Sui NFTs:带领DeFi走向大规模采用
原文作者:six0hfour,Typus 团队
原文编译:Kyrie
原文来源:Typus Finance

本研究旨在探讨 Sui 的基于物件(objects)的程式设计模型,以及它如何活用各式各样的 NFT 结构,借此对 DeFi 的大规模应用做出贡献。
我们之前撰写了一份报告,讲述为何我们认为若要定义和建立基于区块链的 DeFi 原生资产,Sui 会是最佳选择。 Sui 的基础设计捕捉了区块链上数位资产的本质,并使智能合约能够在其上运作,取代中间人的功能。
链上与链下的差异
在像 EVM 或 Solana 这样的区块链上,数位资产的状态(the state of digital assets),或说 NFT,是存储在链下的。对于静态(static)的 NFT,这是一种可接受的模型,因为这些 NFT 不会被进行转移或进行任何状态更改。
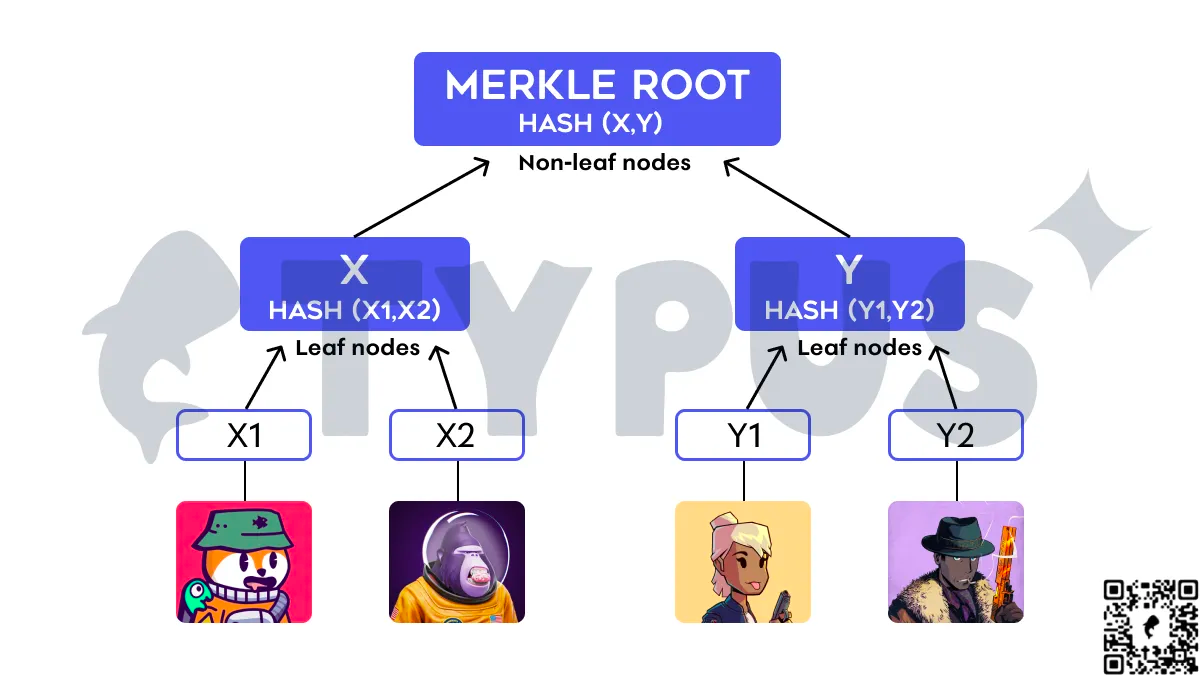
一个简单的类比是默克尔树,其中 NFT 是其叶子,而在区块链上发布的只是树的根。
如果使用者经常创建新的 NFT,且创建后也不太关注他们,这种模型是有效的;他们不需要对其进行任何修改或转移。然而,如果需要对其中一个 NFT 字段进行转移或更新,这将变得更加昂贵且需要更长的交易哈希。由于只有树的根被发布在区块链上,每次更新都需要一个默克尔证明。即使是读取 NFT 也需要一个默克尔证明。
最近由a16z crypto 发表的一篇论文《关于可撤销性证明系统的限制,对无状态区块链的影响》探讨了无状态区块链(stateless blockchain)的概念及其取舍。该概念源于对区块链范式的一个挑战,传统上每个验证者都需要存储整个系统的完整状态。这种要求引起了对中心化的担忧,因为随着状态变得越来越大,只有资金充足的组织才能负担得起存储费用。
这引出了无状态区块链设计的概念,该概念建议验证者仅存储系统的一小部分全局状态(例如,仅存储默克尔树的根)。需要发起交易的使用者必须发布证明,证明他们的交易是有效的(例如,指向叶子的默克尔证明路径)。
该论文发现了一个问题:「…当其他(无关的)交易更新全局状态时,使用者必须监控网络并定期更新他们的证明,这可能让使用者的证明变得无效。」不幸的是,这引入了新的安全威胁,因为链下状态管理变得相当繁琐。
当元数据(metadata)存在于链下时,智能合约的调用将会受限。这不仅无法提高产品效率,也无法提高分发效率。从根本上讲,它未能实现去中心化基础设施的目的。
Sui 允许我们将 NFT 的元数据完全存储在链上,其中最值得注意的特点就是能够在链上存储大量的任意数据。在我们之前的报告中,我们给出了关于传统存储成本运作方式的类比。
来用一个简单的例子说明传统存储成本运作的问题:
Alice 从 Sui Network 上线初期开始使用,当时在链上还没有存储太多的数据,她享受着较低的气费(gas fee)。
而 Bob 在 Sui Network 成熟后开始使用,因为那时在链上已经存储了大量的数据,导致 Bob 得支付较高的气费。
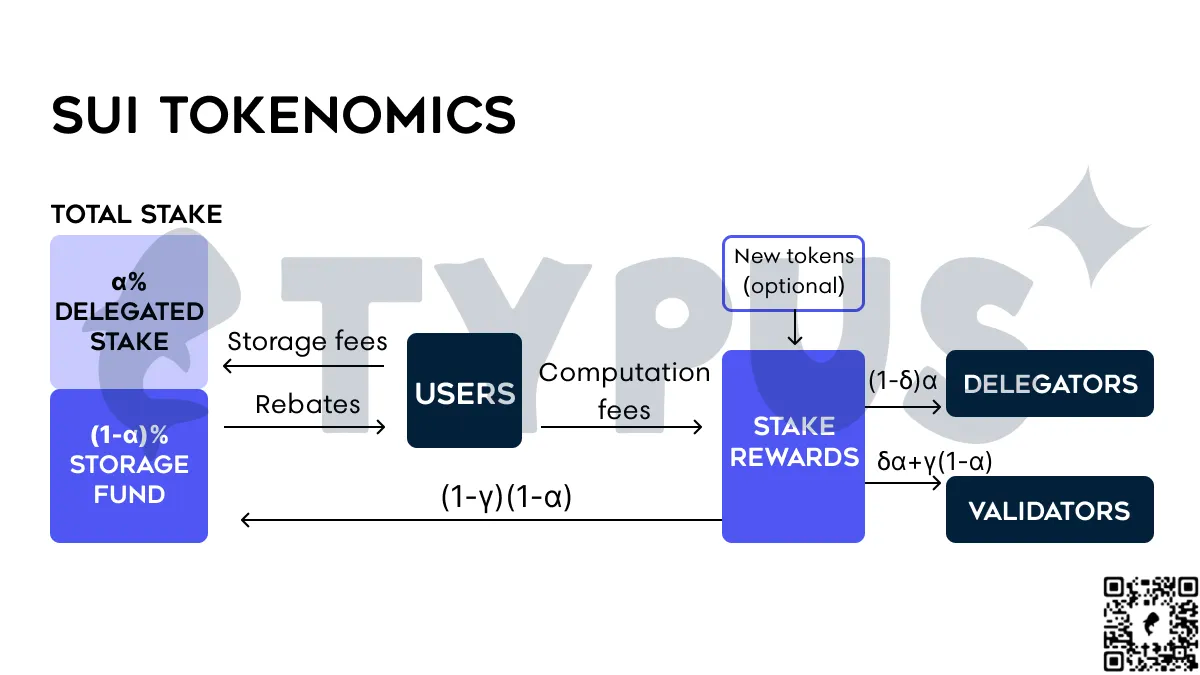
Sui 的代币经济模型通过存储基金(storage fund)来应对存储成本,具体来说是将过去的交易手续费重新分配给未来的验证者。当链上的存储需求很高时,验证者将获得额外的奖励来弥补他们的成本,而当存储需求较低时,则相反地降低奖励。
它还包括一个删除选项,允许用户透过删除之前存储的链上数据来获得退款。这个机制让用户只会将必要的数据存储在链上。这种租赁模型,通过按期支付的方式支付存储费用,对于在 Sui 上面的项目来说是很有效率的。当存储成本变得不经济时,它引入了一种基于市场的机制来释放存储空间。
将元数据(metadata)存储在链上确保了代币的可编程性。资产可能会发生变异,有时会组合。通过 Sui 这种物件导向的(object-oriented)语言进行智能合约编程,将结构(structs)存储在链上有助于可组合性(composability)。如果 NFT 能够互相通信,甚至是来自不同格式的 NFT,那么将会开启新的垂直领域。
在其他区块链上,NFT 仅仅是一个拥有权记录,其中包含指向特定链下存储的 URL。众所周知,这将让区块链的全面应用有很多局限。
与其他区块链不同,Sui 能够在链上存储 jpeg 图像,并具有丰富的可变(mutable)和不可变(immutable)属性。 NFT 不仅仅是我们今天所知道的那样,它们成为了在 Sui 内具有状态动态(stateful dynamic)特性的链上应用程序。这最终将推动更多创造力的释放、用户的采用和消费者价值的提升。
动态的可演进性
Sui 对 NFT 的愿景为区块链提供了一种不同的想像空间。资产是动态的;它们会变异,经历生命周期,有时甚至组合起来。为此,我们需要有一个基础架构,好让我们能够准确地模拟这些资产的生命周期。
如果 NFT 不能够模拟复杂且不断演化的资产,它们的用途就被限制在静态的资产上,例如货币、静态 PFP 等等。 Sui 中的动态栏位(dynamic field)很好地模拟了动态资产的生命周期;它们可以存储异质值(heterogenous value)并在访问时仅受到气费的影响,可以随时添加或移除。
想象一下,组合性(composability)和条件逻辑(conditional logic)可以创造出什么:
一个基于您在 DeFi 协议上的交易活动而演进的 NFT,随着您的等级提供动态奖励。
一个反映我们宏观环境变化的链上结构化产品。
一幅艺术作品,在艺术家签名或拍卖时发生变化。
一个游戏资产,在您领导一场战斗或进入前十名玩家排行榜时升级。
Sui 的编程语言允许在基本层面上对这些生命周期进行建模。这些资产的可演进性不依赖于 Sui 上的合约更新,让你可以在动态栏位中进行内部状态变更,或者移除和添加子物件(child objects)。
让我们来看一个名为 Tails 的示例,它具有两个功能 — — key 和 store。 key 将其定义为可拥有的物件,就像一个 NFT 出现在您的钱包中。 store 功能允许免费转移和封装。底部的 Tail Badge 是一个配饰,在满足某些条件时可以添加或移除。
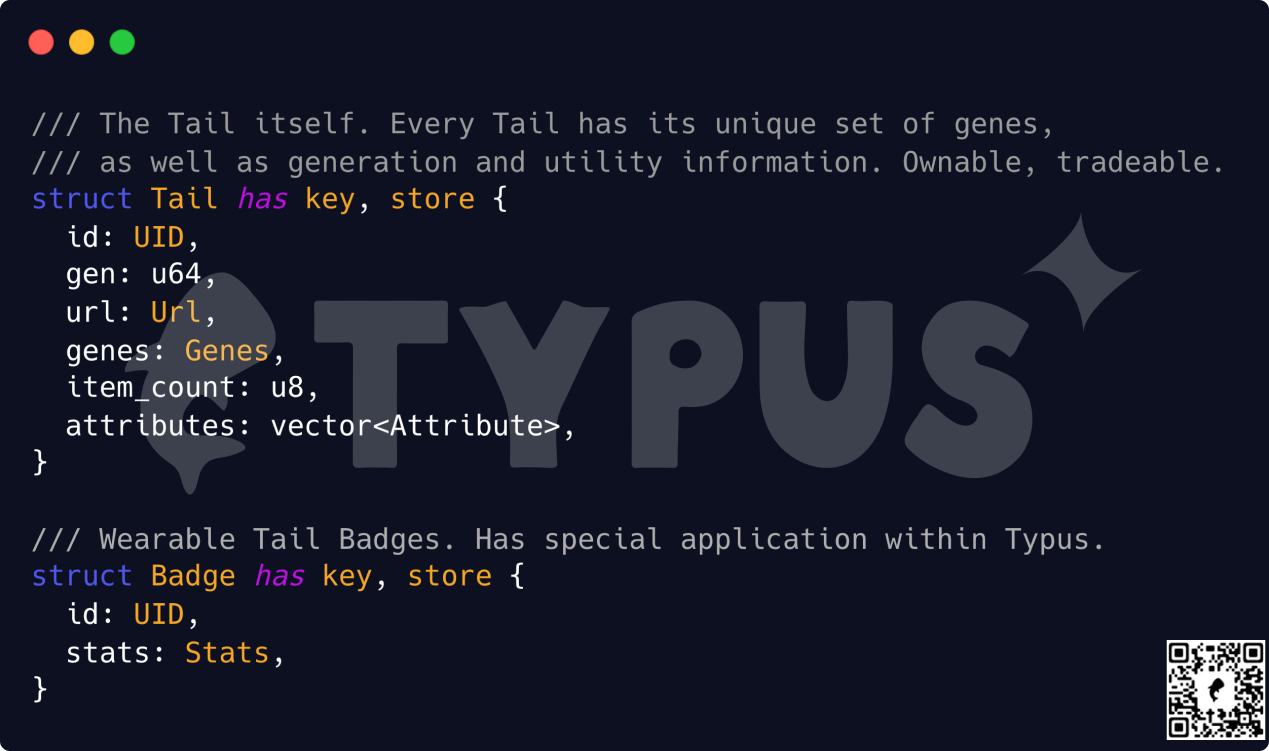
透过动态栏位,我们可以实现「佩戴徽章」的行为。徽章变成了一个可以存储在 Tail 内的子物件。
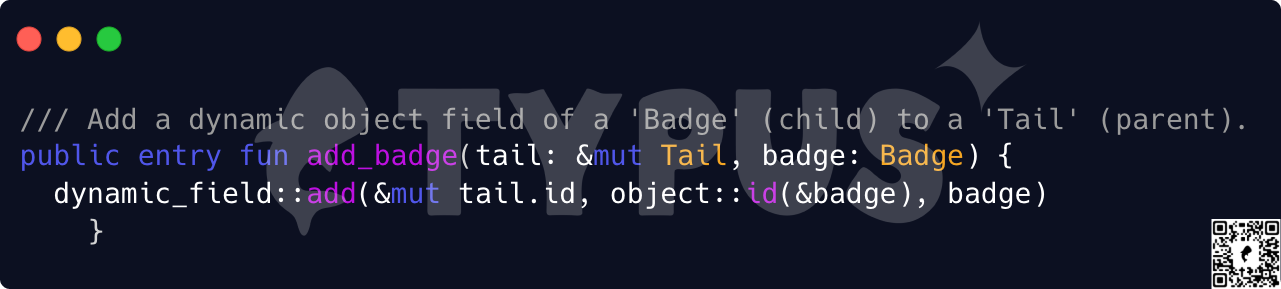
只需一行程式码就能创建 NFT 的动态属性。这些动态 NFT 和可组合性将使我们进入现代链上 dApps 的不同层次。通过链上存储的数据,验证者能够知道在哪里查找数据,而无需用户提供。
Kiosk 标准
为什么区块链无法带来太多的颠覆性变革呢?
数位资产必须将规则编码,如果这些规则无法由智能合约执行,它就无法实现去中介化,因为它将依赖中央实体来遵守规则。 NFT 应该将规则编码,例如二次销售的版税、版权验证以及签署。
EVM 链和 Solana 无法模拟随着生命周期演变的资产、在链上存储元数据和执行规则。现有的框架足以模拟简单的、定型的资产,但对于颠覆性行业变革来说还不够。
就在去年,Solana 上发生了一场严峻的版税讨论。许多人提出了他们的需求:艺术家迁移到Web3需要有强大的诱因。如果不调整 NFT 标准,市场、工具和艺术家将失去在此建立的激励。
Sui 已经实施了一个名为 Kiosk 的 NFT 标准,解决了这个问题。作为创作者,Sui Kiosk 支持对转移政策和相关规则的严格执行,以保护资产并执行资产所有权。 Sui Kiosk 使创作者能够更好地控制自己的作品,让创作者和拥有者能够掌握自己作品的使用方式。
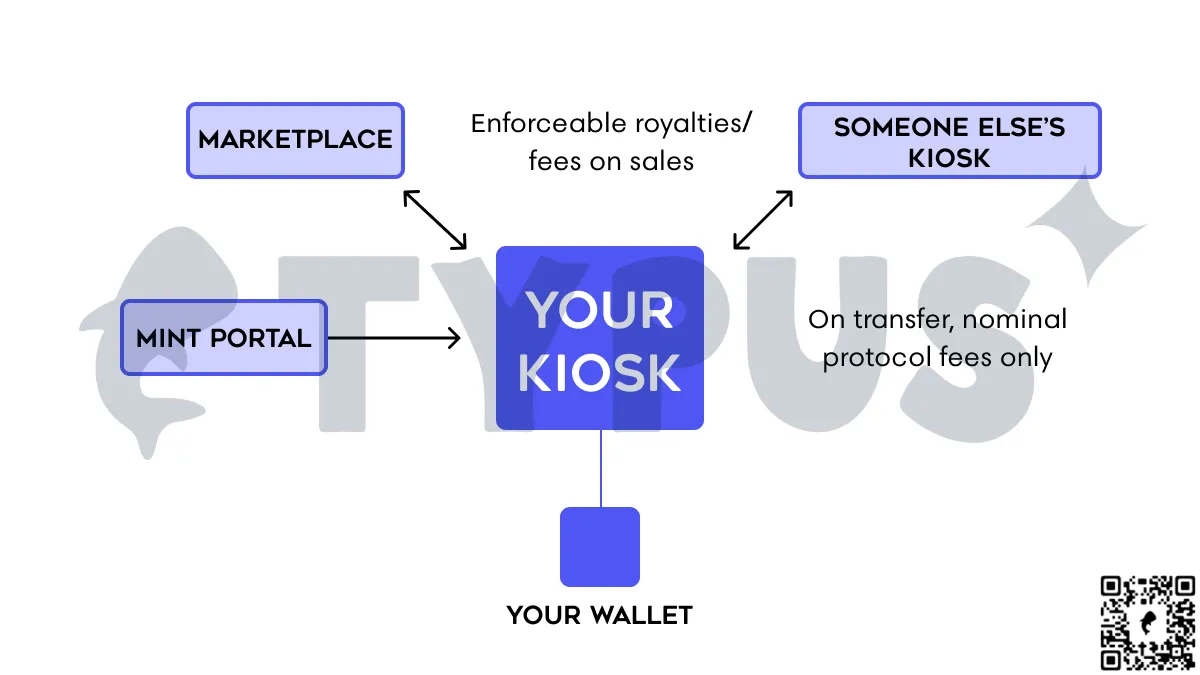
这意味着 Sui 上的数位资产允许将规则进行编码,使其可由智能合约执行,为艺术家和创作者打造绝佳的创作环境。
可组合的 NFT
具有可组合性的 NFTs 更能准确地描绘消费者的需求。这些可组合的部分作为行为指标,使协议无需收集大量数据的同时,又能让个人化的忠诚度系统得以充分发挥。
协议将能够抛弃过于简单的会员等级制度(如铜牌、银牌、金牌),并提供真正个人化的忠诚度系统,以反映消费者的独特性。
新的方案是可组合的 NFT,它们会根据使用者的互动来动态演化。这种演化可以由链下数据(天气、位置等)和链上数据(与特定协议的交易)触发。每个 NFT 都会在外观上反映您的状态。之前缺乏动机的低活跃用户现在可以立即看到他们活动的影响。高活跃用户继续看到反映和解锁与独特性和特权相关的奖励。
利用 NFT 特性解锁独特的奖励
NFTs 之所以拥有高人气,是因为用户可以获得不同的特性,并带给用户稀有性和独特性的感觉。通过替换传统的铜牌、银牌和金牌等级,NFTs 将根据不同类型的用户活动演化并添加不同的特性,从而生成针对用户量身定制的具体奖励。
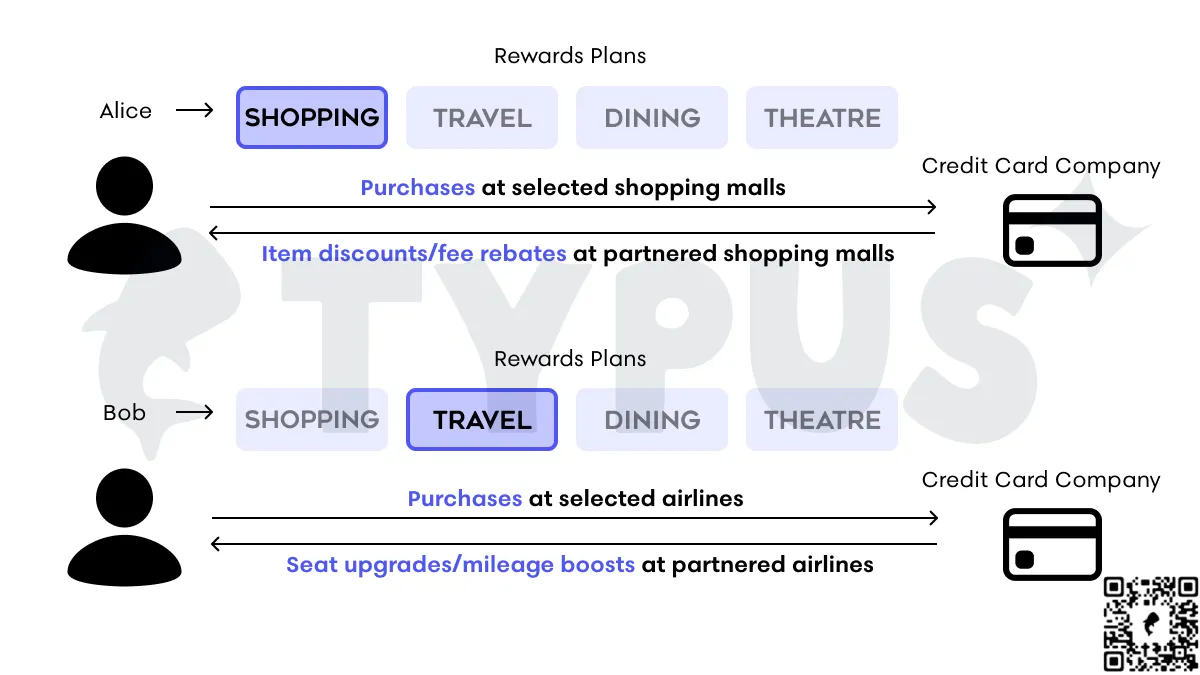
一个很好的 Web 2.0 的例子是信用卡奖励系统。现在有许多信用卡公司根据用户的购买情况提供定制的奖励计划。
例如,Alice 经常在购物中心购物。她选择的奖励计划是与购物中心合作的购物计划。她在购物中心购买的越多,累积的积分就越多,可以立即兑换商品折扣或费用回扣。另一方面,Bob 经常旅行,并且使用同一张信用卡购买机票。他选择的奖励计划是与航空公司合作的旅行计划。他在航空公司的购买越多,累积的积分就越多,可以兑换座位升级或里程提升。
喜爱在餐厅使用信用卡的美食家可以获得餐饮奖励,经常购买电影票的电影爱好者可以获得电影院奖励。 Alice 和 Bob 可以自由切换所选的奖励计划,提供个性化定制的激励系统。
拥有可组合性的 NFT 在Web3的世界中可以实现无摩擦的交互。想像一下,如果 Bob 在一个 DeFi 协议上进行游戏资产的交易,他的头像就会添加一个剑的特征,如果 Bob 进行更多交易,剑的样式就会改变以显示更高的身份地位。这里的剑特征代表了与该 DeFi 协议合作的 GameFi 项目中独有的游戏内费用优惠。对于 Alice 来说,她的头像会添加一个金链特征,因为她经常通过在 DeFi 协议上存入项目代币来提供流动性。金链特征代表了与该 DeFi 协议合作的项目中独有的额外收益机会。
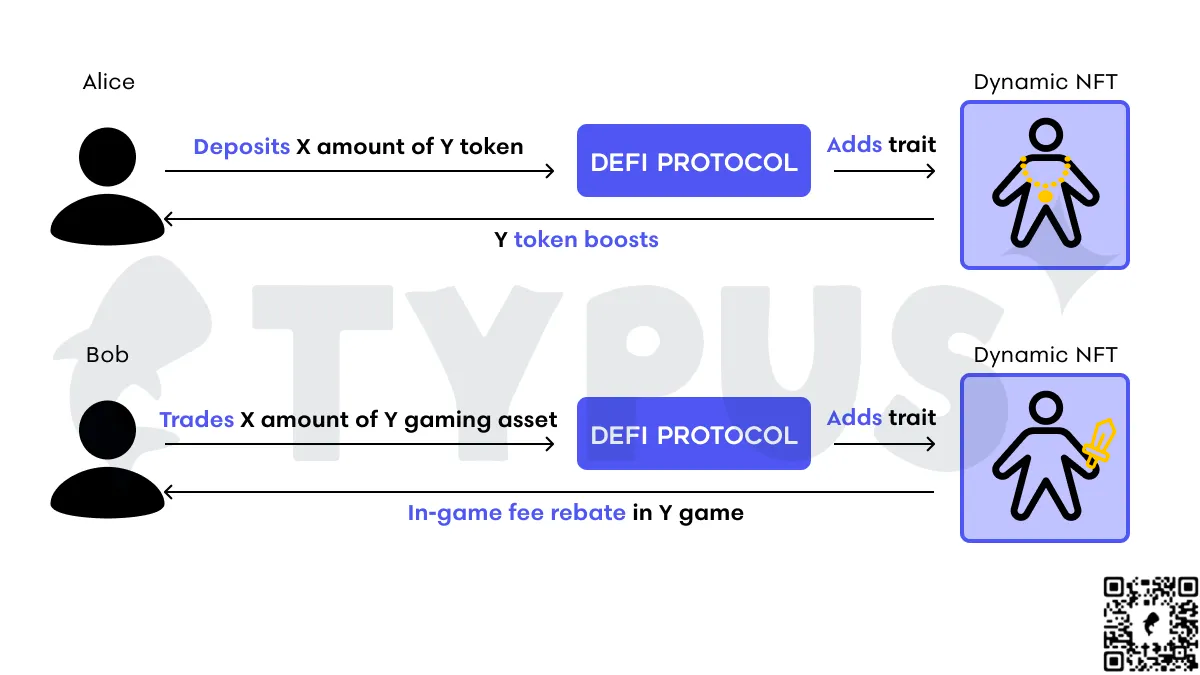
这里的重点是,不需要使用某个单一的状态标志,每个用户的状态都将通过一组独特的特征来体现。因此,即使 Alice 和 Bob 的交易金额相同,他们所代表的状态也完全不同。将它们联系在一起的是与特征相关的稀有程度。不是每个人都对相同的奖励感兴趣,协议可以通过发展各种合作关系为用户提供不同的奖励,每个奖励通过可组合 NFT 的特征演化来访问和解锁。
DeFi 与 NFT 有什么关系?
可组合的 NFT 能够相互交互并像乐高积木一样运作。它们为区块链上不同种类的应用程序之间的互通性开创了全新的世界。更好的比喻是,可组合性对于企业所起的作用,就像开源对软体开发所起的作用一样。这创造了一种新的金融基础设施,使得随着新的应用场景的出现和Web3的普及,区块链更加能够迈入大众视野。
先前提到的特点使得 Sui 成为 NFT 和游戏资产的超级链。 Sui 的一个核心策略是专注于为 NFT 建立一个优秀的环境,以推动用户增长并实现大规模采用。
这一点尤其重要,因为 DeFi 协议无法仅通过 DeFi 自身实现大规模采用。正如我们在其他L1上所看到的,如果只有 DeFi,市场热度、总锁仓量和流动性都难以长期维持。相反,流动性应该来自创建、交易和交换 NFT 社区和 GameFi 项目中的数字资产的零售用户。
DeFi 协议的角色是作为一种基础设施,使资产能够被自由交易和使用。
Sui 能够将元数据保存在链上,使得 NFT 在 Sui 内部成为有状态的动态链上应用程序。这种动态的可进化性使它们能够成为 DeFi 协议生态系统内的一个工具,从而为项目探索提供更多创意。想像一下:通过可组合的 NFT 构建完全在链上的 DeFi 用户激励系统。
使用 Sui Kiosk 标准来鼓励创作者、艺术家和建造者在链上创建数字资产。随着越来越多的链上资产在流通,将出现资产赋能和提高资产效率的这类金融需求。想像一下:通过买权、卖权期权机枪池来获取原生 NFT/游戏资产的收益。
随着新颖的 Sui 功能的建立,我们看好 Sui 能真正为区块链带来颠覆性。 Typus 始终站在实施新功能的前沿,对于动态链上 Sui 资产和 DeFi 生态系统的高度可组合性和凝聚力感到兴奋。想像一下:通过 zk 登录、赞助交易、优惠券、动态属性、交易 cookie,引导Web2用户参与实验性 NFT 收藏。
未来是 Sui 的。
参考文献
https://twitter.com/kostascrypto/status/1668149010861899776
https://medium.com/mysten-labs/announcing-sui-tokenomics-9cb829086e30
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yRbajb10lIk
https://docs.sui.io/testnet/build/sui-kiosk
Suinami Riders TG groupchat



