详解Uniswap v4「截断式预言机」:概念、运行机制和作用
原文标题:《Uniswap v4 Truncated Oracle Hook》
原文编译:Frank,Foresight News
Uniswap 协议是数百万交易者的重要加密基础设施,并通过提供深度流动性来支持超过 1.6 万亿美元的交易量,而 Uniswap v4 是该协议的最新演进版本,允许开发人员使用钩子(Hooks)在 Uniswap 之上构建自定义 AMM 功能。
之前我们写过关于时间加权平均做市商钩子的文章,今天我们将重点介绍「截断式预言机」(truncated oracle)。
众所周知,价格预言机(如 Uniswap v3 池中的预言机)可向其他 DeFi 协议传递有关流动性池的价格信息,而作为可选的 v4 钩子部署的截断式价格预言机,则可以降低大额交易对价格产生的影响,并使其更具预言机抗操纵能力,从而更安全地用于 DeFi 场景。
价格预言机的角色
价格预言机是一种用于查看特定资产价格信息的工具。这些链上预言机是反映链上数据的去信任的价格源。Uniswap v3 价格预言机允许智能合约集成和使用链上定价数据,以跨 DeFi 创建更多可组合的应用程序。
Uniswap v3 价格预言机在构建时考虑了以太坊的工作量证明(PoW)机制,但在以太坊的共识算法转为权益证明(PoS)后,该预言机的一些关键假设发生了改变,从而使其安全性降低。
尽管在 Uniswap v3 上操纵高流动性池的价格成本太高,但价格预言机的重要性,也使其成为恶意行为者的攻击目标,攻击者有足够的经济动机来操纵价格预言机。
所以我们需要修改预言机以使其更具韧性,而截断式价格预言机使用不同的公式来计算价格,并可以提供更可靠且不易被操纵的喂价。
什么是截断式预言机的 Hook?
截断式预言机是一种链上价格预言机,它使用几何平均公式记录 Uniswap 流动性池中资产的价格,然后对该预言机的喂价进行截断——这意味着在单个区块内,记录的价格只能向上或向下移动到最大值。
这种截断有助于消除大额交易对价格的长期影响——无论这些大额交易是合法的还是恶意的,因为如果一个恶意行为者试图操纵价格,则必须在多个区块上持续进行操纵,这使得截断式预言机的操纵成本变得很高。
截断式预言机 Hook 如何运行?
该 Hook 的智能合约合约存储了对应流动性池的价格的副本,其中在 Uniswap v3 和 v4 中,这些价格以一个个点位(Tick)表示。
在进行交易或 LP 调整之前,Hook 会将流动性池的当前价格变动与其合约中存储的价格变动进行比较,如果这两个数字之间的差异小于某个数字单位(根据我们的研究,我们使用 9, 116),那么 Hook 将更新到这个新的价格点位。
但是,如果流动性池的当前价格变动超过 9116 个数字单位,则预言机会将其价格上限限制为 +- 9116 ,从而在一个区块中限制流动性池的价格点位移动量。
Hook 更新后,交易或 LP 调整才会执行,直到对应区块结束,然后循环重复下一个触发 Hook 智能合约的区块。
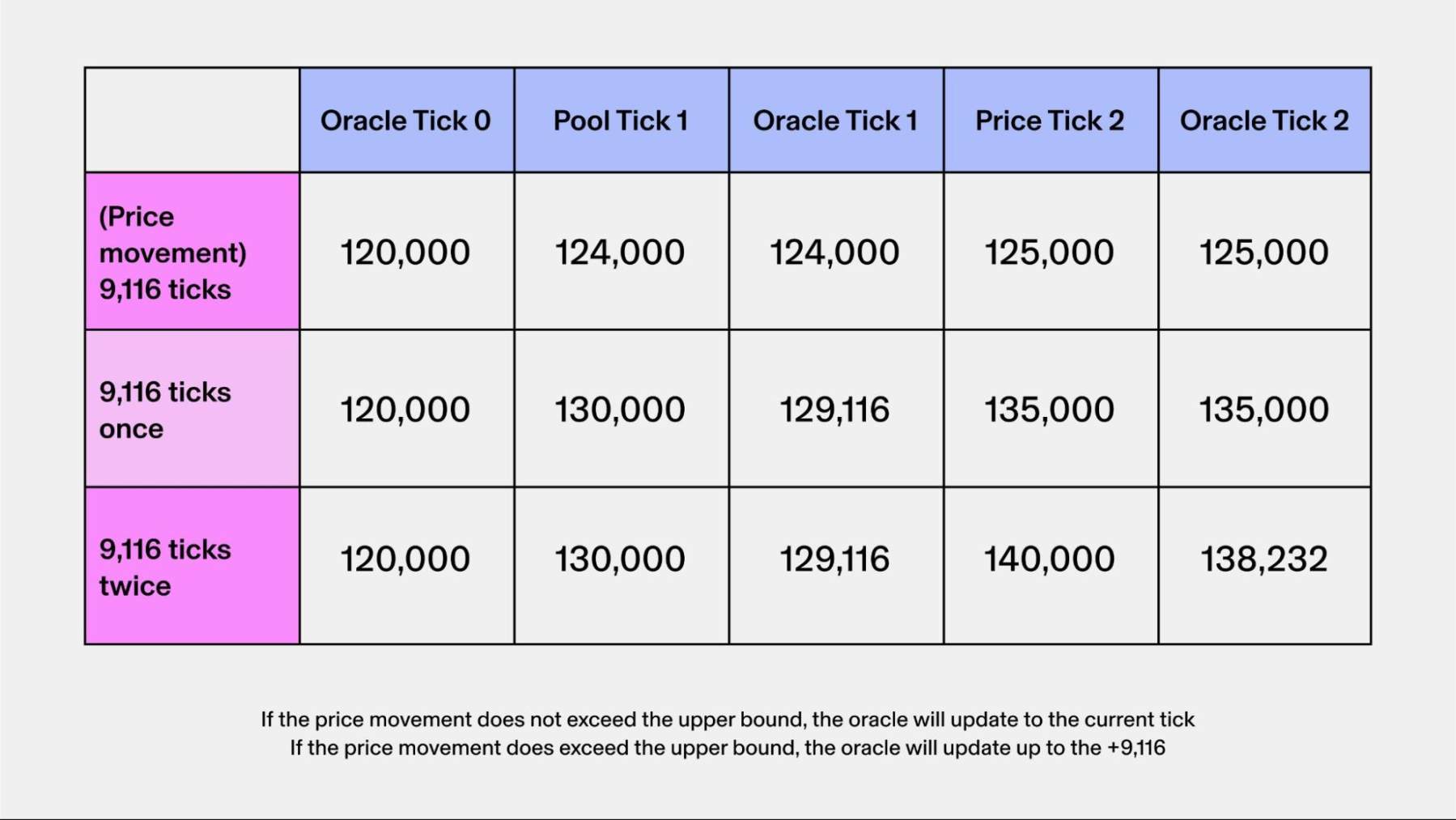
通过截断可记录的价格(点位)剧烈波动的程度,该预言机可以忽略异常值并消除大额交易对价格的影响。如果价格持续大幅波动,那么预言机也将会迅速适应流动性池的价格点位。
截断预言机更加安全
让我们以借贷市场为例,来更好地理解截断式预言。DeFi 借贷市场允许用户存入资产作为抵押品,以便借出其他资产,且最高可借出抵押品价值的一部分资产数额。
例如,如果借贷市场的抵押率为 1.5 ,那么 Alice 需要提供至少 1500 美元的抵押品才能借出 1000 USDC,也即如果 ETH 为 1000 美元,那么 Alice 需要存入至少 1.5 枚 ETH。
且在借贷过程中,Alice 需要保持至少 1.5 的比率,这意味着如果她的 1.5 枚 ETH 的价格下跌,那么任何人都可以偿还她的坏账并获得这 1.5 枚 ETH 的抵押品。
而借贷市场使用价格预言机来比较 ETH 和 USDC 的价格。虽然目前在 Uniswap v3 上操纵 ETH/USDC 流动性池在经济上是不切实际的,但恶意行为者 Bob 可以通过执行大额交易并压低 ETH 的价格来影响较小规模的 DEX。
这使得 Bob 可以操纵借贷市场,使 Alice 的头寸需要清算,然后 Bob 可以以不到 1500 美元的价格还清 Alice 的贷款,并拿走她的 1.5 枚 ETH。
这种类型的操纵是依赖于价格预言机的 DeFi 协议被操纵造成损失的最常见方式之一,借贷协议只是一个例子,其他 DeFi 原语(例如永续合约)也依赖于链上价格预言机。
如果 Alice 所在的 DeFi 借贷市场使用截断式价格预言机,那么 Bob 将不得不持续一段时间进行市场操纵。譬如在这个例子中,Bob 必须等待 15 个区块才能让预言机的价格实现他想要的波动,然后他才能尝试清算 Alice 的头寸。
但在这五分钟内,套利机器人可能会吃掉 Bob 的对应交易,让他一无所获,对于 Bob 来说,这个成本太高了。
目前 Uniswap v4 和截断式预言机 Hook 仍在开发中,最终规格可能会有所变化。



