LD Capital:LayerZero跨链创新的未来之路与明星项目
原文作者:Jill,LD Capital

一、什么是跨链互操作性
区块链目前的发展趋势是多链并行,但是区块链本身不具备与外部系统或 API 通信的能力,数据和价值不能跨网络进行无障碍传输,所以造成了生态系统的孤立的,彼此无法交换信息。
从开发者的角度看,每一个部署构成了一个孤立的独立实体,导致后端合约彼此之间没有联系,也不知道彼此的存在。例如,去中心化交易平台(DEX) DApp 可能分别需要在以太坊、BNB Chain 和 Polygon 网络上部署,这样每个版本的 DApp 都是彼此独立的。
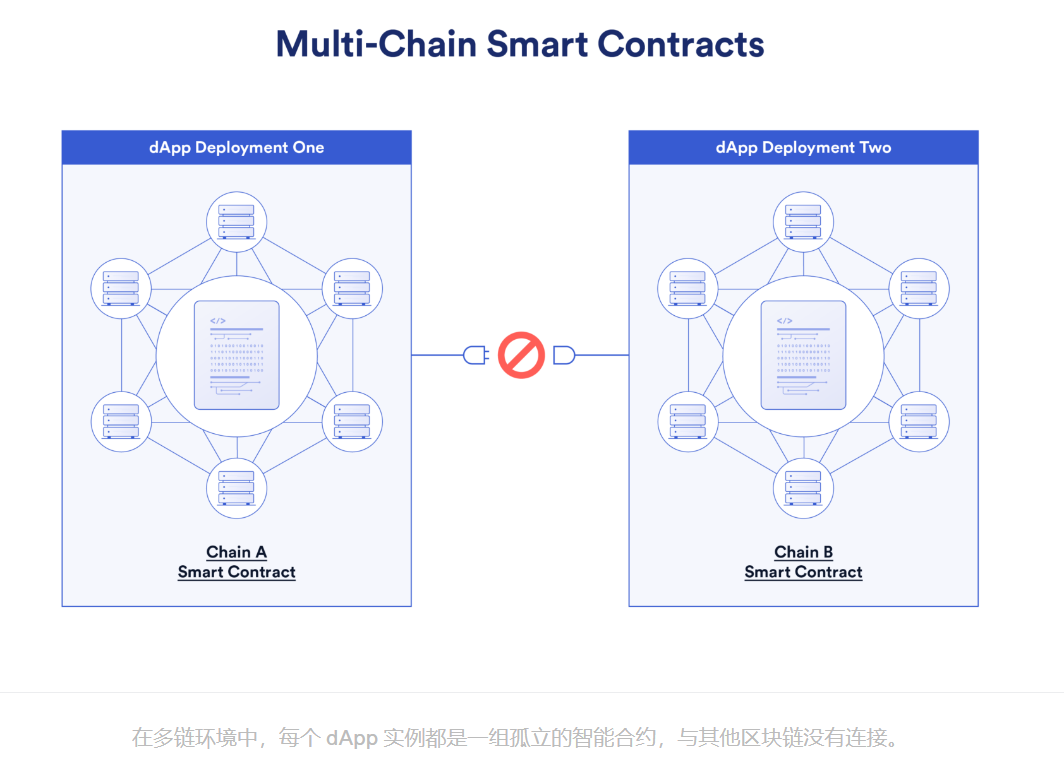
来源:Chainlink
对于用户来说,这种多重部署方式也增加了其采用的困难性:
1)用户无法将代币从一个区块链无缝转账到另一个区块链。
2)转账过程耗时且体验欠佳,因为资产通常是在源区块链上被销毁,然后使用第三方桥接在目标区块链上重新铸造。
3)在多个区块链上持有资产的安全风险也很高,容易被黑客攻击,导致资金丢失。
由于区块链生态系统繁多,这些不同的链上环境能够相互操作和通信至关重要。不同区块链之间,交换数据和资产的基础设施关键部分就是跨链互操作性协议。跨链互操作性使开发人员能够构建一个统一的跨链应用程序,即同个 dApp 可以部署在多个不同区块链上,而不必在不同的链上部署多个独立的版本,释放更高的资本效率和更好的流动性条件。
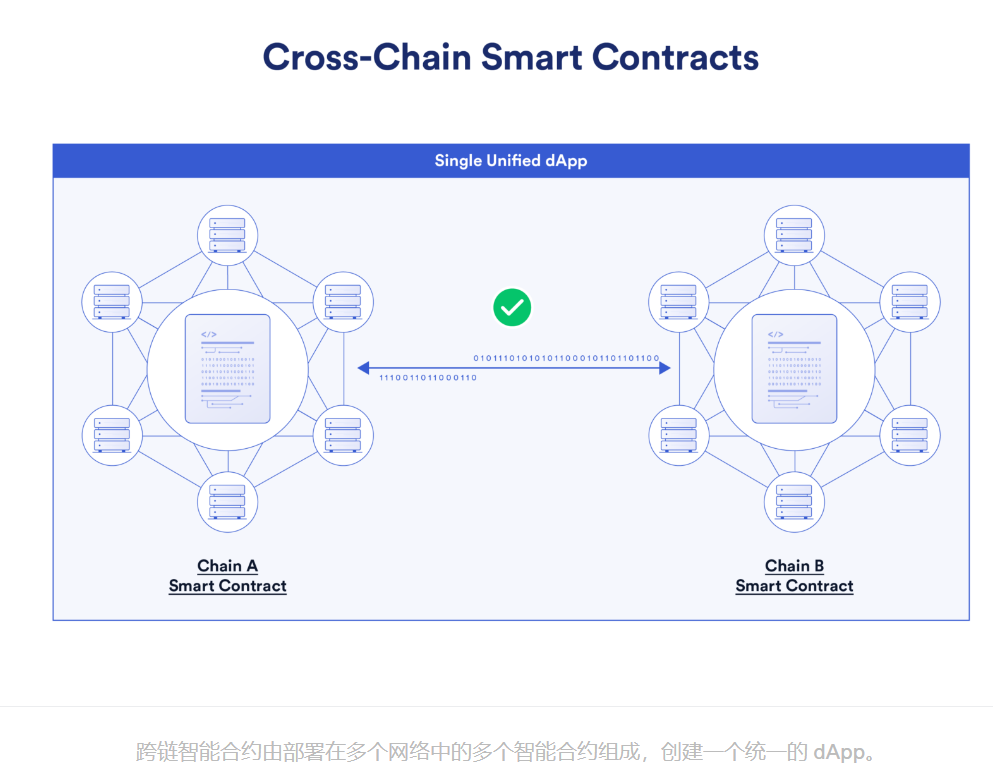
二、跨链解决方案
跨链解决方案通常涉及验证源区块链的状态并将后续交易中继到目标区块链,其基础设施的一个关键部分是跨链桥,它使资产能够从源区块链转移到目标区块链。跨链桥通常涉及通过智能合约在源链上锁定或销毁资产,并通过目标链上的另一个智能合约解锁或铸造它们。实际上,跨链桥的用例非常狭窄,其承担的角色就是在不同区块链之间传输资产。因此,跨链桥通常是两个区块链之间的特定于某个应用程序的服务。
目前开发人员构建了多种跨链解决方案,例如:
Chainlink 正在开发跨链互操作性协议(CCIP),这是一种支持跨链通信(包括发送信息和代币转账)的开源标准。CCIP 的目标是使用标准化接口在数百个区块链网络之间实现通用连接,有希望降低构建跨链应用程序和服务的复杂性。
Wormhole 协议是一种通用互操作性协议,该协议能实现代币和消息在不同区块链网络上进行传输。网络监护人监测源链上的信息,并对其进行验证,促进其向目标链的传输。使用 Wormhole 的开发人员可以构建称为 XDApp 的跨链去中心化应用程序。
跨链信息传输协议(IBC)是 Cosmos 网络中的区块链交互的标准协议,旨在实现不同区块链之间的互操作性。IBC 定义了跨链标准(ICS)中指定的一组最小函数,这些函数定义了区块链之间如何相互通信和交换数据。
LayerZero 是一种全链互操作性协议,用于区块链之间的轻量级信息传递,提供安全可靠、去信任化的信息传递。
本文主要是介绍全链互操作性协议 LayerZero,它只专注于链与链之间的信息传递,能够向支持的任何链上的任何智能合约发送消息,也就是负责区块链之间的智能合约通信,其不负责资产的跨链,资产跨链由 LayerZero Labs 开发的 Stargate 完成。
三、LayerZero 技术特点与优势
1. 技术特点
LayerZero 最突出的特点是其超轻量级的节点,利用超轻节点技术,通过中继者和预言机在不同链的端点之间传输消息,在保证安全性的前提下降低费用。
1)超轻节点
首先,区块链网络中的每一个节点,其实就是存储数据的每一台电脑或者服务器终端,轻节点只是节点的一种运作模式,和全节点不同的是,轻节点只存储区块链数据的一小部分,如区块头和其他一些信息,不存储区块内的具体交易信息。超轻节点与轻节点相比,它们的验证方式相同,但因区块链写入成本很高,持续的传输区块头很昂贵,因此超轻节点不会保留所有区块头,而是通过预言机按需流式传输这些区块头,从而更高效的同步链外实体以达到所需状态,改变了原来的连续流式传输方式。
这样做的好处便是,不依赖轻节点从头开始的区块头数据流,但缺点就是缺乏历史顺序数据流,那一旦预言机和中继者同时作恶即可通过验证,那么就会导致恶意的信息被执行。所以,LayerZero 在极大程度的验证成本降低和一定程度的安全性损失之间做出了取舍,而这种取舍是否值得,可能就要看其基于自身场景如何权衡。
2)核心组件
在 LayerZero 官方白皮书中可以看到,承担两条链之间信息传递的核心组件分别为端点(Endpoint)、预言机(Oracle)和中继器(Relayer)。
端点是和用户或者应用直接交互的设施,负责处理消息传输、验证和接收,他们的目的是在用户使用协议发送消息时保证有效传递。在 LayerZero 协议中,每个链都需要部署端点,这些端点也可以被其它同链的 App 调用,负责发送信息给外链。
预言机是第三方服务,提供一种独立于其他 LayerZero 的机制组件,能从一个链中读取一个块头和将其发送到另一个链上,这样能在目标链上验证源链上交易的有效性。LayerZero 目前采用 Chainlink 充当其预言机。
中继器是一种链下服务,在功能上类似于预言机,但它不是获取区块头,而是获取指定交易的证明。为了确保有效地传递,唯一的要求是对于使用 LayerZero 协议发送的任何给定消息,预言机和中继器必须相互独立。任何主体都可以承担预言机和中继器的角色,LayerZero 甚至可以实现自己的中继服务。
在 LayerZero 中一个重要的信任假设就是 — — 预言机和中继者彼此之间独立运行。预言机提交的区块头将与中继器提交的交易证明进行交叉验证,二者不形成任何共识,只传输消息。简单来说,预言机作为 LayerZero 跨链中的公证人角色,让目标链知道验证的结果如何,而中继器就负责提供验证交易所需的证明过程以及跨链信息的具体内容。为了确保信息的有效传递,一旦中继器或是预言机之间的信息传递出现任何争议,那么智能合约将会暂停且不会将信息提交给目标链。
参考《详解互操作协议 LayerZero 技术与特性》
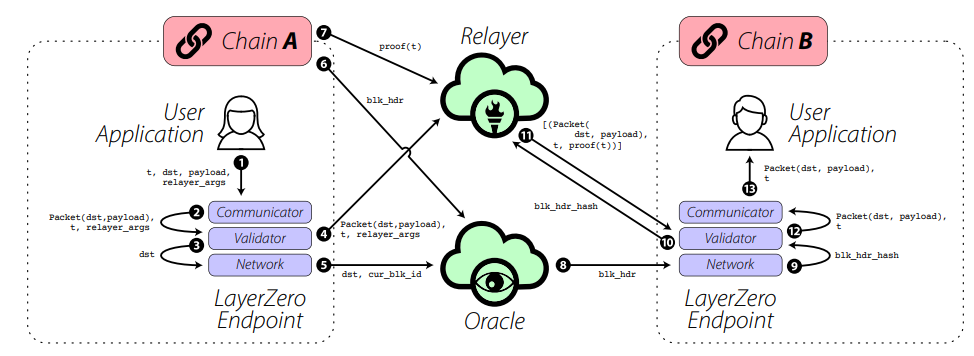
如果从 A 链跨一笔交易到 B 链,那么整体流程大概如下:
这笔交易会从用户启动应用程序开始,然后通过预言机和中继器在 LayerZero 端点的协助下,将这笔交易分解成多个部分(证明和区块头)。一旦预言机和中继器在目标链上发送各自的信息(签署交易上链),并且 LayerZero Endpoint(合约)验证了信息的正确性,消息就会被转化并在目标链上执行。
2. 优势
1)安全性
作为底层协议,LayerZero 的安全性是独立于外部协议的,从而确保了整个协议共识的稳定性。另外,得益于独特的预言机和中继器设计,二者相互独立,只有都被认为是真实的情况下才会完成交易,保障了信息传输的安全性。
2)扩展性
LayerZero 作为一个通用的消息传递层,这意味着可以将任何合约从 A 链转移到 B 链实现与一层网络的跨链互操作。通过创新的端点设计,LayerZero 可以很轻松的进行扩展以支持任何链,为区块链生态系统带来了更广泛的应用场景。
3)高效率
首先,LayerZero 的超轻节点技术可以实现更高的传输效率,并在保证安全的前提下降低了验证成本;其次,LayerZero 的中继器或预言机都没有形成任何共识,只简单传输消息,所有的验证都在自己的目标链上完成,所以速度和吞吐量的限制完全取决于两个交易链的属性。
四、融资
LayerZero 总共进行过三轮融资,已披露的金额共计达到 2.93 亿美元,参投方包括 Multicoin、Binance Labs、a16z、红杉资本等知名加密投资机构。最新一轮融资在 2023 年 4 月 4 日,以 30 亿美元估值融资 1.2 亿。
FTX 曾作为领投方参与 2022 年 3 月 30 日的 A 轮融资,受其暴雷影响, 2022 年 11 月 11 日,LayerZero 官方发文表示,已从 FTX 手上回购 100% 的股权、币权及其它协议。
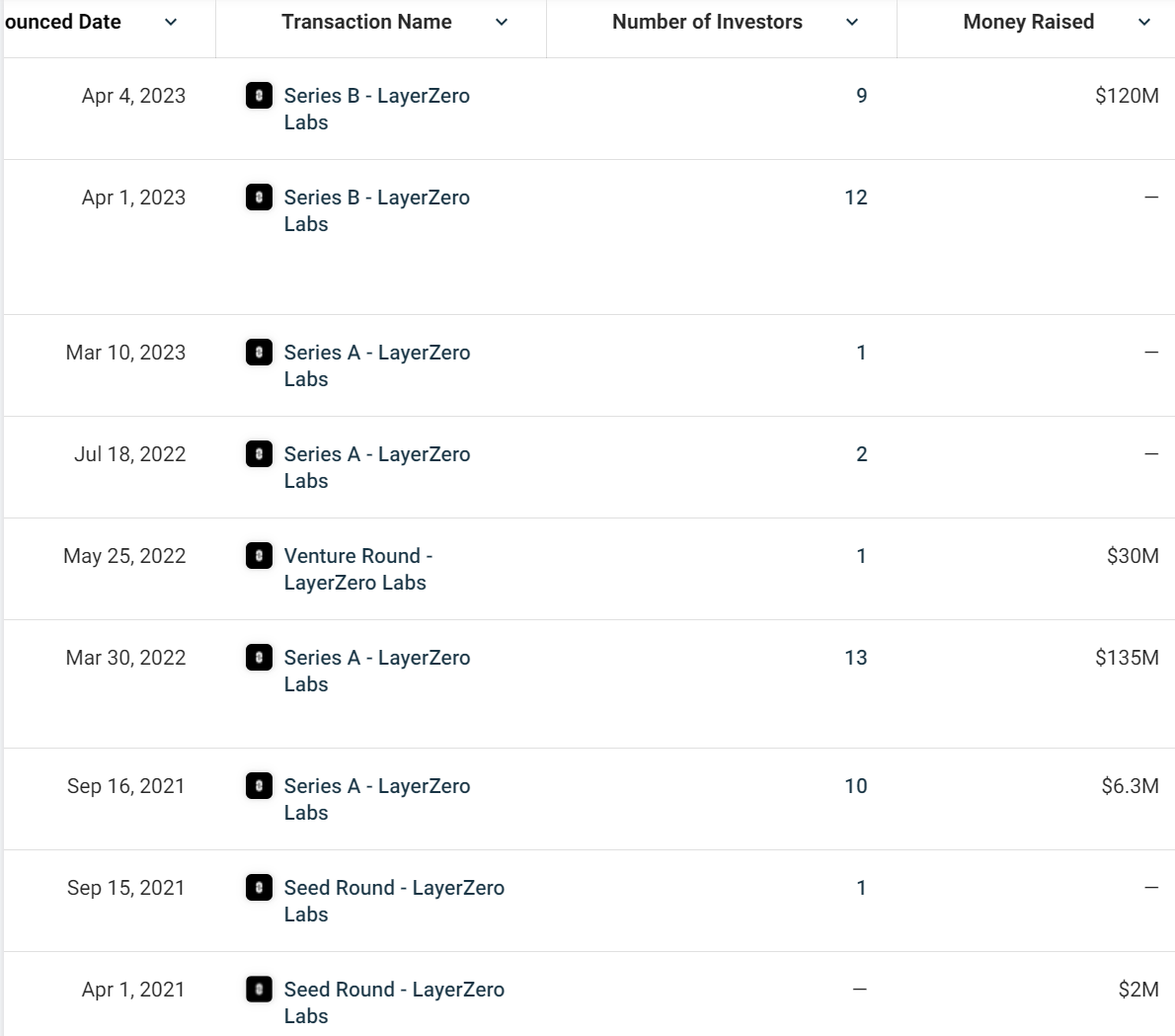
来源:Crunchbase
五、生态
截止目前 LayerZero 已经支持了 Ethereum、BNB Chain、Aavalanche、Polygon、Base 等在内的共计 20 多条链。独立用户数达到 300 万名,累积交易笔数达到 5, 600 万笔,但是 35% 的用户只有 1 笔交互记录,超过 2 笔交互记录的用户只有 73 万左右。
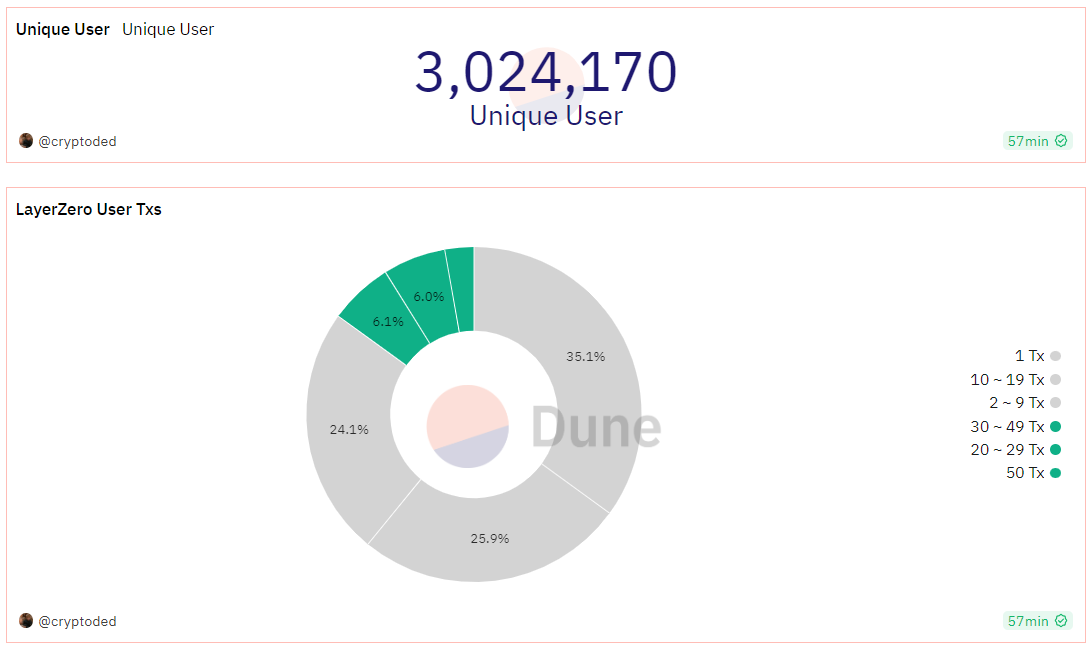
来源:Dune Analytics
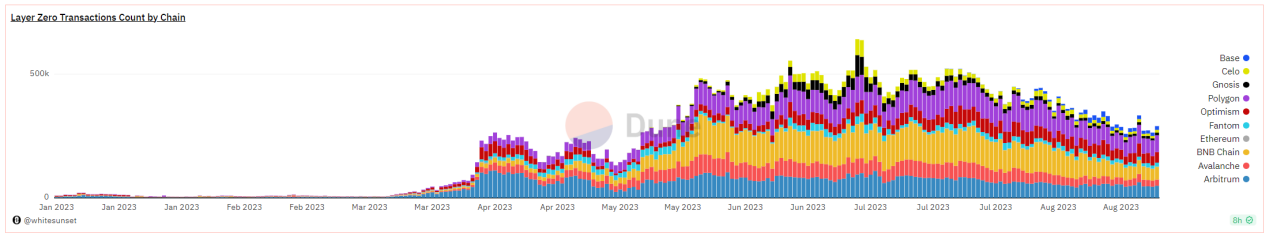
用户交互活动主要发生在 BNB Chain、Arbitrum 和 Polygon,尤其自 Arbitrum 发币之后,社区撸空投情绪浓厚,空投预期也带动 LayerZero 上的用户活跃度大幅提高。
以 Arbitrum 交互数据为例,交易笔数达到 1, 200 万左右, 2023 年 4 月份是用户活动高峰期,随着大盘行情的冷淡,用户活跃度也略有下降。
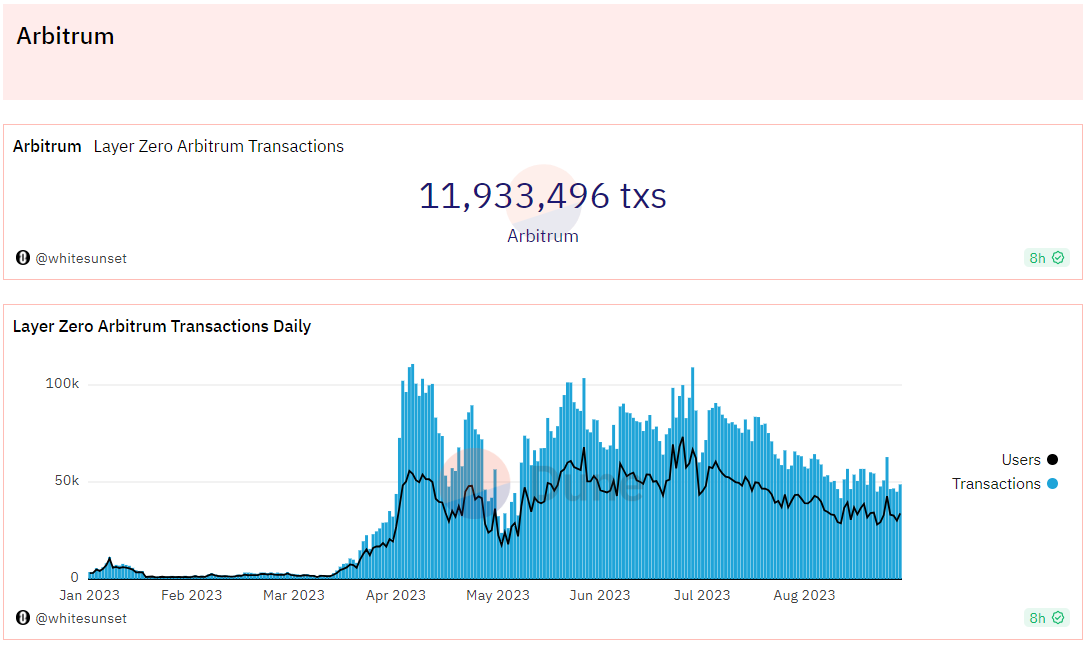
来源:Dune Analytics
LayerZero 的极简架构赋予了该协议无限的可能性,其较低的开发者接入复杂度使得 LayerZero 目前集成或正在使用其技术的 dApp 超过 50+。
来源:Twitter
明星项目
1. Stargate Finance
由 LayerZero Labs 开发的首个基于 LayerZero 协议的 dApp,其构建了第一个完全可组合性的原生资产桥,愿景是让跨链流动性转移成为一个无缝的、单一的过程,产品亮点为采用独特的“Delta 算法”解决跨链桥存在的“不可能三角”问题,而不必在其中做出取舍。
Stargate 团队认为跨链资产桥存在“不可能三角”:
1)即时验证确认:资产在交易确认时就可成功跨到目标链,时效性能够得到保证;
2)统一流动性:单个流动性池在多条链之间共享;
3)资产原生性:用户通过跨链桥直接获得原生资产,而非合成、封装资产。
当然,在保证即时验证确认和资产原生性的时候,如果不涉及更复杂的流动性动态分配算法,就只能在每两条链之间搭建一个流动性池,这样会使得资本效率降低。
依据 defillama 数据显示,从近一个月的交易量来看,Stargate 在一众跨链桥协议中位居榜首, 24 小时交易次数可达 9.6 万笔。
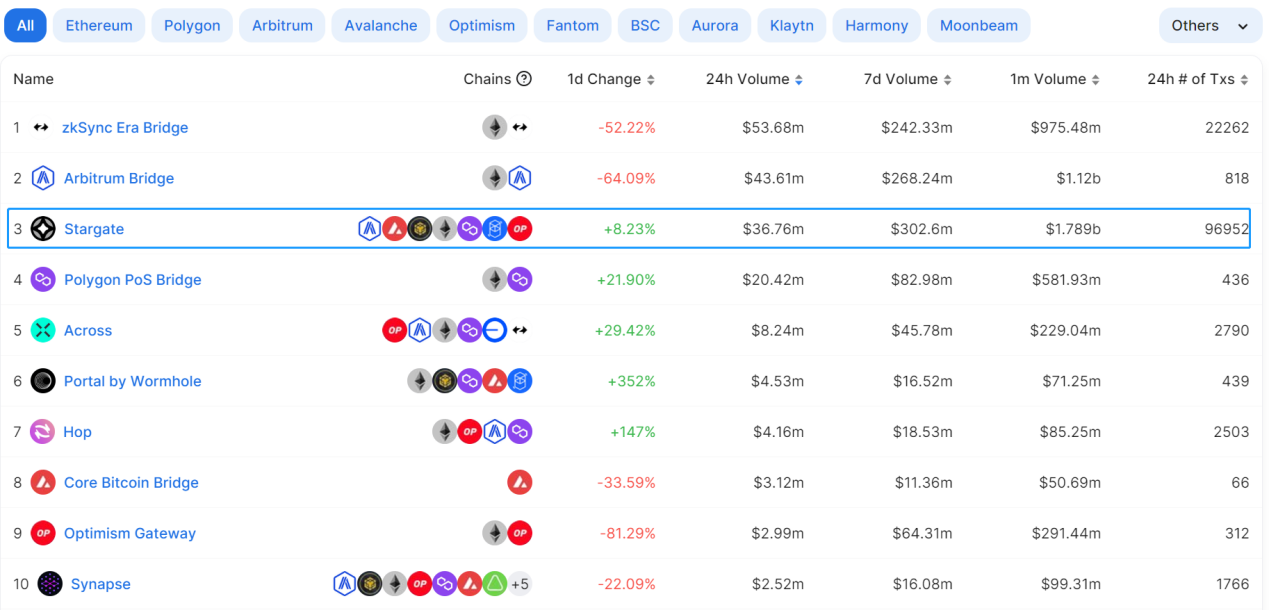
来源:defillama
协议营收
Stargate 是 LayerZero 上首个上线的 dApp,其协议费用和收入自 2023 年 3 月起开始稳步增长,也是这一时期开始因空投预期链上交易活跃度大幅增加。目前协议月度收入超过 100 万美元。
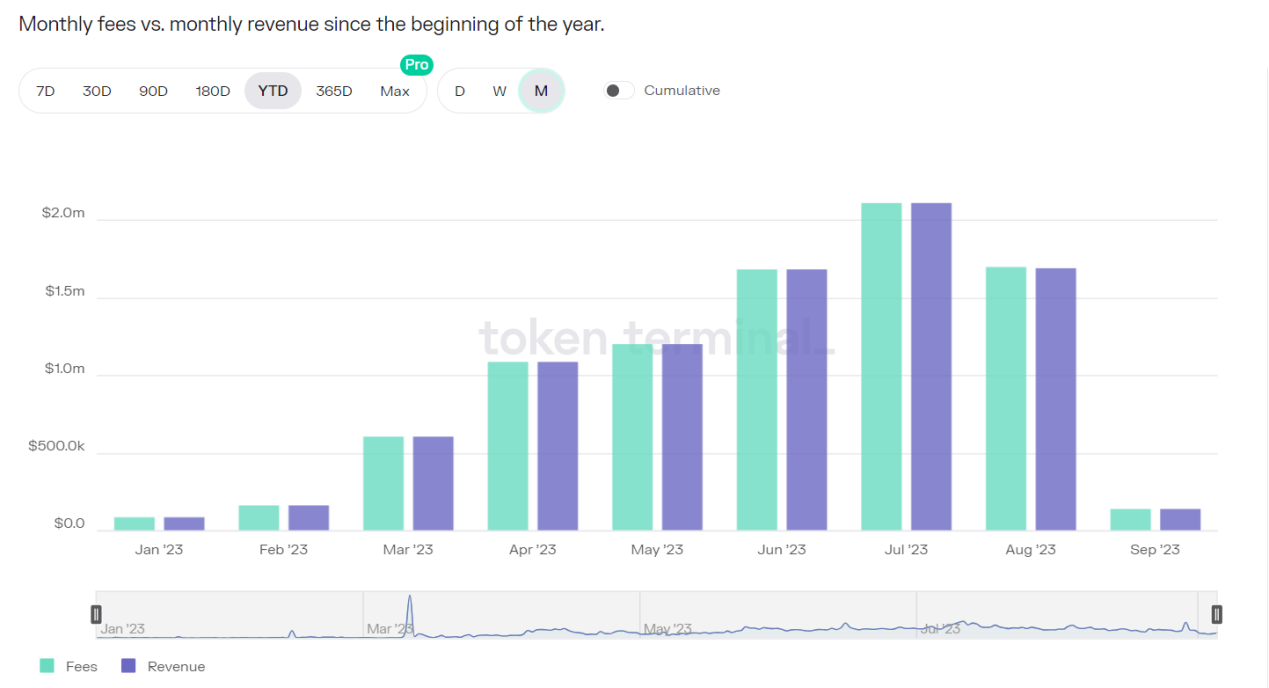
来源:Token Terminal
经济模型
STG 代币总量 10 亿,流通量达 2 亿,代币作用:
1)资产跨链转账手续费,非 STG 代币转账都将产生 0.06% 的手续费,其中 0.045% 将分配给流动性提供者, 0.015% 分配给协议的财库;
2)治理,通过质押并锁定 STG 代币 3 至 156 周可获得治理代币 veSTG,STG 锁定时间越长,投票权重越大;
3)协议奖励,稳定币流动性池和流动性挖矿奖励。
代币发行时间为 2022 年 3 月 17 日,初始分配详情如下:
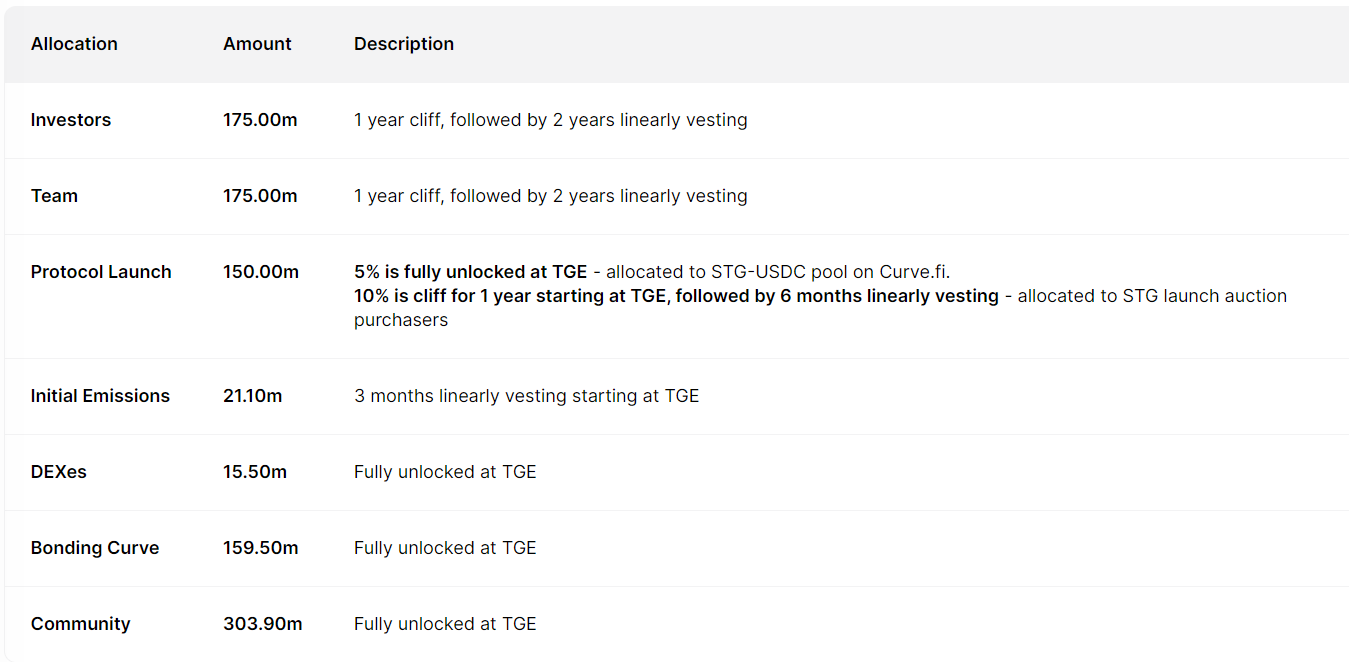
来源:tokenunlocks
分配给早期 DEX 流动性、Bonding Curve、初始释放计划以及社区的在代币初始发行时就直接解锁,共计 4.78 亿枚。
分配给协议启动的部分,其中 5% (5, 000 万枚)直接释放,剩余 10% 有 1 年锁定期,之后在 6 个月内线性释放,目前已释放 1.45 亿。
分配给投资人和团队的部分有 1 年锁定期, 2 年线性释放。
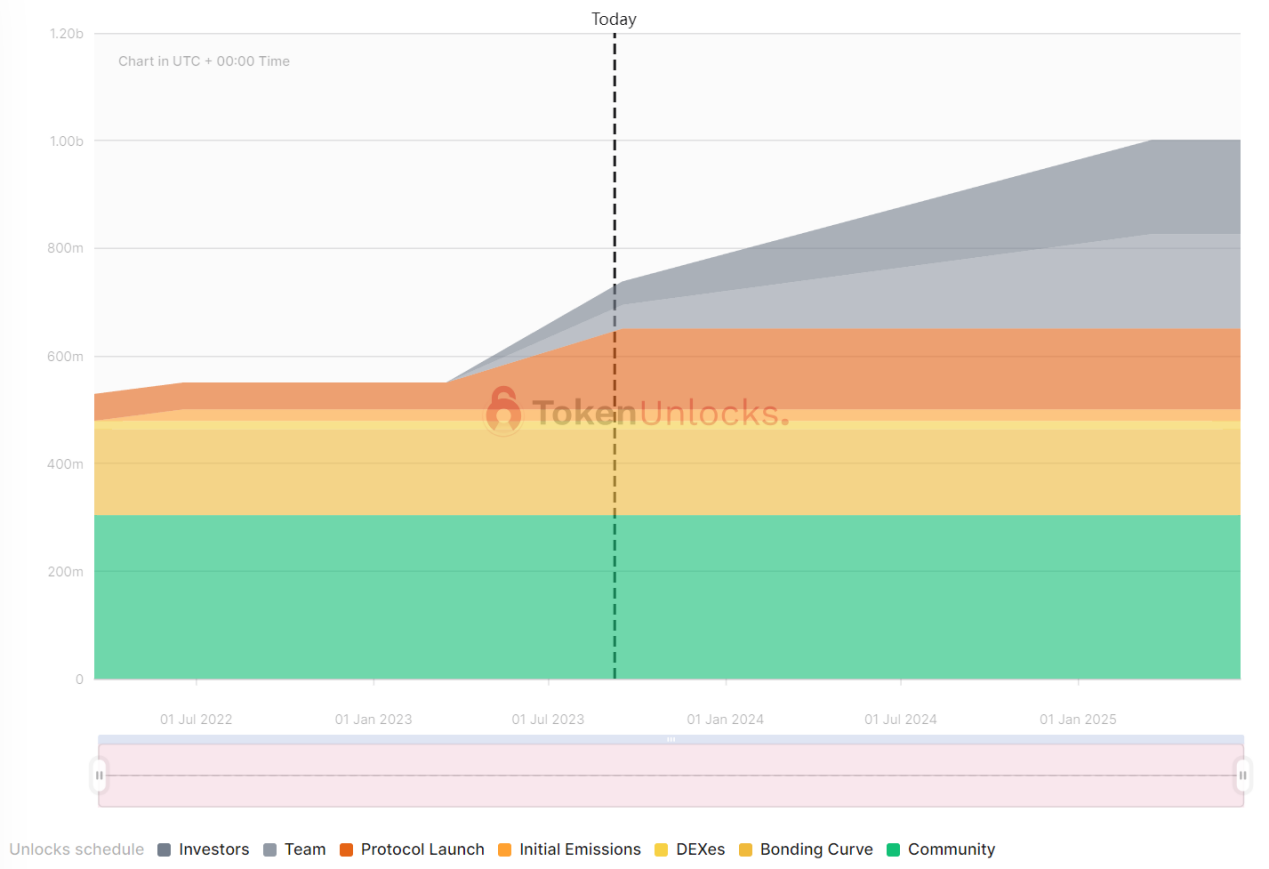
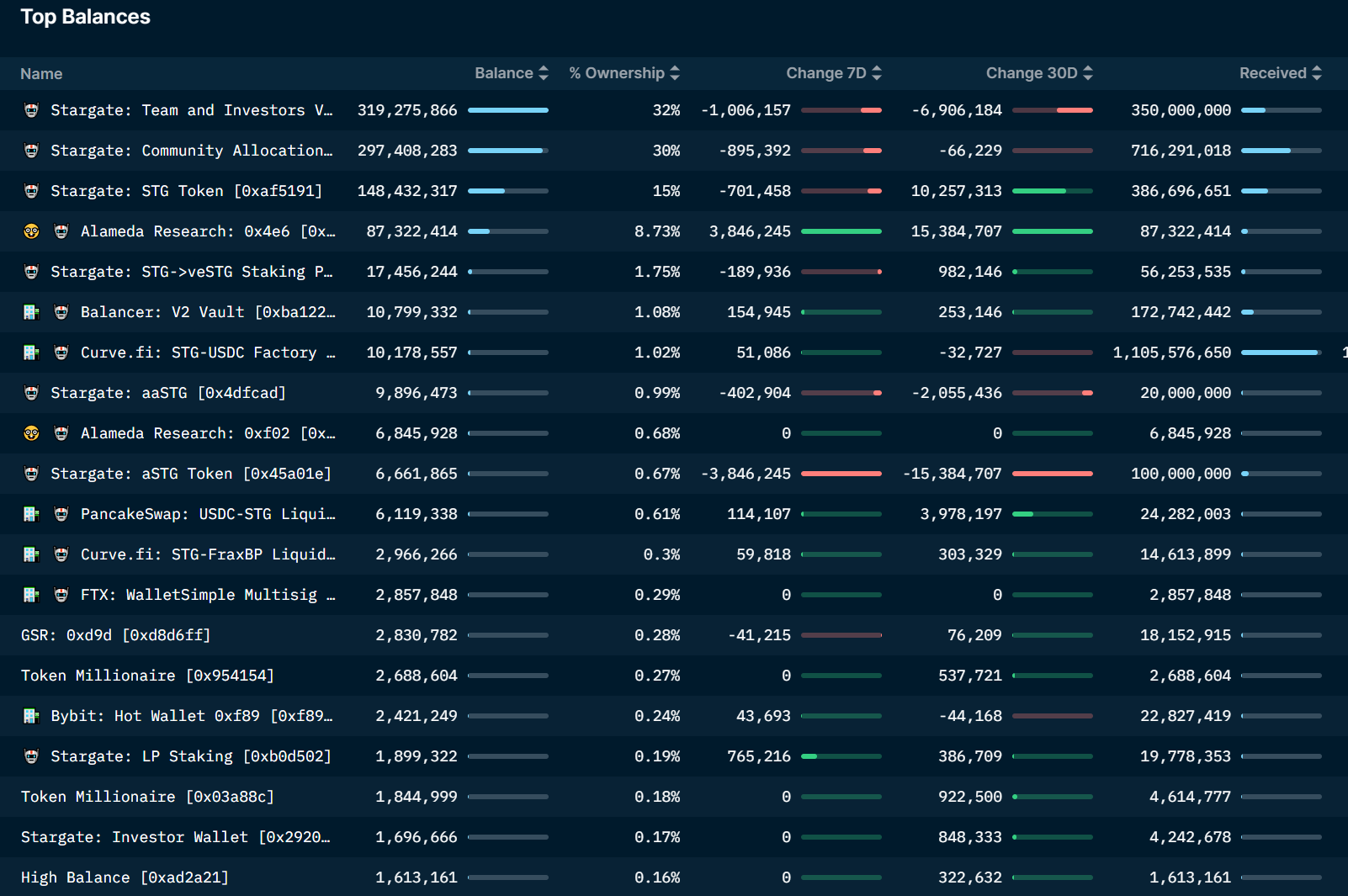
依据上述代币分配,STG 名义排放已达到 7.29 亿。根据 STG 持仓地址分布可以清晰地看到,分配给社区的 3.04 亿目前剩余 2.97 亿尚未流通,分配给投资人和团队的部分剩余 3.2 亿未流通,这两部分共计流通 6, 700 万枚左右,占比约 6.7% 。
从持仓地址分布来看,前 20 持仓占比达到 94% ,其中前两大地址均为官方所有,尚未进行流通,占比已达 62% ,剔除这两部分,剩余地址持仓占比达 32% ,其中 Alameda 持仓 9.42% ,个人大户地址持仓占比仅有 0.6% ,大户手里累积的筹码比较少。
Alameda 联席 CEO Sam Trabucco 曾在社交媒体发文表示,Alameda Research 参与了 3 月 18 日跨链桥项目 Stargate 的公开发行并购买了所有份额的 STG(1 亿枚,也就是上文提到的协议启动的 10% )。不过,Sam Trabucco 表示 Alameda 在 3 年内不会出售 STG,将对该项目和团队进行长期投资,同时不会干预项目的治理,将放弃其 aSTG 的投票权,以便投票权在早期社区成员之间更加平等地分配,目前已释放 9.42% 。
2. Radiant Capital
Radiant 是跨链 DeFi 借贷协议,通过使用 LayerZero 作为跨链基础设施,来实施全链杠杆借贷和可组合性,使用户可以在其支持的 DeFi 协议中获得杠杆,简化用户在不同链间的资产跨链借贷操作。
Radiant 本质上与当前的 Aave、Compound 等借贷协议运作机制相似,不同之处就在于其要做全链借贷协议,即用户可以在 A 链上存入抵押品,然后在 B 链上进行借贷。不过,当用户需要使用跨链借贷服务时,需要先在支持的链上存入一定的资产,成为动态流动性提供者(dLP),然后才能贷出目标链所需资产。
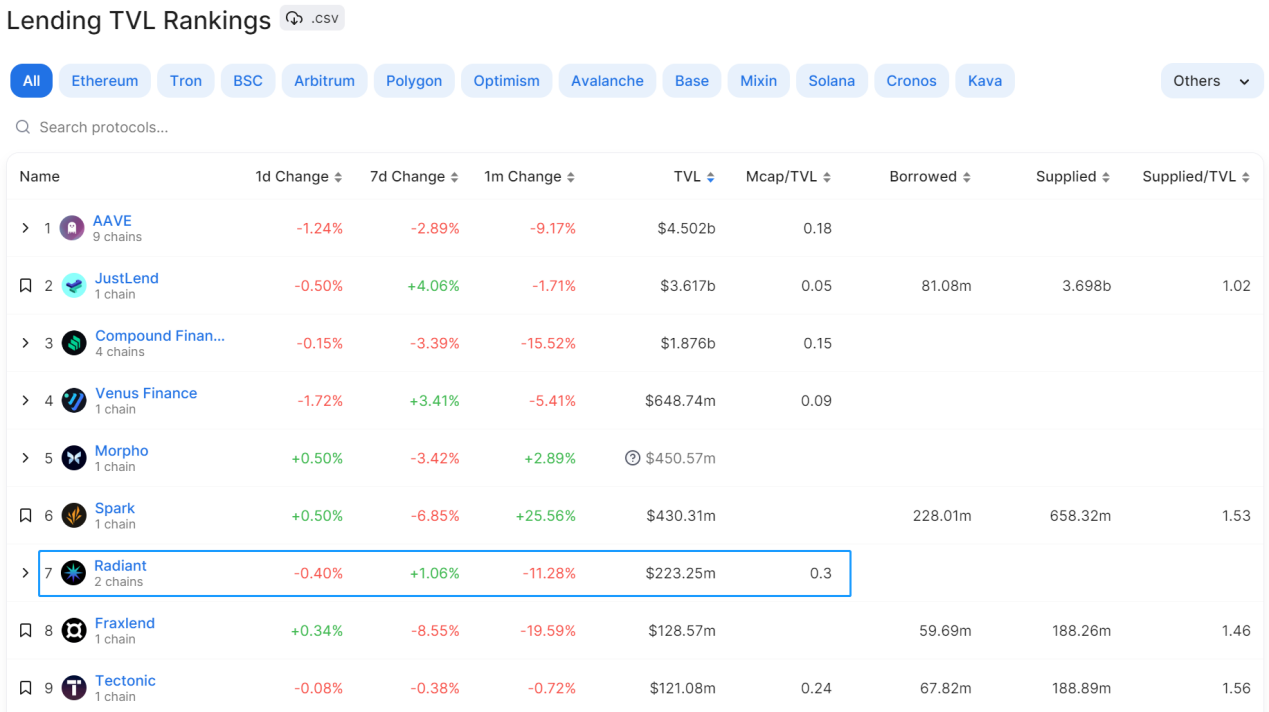
Radiant 目前已在 Arbitrum 和 BSC 链进行部署,TVL 规模达 2.2 亿美元,在一众借贷协议中排名较为靠前,目前已占得一定的市场份额,是 Arbitrum 上的借贷龙头。
协议营收
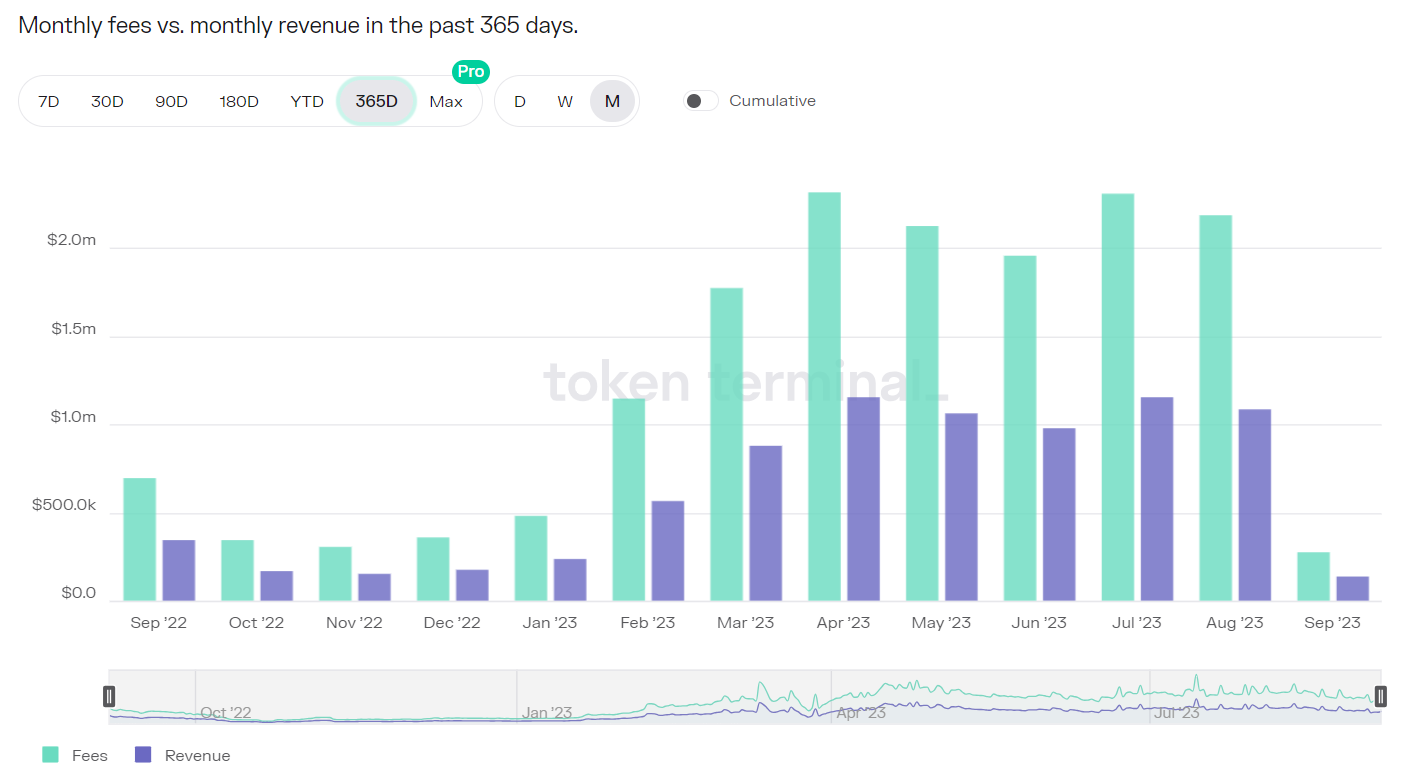
在 Radiant 中,协议收入(Revenue)=借款支付的费用(Fees)-存款利息(Supply-side fees)。自今年 2 月份起,协议获得的费用稳定在 200 万美金左右,协议月度收入达到 100 万美金左右。
经济模型
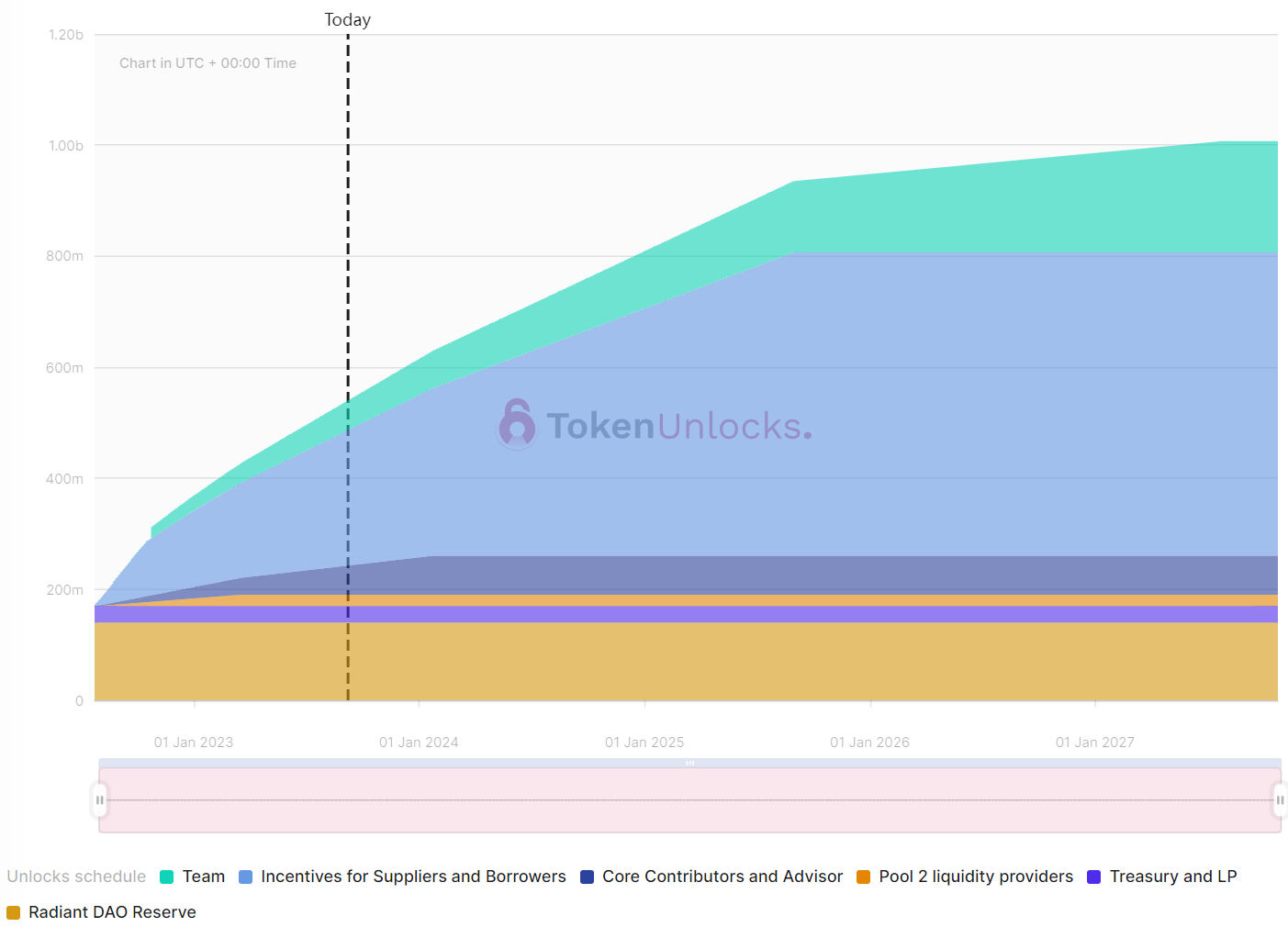
RDNT 代币总量 10 亿,流通量达 3 亿,其代币的主要作用就是治理和流动性激励。
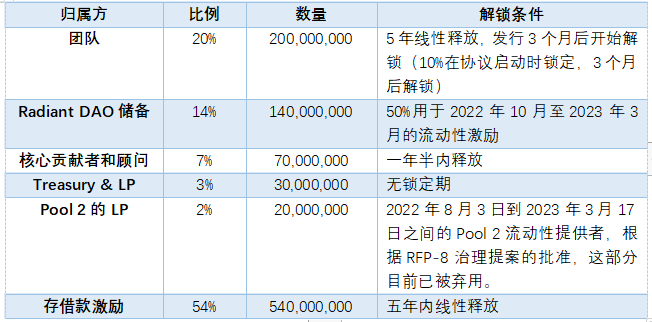
依据 Token Unlock 数据显示,分配给 2 池流动性提供者、Treasury 和 Radiant DAO 储备的部分已全部解锁。目前仍在解锁的就是团队、核心贡献者以及存借款人激励,其中分配给存借款人的部分每秒释放 4.85 RDNT。如果按照这个速率计算,每月释放接近 21 万枚。
从代币持仓分布来看,排名前 20 代币地址占比 92.3% ,其中排名第一的为官方合约地址,尚有 23.4% 未分发,分布在 DEX 中的代币占比 27.6% ,排名前 20 中大户地址持仓占比仅为 3.8% 。
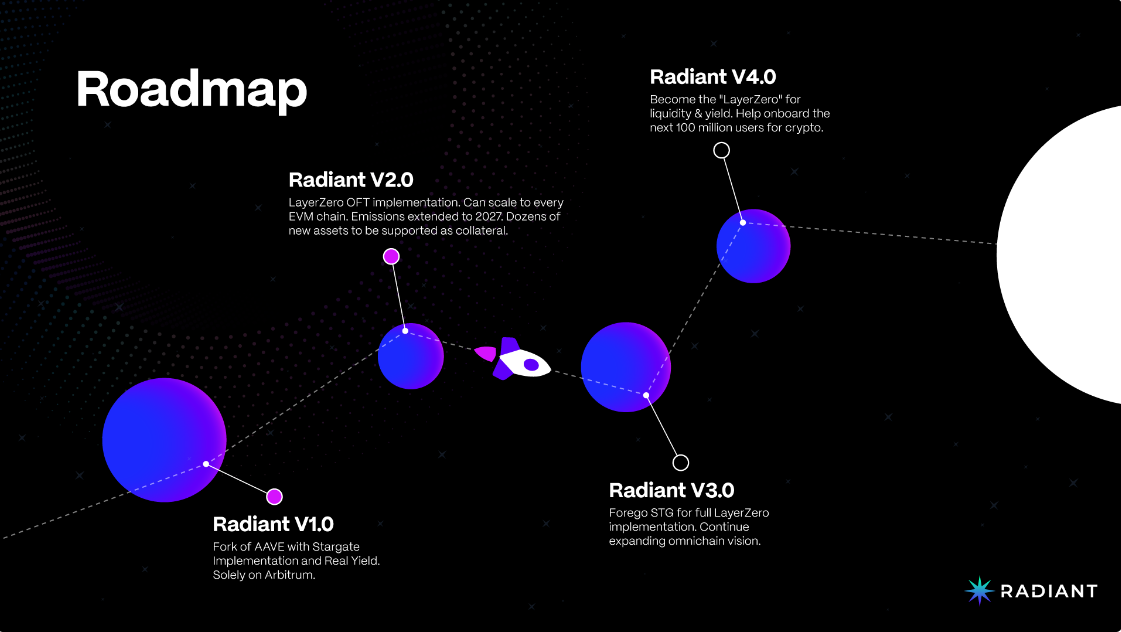
路线图
Radiant 官方团队在其文档中披露过简易的路线图,其版本目前处于 2.0 阶段,首要任务就是部署 Radiant 跨链以及增加应用内抵押品规模。在V3版本则计划摆脱对第三方跨链桥 Stargate 的依赖,完全集成 LayerZero,V4版本则计划完全实现全链流动性借贷。
总结
多链是区块链的发展趋势,跨链互操作协议是区块链间通信的关键组件,其发展前景相当广阔。LayerZero 目前还处于发展初期,可参与的原生项目还较少。其背后拥有众多知名投资机构的支持,行业资源丰富,发币预期吸引着全加密市场的目光。
参考资料
《详解互操作协议 LayerZero 技术与特性》



