Original title: Intermediate Economics
One of the main hurdles to scaling the crypto market in 2023 is how to implement a more efficient DAO to internalize the nature of the firm and divide costs appropriately in an already decentralized autonomous market.
This article will analyze existing business models from the perspective of Intermediate Economics, and define companies, markets, and assets based on the current status of the cryptoeconomic market. The specific framework is as follows:
Traditional Typical Business Model: Walmart, Sysco, and McDonalds
Economic Markets and Regulatory Costs: Black, White, and Gray
Internet platform business models: Uber, AirBnB and Amazon
New Media Forms: The Fifth Estate/Power
first level title
Traditional Typical Business Model: Walmart, Sysco, and McDonalds
A common business model has permeated our lives. Many readers have seen the surrendered McDonalds employee meme. In the United States, Wal-Mart is almost a replica of the consumer version.
Walmart is an interesting phenomenon for the American consumer. Town centers are preferred locations for socialization, and a lack of infrastructure limits job opportunities and employment. Walmart, however, optimizes its location in this context, operating on an already existing network of interstate highways. The same applies to McDonalds. McDonalds optimized the roadside restaurant and franchise structure and formed the basis of the gig economy.

Why put Sysco together with Wal-Mart and McDonalds? Heres why: All three firms fit Ronald Coases essence of the firm, a business firm that minimizes the sum of its production costs by internalizing costs. All three companies have grown to near monopoly status, in part because they can benefit from the Federal Highway Aid Act of 1956 and the gradual stabilization of global trade routes. In both cases, the nation-state bears some of the infrastructure costs, but affiliated companies are free to capitalize the proceeds. Coase also explains the overhead limit on firm size, which also applies to taxes, but well come back to that later.
first level title
Economic Markets and Regulatory Costs: Black, White, and Gray
Everyone has heard the term black market, but only a small percentage of people have heard of gray market. They all follow the same principle: Regulatory costs cannot exceed total global capital production. Of course, the more morally condemnable a good or service is, the more regulatory costs are allowed and expended.
In Gray Markets: Prevention, Detection, and Litigation, several black markets are described: street drugs, human exploitation, wire fraud. When there is tariff commodity arbitrage against end users or resale of unofficial products to other resellers, there is considerable volume that cannot be regulated. In fact, unregulated financial markets may trade commodity futures and the like in the gray market.
The larger the economy, the less efficient it is to fix regulatory costs. A popular argument since marijuana legalization has been that over-regulation, by driving concentrated growth into the black market and increasing flow into the prison-industrial complex, is its own form of extortion. Coase may just disagree and claim this is an overhead cost of an overgrown company.
Maybe the criminals and the police are just opposing nodes that generate an adversarial network. Traffickers learned how to smuggle one way, and police soon found a way to detect it. The more BE an area experiences, the potential victims buy better locks and surveillance. In this lens, we may see one of the most important aspects of the black market: what kind of autonomy the market most chooses. We can see that the economy contains certain incentives and certain costs. As Charlie Munger said, Show me the incentives and Ill show you the results. Notwithstanding the social and cultural costs, it is no surprise that the economy expands to join supply and demand.
first level title
Internet platform business models: Uber, AirBnB and Amazon
One of the largest drug marketplaces is the Darknet Market, where Walmart, Sysco, and McDonalds all use web apps to coordinate orders. In Optimal Economics, there is an ecological metaphor of a large pyramid covered by more superficial pyramids and obelisks. Starting from the ground up, all of the above companies rely on a globally maintained physical layer infrastructure for internet traffic. However, they differ at a higher digital layer (the network).
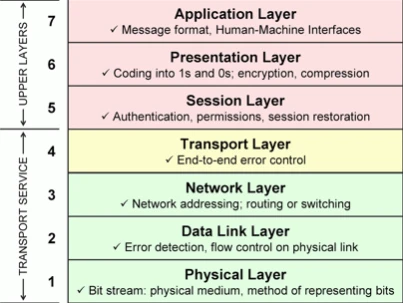
The dark web utilizes onion routing (among other technologies), while large enterprises may rely on cloud-based VPNs (among other technologies). The richer the company operates within the legal sphere, the more trusted intermediaries it will have. For example, a cloud service provider will be more resistant to DDoS, malicious or benign, than a random dedicated server hosting an illicit web business.
Post-dotcom critique: Why spend money on growing a business online? Its just a speculative investment in a skeuomorphic business model. No fundamental functional gain. Fixing this will require more effort and more engineering, but there is no doubt that speculative bubbles precede large-scale economic booms. More precisely, many brick-and-mortar businesses were outcompeted by more nimble, lower-total-cost online players.
For example, its no secret that Amazon sells durable goods like books, and brick-and-mortar stores like Borders and Barnes Noble lose market share. Sales of most durable goods are outpaced by online retailers, so this trend has come a long way. But what about services like transportation? Whether Uber is omnipotent or a terminator is unclear, but the taxi license scheme has certainly been affected.
first level title
New Media Forms: The Fifth Estate/Power
image description

This comic plays with the late 19th-century trend of corporate trust breaches
The Industrial Revolution was actually the end of the classic three political states. Company allows for further class breakdowns such as directors or unions for tertiary estates, or LLCs, trusts or PACs for secondary estates. Furthermore, in democratic republics and parliamentary monarchies, industrialization and corporations control the massive flow of information. By the early 20th century, the fourth estate (often thought of as print, newspaper-based journalism) oversaw established power.
It should be emphasized at this point that the Fourth Estate is not necessarily incorruptible or effective. While Ida Tarbell was exposing Standard Oils anticompetitive practices, shoddy newspapers were flooding the streets. It should also be noted that the Fourth Estate is not owned and operated by some non-corporate aspect of society; it would be more accurate to describe the Fourth Estate as the arena where all corporations compete for the greatest flow of information.
The fourth estate includes radio, television, and other mass media such as social media. Others argue that these have become the equivalent of modern religion, so that the concept of a first estate has somehow been superseded by popular culture transmitted through the mass media.
One can quote Nietzsche: God is dead! Coase distinguishes firms and markets as independent coordination mechanisms; firms coordinate how to produce optimally to maximize capital gains, and markets coordinate optimal capital exchanges to maximize growth. With respect to the notion of religious mass media, it can be asserted that markets displace firms (given denominations) over time by reducing social unrest (i.e. socialized capital losses).
The internet, and the information age more broadly, is a marketplace for non-scarce ideas.

Beginning with unlicensed Pirate radio, marketplaces for ideas began to enter the public domain without any form of corporate intermediary. Television is not completely disintermediated, but over time, television viewing by the general public has become more common. A mass media effectively transforms into a self-regulating gray market. By early 2010, this gray market had become an integral part of society. If a particular second estate closes the market to suppress the fourth estate, the third estate will riot. If any political class seeks to subvert political discourse, the second and third estates may choose to revoke their entitlement economic and/or ideological patronage.
The Internet did not provide a completely disintermediated marketplace of ideas for the tertiary industry, but it forced a certain form of aging. One rebuttal to this is the lindyness of trends/products, but look at what a lindy brand like the NYT actually is. It only existed in the last century of the printing press trend, but only two decades of the information age has completely dismantled its revenue model. Arguably, the Fifth Estate began with the repositioning of the First and Fourth Estates as mass forums for self-cannibalization.
Now, a lot of terms about encryption, web3, DAO, etc. are starting to appear. But all of this started a long time ago. In 1995, Phil Zimmerman released the source code for PGP, partly because it was over-regulated as a prohibited munition for export. In 1992, Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor released a proof of work to combat spam. These lead to open-source forms of regulatory code without a trusted third party. While the Fifth Estate can be seen as an alternative to the Fourth Estate, we also see it as a gray marketplace of ideas with ancillary, unspoken property rights. In this respect, while 90% of the Internet can be derided as porn, spam, and trolls, it is a self-regulating digital realm with a dense core of old prestige and entitlement. In other words, the fifth estate not only inherits the speech of the fourth estate, but also inherits the money, prestige and power of the second estate.
first level title
Combination of decentralized tools and existing businesses: mesoeconomic realization
The focus is on developing modules that support any third party to perform a given production process. The combination of decentralized tools and existing businesses requires the design of the following modules:
A socially restorable reputation system for onboarding and offboarding workplace operators, long-haul trucking companies, vehicle ownership, and land ownership in logistics networks. Gitcoin Passport can be recursive, public VC, EIP-4337 and Gnosis Safe wallets can be socially recoverable (and recursive). Protocols like UniRep and Sismo are potentially anonymous methods for maintaining reputation without unnecessary intrusive forms of social credit. TaterDAO, a sub-DAO of LexDAO, may be a suitable intermediate owner of real-world assets. Perhaps the DAOs delegation in the voting system would also lead to reputable trustees acting as proper operators of real-world ownership and feedback. It is important to note that markets such as real estate brokerage fail without domain-specific expertise in pricing the market.
A general-purpose tamper-resistant, fully fail-safe physical security architecture. So far, Ive seen physical primitives for coins and cash. I also saw a proof of concept using the EIP-712 for physical gating.
Thats a promising start, but lets consider a real demand use case: a locker center for temporary storage. This is desperately needed in lower security areas like homeless shelters, as well as higher security areas like workplace equipment storage. This becomes even more salient as real-world places of employment become more seamlessly licensed. A central precursor to unlicensed contributions is the inherent reduction in regulatory costs for companies. However, physical security requires a minimum level of oversight as a failsafe for physical failure. Ultimately, this means that the reputation system needs to temporarily allow guardians to bypass some security, and it also means that lockers need to record varying degrees of acceptable access. Among other use cases, borrowing equipment such as rental vehicles requires recording various forms of usage metadata. This also raises the question of how much finality and supervision is needed (IMHO there are no easy answers).
For last-mile businesses like Uber, Amazon, and Sysco deliveries (among many others), there needs to be a separate, compartmentalized database of critical information. In the case of Uber, reputable users will still need to hide their destination and other personal details or risk being denied service. Additionally, both drivers and users need to rely on censorship-resistant mapping and tracking within their respective mobile apps. Nominal deliveries of goods, even on the last mile, can be very valuable goods. There needs to be a layer of privacy even between the delivery people and their goods.
All companies need a social negotiation resource that is some maximized combination of neutrality and nuance. One could argue that many public infrastructure projects have stalled in part because the manner in which they are executed is a bone of contention between several self-interested factions: corporations, labor and land ownership. Again, this would likely require extensive development of an anonymous reputation system, as neutral negotiations would require some checks for retaliation and subversion. Neither the second nor the fourth political class is a sufficient source of arbitration.
Refactoring and disruption: One aspect of NFTs is their potential for many object-oriented paradigms beyond p2p collectibles; in the same vein, DAOs have the potential to operate autonomously outside corporate law. While most DAOs are presented as limited liability DAOs, there are also suprajudicial DAOs that require the separation of individual operations into subordinate limited liability companies.
Firms also depend on infrastructure continuity, but SMEs and consumers are taxed more than necessary because secondary fiscal policy is less optimal than necessary. One of the main network states is a global DAO that strictly maintains public goods (such as infrastructure), and many companies around the world will internalize membership costs as well as lobbying costs for global tax cuts. This also affects the regulatory costs of maintaining the continuity of globalization. Also, this could be an entirely new monetary policy similar to seigniorage, rather than an explicit itemized cost.
Intermediation is a delicate, fundamental function of modern economics, but it is notoriously not a perfect function in a society of checks and balances. The best form of intermediary would be an open source standard for many companies to implement themselves. The main hurdle for 2023 and beyond is implementing a more efficient DAO to internalize the nature of the firm and divide costs appropriately in an already decentralized autonomous market.










