全方位解读EVM生态:哪些公链兼容 EVM?哪些不兼容?
原文标题:《深入解读 EVM 的生态帝国》
原文作者:GravityX Capital
原文编译:Captain Hiro,DeFi 之道
以太坊虚拟机(EVM)是区块链开发者中的事实标准,它背后有一个巨大的社区支持。这导致其他兼容以太坊虚拟机的区块链也开始探索这个系统,而非以太坊虚拟机兼容的区块链则在此基础上建立以太坊虚拟机兼容层。
铁子们,接下来就让我们深入了解一下以太坊虚拟机兼容性的相关内容!

在推出取得有限的成功后,所谓的 「以太坊杀手们」正在链上建立解决方案,以进一步支持以太坊虚拟机。例如,波卡的 Moonbeam,NEAR Protocol 的 Aurora,Cosmo 的 Evmos 以及 Solana 的 Neon。
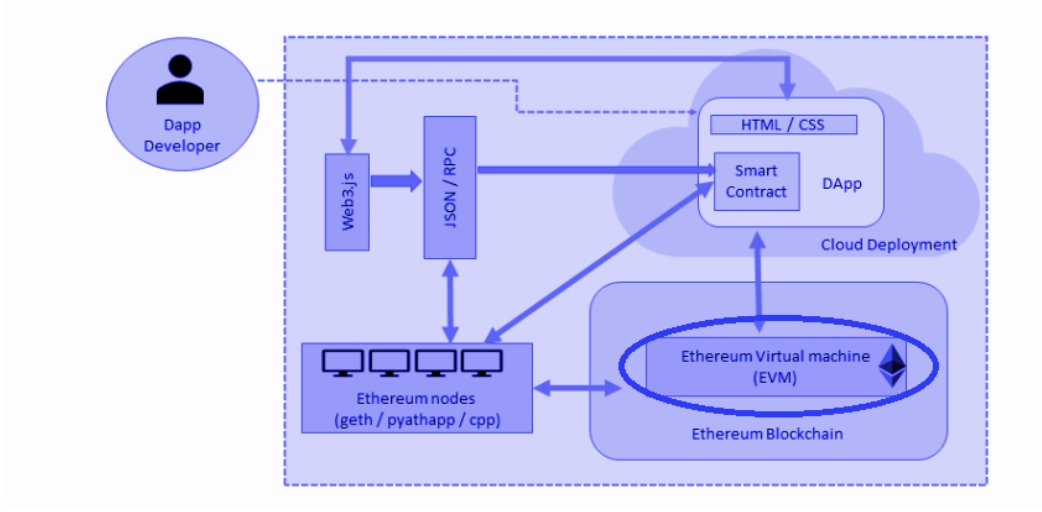
什么是 EVM?
以太坊虚拟机负责定义计算区块到区块间新的有效状态的规则。以太坊虚拟机是每个以太坊节点内的一个强大的沙盒式虚拟堆栈,它负责合约字节码的执行。
当前,以太坊的开发者正在领导 Web3 的开发活动,每月约有 4000 多名活跃的开发者。以太坊继续拥有最大的工具、应用程序和协议的生态系统,它是第二大生态系统的 2.8 倍。每五个新的 Web3 开发者中就有一个在以太坊上进行搭建工作。
Solidity 和以太坊虚拟机是区块链的事实标准。
以太坊是第一个允许链上智能合约执行的区块链,为此,他们发布了 Solidity,一种与以太坊虚拟机兼容的编码语言。几乎所有成功的去中心化应用程序(dApp)都使用了 Solidity 和以太坊虚拟机来执行智能合约。
随着以太坊开始获得更多的使用和关注,网络上出现了很多不同的工具来缓解和加快智能合约在以太坊(以及以太坊虚拟机)上的执行和部署。你可能知道像 Truffle、Ganache、Infura、OpenZeppelin、Hardhat 等协议。
除此之外,以太坊还是第一个部署智能合约的网络,而现在它仍然是竞争链中的黄金标准。但由于其规模和巨大的用户数量,以太坊的可扩展性现在已成为了一个不容忽视的问题。
EVM 兼容链
其他无权限区块链通过提供更低的 gas 费用和更快的交易,迅速对当前以太坊上的问题做出了反应。但这些区块链的开发者并没有开发新的实现智能合约的方式,而是简单的复制了以太坊网络的部分内容。
这些以太坊的竞争链提供了什么?
对于消费者来说,与以太坊虚拟机兼容的链提供更便宜的 gas 价格,更快的交易和与以太坊相同的地址格式,这提供了用户友好的环境。它加速了流量和生态系统的扩展,因为以太坊的用户可以轻松过渡到其他链。
而对于开发者来说,兼容以太坊虚拟机的链建立了一个与以太坊虚拟机相当的代码执行环境。这意味着以太坊开发者可以快速和轻松地将协议部署到其他竞争链上,而不必从头开始创建代码。
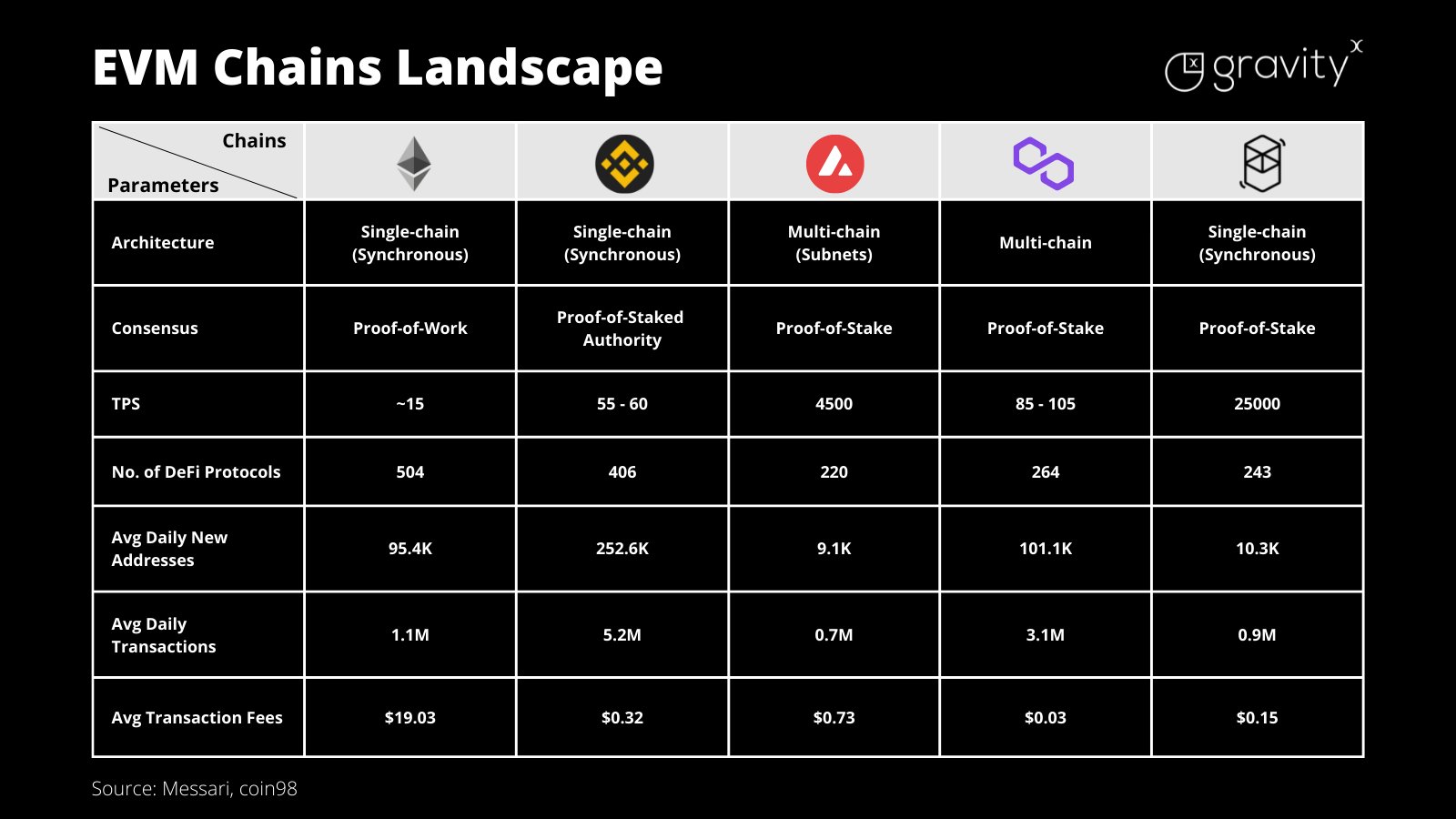
当前,围绕着以太坊虚拟机兼容链发展出了一个巨大的生态系统,如 Avalance,币安智能链,Fantom,以及第二层解决方案,如 Arbitrum 和 Optimism。大家可以从下图看到基于以太坊虚拟机的智能合约平台的比较:
非 EVM 兼容链
各种区块链介入解决以太坊的可扩展性问题,它不支持以太坊虚拟机并使用不同的虚拟机标准,如 CosmWasm。这些区块链链的流行例子是 Solana、Cosmos、Near Protocol 和波卡。
非 EVM 区块链启用 EVM
最初,那些发布的没有兼容以太坊虚拟机的区块链有优越的设计,如流行的编程语言和速度。而在包括以太坊虚拟机的兼容性后,这些区块链放弃了它们最初的目标,即开发一个替代以太坊的技术栈。
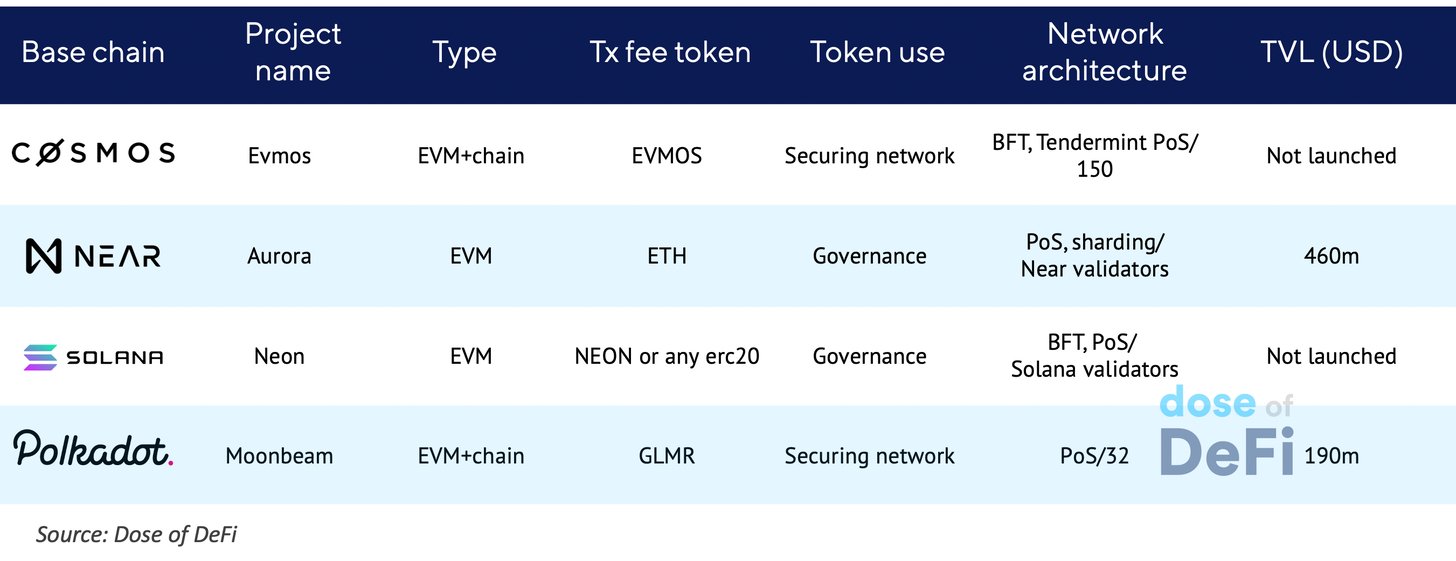
在非 EVM 链上建立 EVM 兼容性的项目
NEAR Protocol 上的 Aurora
波卡上的 Moonbeam
Cosmos 上的 Evmos
Solana 上的 Neon
Oasis Swao 上的 Oasis Emerald Paratime
Algorand 公布的计划
Aurora 是一项使以太坊合约在更高性能的环境中,即 NEAR 区块链上执行的技术,这是一个当代的第一层区块链,它的速度快(2-3 秒完成交易),可扩展强,而且环境友好。
波卡和 Cosmos 是多链区块链,它们分别支持 Moonbeam 和 Evmos。它们选择不与主虚拟机一起实施以太坊虚拟机,而是专门为其提供一个子链。
Moonbeam 是支持以太坊虚拟机兼容性并在波卡上部署去中心化应用程序的平台。随着项目不断部署到 Moonbeam,它已经成为为网络带来实用性和互操作性的关键所在。
Cosmos 上的 Evmos 是一个与应用无关的链,它将通过 IBC(区块链间通信)与以太坊主网、以太坊虚拟机兼容环境和其他 BFT(拜占庭容错)链进行互操作,使用户和开发人员能够轻松地在链之间转移价值。
Neon 是一个虚拟机,它允许开发者使用 Solana 的可扩展性、流动性和以太坊的工具。这意味着去中心化应用程序开发者可以获得较低的 gas 费用,更快的交易,并行的交易处理,高吞吐量,以及对 Solana 市场的访问。
Oasis 网络上的 Emerald Paratime 旨在通过将吞吐量提高到每秒 1000 笔以上来降低交易成本。该以太坊虚拟机支持去中心化应用程序,包括 DeFi(去中心化金融)、NFT、元宇宙和加密货币游戏项目。此外,它还实现了跨链的互操作性。
Algorand 最近宣布了 2000 万美元的资金,以加速其生态系统的发展。其基金会官员表示,1000 万美元的拨款将用于能够提供以太坊虚拟机兼容性解决方案的开发者。
具有 EVM 兼容性的 rollup
zkEVM 是一个虚拟机,它可以与零知识证明计算兼容的方式执行智能合约。
Hermez zkEVM 是一种优化的 zkEVM 兼容技术,它提供完全的 OPCODE 兼容性和以太坊的安全性。
Scroll ZK rollup 是一个兼容以太坊虚拟机的 rollup,它具有强大的网络,一个强大的外包机制,激励使用者(roller)产生零知识证明,并且与所有现有的以太坊基础设施兼容,无需进行任何修改。
以太坊虚拟机的环境可以作为资产从以太坊虚拟机链进入这些基础链的入口。用户将选择对他们来说方便和安全的桥。下面的图形描述了 Cosmos Hub 和 Evmos 与以太坊虚拟机链的互动。
以太坊虚拟机是智能合约执行的事实标准。它促进了流动性从以太坊区块链转移到这些更快、更便宜和可扩展的以太坊虚拟机解决方案。此外,随着以太坊虚拟机周围的开发者社区不断增长,它将解决以太坊主链的大部分问题。



