lead to unexpected behaviors or vulnerabilities.
3) Integer overflow: The contract does not handle integer operations correctly, resulting in overflow or underflow.
4) Price manipulation: The attacker launches an attack by manipulating the oracle price.
5) Loss of precision: Calculation errors occur due to floating point or integer precision issues.
6) Lack of input validation: User input is not adequately validated, leading to potential security issues.
The fourth category: governance risk. Governance risk involves the core decision-making and control mechanisms of the project. If used maliciously, it may cause the project to deviate from its intended goals and even lead to serious economic losses and a crisis of trust. Common risk types include:
1) Private key leakage
Privileged accounts in some DeFi projects are controlled by EOA (Externally Owned Accounts) or multi-signature wallets. If these private keys are leaked or stolen, attackers can manipulate contracts or funds at will.
2) Governance Attacks
Although some DeFi projects have adopted decentralized governance solutions, they still have the following risks:
Borrowing governance tokens: The attacker can manipulate the voting results in a short period of time by borrowing a large number of governance tokens.
Control of majority voting rights: If governance tokens are highly concentrated in the hands of a few people, these people can control the decision-making of the entire project through concentrated voting rights.
Q3: What dimensions or parameters can be used to preliminarily evaluate the security and risk level of DeFi projects?
BlockSec Security Team: Before participating in a DeFi project, it is very necessary to conduct an overall security assessment of the project. Especially for participants with large amounts of funds, necessary security due diligence can maximize the security of funds.
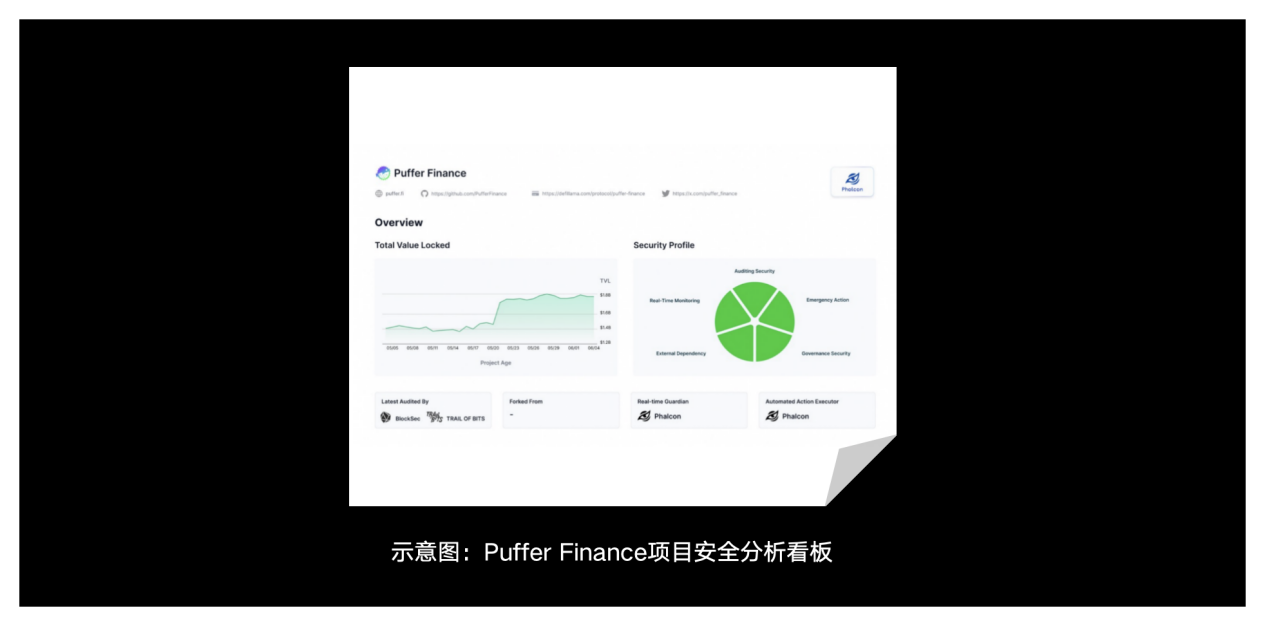
First, it is recommended to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the project's code security, including whether the project has been audited and whether it has been audited by an auditing company with a good security reputation, whether multiple auditing companies are involved, whether the latest code has been audited, etc. Generally speaking, if the code running online has been audited by multiple security companies with a good security reputation, the risk of security attacks will be greatly reduced.
Second, it depends on whether the project party has deployed a real-time security monitoring system. The security guaranteed by security audits is static and cannot solve dynamic security issues caused after the project goes online. For example, the project party improperly adjusts the key operating parameters of the project, adds new pools, etc. If the project party adopts some real-time security monitoring systems, then the safety factor of its operation will be higher than that of protocols that do not adopt such solutions.
Third, we need to see whether the project has the ability to automatically respond in an emergency. This ability has long been ignored by the community. We found that in multiple security incidents, the project was unable to automatically perform function fuses (or fuses for sensitive fund operations). In emergencies, the project mostly used manual methods to handle security incidents, which has proven to be inefficient or even ineffective.
Fourth, we need to look at the external dependencies of the project and the robustness of the external dependencies. A DeFi project will rely on information provided by third-party projects, such as price, liquidity, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the security of the project from the perspective of the number of external dependencies, the security of the external dependent projects, and whether there is monitoring and real-time processing of abnormal data of external dependencies. Generally speaking, projects with external dependencies that are head projects and have fault tolerance and real-time processing of abnormal data of external projects will be safer.
Fifth, whether the project has a relatively good community governance structure. This includes whether the project has a community voting mechanism for major events, whether sensitive operations are completed with multi-signatures, whether the multi-signature wallet introduces community neutral participation, whether there is a community security committee, etc. These governance structures can improve project transparency and reduce the possibility of users' funds in the project being rugpulled.
Finally, the past history of the project is also very important. Background checks need to be conducted on the project team and core project members. If the core members of the project have had multiple attacks or rugpull records in their past projects, then the security risk of such a project will be relatively high.
In short, before participating in a DeFi project, users, especially those with large amounts of capital, should do a good job of research, from code security audits before the project goes online to real-time security monitoring and automatic response capability building after the project goes online, to examine the project's security investment and security, and to do a good job of adjustment from the perspectives of external dependence, governance structure, and the project's past history to ensure the safety of funds invested in the project.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: Although the security of DeFi projects cannot be 100% guaranteed, users can preliminarily evaluate the security and risk level of DeFi projects by cross-combining the following dimensions.
1. Project Technical Security
1. Smart Contract Audit:
1) Check whether the project has been audited by multiple auditing firms and whether the auditing firms have a good reputation and experience.
2) Check the number and severity of issues reported in the audit report to ensure that all issues have been fixed.
3) Check whether the code deployed by the project is consistent with the audited code version.
2. Open source code:
1) Check whether the project's code is open source. Open source code allows the community and security experts to review it, which helps to discover potential security issues.
2) Development Team Background: Understand the background and experience of the project development team, especially their experience in blockchain and security, as well as the team’s level of transparency and public information.
3) Bug bounty program: Does the project have a bug bounty program to incentivize security researchers to report vulnerabilities?
3. Financial and economic security
1) Funds locked: Check the amount of funds locked in the smart contract. A higher lock-up may mean that the project has a higher level of trust.
2) Trading volume and liquidity: Evaluate the trading volume and liquidity of the project. Low liquidity may increase the risk of price manipulation.
3) Token economic model: Evaluate the token economic model of the project, including token distribution, incentive mechanism and inflation model. For example, whether there is excessive concentration of token holdings, etc.
4. Operational and management security
1) Governance mechanism: Understand the governance mechanism of the project, whether there is a decentralized governance mechanism, whether the community can vote on important decisions, and analyze the distribution of governance tokens and the concentration of voting rights, etc.
2) Risk management measures: Does the project have risk management measures and emergency plans, and how to deal with potential security threats and economic attacks. In addition, in terms of project transparency and community communication, you can see whether the project party regularly publishes project progress reports and security updates, and whether it actively communicates with the community and solves user problems, etc.
5. Market and community evaluation
1) Community activity: Evaluate the project’s community activity and user base. An active community usually means that the project has broad support.
2) Media and social media reviews: Analyze the project’s reviews in the media and social media to understand what users and industry experts think of the project.
3) Partners and Investors: Check whether the project has the support of well-known partners and investors. Reputable partners and investors can increase the credibility of the project, but this cannot be a decisive factor in judging its safety.
Q4: How should users view audit reports, open source status, etc.?
BlockSec Security Team: For audited projects, the project owners usually publish audit reports to the community through official channels. These audit reports are usually in the project owner's documents, Github code base and other channels. In addition, the authenticity and identification of the audit report are also required. The identification methods include checking the digital signature of the audit report and contacting the audit company for secondary confirmation.
So, after receiving such an audit report, how should investors study it?
First, check whether the audit report has been audited by some security companies with a high security reputation, such as Open Zeppelin, Trail of Bits, BlockSec and other leading audit companies.
Second, we need to see whether the problems mentioned in the audit report have been fixed. If not, we need to see whether the project party has sufficient reasons for not fixing them. It is also necessary to distinguish between valid vulnerability reports and invalid vulnerability reports in the audit report. Since there is no unified industry standard for audit reports, security audit companies will conduct project vulnerability risk rating and reporting based on their own security awareness. Therefore, for the vulnerabilities found in the audit report, we should focus on valid vulnerability reports. It is best to introduce your own security consulting team to conduct a third-party independent assessment in this process.
Third, check whether the audit time in the audit report published by the project party is consistent (or close) to the upgrade and update time of the latest project. In addition, it is also necessary to pay attention to whether the project party's code in the audit report covers all the project party's current online codes. For economic and time cost considerations, the project party usually conducts partial code audits. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to determine whether the audited code is the core protocol code.
Fourth, we need to see whether the code running online by the project party has been verified (open source), and whether the verified code is consistent with the audit report. Usually the audit is based on the code on the project party's Github (rather than the code that has been deployed online). If the code that the project finally deploys on the chain is not open source, or has significant differences with the audited code, these are points that need to be paid attention to.
In short, reading the audit report itself is a highly professional matter, and it is recommended to introduce independent third-party security experts to provide consulting opinions during the process.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: Users can view the audit report and open source status of smart contracts through the DeFi project official website or third-party websites, such as OKLink. The following are common steps for viewing project audit reports and open source status:
First, look for official announcements or websites. Most credible DeFi projects will display relevant documentation information on their official websites. On the project documentation page, there is usually a page such as "Security", "Audit" or "Contract Address" that links to the audit report and the contract address deployed by the project party. In addition to the official website of the project party, it usually also displays the audit report and deployed contract address information on official social media such as Medium, Twitter, etc.
Second, after reading the official website of the project party, you can use the OKLink browser to query the deployed contract address information given by the project party, and view the open source code information of the contract deployed at the address in the "Contract" column.
Third, after getting the project's audit report and the open source code information of the deployed contract, you can start reading the project's audit report. When reading the audit report, pay attention to the following points:
1) Understand the structure of the audit report and have a general idea of the content of the audit report. The audit report is roughly divided into introduction, problems found, solutions and suggestions, and audit results.
2) When reading the introduction, we need to pay attention to the scope and objectives of the audit report. Usually, the audit report will mark the Github Commit Id where the audit file was submitted. We need to compare whether the files audited in the audit report are consistent with the open source code deployed on the chain.
3) When reading the Issues Found, Solutions and Suggestions and Audit Results sections, we need to focus on whether the project team has fixed the discovered vulnerabilities as recommended, and whether the project party has conducted a follow-up audit on the modified content to ensure that all issues have been properly addressed.
4) Compare multiple reports. If the project has been audited multiple times, check the differences between each audit report to understand the security improvements of the project.
Q 5: What is the reference value of hacker attack history and bounty programs to the security of DeFi projects?
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: The history of hacker attacks and bounty programs provide a certain reference value for the security assessment of DeFi projects, which is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
First, the history of hacker attacks
1) Revealing historical vulnerabilities: Attack history can show specific security vulnerabilities that have existed in the project, allowing users to understand which security issues have been exploited in the past and whether these issues have been thoroughly fixed.
2) Evaluate risk management capabilities: How a project responds to historical security incidents can reflect its risk management and crisis handling capabilities. A project that actively responds, fixes vulnerabilities in a timely manner, and compensates affected users is generally regarded as a more reliable and mature investment option.
3) Project reputation: Frequent security issues may undermine users’ trust in a project, but if a project can demonstrate the ability to learn from mistakes and strengthen security measures, this can also build its long-term reputation.
Second, the bounty program
The implementation of bounty programs in DeFi and other software projects is an important strategy to improve security and uncover potential vulnerabilities. These programs bring many reference values to the security assessment of projects:
1) Enhanced external audits: The bounty program encourages security researchers around the world to participate in the security audits of the project. This "crowdsourcing" security testing can reveal issues that may be overlooked by internal audits, thereby increasing the chances of discovering and resolving potential vulnerabilities.
2) Verify the effectiveness of security measures: Through actual bounty programs, projects can test the effectiveness of their security measures in real combat. If a project's bounty program lasts longer but reports fewer serious vulnerabilities, this may be an indicator that the project is relatively mature and secure.
3) Continuous security improvement: The bounty program provides a mechanism for continuous improvement. As new technologies and new attack methods emerge, the bounty program helps project teams update and strengthen their security measures in a timely manner to ensure that the project can cope with the latest security challenges.
4) Establish a security culture: Whether a project has a bounty program, as well as the seriousness and activity of the program, can reflect the project team's attitude towards security. An active bounty program shows the project's commitment to building a solid security culture.
5) Enhance community and investor confidence: The existence and effectiveness of the bounty program can prove to the community and potential investors that the project attaches great importance to security. This can not only enhance user trust, but also attract more investment, because investors tend to choose projects that show a high sense of security responsibility.
Q 6: How do users build monitoring awareness when participating in DeFi?
BlockSec Security Team: Take whale users as an example. Whales mainly refer to individual investors or small investment institutions. These users have large funds, but usually do not have very strong security teams or the ability to develop their own security tools. Therefore, so far, most whales do not have sufficient risk perception, otherwise they would not have suffered such huge losses.
Faced with the risk of huge losses, some whale users have begun to consciously rely on some public security tools to monitor and perceive risks. Now, there are many teams working on monitoring products, but how to choose is very critical. Here are a few key points:
First, there is the cost of using the tools. Although many tools are very powerful, they require programming and are not cheap to use. For users, it is not easy to figure out the structure of the contract or even collect addresses.
Second, accuracy. No one wants to receive several alerts in a row while sleeping at night, only to find out that they are false alarms, which will make people upset. Therefore, accuracy is also very critical.
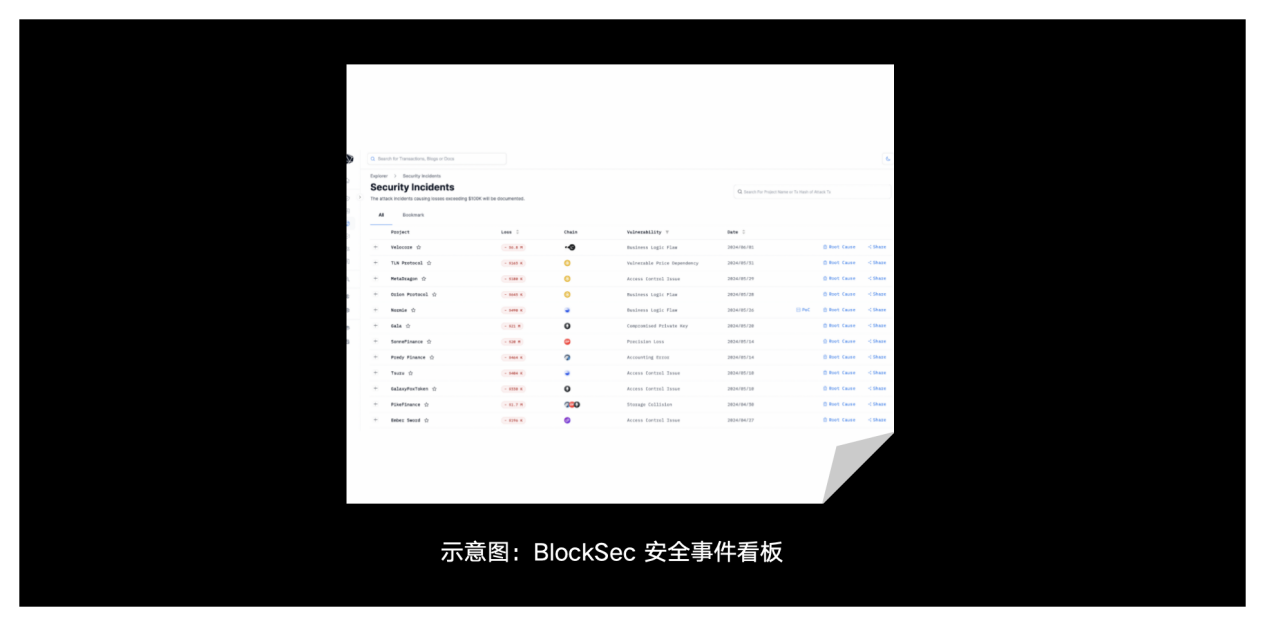
Finally, there is security. Especially at this scale of funding, the various security risks of tool development and its team cannot be ignored. The recent Gala Game attack was said to be due to the introduction of an unsafe third-party service provider. Therefore, a reliable team and a credible product are crucial.
So far, many whales have found us, and we will recommend professional asset management solutions to them, so that whale users can not only ensure the safety of funds, but also take into account daily fund management such as "mining, withdrawing and selling", perceive risks, and even withdraw funds in emergency situations.
Q7: Security advice for participating in DeFi and how to deal with security risks
BlockSec Security Team: For large-scale participants, the first thing to do when participating in DeFi protocols is to ensure the safety of the principal and invest after conducting a comprehensive study of possible security risks. Funds can usually be ensured to be safe in the following ways.
First of all, we need to judge the security emphasis and investment of the project party from multiple aspects. This includes whether it has undergone a relatively thorough security audit, whether the project party has the ability to monitor and automatically respond to project security risks, whether it has a relatively good community governance mechanism, etc. All of these can reflect whether the project party attaches great importance to the security of user funds and whether it has a highly responsible attitude towards the security of user funds.
Secondly, participants with large amounts of funds also need to build their own security monitoring and automatic response systems. After a security incident occurs in the investment protocol, investors with large amounts of funds should be able to perceive and withdraw funds as soon as possible to recover losses as much as possible, rather than pinning all their hopes on the project party. In 2023, we can see that many well-known projects have been attacked, including Curve, KyberSwap, Euler Finance, etc. Unfortunately, we found that when the attack occurred, large investors often lacked timely and effective intelligence, and did not have their own security monitoring and emergency retreat systems.
In addition, investors need to choose good security partners to continuously pay attention to the security of the investment projects. Whether it is the upgrade of the project code or the change of important parameters, it is necessary to be able to perceive and assess the risks in a timely manner. Such things are difficult to accomplish without the participation of professional security teams and tools.
Finally, it is necessary to protect the security of private keys. For accounts that need to trade frequently, it is best to use a combination of online multi-signature and offline private key security solutions to eliminate the single point risk after the loss of a single address and a single private key.
What should we do if an investment project faces security risks?
I believe that for any whale and investor, the first reaction to a security incident must be to protect the principal first, and withdrawing funds as soon as possible is the top priority. However, attackers are usually very fast, and manual operations are often too late, so it is best to automatically withdraw funds based on risks. Currently, we provide relevant tools that can realize automatic withdrawal after discovering attack transactions, helping users to withdraw first.
Secondly, if losses are really incurred, in addition to learning lessons, the project party should also actively seek help from security companies to trace and monitor the damaged funds. As the entire Crypto industry pays more attention to security, the proportion of recovered funds is gradually increasing.
Finally, if you are a large investor, you can also ask a security company to check whether other projects you have invested in have similar problems. The root causes of many attacks are the same, such as the precision loss problem of Compound V2. Last year, many projects had similar problems and were attacked continuously. Therefore, you can ask a security company to analyze the risks of other projects in your investment portfolio. If risks are found, you should communicate with the project owner or withdraw as soon as possible.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: When participating in DeFi projects, users can take a variety of measures to participate in DeFi projects more safely, reduce the risk of capital loss, and enjoy the benefits of decentralized finance. We will start from the user level and the OKX Web3 wallet level.
First, for users:
1) Choose audited projects: Give priority to projects that have been audited by well-known third-party auditing companies (such as ConsenSys Diligence, Trail of Bits, OpenZeppelin, Quantstamp, ABDK), review their public audit reports, and understand potential risks and vulnerability fixes.
2) Understand the project background and team: Ensure the transparency and credibility of the project by studying the project’s white paper, official website, and development team background. Pay attention to the team’s activities in social media and development communities to understand its technical strength and community support.
3) Diversify your investments: Don’t invest all your money in a single DeFi project or asset. Diversifying your investments can reduce risk. Choose multiple different types of DeFi projects, such as lending, DEX, Farming, etc., to diversify your risk exposure.
4) Small-amount test: Before making large-amount transactions, conduct small-amount test transactions to ensure the security of operations and the platform.
5) Regularly monitor accounts and handle emergencies: Check your DeFi accounts and assets regularly to detect abnormal transactions or activities in a timely manner. Use tools (such as Etherscan) to monitor on-chain transaction records to ensure asset security. Take emergency measures in a timely manner after detecting anomalies, such as revoking all authorizations of the account, contacting the wallet security team for support, etc.
6) Use new projects with caution: Be cautious about new projects that have just been launched or have not been verified. You can invest a small amount of money to conduct experiments and observe their operation and safety.
7) Use mainstream Web3 wallets for transactions: Only use mainstream Web3 wallets to interact with DeFi projects. Mainstream Web3 wallets provide better security protection.
8) Prevent phishing attacks: Be cautious when clicking on unfamiliar links and emails from unknown sources. Do not enter private keys or mnemonics on untrusted websites. Make sure the links you visit are official websites. Use official channels to download wallets and applications to ensure the authenticity of the software.
Second, from the perspective of the OKX Web3 wallet:
We provide many security mechanisms to protect user funds:
1) Risky domain name detection: When a user accesses a DAPP, the OKX Web3 wallet will perform detection and analysis at the domain name level. If the user accesses a malicious DAPP, it will be intercepted or reminded to prevent the user from being deceived.

2) Pixiupan token detection: OKX Web3 wallet supports comprehensive Pixiupan token detection capabilities, actively blocking Pixiupan tokens in the wallet to prevent users from trying to interact with Pixiupan tokens.
3) Address tag library: OKX Web3 wallet provides a rich and complete address tag library. When users interact with suspicious addresses, OKX Web3 wallet will give timely warnings.
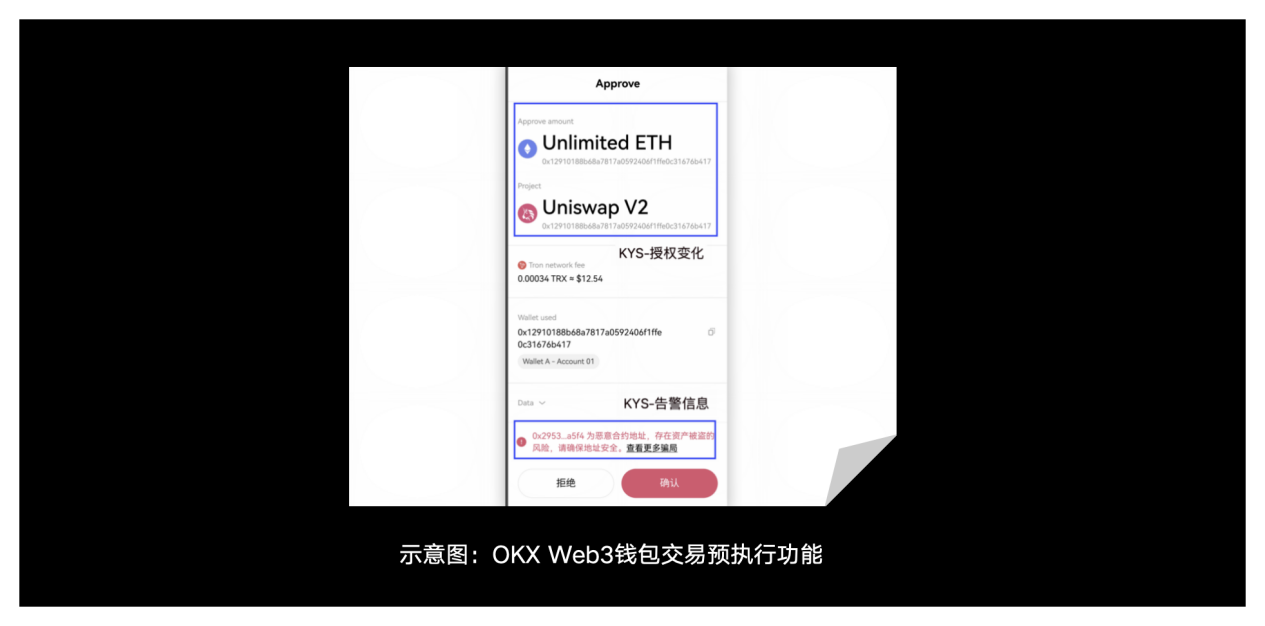
4) Transaction pre-execution: Before a user submits any transaction, the OKX Web3 wallet will simulate the transaction and display the asset and authorization change results for the user’s reference. The user can judge whether the result meets expectations based on the result, so as to decide whether to continue submitting the transaction.
5) Integrated DeFi applications: OKX Web3 wallet has integrated services of various mainstream DeFi projects. Users can safely interact with integrated DeFi projects through OKX Web3 wallet. In addition, OKX Web3 wallet will also recommend paths for DeFi services such as DEX and cross-chain bridges to provide users with the best DeFi services and the best Gas solutions.
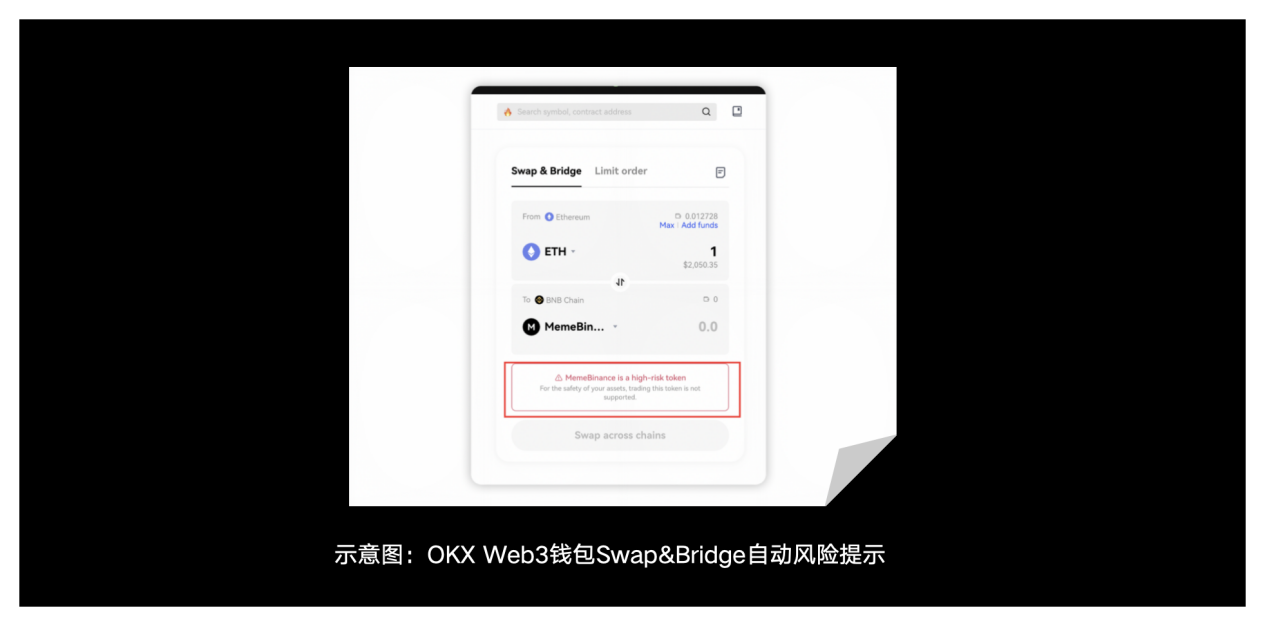
6) More security services: OKX Web3 wallet is gradually adding more security features and building more advanced security protection services, which will better and more efficiently protect the security of OKX wallet users.
Q 8: Not only users, but also DeFi projects face what types of risks and how to protect themselves?
BlockSec Security Team: The types of risks faced by DeFi projects include: code security risks, operational security risks, and external dependency risks.
First, code security risks. That is, the potential security risks that DeFi projects may have at the code level. For DeFi projects, smart contracts are their core business logic (front-end and back-end processing logic, etc. belong to traditional software development business and are relatively mature), and are also the focus of our attention and discussion, including:
1) First, from a development perspective, it is necessary to follow the industry-recognized smart contract security development practices, such as the Checks-Effects-Interactions pattern for preventing reentrancy vulnerabilities. In addition, commonly used functions should be implemented using reliable third-party libraries as much as possible to avoid unknown risks caused by reinventing the wheel.
2) Secondly, internal testing is important in software development and can help discover many problems. However, for DeFI projects, local testing alone is not enough to expose problems. Further testing is required in a deployment environment that is close to the actual online deployment. This can be achieved by using tools such as Phalcon Fork.
3) Finally, after the test is completed, contact a third-party audit service with a good reputation. Although the audit cannot ensure 100% problem-free, systematic audit work can help the project party to locate various known common security issues to a large extent, which are often unfamiliar to developers or difficult to touch due to different ways of thinking. Of course, due to the differences in expertise and direction of various audit companies, if the budget allows, it is recommended to involve 2 or more audit companies in practice.
Second, operational security risks. That is, security risks generated during the operation of the project after it goes online. On the one hand, the code may still have unknown vulnerabilities. Even if the code has been well developed, tested and audited, there may still be undiscovered security risks. This has been widely proven in decades of security practices in software development. On the other hand, in addition to problems at the code level, the project faces more challenges after it goes online, such as private key leakage, incorrect settings of important system parameters, etc., which may cause serious consequences and huge losses. The response strategies for operational security risks include:
1) Establish and improve private key management: adopt reliable private key management methods, such as reliable hardware wallets or MPC-based wallet solutions.
2) Perform operational status monitoring: The monitoring system can perceive privileged operations and the security status of project operations in real time.
3) Build an automated response mechanism for risks: For example, using BlockSec Phalcon, you can automatically block attacks and avoid (further) losses.
4) Avoid single point risks of privileged operations: such as using a Safe multi-signature wallet to perform privileged operations.
Third, external dependency risk refers to the risk brought by the external dependencies of the project, such as relying on price oracles provided by other DeFi protocols, but problems with the oracles lead to incorrect price calculation results. Recommendations for external dependency risks include:
1) Choose reliable external partners, such as reliable head protocols recognized by the industry.
2) Perform operational status monitoring: Similar to operational safety risks, but the monitoring object here is external dependencies.
3) Build an automated response mechanism for risks: Similar to operational security risks, but the handling methods may be different, such as switching to backup dependencies instead of directly pausing the entire protocol.
In addition, we also provide some monitoring suggestions for project parties who want to build monitoring capabilities.
1) Accurately set monitoring points: Determine which key states (variables) exist in the protocol and where to monitor. This is the first step in building monitoring capabilities. However, it is difficult to set monitoring points to cover all aspects, especially in attack monitoring. It is recommended to use an external professional third-party, field-tested attack detection engine.
2) Ensure the accuracy and timeliness of monitoring: The accuracy of monitoring means that there should not be too many false positives (FP) and missed negatives (FN). A monitoring system that lacks accuracy is essentially unusable; timeliness is a prerequisite for responding (for example, whether it can be detected after the suspicious contract is deployed and before the attack transaction is uploaded to the chain). Otherwise, it can only be used for post-analysis, which places extremely high demands on the performance and stability of the monitoring system.
3) Automated response capabilities are required: Based on accurate and real-time monitoring, automated responses can be built, including the pause protocol to block attacks, etc. A customizable and reliable automated response framework is required to support this, which can flexibly customize response strategies and automatically trigger execution according to the needs of the project party.
In general, the construction of monitoring capabilities requires the participation of professional external security suppliers.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: DeFi projects face a variety of risks, mainly including the following:
1) Technical risks: mainly include smart contract vulnerabilities and network attacks. Protective measures include adopting secure development practices, hiring professional third-party auditing companies to conduct comprehensive audits of smart contracts, setting up bug bounty programs to incentivize white hat hackers to find vulnerabilities, and doing a good job of asset isolation to improve the security of funds.
2) Market risks: mainly include price fluctuations, liquidity risks, market manipulation and combination risks. Protective measures include using stablecoins and risk hedging to prevent price fluctuations, using liquidity mining and dynamic fee mechanisms to deal with liquidity risks, strictly reviewing the types of assets supported by DeFi protocols and using decentralized oracles to prevent market manipulation, and responding to competition risks through continuous innovation and optimization of protocol functions.
3) Operational risks: mainly include human error and governance mechanism risks. Protective measures include establishing strict internal controls and operating procedures to reduce the occurrence of human errors, using automated tools to improve operational efficiency, and designing reasonable governance mechanisms to ensure a balance between decentralization and security, such as introducing voting delays and multi-signature mechanisms. In addition, we should monitor and develop emergency plans for the projects that are launched, so that we can take immediate measures to minimize losses in the event of an abnormality.
4) Regulatory risks: Legal compliance requirements and anti-money laundering (AML)/know your customer (KYC) obligations. Protective measures include hiring legal counsel to ensure that the project complies with legal and regulatory requirements, establishing a transparent compliance policy, and proactively implementing AML and KYC measures to enhance the trust of users and regulators.
Q 9: How can DeFi project parties judge and choose a good auditing company?
BlockSec Security Team: How can DeFi project parties judge and choose good audit companies? Here are some simple standards for reference:
1) Whether it has audited well-known projects: This indicates that the audit company is recognized by these well-known projects.
2) Whether the audited projects have been attacked: Although theoretically auditing cannot guarantee 100% security, practical experience shows that most projects audited by auditing companies with a good reputation have never had a record of being attacked.
3) Judging audit quality through past audit reports: Audit reports are an important indicator of the professionalism of audit companies, especially when the same audit projects and the same audit scope can be compared. You can focus on the quality (degree of harm) and quantity of vulnerability discoveries, and whether the vulnerability discoveries are usually adopted by the project party.
4) Professional practitioners: The personnel composition of the audit company, including academic qualifications and work background, etc. Systematic education and work experience are of great help in ensuring the quality of the audit.
Finally, thank you for reading the 05th issue of the OKX Web3 Wallet "Security Special Issue". We are currently preparing for the 06th issue, which will include real cases, risk identification, and security operation tips. Stay tuned!
Disclaimer
This article is for reference only and is not intended to provide (i) investment advice or investment recommendations; (ii) an offer or solicitation to buy, sell or hold digital assets; or (iii) financial, accounting, legal or tax advice. Holding digital assets (including stablecoins and NFTs) involves high risks and may fluctuate significantly or even become worthless. You should carefully consider whether trading or holding digital assets is suitable for you based on your financial situation. Please be responsible for understanding and complying with local applicable laws and regulations.