全景解析DEX聚合器: 生态发展、产品对比、聚合算法
原文作者:Andrea
原文编辑:Yaoyao
原文来源:DODO Research
流动性对于任何金融产品来说都至关重要。自 2020 年 DeFi Summer 以后,各类 DeFi 产品如雨后春笋般出现,一方面促进了 DeFi 生态的发展,另一方面也使得流动性被分散到各个不同的协议中,使得交易市场变得碎片化。旨在将流动性集中的聚合类产品,也在这时应运而生。
根据功能和实现方式,聚合器可分为:
1.收益聚合器:将资金聚集到资产池,通过策略分布到不同的 DeFi 平台进行挖矿,获得的收益在资产池间分配。代表项目有 Yearn Finance, Idle Finance, APY.Finance, Harvest Finance。
2. DEX 聚合器:聚合多个协议的流动性,通过算法寻找最佳交易路径,降低交易成本。代表项目有 1inch, DODO, Matcha, Paraswap, KyberSwap, CowSwap。
3. 多功能聚合器:在同一终端接入多个 DEX 流动性,如 Uniswap、Balancer 等,但不具备拆单功能,即不会在多个 DEX 间分配交易。代表项目有 Zapper, Plasma Finance, InstaDapp。
本文聚焦于 DEX 聚合器,围绕生态发展、产品对比以及聚合算法三方面,详细介绍了 DEX 聚合器的过去和现状,以及对未来的展望。
回顾 DEX 聚合器的发展
1inch于 2019 年 5 月推出,是第一个将其他多个去中心化交易所流动性汇集的 DEX。1inch 于 2020 年 11 月发布了第二版协议,对初始协议进行了改进,推出了应用程序接口 Pathfinder 组件。Pathfinder 组件包含了价格发现和路由算法,将交易拆分到许多去中心化交易所 (DEX) 甚至同一 DEX 的不同市场深度,以确保用户以最佳汇率和最快的速度处理交易。
DODO由最早的 PMM 算法发展到聚合算法。DODO 既是流动性供应商,也是流量分销商。DODO 的自建路由通过聚合链上各头部交易所的流动性,为用户计算出最优的交易路径;既支持在不同协议之间进行拆分,也支持在同一协议内的不同市场深度进行拆分。获得路径后,链上的智能合约将为用户执行交易动作,智能合约中的安全性验证保证了用户的资金安全和报价有效性。
可以说 DODO 既保留了 DEX 的交互体验,又发挥了聚合器的功能。
0 x API 为其他基于以太坊的应用程序提供点对点流动性功能,它可以在任何应用程序中启用可组合资产交易来分解流动性。当 0 x API 将订单接受者连接到 DEX 时, 0 x 就是一个聚合器。除了将订单连接到交易所, 0 x 还提供自己的做市商服务。做市商和应用开发人员是 0 x 目标用户, 0 x 通过代币经济激励他们优化最终用户体验。例如 Match 就是基于 0 x API 构建的聚合器。
DEX 聚合器生态
不同的 DEX 聚合产品采用了不同的方式实现订单路由。这里简要介绍几个常见 DEX 聚合器的主要功能特点,以及比较区分。
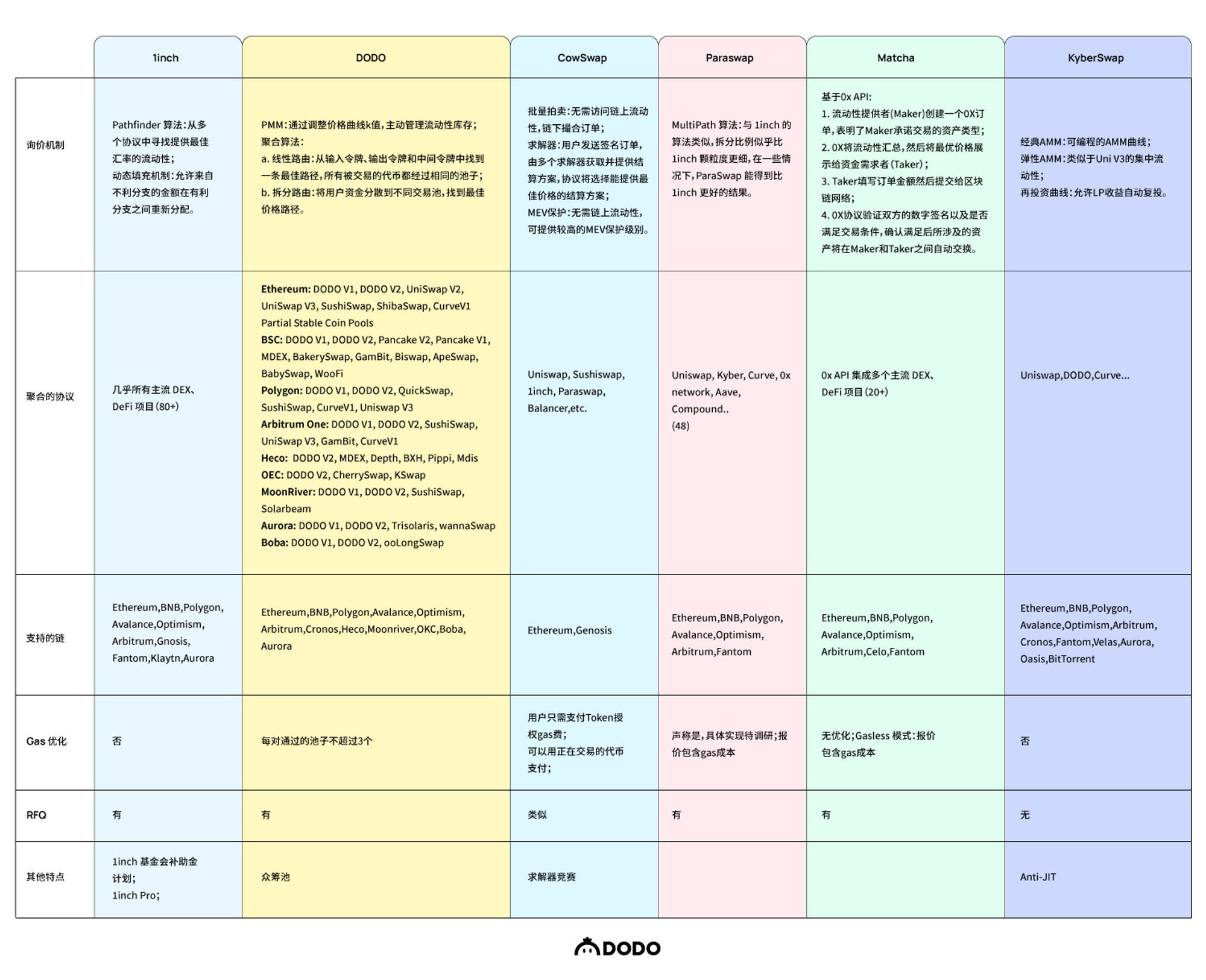
1inch
路由算法 Pathfinder
可以找到最有效的代币交换路径,将交易拆分为跨不同协议的多个子交易,甚至协议内的不同订单深度,从而提供最佳汇率。
除了优化交易利率之外,Pathfinder 还可以通过部分和动态填充机制来降低交易失败的可能性。当用户提交交易时,探路者首先将交易拆分为多个流动性来源。如果在此过程中一个协议的速率发生不利变化,则可以取消该路由的特定分支,仅执行有利的分支。动态填充甚至允许来自不利分支的金额在有利分支之间重新分配,并可以以界面中公布的速率完全完成交换。
零费用限价单功能
当用户下达限价单时,它会被添加到由 1inch 管理的中心化数据库中。然后这些订单可以由任何其他用户 write,包括 CEX 和 Pathfinder 在聚合协议中创建的订单。除交易价值外,限价订单的接受者还包括 gas 成本,这对用户来说是是一笔零费用订单。该实施还允许动态定价、用户设置执行条件的条件报价以及针对特定订单大小的报价请求 (RFQ) 报价。。
DODO
流动性供应 & 分销
如前所述,DODO 协议既是流动性供应商,也是流量分销商。
流量分销的主要体现是:DODO 在交易端提供了聚合器的功能,可以实现同一网络上两个任意代币之间的交易,智能地从流动性来源中找到最佳的订单路由,为交易者提供最佳的价格和最低的滑点。
Trade API
DODO Trade API 当前支持 Ethereum、BSC、Polygon、Arbitrum One、MoonRiver、Aurora、Boba、HECO、OEC、Avalanche、Optimism、Cronos 这十二个网络下任意币互换的实时报价以及可直接使用的与合约交互 ABI 数据。DODO Trade API 也集成了 DODOV 1、DODOV2、专业做市商、1inch API、 0 x API、ParaSwap API 以及 DODO 自建的聚合算法等多源实时的报价信息,并返回当前多源中最优报价,以确保 DODO Trade API 始终具有较强的竞争力。
CowSwap
在 CowSwap 上,订单在链下下达,并不会立即执行,而是通过收集和汇总的形式分批结算。一旦用户提交交易,解决者必须找到在分配时间内获得交易承诺价格的路径。
批量拍卖
无需访问链上流动性,链下撮合订单;用户发送签名订单,由求解器获取并提供结算方案,协议将选择提供最佳价格的结算方案。
采用批量拍卖的主要原因有:
1 )在以太坊的同一区块中建立任何代币相同的价格;
2 )将统一清算价格和需求巧合的新经济机制结合,改进 DEX 报价机制。
需求巧合(Coincidence of Wants)
本质就是订单撮合。在所有订单中共享流动性,构建环形交易,允许拆单所以无需完美匹配订单。
ParaSwap
路由算法 MultiPath
能够考虑间接交易路线(多跳),并与各类去中心化服务(如 Aave 和 Compound 等借贷平台)无缝交互。例如,ParaSwap 可以一步完成以下操作:将 ETH 兑换成 DAI,然后将 DAI 存入 Aave 以获得 aDAI。
KyberSwap
Kyberswap Elastic 的 Anti-JIT 功能是作为奖励锁定引入的。该锁定根据流动性贡献的持续时间授予。攻击与流动性提供者的正常活动之间的区别在于它们的贡献持续时间。当 JIT 攻击发生时流动性提供者(LP)向协议提供的资金面临着无常损失的风险。但在攻击者立即提取资金的情况下,协议可以预先计算无常损失,从而保证 LP 利润。
以下是 1inch,DODO,CowSwap,Paraswap,KyberSwap 的完整对比图:
聚合算法
DEX 也可以有自己的聚合算法,例如 Uniswap V3,Balancer 等都将一笔交易拆分到多路径中完成。DEX 聚合算法和聚合器的区别在于,聚合算法仅基于自己的报价池,而聚合器则充分利用了 DeFi 的可组合性,不仅接入自己的池子,也会接入其他 DEX 的池子。这最大化的利用全链的流动性源,以期为用户提供最好的报价。
聚合算法要解决的主要问题是:从 A Token 到 B Token,怎样在一系列池子中,找到最优兑换路径。通常情况下,这个问题有两种路径解决方案:线性路由和拆单路由。
线性路由
线性路由指在寻找交易路径的过程中,一交易对只经过一个池子,在此基础上寻找目标 token 报价最优的路径。例如用户需要将 A Token 换为 B Token,线性路由所找到的最优路径为 A-C-B,而非[A-C-B]+[A-D-B](即 A Token 不会拆分为两个或多个部分选择不同的路径)。最终的路径只经过两个池子——这两个池子可能来自不同协议。
拆单路由
同样是将 A Token 换为 B Token,拆单路由可以使 30% 的 A Token 使用 A-C-B 路径;剩余的 70% 则使用 A-D-B 路径。拆单是为了使用户的资金按最优比例配置到不同池子进行兑换,以获得最优的目标 token 报价。
拆单后的路径根据中间 token 的数量又可分为:零跳询价和多跳询价。
例如,将 1000 个 A Token 兑换为 B Token,简单来说有两种方法:
A→B 即 A 直接兑换为 B,但可将这 1000 个 A Token 拆成多份,经过一系列的同名池子兑换为 B Token,这种方式叫做零跳询价;
A→C 1 →C 2 …Cn→B, 即中间经过多个不同的交易对,最终兑换为 B Token,这种方式也叫做多跳询价,多跳询价也可以看作是由多个零跳询价组成。
1 )零跳询价
零跳询价要解决的问题是:假如有 N 个同名池子, 1000 个 A Token 拆分为 K 份,那么对于每一个池子 Ni 将询价 K 次,将 K 份中的每一份记作 Ki,每次报价输出记作 Oi,那么求解最优路径即为找到一个拆分为 K 份的方式,使得每次输出的 Oi 之和为最大。这其实是一个背包问题。
背包问题(Knapsack problem)是一种组合优化的 NP 完全问题。问题可以描述为:给定一组物品,每种物品都有自己的重量和价格,在限定的总重量内,我们如何选择,才能使得物品的总价格最高。问题的名称来源于如何选择最合适的物品放置于给定背包中,背包的空间有限,但我们需要最大化背包内所装物品的价值。背包问题通常出现在资源分配中,决策者必须分别从一组不可分割的项目或任务中进行选择,而这些项目又有时间或预算的限制。
-- 维基百科
对于零跳询价来说,拆分数越小,询价速度越快,离散误差越大;拆分数越大,询价速度越慢,离散误差越小。
1inch 基本采用固定拆分数,对于单跳,可选拆分数在 100 内,常用值为 50 ;Paraswap 的拆分数相对更灵活。
DODO 则采取二分法辅助确定拆分数以尽可能地减少固定的拆分数带来的离散误差。具体实现为:在 0 ~ 100 的拆分数内随机选择一个拆分数 n,计算最优报价 p 1 ;再计算拆分数为 2 n 时的最优报价 p 2 , 若 p 1 和 p 2 的相对差值小于 0.001 ,则认为 n 为最优拆分数,否则,以 2 n 为新的当前拆分数,继续进行二分检验,至差值小于 0.001 为止。
2 )多跳询价
A→C 1 →C 2 →…→Cn→B 这样一个路径可以使用多次零跳询价完成。先求解 A→C 1 ,再 C 1 →C 2 ,以此类推,即可获得最优价格和拆单方式。这样的方式也会增加询价时间和 gas 成本,因此,DODO 将中间币控制在两个以内,最优化交易路径。
未来展望
目前来看,DEX 龙头如 Uniswap、Curve 等仍然占据链上交易的主要份额;而 DEX 聚合器交易量占比不到 50% ,仍具有很大的市场空间。
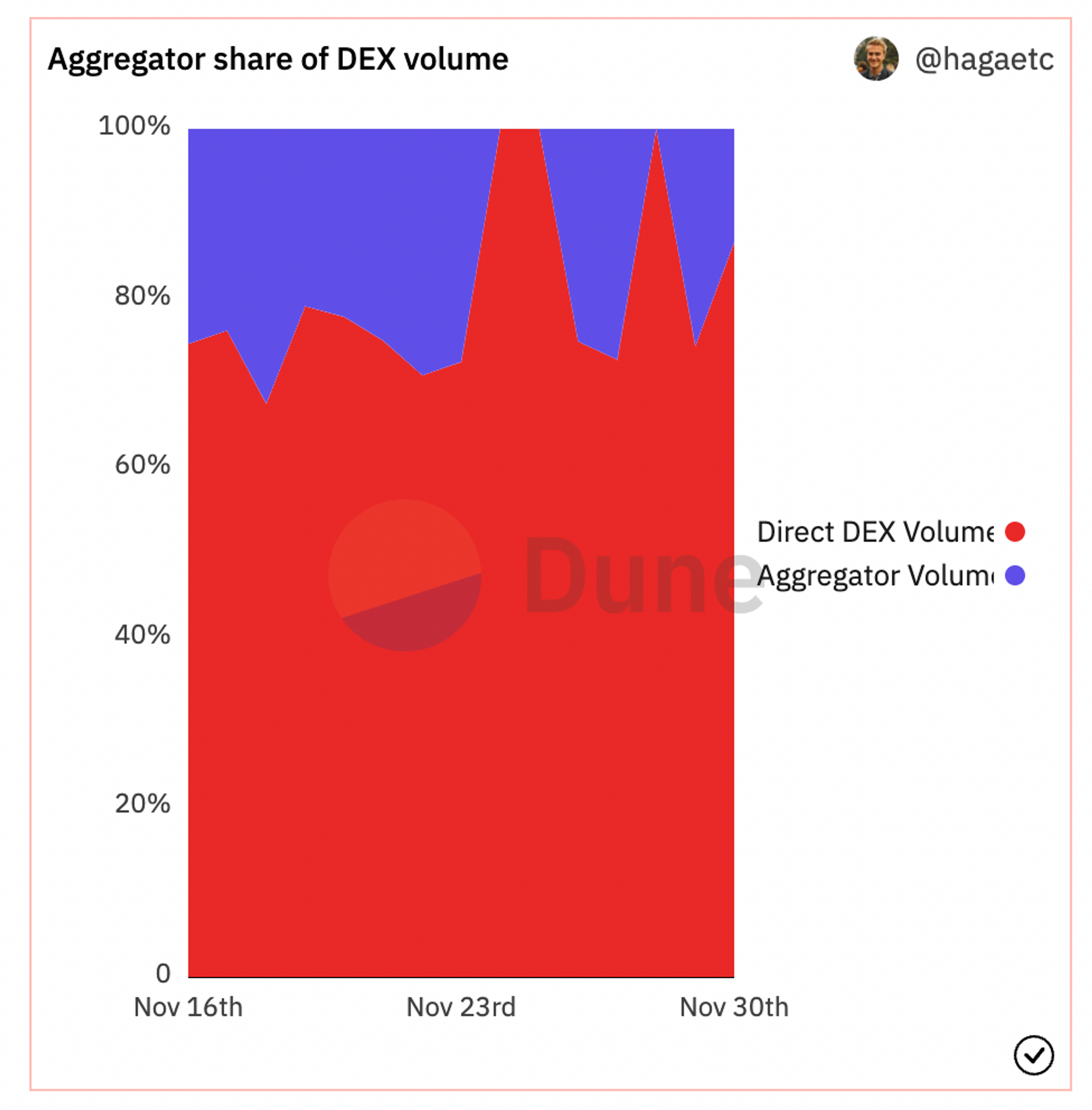
来源:Dune Analytics
DEX 聚合器的市场份额能够继续增加,主要取决于两点:
增加更多的流动性来源:自动路由技术除了集中链上流动性,也可以拓展到链下流动性,例如 增加 RFQ 做市商报价;
降低 gas 成本: 随着公链性能的提升,链上成本降低,做市商可以更高频、更激进地进行报价,而这又可以进一步丰富流动性来源,吸引更多的做市商参与。可以预见的是,有一大批面向终端用户的应用将会连接到聚合器的 API 上,以此形成良好的正向循环
未来很有可能大部分的手动交易员会使用诸如 1inch、DODO、CowSwap 这样的 DEX 聚合器或者其他的类似产品来完成交易,而 DEX 则作为一个类似于后端的流动性供应商。DEX 聚合器提供更为接近中心化交易所的前端体验,如 DOOD 已经提供限价单交易、免 gas 交易等功能。
DODO DEX 提供 K 线视图,限价单,免 gas 交易功能。
相信随着路由聚合算法的优化,更多流动性来源的集成,前端体验更符合交易需求,DEX 聚合器的不断完善成熟,终能获得更大的市场份额,让加密经济的 “去中心化” 属性真正地被广泛接纳,去中心化金融实至名归。



