How does Sei use the order book engine to resist MEV?
text
,author:3 V Labs,author:@Macr 0 Mark
Designed to handle institutional-grade order flow at scale, the Sei Network employs three major technological innovations:
native order matching
Twin Turbo Consensus
text
What is a native order matching engine? Why does this feature take MEV protection to a whole new level?
first level title
What is MEV, and why is it the biggest problem threatening all Layer 1s?
In the eyes of the Sei team, there are two types of MEV, one is the robot/validator of the front-end transaction, and the other is the liquidator/arbitrageur. The former has negative consequences, while the latter is acceptable for a robust transactional economic model.
Sei attempts to minimize bad MEV through frequent batch auctions (FBA), while maximizing good MEV through off-chain lightning bot-style auctions.MEV-boostCapturing token value from gas fees is not profitable enough for a high-throughput chain like Sei. Therefore, Sei plans to capture value accretion by distributing auction profits generated by benign MEV bots to validators and stakeholders. Sei’s auctions will be private and off-chain, similar to the Lightning Bot model (a
implementation that allows Ethereum to perform pre-run protection). The system is private, meaning it is a blind auction (also known as a first-price closed-bid auction), where bidders can submit their exact transaction order preferences without revealing their bids and without paying for unsuccessful bids. pay.
This auction will allow bots to compete for typical MEV transactions such as liquidations and arbitrage. Instead of congesting the P2P network and raising gas prices. Robots will bid on the economic value of the deal, and the winning bid will be close to the actual value of the deal. With enough market participants, the winning bid may be slightly lower than the deal value, with some going to the winner and the rest being distributed.
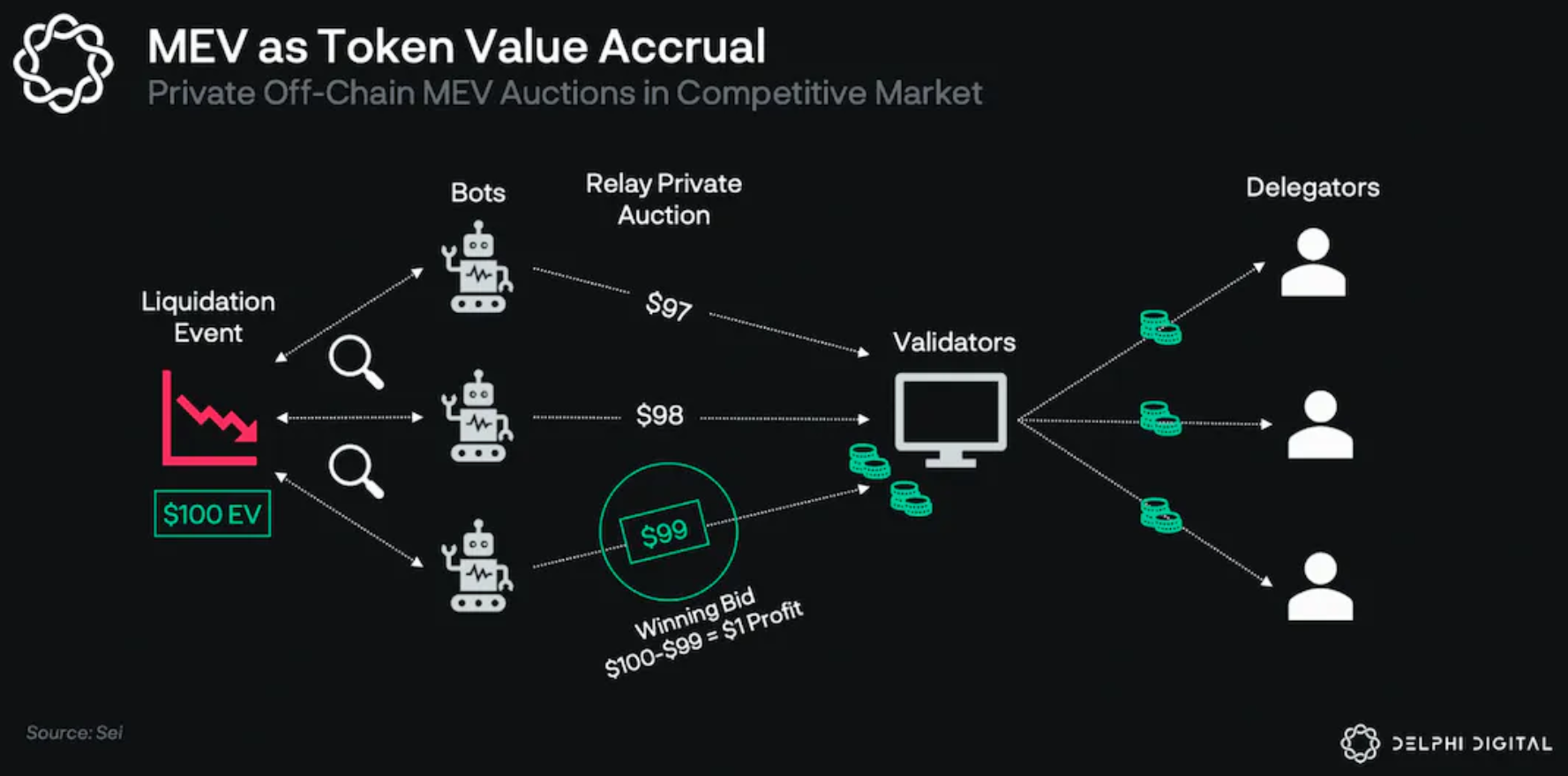
For example, in a liquidation worth $100, bots will compete and mark up the price in order to participate in the liquidated transaction, but instead of spamming the Sei chain, they do it off-chain, overriding the gas fee. In an efficient market, the winning bid might be worth roughly $99, of which $1 would be awarded to the robot and the remaining $99 would be split between validators and delegators.
"Let's take a step back and look at what MEV is."。
Maximum Extractable Value, the process of maximizing economic value from block production by including, excluding, and reordering transactions in blocks
For a more in-depth study on MEV, check out thisguide。
guide
In his book, The Lightning Boy, Michael Lewis investigates the original Wall Street "first striker," in which high frequency trading (HFT) and unethical arbitrage practices led to the formation of a rigged market.
When choosing where to place their liquidity, market makers (MMs) value speed, finality, and latency. In order to provide market depth, MM tracks and updates their bilateral prices every block. Therefore, sub-second block times mean smaller price differences, so there is less risk of being exploited by high-frequency traders. Take profit in the time frame between price update and MM reaction.

image description
first level title
How does Sei's native hOMiE achieve pre-transaction protection?
The Order Matching Engine (OME) matches buy and sell orders on all kinds of trading markets including crypto markets.
Like your car engine, OME is responsible for speed (TPS and finality) and torque (throughput).
Let's break down why Sei has a "Ferrari" engine.
Sei's OME is native, which means that any transactional application built on top of Sei's infrastructure can use order placement and matching ("plug and play"), it is not a smart contract that needs to be forked.Sei's OME usesFrequent Lot Auction
Combined with single block order execution
FBA can aggregate every market order at the end of a block, and then execute all orders at the same uniform clearing price.
Sei also combines order placing and execution into one block to create a faster trading experience. Regardless of the order of your transactions, you will still get the same price as everyone who posted a transaction within that block time (~450ms).
Suppose there are two orders on the order book, one to sell $Sei at $10 and the other to sell $Sei at $11, and then two buyers come in. Normally the first buyer gets filled for $10 and the second for $11, but using frequent lot auctions, both orders get filled for $10.50, which is a uniform liquidation Price, obtained by dividing the sum of the two prices by two, (P 1+P 2 )/2 .: This model was created as a solution to the huge arbitrage opportunity of the Continuous Double Auction Model (CDA). CEXs typically use CDA, where orders are processed as soon as they hit the order book (or are filled by other bids or asks), which requires high throughput at times of high volatility. For DEXs, this often results in significant delays due to network congestion.
first level title
Is Sei's engine really unique? Comparison with Injective, dYdX and Serum
New AMM models have the benefit of "possibly" unlimited liquidity, but they restrict users to only accept prices. On the other hand, users of the Central Order Book Exchange (CLOB) can take or place orders.
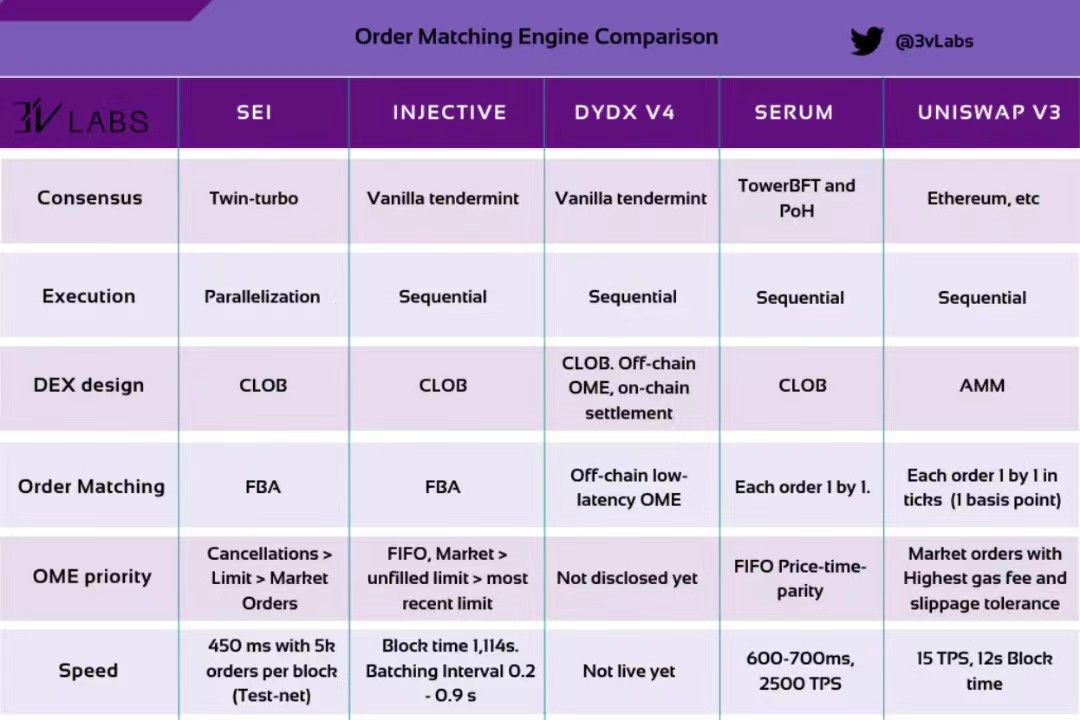
OME Comparison @ 3 vLabs
Injective
secondary title
Injective has over $9.2M in total lockup and a market cap of $293M (as of February 22, 2023), based on the Cosmos SDK and targeting the most liquid market makers, DEXes and traders group.
In order to reduce front-end transactions, Injective also adopts the Frequent Batch Auction (FBA) model and introduces three main features.
Discrete time characteristics: It is stipulated that cross orders are filled with "first in first out" priority within a discrete time period;
Sealed Bids: Orders are not made public in the order book until the auction interval ends and the batch is executed.
Serum
secondary title
For Serum, with a total lock-up of $566K and a market cap of $124M (as of February 22, 2023), its order matching engine is fairly simple. The model aggregates the highest bid and lowest take price to set the current market price at which traders can execute orders immediately, thereby tightening bid-ask spreads.
In Sei, all centralized order book transactions are executed atomically within the scope of a block, unlike Serum, which requires two separate transactions to handle order placement and execution.
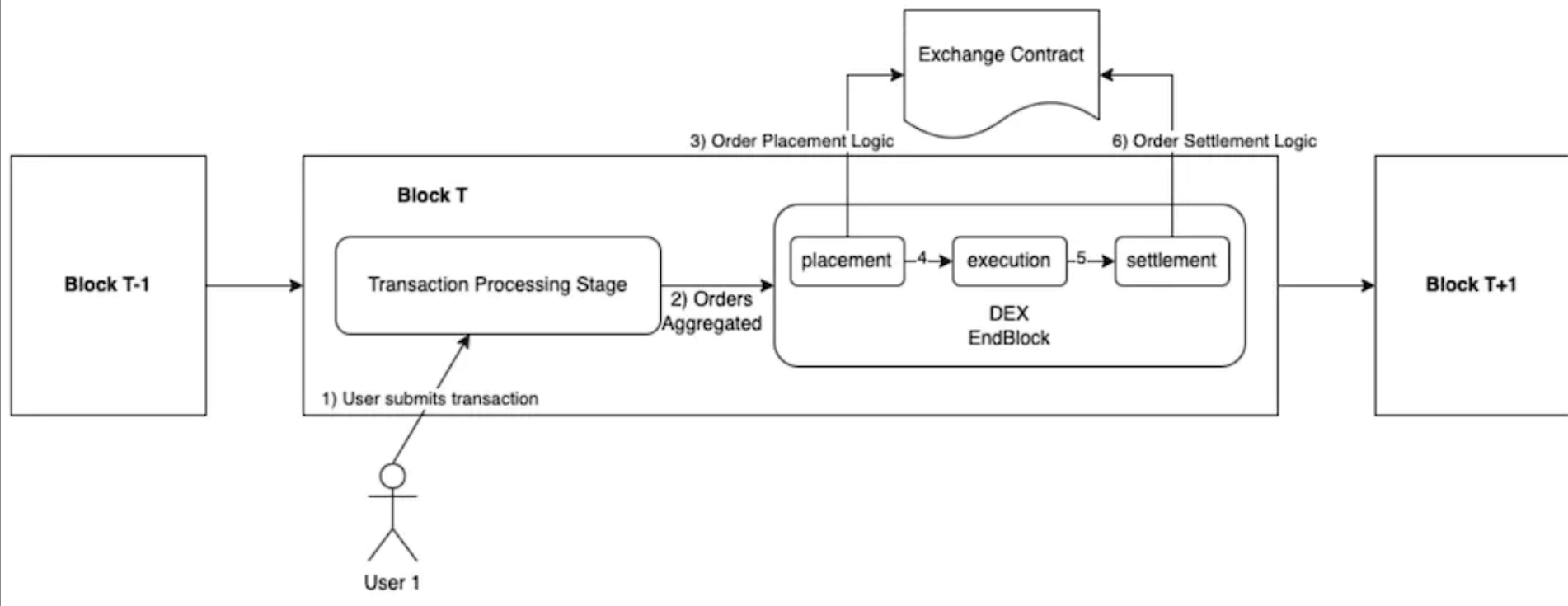
image descriptionhttps://github.com/sei-protocol/sei-chain/blob/master/whitepaper/Sei_Whitepaper.pdf
DYDX
secondary title
Speaking of dYdX, there are two problems with the current version: the performance of both the Ethereum and StarkEX applications is insufficient for dYdX's needs, and also, v3 is operated through a centralized sequencer, which has authority to review transactions.
In the words of the dYdX team:
"The fundamental problem with every L1 or L2 we can develop is that none can handle anywhere close to the throughput required to run a state-of-the-art order book and matching engine."
In terms of performance, the current version 3 handles 10 trades per second and about 1,000 orders/cancellations per second.
Sound familiar?
first level title
Sei's optimization settings will further improve the performance of these order matching engines by:
secondary title
Parallel processing of blocks
Market-Based Parallel Processing: By default, Sei treats all order book trades touching different markets as independent (if they do not affect the same market in the same block).
secondary title
Sei’s price oracles are responsible for bringing off-chain price data into the blockchain, they are built into the chain. This means that all validators need to propose their price (exchange rate) when submitting a block. Blocks are only created when all validators agree on a common price. If validators miss some voting windows or offer prices that deviate too far from the median, they will be slashed (punished).
secondary title
Market makers can cancel and create orders in multiple markets in one transaction (ie, all orders for BTC perpetual contracts for a specific market will be combined into one smart contract call).
first level title
Dive into Order Matching Priorities
Sei's Order Matching Engine (OME) will prioritize all order cancellations, removing limit orders from the order book to which they relate. Then, all limit orders will be added to the order book. This ensures that orders are filled with maximum liquidity. The matching engine will then process the market order.
The Injective protocol operates on a first-in-first-out (FIFO) principle, where market orders are executed first, followed by unfilled limit orders and finally the latest limit orders.
Serum Dex also adopts a FIFO strategy with "price-time-priority" matching, orders are ranked according to their price, and orders with the same price are ranked according to the time they were posted in the order book.
first level title
References
ReferencesEthereum.org"Maximum Extractable Value (MEV)",
developer documentation
White Paper "Sei: Layer 1 Customized for Trading, Offering Unique Advantages to Exchanges", Sei Labs"Latency and Throughput", from Sei Co-founder
Tweet by @jayendra_jog
"Why dYdX is Leaving Ethereum and StarkWare to Build a Local Chain on Cosmos", Cryptoslate, Liam Wright
"Serum - Central Limit Order Book vs Automated Market Maker", DoDao.io
Learn more about Sei:https://www.sei.io/
Sei official website:https://twitter.com/SeiNetwork
Sei official twitter:https://twitter.com/Ship_DAO



