Sau khi FTX bùng nổ, các nhà tạo lập thị trường vỡ mộng
Nguồn gốc: DODO Research
Nguồn gốc: DODO Research
Biên tập gốc: Daidai
FTX bùng nổ, đế chế sụp đổ, hàng loạt nền tảng hàng đầu bị ảnh hưởng nặng nề, các nhà tạo lập thị trường và cho vay trở thành lĩnh vực chịu ảnh hưởng nặng nề nhất: Alameda, với tư cách là một trong những nhà tạo lập thị trường lớn nhất trong ngành tiền điện tử, đã bị phá hủy trong trò hề này và chính thức ra mắt vào ngày Ngày 10 tháng 11. Kết thúc giao dịch Genesis, công ty tạo lập thị trường và cho vay trực thuộc DCG, cũng đang phải đối mặt với tình thế tiến thoái lưỡng nan vì không đủ khả năng thanh toán.
Nhà tạo lập thị trường hàng đầu sụp đổ, một lượng lớn tiền gốc bị phá hủy và thị trường đơn phương sắc nét... Điều này đã gây ra sự hoảng loạn chưa từng có giữa các nhà tạo lập thị trường trong ngành. các bài kiểm tra căng thẳng khổng lồ.Thanh khoản thị trường ngành công nghiệp mã hóa đã giảm mạnh.
Bất kể thị trường truyền thống hay thị trường mã hóa, đối với các nhà đầu tư đại chúng, nói về các nhà tạo lập thị trường luôn giống như chơi trò mù bắt voi.
Mục lục
Mục lục
01. Nhà tạo lập thị trường trong lĩnh vực mã hóa
- Nhà tạo lập thị trường là gì, cách tạo lập thị trường và cách tạo ra lợi nhuận
- Các nhà tạo lập thị trường trong thị trường tiền điện tử
- Công dụng của nhà tạo lập thị trường là gì
- Chiến lược tạo thị trường
- Cơ hội, rủi ro và miền Tây hoang dã
02. Có hoặc Không: Mọi người đều là nhà tạo lập thị trường
- Nhà tạo lập thị trường và Nhà tạo lập thị trường tự động
- AMM: Mọi người đều là nhà tạo lập thị trường
- Tại sao LP mất tiền
03 Nhà tạo lập thị trường hàng đầu sụp đổ: sau khi thị trường mất thanh khoản
- Nhà tạo lập thị trường trong Dominoes
- Sau khi thị trường mất thanh khoản
tiêu đề cấp đầu tiên
0 1 .
tiêu đề phụ
Nhà tạo lập thị trường là gì, cách tạo lập thị trường và cách tạo ra lợi nhuận
Wikipedia giải thích rằng nhà tạo lập thị trường được gọi là "chuyên gia" tại Sở giao dịch chứng khoán New York, "nhân viên ngân hàng" trên thị trường chứng khoán Hồng Kông và "nhà tạo lập thị trường" tại Đài Loan.
Như tên cho thấy, nhà tạo lập thị trường là người tạo ra một "thị trường".
Trong các thị trường tài chính truyền thống, nhà tạo lập thị trường là một tổ chức thương mại, thường là công ty môi giới, ngân hàng lớn hoặc tổ chức khác, có công việc chính là tạo thanh khoản trên thị trường bằng cách mua và bán chứng khoán.
Tạo lập thị trường là một hoạt động tài chính đã được thiết lập và trưởng thành. Trong quá trình này, các nhà tạo lập thị trường cung cấp tính thanh khoản và độ sâu cho thị trường. Người mua và người bán không cần đợi đối tác xuất hiện, miễn là nhà tạo lập thị trường tiến tới đảm nhận đối tác . Một thỏa thuận được ký kết và nhà tạo lập thị trường kiếm được lợi nhuận bằng cách thu được chênh lệch giá mua-giá bán từ cả hai bên. Chênh lệch giữa giá mua và giá bán trên thị trường được đề cập ở đây là Chênh lệch giá mua và giá bán (Bid-Ask Spread) Các nhà tạo lập thị trường phải trả để tăng khối lượng giao dịch và tăng lợi nhuận).
Mô tả hình ảnh
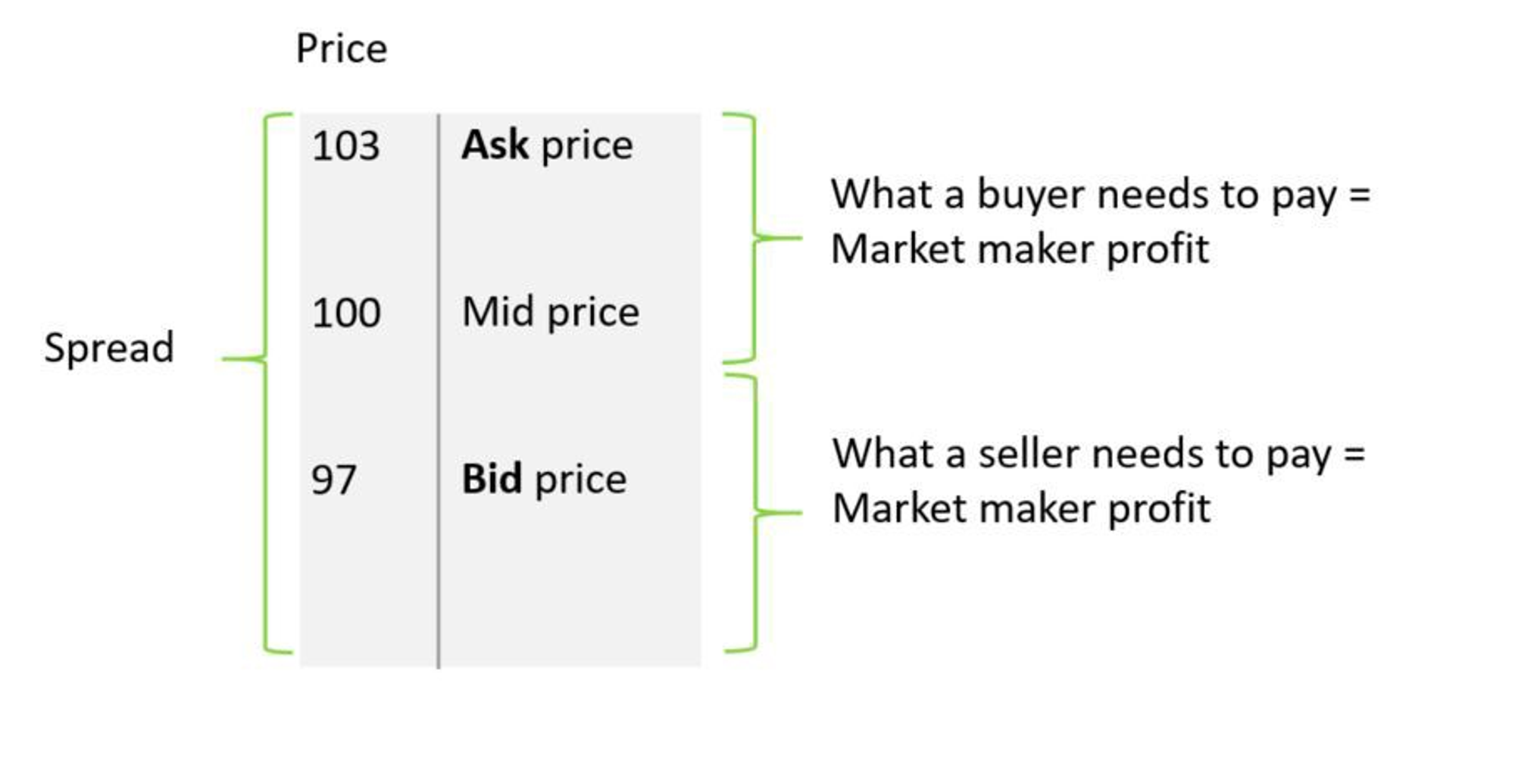
Mua tài sản này cần 103, bán tài sản này được 97 và nhà tạo lập thị trường nhận được mức chênh lệch là 6
tiêu đề phụ
Nhà tạo lập thị trường trong thị trường tiền điện tử
Bất kể trong thị trường truyền thống hay thị trường mã hóa, tính thanh khoản là huyết mạch của tất cả các thị trường giao dịch và các nhà tạo lập thị trường đang nắm quyền. Trong thị trường mã hóa, các nhà tạo lập thị trường còn được gọi là nhà cung cấp thanh khoản (LP), có thể trực tiếp chỉ ra:Giống như các thị trường truyền thống, thị trường tiền điện tử cần các nhà tạo lập thị trường giải quyết các bẫy thanh khoản bằng cách giúp hướng dẫn “bàn tay vô hình” của thị trường.
Bẫy thanh khoản này chủ yếu được phản ánh trong một vòng luẩn quẩn: các dự án tiền điện tử cần những người (sàn giao dịch tiền điện tử và nhà đầu tư tiền điện tử) đóng góp vào tính thanh khoản của mã thông báo; đồng thời, chỉ khi mã thông báo có thanh khoản thị trường, những người này mới tham gia. Và đây là lúc Market Maker xuất hiện.
Chỉ cần đặt,Thanh khoản của nhà tạo lập thị trường tạo ra thanh khoảnMô tả hình ảnh

tiêu đề phụ
source:Wintermute
Công dụng của nhà tạo lập thị trường là gì
Lấy tiền điện tử làm ví dụ. Tất nhiên, một trong những điểm cốt lõi là tính thanh khoản được đề cập nhiều lần. Bởi vì tính thanh khoản là nền tảng của bất kỳ thị trường hiệu quả nào.
Các tính năng định giá mạnh mẽ:Các nhà tạo lập thị trường có thể theo dõi sự thay đổi giá trong một thời gian dài, đưa ra phán đoán về giá hợp lý của thị trường và cung cấp các báo giá được tham khảo nhiều nhất. Ví dụ: các nền tảng như 1inch không chỉ chuyển tiền đến các nhóm quỹ khác nhau mà còn yêu cầu một số nhà tạo lập thị trường (chẳng hạn như Wintermute) báo giá.
Tăng cường thanh khoản thị trường:Nhà đầu tư có thể giao dịch trực tiếp với các nhà tạo lập thị trường mà không cần chờ đợi hay tìm đối tác. Tạo lập thị trường là việc cung cấp báo giá song phương cho bất kỳ thị trường nhất định nào và đây là trọng tâm của việc cung cấp tính thanh khoản.
Nâng cao hiệu quả chung của thị trường:Các nhà tạo lập thị trường báo giá thông qua các nền tảng giao dịch khác nhau và loại bỏ sự nhầm lẫn thị trường thông qua chênh lệch giá, giúp cải thiện hiệu quả chung của thị trường. Ví dụ: Kairon Labs hiện được kết nối với API của hơn 120 sàn giao dịch để giúp giảm tác động của biến động giá.
Tạo điều kiện quảng bá mã thông báo mới và giảm chi phí phát hành:Các nhà tạo lập thị trường sẽ thúc đẩy khối lượng giao dịch tăng lên và một loạt các mã thông báo mới xuất hiện trên nhiều sàn giao dịch tiền điện tử.
Tăng khối lượng và kỳ vọng thị trường:Thu hút sự chú ý của các nhà đầu tư, nâng cao niềm tin của thị trường và thúc đẩy giá của mã thông báo
Tạo thuận lợi cho việc kết thúc các giao dịch lớn:tiêu đề phụ
chiến lược tạo thị trường
Chiến lược tạo thị trường đề cập đến chiến lược thiết lập các lệnh mua và bán giới hạn riêng biệt, sử dụng sự biến động của giá mục tiêu để kích hoạt lệnh giá giới hạn và thu được thu nhập giao dịch thông qua chênh lệch giá giữa lệnh mua và bán. Đây là một chiến lược chênh lệch chênh lệch trung tính với rủi ro trong các chiến lược giao dịch tần suất cao. Nói một cách đơn giản, chính người trung gian được đề cập ở trên là người kiếm được phần chênh lệch.
Mô tả hình ảnh
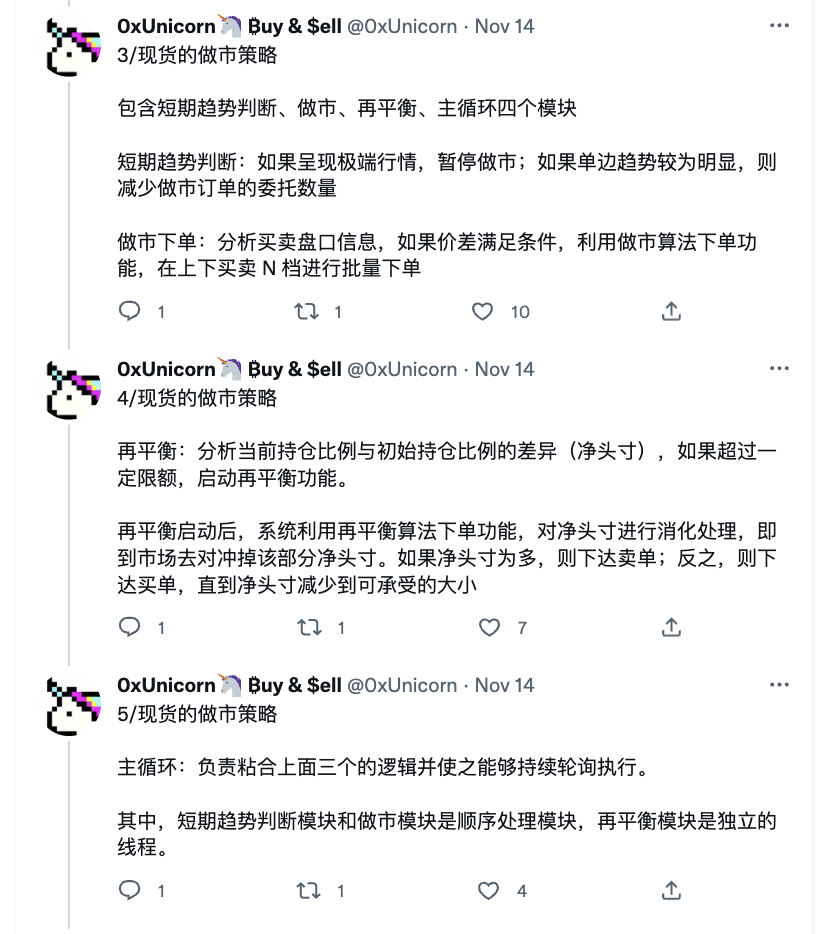
https://twitter.com/0 xUnicorn/status/1592007930328776706
Về cốt lõi, điều mà một chiến lược tạo lập thị trường tập trung vào làSố lượng lệnh giới hạn và cài đặt khoảng cách giữa báo giá thầu và lệnh và giá trung bình,tiêu đề phụ
Rủi ro, Cơ hội và Miền Tây hoang dã
Như đã đề cập ở trên, rủi ro chủ yếu đến từrủi ro tồn kho。
Khi một lượng lớn hàng tồn kho được tích lũy trong tay, điều đó cũng có nghĩa là nhà tạo lập thị trường có nhiều khả năng không tìm được người mua cho hàng tồn kho của mình, dẫn đến rủi ro:Nắm giữ nhiều tài sản không đúng lúc (thường là trong giai đoạn khấu hao).Trong một kịch bản khác, các nhà tạo lập thị trường phải bắt đầu bán lỗ hàng tồn kho để duy trì hoạt động khi giá tài sản tăng.
Trong DeFi, rủi ro tạo lập thị trường có thể được xử lý thận trọng hơn. Ví dụ, hợp đồng vĩnh viễn. Các nhà tạo lập thị trường thường sử dụng tỷ lệ tài trợ của hợp đồng vĩnh viễn (cốt lõi của cơ chế là neo giá hợp đồng với giá giao ngay) cho chênh lệch giá giao ngay và chênh lệch đòn bẩy. Một câu tóm tắt phương pháp chênh lệch giá này: tạo một vị trí có cùng giá trị vị trí và ngược hướng vị trí trong thị trường hợp đồng giao ngay/đòn bẩy và vĩnh viễn tương ứng.Do đó, dưới những biến động giá bất thường, các nhà tạo lập thị trường sẽ phải đối mặt với rủi ro thanh lý lớn, bởi vì họ có thể nắm giữ các vị thế lớn do chênh lệch tỷ lệ tài trợ khác nhau.
Cơ hội đến từ lợi nhuận cao đằng sau rủi ro cao. Ngay cả với mức chênh lệch là 0,01 đô la, khi một lệnh giao dịch như vậy được thực hiện một triệu lần trong một ngày, lợi nhuận sẽ đạt tới 10.000 đô la. Các nhà tạo lập thị trường cũng cung cấp cho các nhà giao dịch đòn bẩy.Sau khi khách hàng thanh lý các vị thế của họ, nhà tạo lập thị trường sẽ có thể thanh lý số tiền ký quỹ của nhà giao dịch. Theo dữ liệu của coinglass, số tiền thanh lý tiền điện tử là 100-1000000000 đô la Mỹ mỗi ngày. Điều này sẽ dẫn đến lợi nhuận khổng lồ cho các nhà tạo lập thị trường.
Không thể phủ nhận rằng thị trường mã hóa vẫn đang ở giai đoạn đầu, so với các hoạt động tạo lập thị trường rất trưởng thành trên thị trường tài chính truyền thống, vẫn có một mặt điên rồ ở đây. Nếu chúng ta phóng to và xem xét một số chi tiết về giao dịch tiền điện tử: tính thanh khoản của tài sản tương đối thấp; rủi ro trượt giá đáng kể; rất dễ xảy ra sự cố flash khi các lệnh lớn xuất hiện hoặc khi một số lượng lớn lệnh bán hủy bỏ giá thầu tốt nhất trong sổ lệnh . Những đặc điểm này cũng thường mang lại một số góc khuất hoặc lợi ích cho việc tạo thị trường tiền điện tử.
Nhìn chung, do các yếu tố kỹ thuật và quy định, các nhà tạo lập thị trường, thị trường mã hóa và người dùng vẫn đầy cảm giác hỗn loạn.
Hãy đến miền Tây hoang dã. Khi một nhà tạo lập thị trường hứa với nhà phát hành mã thông báo một mức khối lượng cụ thể, bước tiếp theo sẽ là một lời hứa thậm chí còn tham vọng hơn: rằng giá mã thông báo sẽ tăng lên một mức cụ thể. Làm thế nào để làm nó?
Wash Trading (giao dịch rửa):Những người chơi cấp dưới sẽ đặt một lệnh bán lớn và trong vài giây sẽ đặt một lệnh mua khác của riêng họ. Người chơi cấp cao sẽ sử dụng các đơn đặt hàng nhỏ hơn, đặt chúng trong một khoảng thời gian dài hơn và hoạt động từ nhiều tài khoản thay vì một tài khoản để tránh bị phát hiện trao đổi.
Bơm và bãi:Trong tất cả các chiến lược thao túng giá, bơm và bánthực hành là đặc biệt phổ biến. Mạng xã hội là những người đi đầu tốt nhất và một khi có đủ tình cảm fomo, một số lượng lớn mã thông báo đã mua trước có thể được bán để kiếm lời.
dốc:Mua nhanh đề cập đến việc tạo ấn tượng của một người mua lớn. Các nhà tạo lập thị trường có thể sử dụng chiến lược này để tạo ra một "người mua lớn" giao dịch số lượng lớn trong một khoảng thời gian cố định và ở đây một lần nữa tâm lý fomo lại có ích khi các nhà giao dịch khác chạy đua để vượt lên trên "người mua lớn" ( Nhưng cuối cùng là kẻ thua cuộc) — khi thị trường chú ý đến hành vi đó, giá sẽ tự nhiên tăng lên. Tất nhiên, sau khi các hoạt động của nhà tạo lập thị trường kết thúc, người mua ma sẽ biến mất một cách bí ẩn và giá mã thông báo có thể sẽ giảm mạnh.
Vào cua:Khi có nhiều nhà tạo lập thị trường cho một mã thông báo cùng lúc, một nhà tạo lập thị trường có thể kiếm tiền bằng cách cố gắng mua hầu hết các mã thông báo có sẵn, buộc các nhà tạo lập thị trường khác phải tăng giá vì họ phải giữ mức chênh lệch ở mức tương tự.
Do hoàn toàn thiếu quy định, các hoạt động đầu cơ này xuất hiện trong các chiến lược thực hiện của các nhà tạo lập thị trường, và cuối cùng chúngtiêu đề cấp đầu tiên
02.
tiêu đề phụ
Nhà tạo lập thị trường và Nhà tạo lập thị trường tự động
Mặc dù các nhà tạo lập thị trường (MM) và các nhà tạo lập thị trường tự động (AMM) nghe có vẻ giống nhau, nhưng chúng là những thực thể hoàn toàn khác nhau.
Như đã đề cập trước đó, trong tài chính truyền thống, nhà tạo lập thị trường là một tổ chức hoặc nền tảng đề xuất các giao dịch mua bán chứng khoán khác nhau cho nhiều sàn giao dịch, cung cấp tính thanh khoản cho thị trường và kiếm lợi nhuận thông qua chênh lệch giữa mua và bán.
AMM là một giao thức trao đổi phi tập trung (DEX). Không giống như các trao đổi truyền thống sử dụng sổ đặt hàng, tài sản được định giá theo một thuật toán định giá cụ thể và công thức định giá thay đổi theo các giao thức khác nhau. Ví dụ: Uniswap sử dụng đường cong toán học sau để xác định giá giao dịch: x * y = k. trong đó x và y là số lượng của hai tài sản trong nhóm thanh khoản, y là số lượng của tài sản khác và k là hằng số cố định có nghĩa là tổng thanh khoản của nhóm phải không đổi.
tiêu đề phụ
AMM: Mọi người đều là nhà tạo lập thị trường
Theo thuật ngữ của tài chính truyền thống, AMM đề cập đến một thuật toán mô phỏng hành vi của các nhà tạo lập thị trường con người, trong lĩnh vực DeFi, nó đã dần phát triển thành một động cơ bạo lực:
Nó sử dụng thuật toán tự động để cân bằng cung và cầu mã thông báo trong nhóm giao dịch, tránh trường hợp một mã thông báo nhất định bị bán khống (thị trường không có người mua/người bán đang chờ lệnh) và không thể giao dịch do điều kiện thị trường đơn phương trong Chế độ sổ đặt hàng và các nhà tạo lập thị trường khác thì khác. Ví dụ: các nhà tạo lập thị trường CEX sử dụng chênh lệch giá mua-bán. Họ sẽ điều chỉnh các vị thế để kiểm soát hàng tồn kho nhằm kiếm lợi nhuận theo chiến lược của riêng họ. Các nhà tạo lập thị trường DEX cung cấp thanh khoản theo một cách khác với CEX. Các nhà tạo lập thị trường DEX cũng sẽ kiếm được phí xử lý, khi phần phí giao dịch này được trao cho các nhà cung cấp thanh khoản, nó sẽ thúc đẩy họ bơm tài sản nhàn rỗi vào nhóm giao dịch để cung cấp thanh khoản và ở một mức độ nhất định sẽ giải quyết vấn đề thiếu hụt độ sâu giao dịch trong chế độ sổ lệnh.
DEX dựa trên AMM đã được chứng minh là một trong những đổi mới DeFi có ảnh hưởng nhất. Chính sự xuất hiện của AMM đã phá vỡ các hạn chế đối với sổ đặt hàng và khớp lệnh, giúp DEX phá vỡ thế độc quyền của CEX trên thị trường giao dịch tiền điện tử, đồng thời cho phép mở và tự do trên -chain giao dịch đã trở thành hiện thực. Nó cũng là AMM, cho phép người dùng thông thường tham gia vào việc tạo lập thị trường một cách không cần xin phép, để mọi DEX có thể hét lên một khẩu hiệu đầy tự hào: Mọi người đều là nhà tạo lập thị trường.
tiêu đề phụ
Tại sao LP mất tiền
Bây giờ chúng ta hãy nhìn vào tầm nhìn và thực tế.
Câu hỏi đầu tiên là, nếu người dùng trở thành LP, liệu việc tạo thị trường trên DEX có mang lại lợi nhuận không? (Một giọng nói: Bạn đã quên mất vô thường chưa?)
Trong một nghiên cứu được trích dẫn rộng rãi về các khoản lỗ LP của Uniswap v3, rekt đã tuyên bố một cách phũ phàng rằng họ (người dùng) nên HODLing tốt hơn là cung cấp thanh khoản trên Uniswap v3.
Như đã trình bày trong bài viết, trong thời gian ra mắt V3 từ ngày 5 tháng 5 đến ngày 20 tháng 9, 17 nhóm tài sản có TVL > 10 triệu đô la Mỹ (chiếm 43% TVL), khối lượng giao dịch vượt quá 100 tỷ đô la Mỹ và kiếm được khoảng Phí 200 triệu USD. Tuy nhiên, trong cùng thời gian đó, khoản lỗ do IL đã vượt quá 260 triệu đô la, dẫn đến khoản lỗ ròng hơn 60 triệu đô la. Nói cách khác, khoảng 50% LP của V3 đang lỗ.
Trong khi Uni V3 phổ biến khái niệm cung cấp thanh khoản đòn bẩy - trong đó phạm vi giao dịch cung cấp thanh khoản được thu hẹp và đạt được hiệu quả sử dụng vốn cao hơn bằng cách loại bỏ các tài sản thế chấp không sử dụng. Đòn bẩy này làm tăng phí kiếm được, nhưng cũng làm tăng rủi ro, vì thanh khoản có đòn bẩy cao sẽ đối mặt với tổn thất tạm thời cao hơn.
Lý do quay trở lại mục tiêu thiết kế của Uni V3: tạo thị trường tùy chỉnh. Đối với người dùng, tính chủ động cao hơn có nghĩa là các hoạt động tạo lập thị trường phức tạp hơn. Thu nhập LP phụ thuộc vào khả năng phán đoán thị trường của LP, điều này làm tăng chi phí ra quyết định của LP và dẫn đến thu nhập LP không cân bằng.Thiết kế này cũng dẫn đến hiện tượng tấn công JIT (Just In Time) (sử dụng thanh khoản tập trung của V3, thiết lập thêm và rút các vị trí LP trong một khối, cho phép phạm vi của các vị trí được xác định chặt chẽ để khớp với các giao dịch nhằm thu được phần phí giao dịch phóng đại).
Mô tả hình ảnh
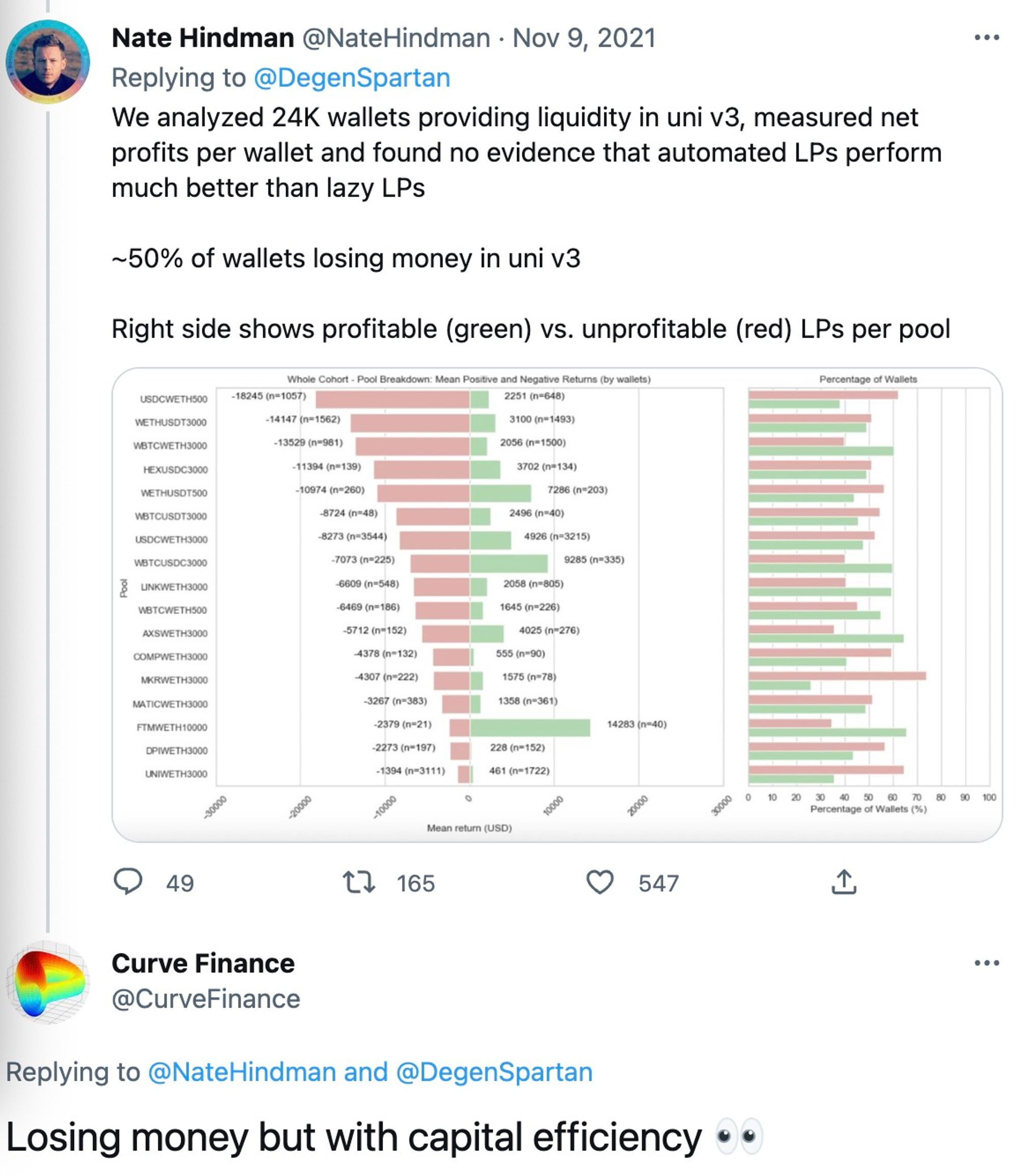
https://twitter.com/NateHindman/status/1457744185235288066? s= 20&t=jb-YsLK 25 pE 8 GuHZaMAudg
Điều này dẫn đến câu hỏi tiếp theo: Liệu người dùng có bị mất tiền dưới dạng LP khi họ đến DEX để tạo thị trường không?
Hãy trả lời ngắn gọn câu hỏi này:Việc một nhà tạo lập thị trường DEX có lãi hay không phụ thuộc vào mô hình của nhóm cung cấp giao dịch, bên cạnh khả năng chủ quan.
Không có sự khác biệt giữa nhóm mô hình AMM truyền thống - logic lợi nhuận của người dùng thông thường cung cấp thanh khoản và logic của các nhà tạo lập thị trường chuyên nghiệp. Các quỹ và báo giá bên ngoài của các nhà tạo lập thị trường bị giới hạn bởi chức năng AMM. Về bản chất, đó là một cuộc thi của TVL, quyết định ai có thể chia sẻ phí xử lý cao hơn.
Các nhóm có giá tùy chỉnh - chẳng hạn như Uni V3, Balancer V2, Curve V2, DODO V2. Loại nhóm này cho phép các nhà tạo lập thị trường chủ động can thiệp vào báo giá của nhóm. Các nhà tạo lập thị trường có thể sử dụng các công cụ này để kiếm lợi nhuận thông qua chênh lệch giá và độ trễ giữa thị trường CEX và DEX (đồng thời, có nhiều công cụ tổng hợp DEX và tốt hơn trích dẫn có nghĩa là Nhóm sẽ có xác suất bị bộ tổng hợp nắm bắt cao hơn).
Một trong những lý do tại sao LP bị mất tiền là họ chọn một kế hoạch không phù hợp với họ.
Tại sao DEX hàng đầu lại cung cấp một nhóm với mức giá có thể tùy chỉnh? Không chỉ Uni V3, khi thanh khoản phân bổ đều trên đường cong sẽ gặp phải vấn đề trượt giá cao và thanh khoản phân tán, do đó các AMM truyền thống muốn nâng cao hiệu quả sử dụng vốn có thể tham khảo Uni V3, Balancer V2, Curve V2, DODO V2 đã nói ở trên , hướng tối ưu hóa đang tiến tới thanh khoản tập trung.
Ngược lại, ưu điểm của tạo lập thị trường chủ động là người dùng có thể tập trung thanh khoản trong một phạm vi nhất định bằng cách điều chỉnh giá, v.v., điều này giúp cải thiện hiệu quả sử dụng vốn, do đó giao dịch có độ trượt giá thấp hơn và độ sâu cao hơn, nhưng nhược điểm cũng nằm ở đây, đó là ở một mức độ nhất định, nó nâng cao ngưỡng cho người dùng thông thường tham gia tạo lập thị trường. So với các nhà tạo lập thị trường chuyên nghiệp, nó phù hợp hơn với các nhà tạo lập thị trường chuyên nghiệp. Thu nhập kiếm tiền có thể tăng lên, nhưng chúng ta phải thừa nhận rằng rủi ro mất tiền cũng tăng lên Xét cho cùng, người dùng thông thường Nó không thể cạnh tranh với các nhà tạo lập thị trường chuyên nghiệp về kỹ năng chuyên nghiệp và độ nhạy cảm với thị trường.
tiêu đề cấp đầu tiên
03.
tiêu đề phụ
nhà tạo lập thị trường trong domino
Đế chế FTX sụp đổ, hàng loạt nền tảng hàng đầu bị ảnh hưởng nặng nề, các nhà tạo lập thị trường và cho vay trở thành lĩnh vực chịu ảnh hưởng nặng nề nhất: Alameda, một trong những nhà tạo lập thị trường lớn nhất trong ngành tiền điện tử, đã bị phá hủy trong trò hề này và chính thức đóng cửa vào ngày 10 tháng 11; Genesis, một công ty tạo lập thị trường và cho vay trực thuộc DCG, đã tạm dừng mua lại và phát hành khoản vay mới do bộ phận cho vay không đủ khả năng thanh toán do vụ nổ mỏ FTX và đang tìm kiếm khoản vay khẩn cấp trị giá 1 tỷ USD từ các nhà đầu tư.
Là một phần quan trọng của domino, nhà tạo lập thị trường mang lại tác động gì:
Thanh khoản thị trường giảm mạnh
Sự cố Thunderbolt của FTX—Sự sụp đổ của nhà tạo lập thị trường—Khoảng cách thanh khoản.Với sự biến mất của các nhà tạo lập thị trường hàng đầu, tính thanh khoản của thị trường có thể sẽ giảm đáng kể.Các nhà tạo lập thị trường khác cũng sẽ chịu nhiều tổn thất hơn do sự sụp đổ của FTX, điều này sẽ tiếp tục nới rộng khoảng cách. Song song với điều này là một thực tế phũ phàng rằng tính thanh khoản của tiền điện tử chỉ bị chi phối bởi một số công ty thương mại, bao gồm Wintermute, Amber Group, B2C2, Genesis, Cumberland và Alameda. Mới chỉ nửa năm kể từ cuộc khủng hoảng tín dụng Three Arrows vào tháng Năm và tháng Sáu. Khi thị trường phủ bóng trở lại, việc tạo lập thị trường trở nên khó khăn.
Theo dữ liệu theo dõi của Kaiko, kể từ khi CoinDesk công bố cuộc khảo sát về tình trạng tài sản của Alameda, tính thanh khoản của BTC trong phạm vi 2% giá trung bình đã giảm từ 11,8 nghìn BTC xuống 7 nghìn, mức thấp nhất kể từ đầu tháng Sáu. Trong bài viết này, cũng có nhiều dữ liệu cho thấy tính thanh khoản của toàn thị trường bị ảnh hưởng đáng kể bởi sự sụp đổ của Alameda và những tổn thất mà các nhà tạo lập thị trường khác phải gánh chịu.
Mô tả hình ảnh
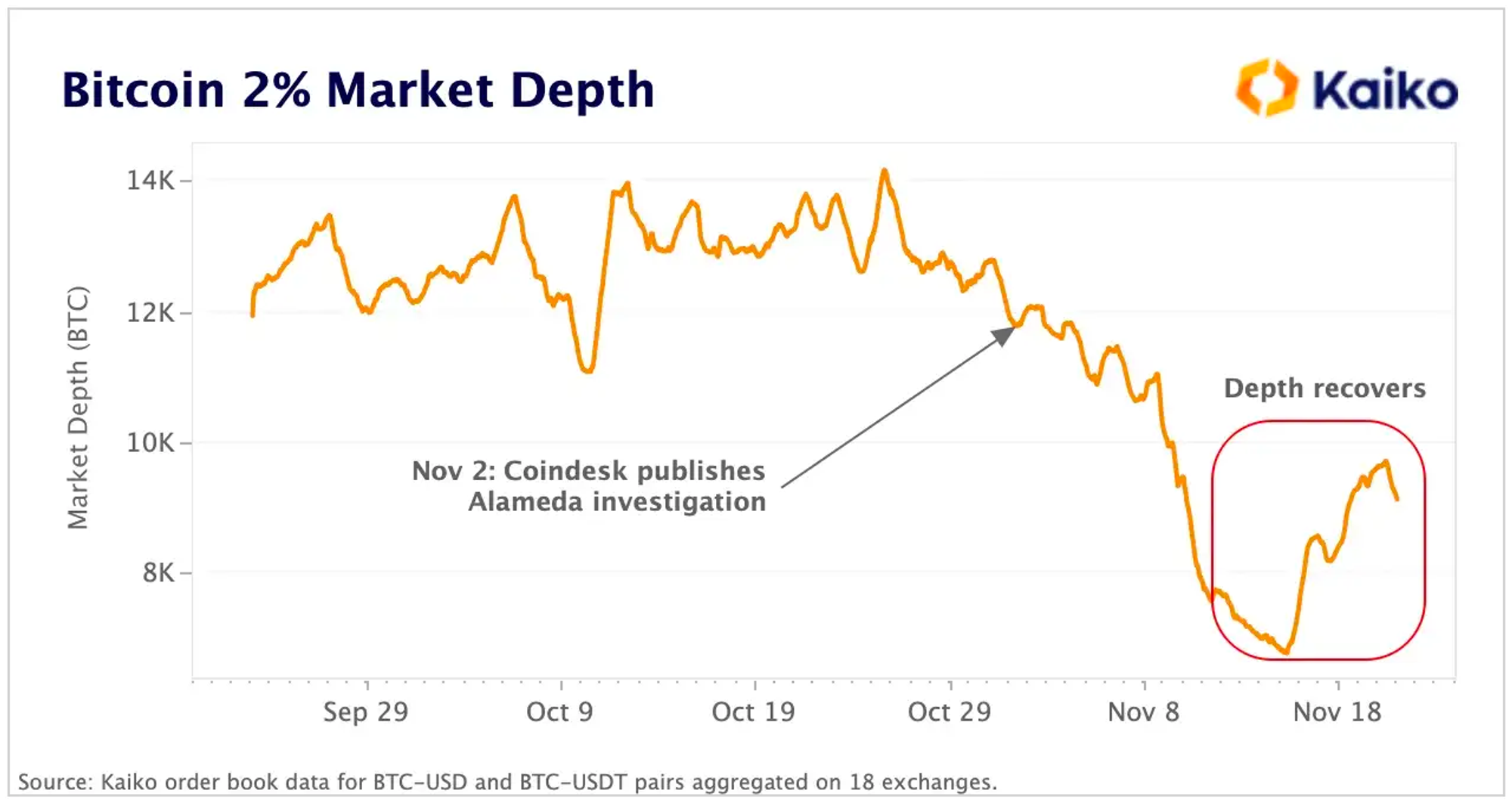
Mô tả hình ảnh
Source: Kaiko
Thanh khoản mã thông báo và thử nghiệm căng thẳng của bên dự án
Alameda đã đầu tư vào hàng chục dự án, nắm giữ các mã thông báo kém thanh khoản trị giá hàng triệu đô la (và vì Alameda cũng là nhà tạo lập thị trường nên họ cũng là nhà cung cấp thanh khoản chính cho các mã thông báo này). Mặc dù chưa rõ toàn bộ số tiền nắm giữ của Alameda với FTX, nhưng “nó là một nhà tạo lập thị trường quan trọng về mặt hệ thống”, theo chi tiết bảng cân đối kế toán của FTX do Financial Times cung cấp. Đặc biệt đối với tính thanh khoản của các mã thông báo khác ngoài BTC và ETH, đối với các bên tham gia dự án này, các điều kiện thị trường khắc nghiệt do sự cố gây ra chắc chắn là một bài kiểm tra căng thẳng rất lớn.
Ví dụ: SOL (Solana), một trong những mã thông báo được nắm giữ nhiều của Alameda Research. Alameda đã nắm giữ khoảng 1,2 tỷ đô la mã thông báo SOL vào ngày 30 tháng 6, theo báo cáo của CoinDesk. SOL, một trong những mã thông báo hoạt động tốt nhất trong đợt tăng giá năm 2021, hiện giảm 95% so với mức cao nhất mọi thời đại.
Mô tả hình ảnh
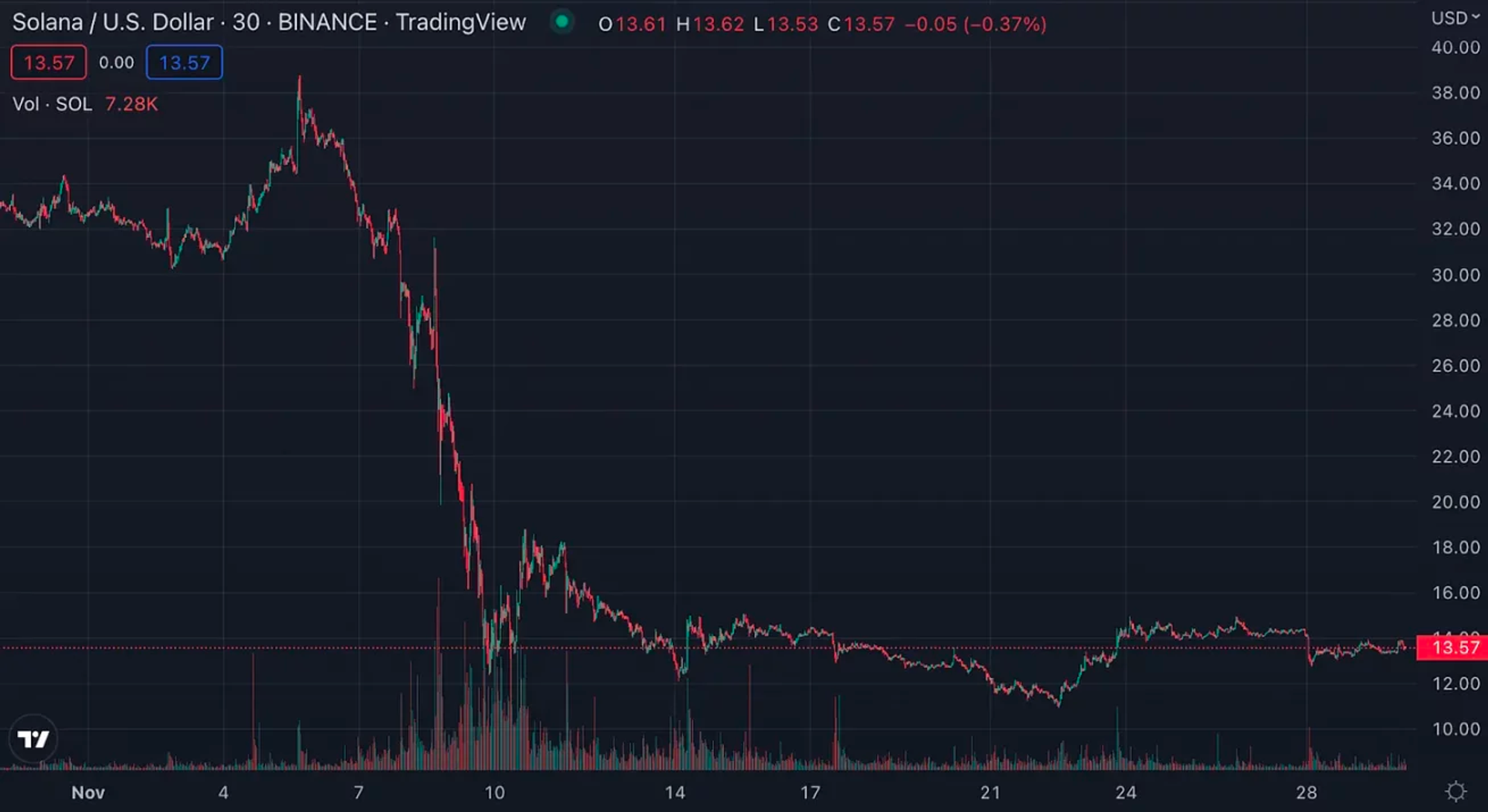
Trong những tuần sau sự bùng nổ của FTX và Alameda, SOL đã giảm mạnh từ ~$35 xuống ~$11, giảm 68,5%
Source: TradingView
Sự sụp đổ kép của niềm tin và niềm tin
Điều quan trọng hơn là sự sụp đổ kép của niềm tin và sự tin tưởng.
Niềm tin: Sự cố "Thiên nga đen" đã ảnh hưởng đến niềm tin của ngành đối với cái gọi là chuỗi công cộng hiệu suất cao và ở một mức độ nhất định đã phá hủy niềm tin của người dùng và những người ủng hộ đối với một loạt dự án sinh thái của FTX. Niềm tin đáng giá hơn vàng, và nỗi sợ hãi tồi tệ hơn địa ngục. Thị trường mã hóa đã trải qua hai khoảnh khắc Lehman trong vòng nửa năm.Sự cố Luna/Terra và Three Arrows Capital đã dạy cho người dùng biết thế nào là sự không chắc chắn và nó cũng gây ra sự hoảng loạn cho thị trường mã hóa vốn nhanh hơn cả sự lây nhiễm vi-rút.
tiêu đề phụ
Khi thị trường mất thanh khoản
Như đã đề cập trước đó, trong bất kỳ thị trường nào, tính thanh khoản là động lực đằng sau nó.
Khi xu hướng chung của thị trường đi xuống, sự ra đi của các nhà tạo lập thị trường hàng đầu chắc chắn sẽ khiến mọi thứ trở nên tồi tệ hơn, điều đó có nghĩa là nhiều dự án và khoản đầu tư có xu hướng bị đình trệ, vì vậy sẽ có một vòng luẩn quẩn khác ở đây (cho đến khi các yếu tố cơ bản phục hồi):
Mô tả hình ảnh
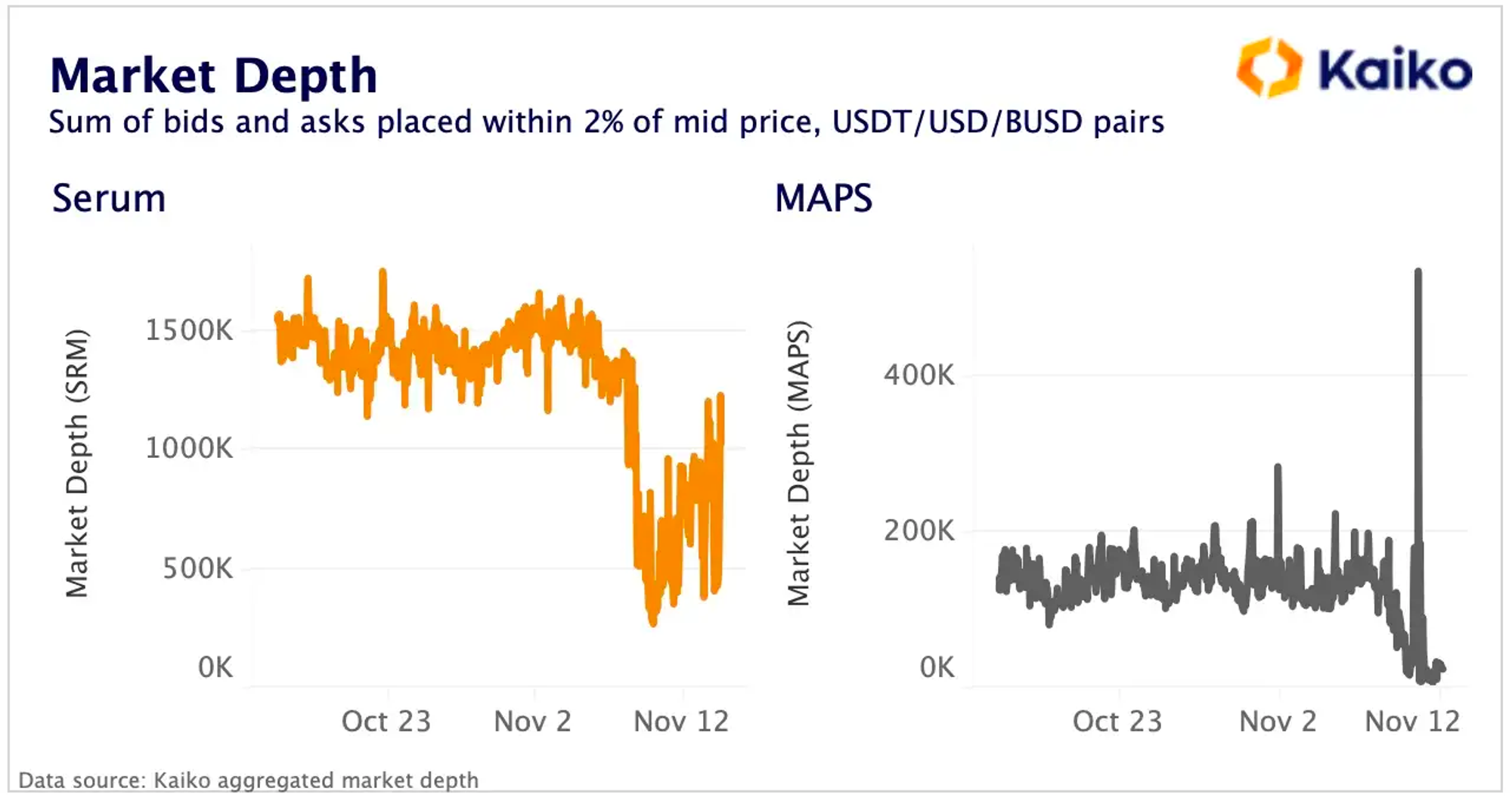
Mô tả hình ảnh
Source: Kaiko
Để duy trì tính thanh khoản trong thị trường tiền điện tử, nhiều nhà tạo lập thị trường cung cấp tính thanh khoản cho các giao dịch tài chính và trao đổi chuỗi khối. Vì vậyTrong trường hợp không có hoạt động tạo lập thị trường hoặc hoạt động tạo lập thị trường giảm mạnh, khối lượng giao dịch có thể thấp và đầu tư giảm.Ở đây chúng ta cần phân biệt: thanh khoản thường sẽ giảm khi nó biến động, điều này là do các nhà tạo lập thị trường đang rút ra các nhiệm vụ đặt giá thầu/đặt giá thầu từ sổ lệnh để quản lý rủi ro và tránh thanh khoản kém; nhưng các sự kiện khủng hoảng lớn, các nhà tạo lập thị trường Với sự sụt giảm mạnh do rút tiền, tính thanh khoản của thị trường sẽ gặp thách thức nghiêm trọng trong một khoảng thời gian.
Có thể thấy rằng sự suy giảm thanh khoản hiện tại nghiêm trọng hơn bất kỳ cuộc suy thoái thị trường nào trước đây và sự phục hồi của thị trường trong thị trường gấu là cực kỳ chậm, điều này cho thấy rằngchữ
tiêu đề phụ
DODO đáp ứng nhu cầu tạo lập thị trường như thế nào?
Như đã đề cập trước đó, chúng tôi thực sự đưa ra hai câu hỏi chính:
Khi các AMM đang tối ưu hóa theo hướng tập trung thanh khoản, khi việc trở thành LP để làm thị trường có thể trở thành thách thức, thậm chí thua lỗ, thì làm sao các nhà tạo lập thị trường được lợi?
Khi sự cố giông bão FTX gây ra sự sụp đổ của nhà tạo lập thị trường hàng đầu và sự sụt giảm thanh khoản của thị trường, làm thế nào để xây dựng lại niềm tin và thực sự sử dụng bản chất phi tập trung của thế giới mã hóa để mang lại thanh khoản khan hiếm cho các bên tham gia dự án? Mang lại sự minh bạch hiệu quả và không cần giấy phép thực sự cho các nhà tạo lập thị trường?
Đối với câu hỏi thứ hai, câu trả lời là hiển nhiên khi được hỏi: Sử dụng DEX, Sử dụng Blockchain. Hãy quay lại chuỗi, quay lại mã và quay lại "đừng tin tưởng, hãy xác minh".
Về câu hỏi đầu tiên, đã có nhiều thỏa thuận hoặc nền tảng trên thị trường cung cấp các công cụ quản lý thanh khoản tương ứng để giúp các LP quản lý rủi ro và ổn định lợi nhuận. Đây có thể là một giải pháp từ DODO: hãy để các nhà tạo lập thị trường chuyên nghiệp tham gia vào chuỗi.
hiện hữu"Phỏng vấn nhà tạo lập thị trường DODO: Cách sử dụng DODO để nâng cao hiệu quả tạo lập thị trường"Trong bài báo, nhà tạo lập thị trường Shadow Labs đã đề cập rằng sau khi trừ tiền xăng và các chi phí khác, họ có thể thu được lợi nhuận ròng từ 30-40% thu nhập công khai trên chuỗi. Ví dụ: nhóm nhà tạo lập thị trường WETH và USDC trên DODO, sau khi trừ các khoản phí khác nhau, thu nhập ròng từ đầu năm đến nay của nhà tạo lập thị trường đạt 500.000 đô la và tỷ lệ hoàn vốn ròng là khoảng 36,2%.
Làm thế nào để làm nó?
Như chúng ta đã biết, AMM thường được gọi là "thanh khoản trơ" vì không thể kiểm soát được điểm giá đưa ra cho các nhà giao dịch, đồng thời không am hiểu và linh hoạt như các nhà tạo lập thị trường truyền thống. Đây là nơi DODO bước vào và do đó đã tạo ra thuật toán PMM (Tạo thị trường chủ động). Thuật toán PMM sử dụng dự đoán giá để điều chỉnh đường cong định giá. Các tham số đơn giản và cực kỳ linh hoạt. Đường cong phẳng hơn giúp cải thiện hiệu quả tỷ lệ sử dụng vốn và giảm trượt giao dịch và tổn thất tạm thời. Liên quan đến việc cải thiện hiệu quả của các thuật toán khác nhau cho thanh khoản tập trung, vui lòng tham khảo "So sánh chuyên sâu các thuật toán tạo thị trường Uni V3, CurveV2, DODO - cải thiện hiệu quả do thanh khoản tập trung mang lại"đọc.
Ngoài những nội dung quen thuộc này, chúng tôi muốn nói về phiên bản V2 của DODO ra mắt vào tháng 3 năm nay DODO Private Pools (DPP) hay còn gọi là pool riêng, là pool được cung cấp đặc biệt cho các nhà tạo lập thị trường chuyên nghiệp để tạo lập thị trường.
Nhóm tư nhân, như tên cho thấy, có thể được tạo lập thị trường độc lập bởi các nhà tạo lập thị trường cung cấp vốn của riêng họ và cấu hình của nhóm riêng tư có thể được sửa đổi linh hoạt trong quá trình tạo lập thị trường, bao gồm tỷ lệ phí giao dịch, giá hướng dẫn bên ngoài hiện tại i, hệ số trượt đường cong K và hỗ trợ đồng thời Điều chỉnh quy mô quỹ của nhóm, v.v. Tất cả những sửa đổi này được thực hiện bằng cách kích hoạt hợp đồng thông minh bằng tài khoản có liên quan (bao gồm hai phương pháp, gọi hợp đồng DODO DPPProxy và gọi trực tiếp nhóm riêng bên dưới để thực hiện các sửa đổi tạo thị trường. Để biết các bước cụ thể, vui lòng tham khảo: Nhóm riêng DODO V2 Sự hướng dẫn vận hành). Do đó, pool này chủ yếu đáp ứng nhu cầu tạo lập thị trường của các nhà tạo lập thị trường chuyên nghiệp.
Mô tả hình ảnh
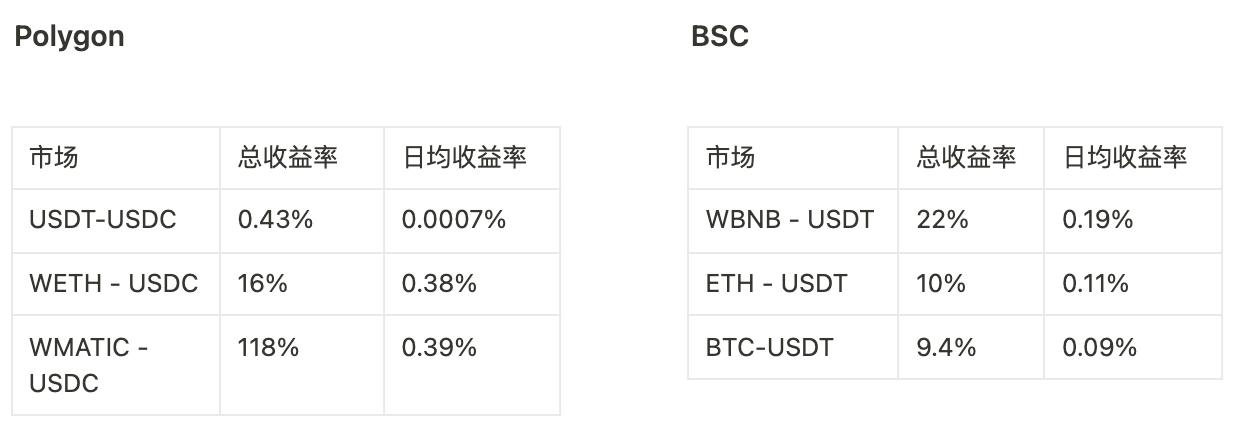
Hiện tại không có nhóm DPP trên Ethereum và hầu hết các nhà tạo lập thị trường chọn xây dựng nhóm trên chuỗi Polygon và BSC với phí gas thấp hơn
Mà còn,"So sánh chuyên sâu các thuật toán tạo thị trường Uni V3, CurveV2 và DODO - sự cải thiện hiệu quả do tính thanh khoản tập trung mang lại“Trong bài báo, việc cải thiện hiệu quả sử dụng vốn do thanh khoản tập trung mang lại được phân tích thông qua hiệu suất của dữ liệu phân phối thanh khoản. Bằng cách chọn nhóm nhà tạo lập thị trường WETH/USDC làm mẫu, bài viết cho thấy giá trị trung bình của tỷ lệ thanh khoản giữa phạm vi giá 2%, 6% và 10%. Tỷ lệ thanh khoản của nhóm tạo lập thị trường của DODO V2 cao tới 83,1% trong phạm vi 2%.
liên kết gốc
Giới thiệu về DODO
"DODO Research" là một nhóm nghiên cứu đầu tư Web3, nhóm này tiếp tục theo dõi DeFi và các dấu vết liên quan, giải mã thế giới mã hóa với chế độ xem rõ ràng và thông tin chi tiết về dữ liệu, đồng thời khám phá giá trị trong tương lai.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/DodoResearch
Đang tuyển dụng:
https://twitter.com/DodoResearch/status/1587274217082404864



