全面解析PoS质押市场:Staking会推动下一轮牛市吗?
原文作者:Glaze 和 Fundamental Labs Research
原文编译:DeFi 之道
内容要点
1.我们把 PoS 质押分成了三部分:节点供应商、液态质押池、金融衍生品
2.大玩家已经主导了整个质押市场
3.新玩家可以通过支持长尾资产,以及更好的用户体验进入市场
4.质押市场仍有以下机会:
数据分析工具
用于启动节点供应商业务的工具包
长期固定利率的定投衍生品
更好的代币经济学设计
引言
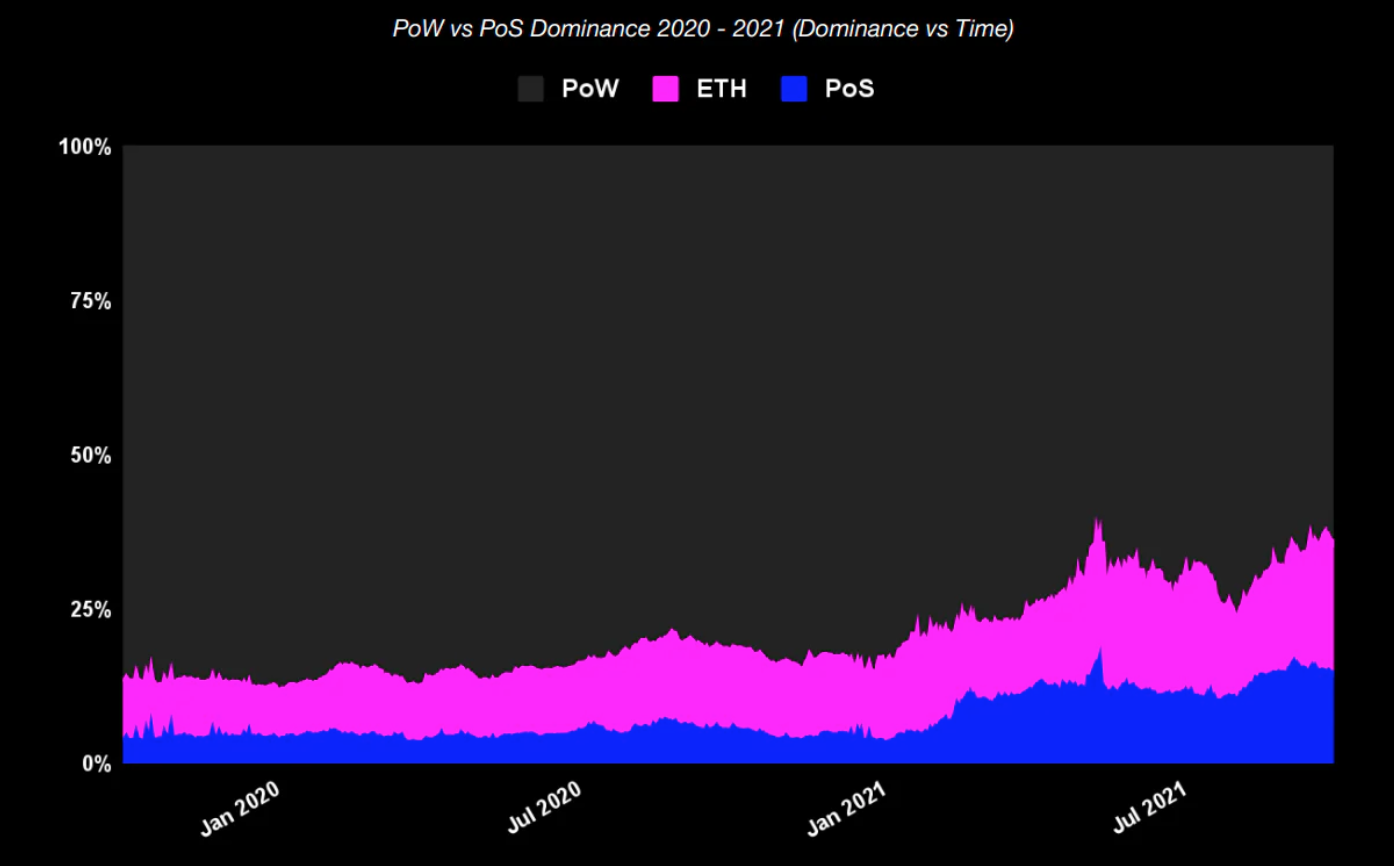
为了获得更高的每秒钟交易量(TPS)和效率,以太坊正在从工作量证明(PoW)过渡到权益证明(PoS)。大多数支持智能合约的主要区块链都使用了权益证明,如 Solana、Cardano 和 Avalanche。
资料来源:2021 年质押生态系统报告
大多数区块链都转向了权益证明,因为与工作量证明方法相比,权益证明使它们能够接受高性能、更快的结算速度、环境可持续性、可扩展性、较低的安全成本以及灵活的架构。
来源:2021 年质押生态系统报告
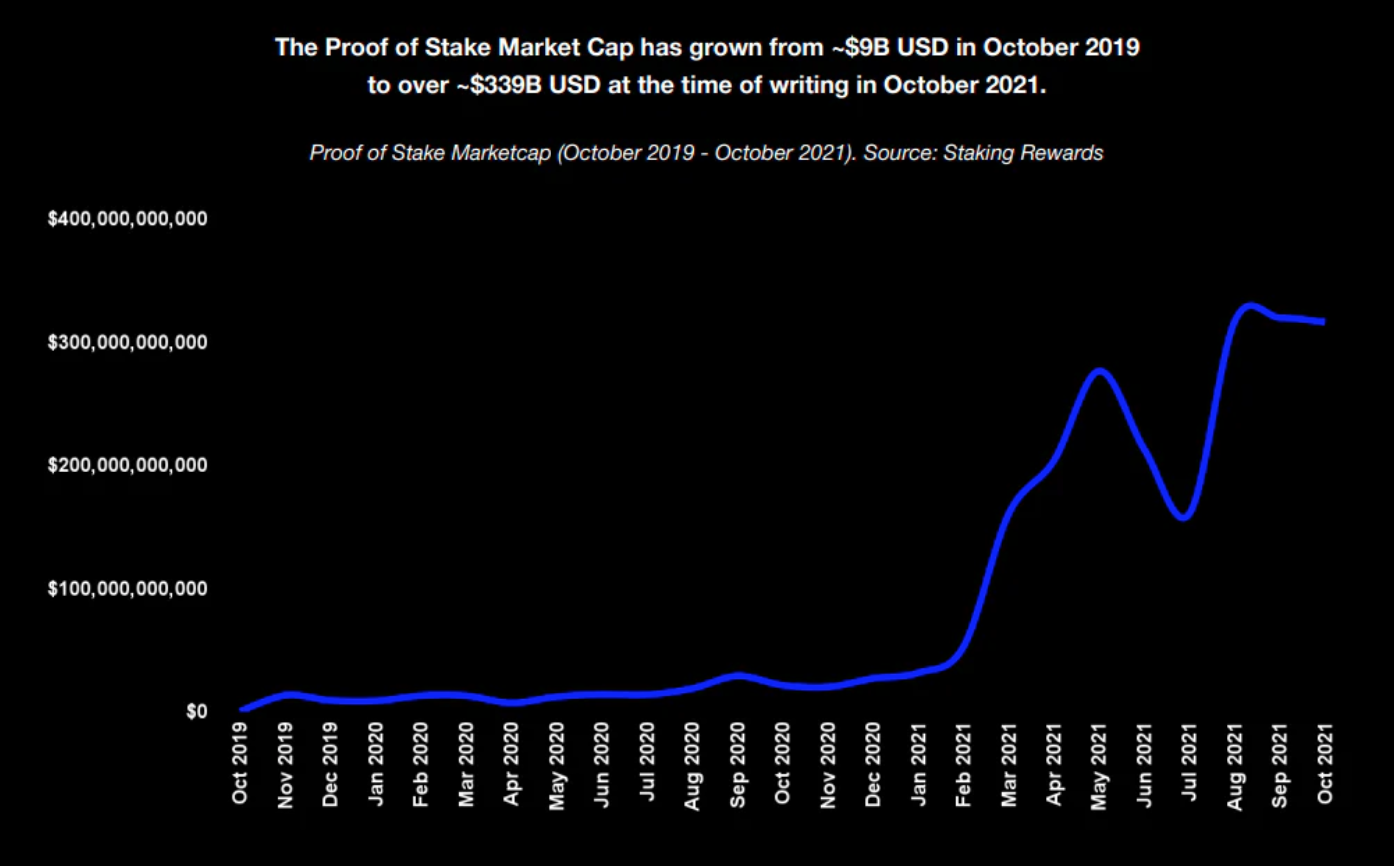
权益证明为用户提供了一种获得稳定收益的新方式。它将原生资产委托给质押节点,这样进行质押的用户就可以获得平均 10%~20% 的年化收益率。这种方式就像国家的国债一样,它是稳定的,低风险的,它比流行的 DEX(去中心化交易所)和借贷平台上的稳定币挖矿更有利可图。
希望这些加密货币国债可以帮助投资者克服法币通货膨胀。下面的图表说明了世界各地的通货膨胀率。法定货币的通货膨胀率约为 3% 到 6%。
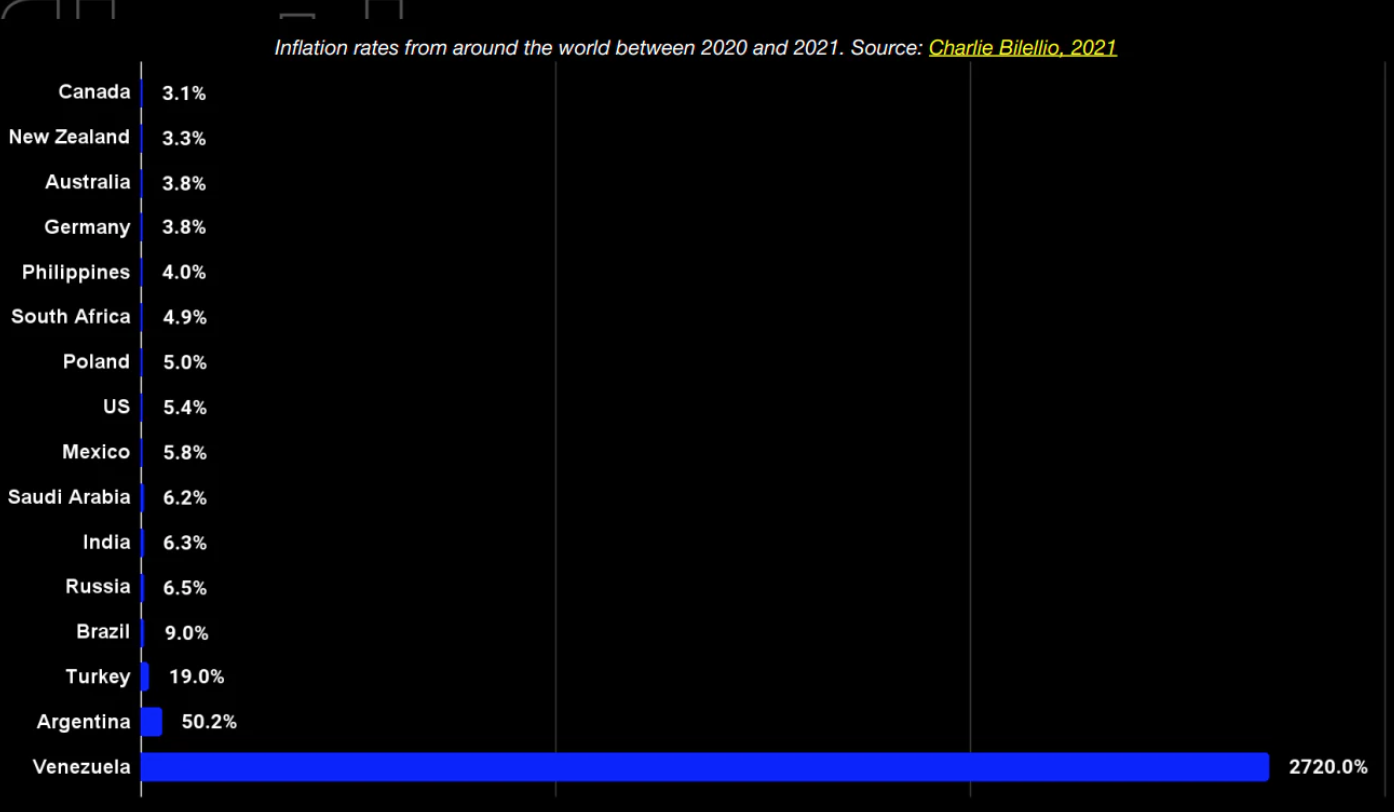
资料来源:2021 年质押生态系统报告
质押的机制
不同的区块链有不同的质押机制,这些机制在提现期和罚没(slashing)规则上有所不同。
以太坊
为了实现可持续性和可扩展性,以太坊正在从工作量证明转向权益证明。
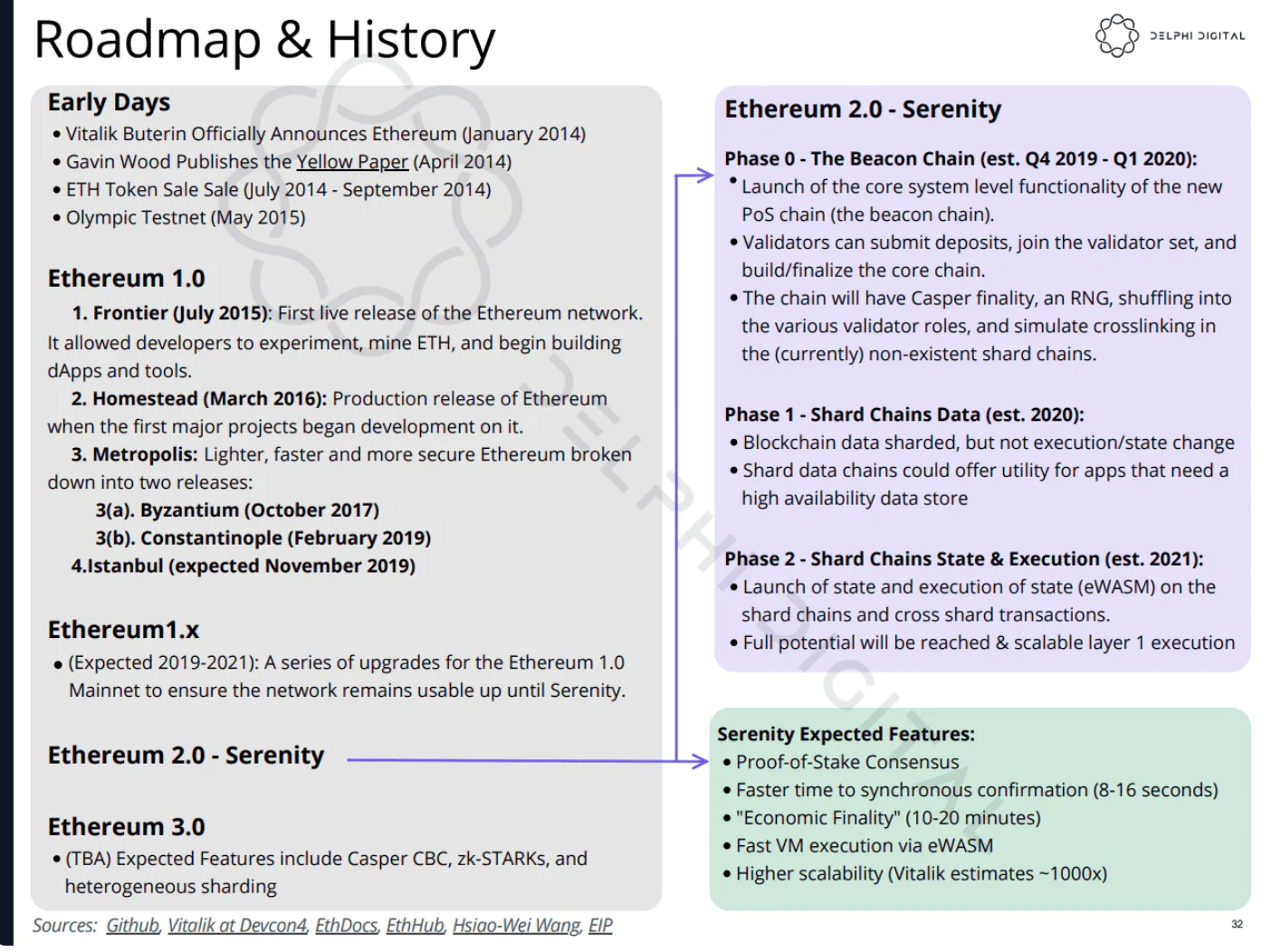
资料来源:Delphi Digital
以太坊将质押的定义描述如下:“质押是指充值 32 个 ETH 来激活验证器软件的行为。作为验证者,你将负责存储数据,处理交易,并向区块链添加新的区块。这将为每个人保持以太坊的安全,并在这个过程中为你赢得新的 ETH。这个过程被称为权益证明,由信标链引入。”
简而言之,为了成为质押者,用户需要质押 32 个 ETH 并运行一个验证器节点。用户至少要在以太坊区块链合并后才能提走自己质押的 ETH。
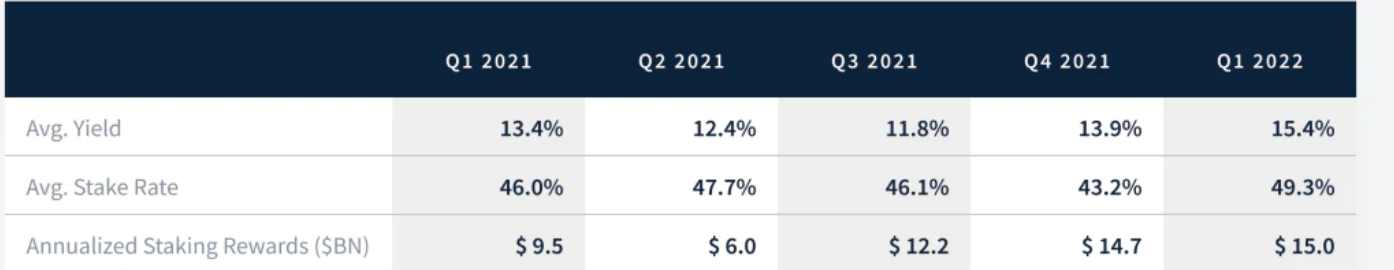
目前,在不扣除服务器成本的前提下,在以太坊上进行质押的用户将获得约 4.2% 的年利率。Kraken 在《2022 年第一季度质押状况》的报告中预计,在以太坊主网合并后,质押用户的年利率将增加到 8.5%-11.5%。
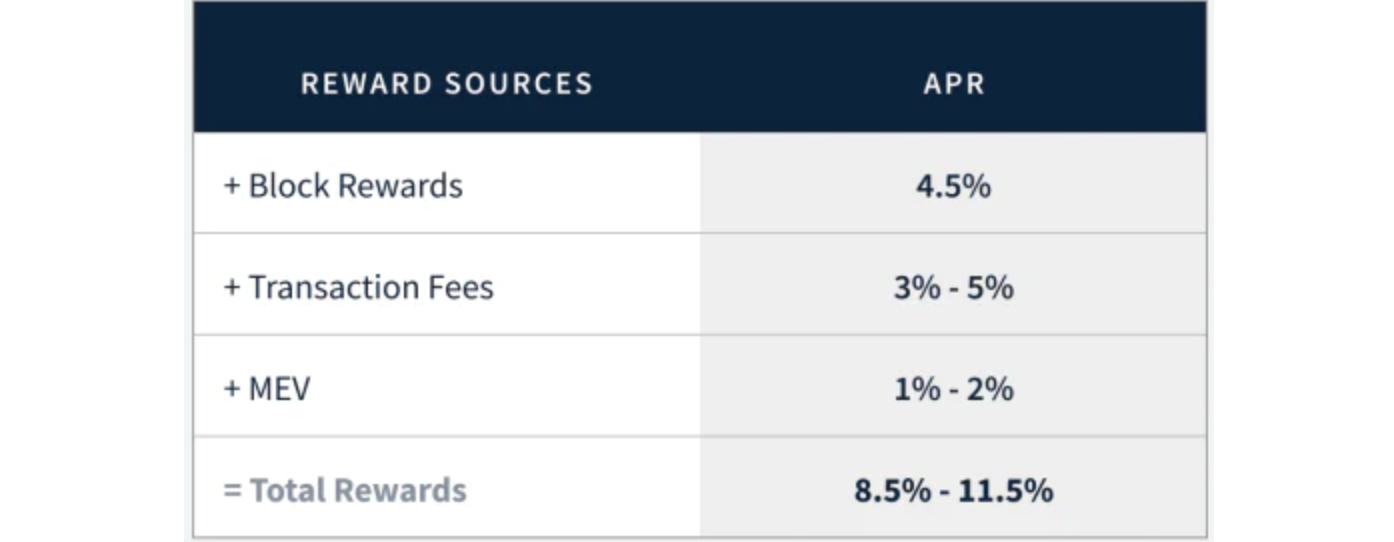
来源:2022 年第一季度的质押状况
运行以太坊节点不需要什么高端的硬件,节点服务器的成本相对较低。推荐的规格是:
超过 4 核的 CPU
16 GB 以上的内存
至少有 500 GB 自由空间的 SSD
超过 25 MBit/s 带宽
基于节点类型,磁盘空间的要求从 400 GB 到 6 TB 不等。
在 ETH2 网络中,一个提议者(proposer)挖出新的区块,证明者(attester)通过投票赞成这个区块是否成为区块链的一部分。
罚没意味着验证者违反了规则,被迫退出。有三种罚没条件:
作为提议者,该节点为一个区块签署了一个以上的信标区块
作为证明者,节点在同一目标上签署了一个以上的证明
作为证明者,节点签署了与历史冲突的证明
如果这些行为中的任何一个被发现,那么该节点将在未来 36 天左右被迫退出信标链。惩罚将在 36 天左右继续发生,直到节点可以退出。惩罚数量将根据网络状况而发生变化。
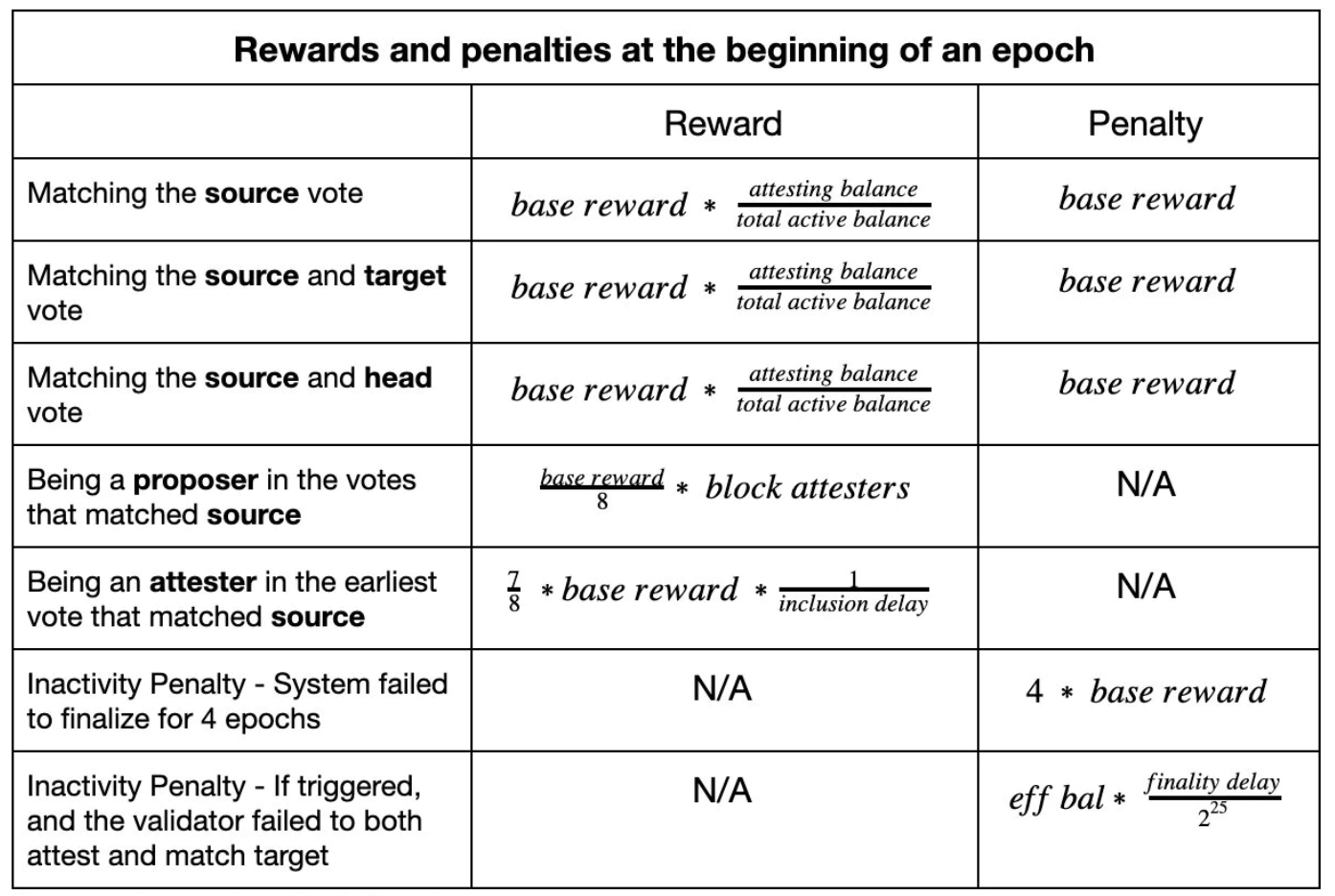
罚没迫使验证者退出网络,但惩罚不会。用户受到惩罚的条件可以归为以下几类:
验证者惩罚
不活跃的泄漏惩罚
当前,以太坊网络总共有 13310531 个 ETH 被质押,总共有 39.6982 万个验证者。下面的图表说明了 ETH2.0 的质押率和质押的 ETH。
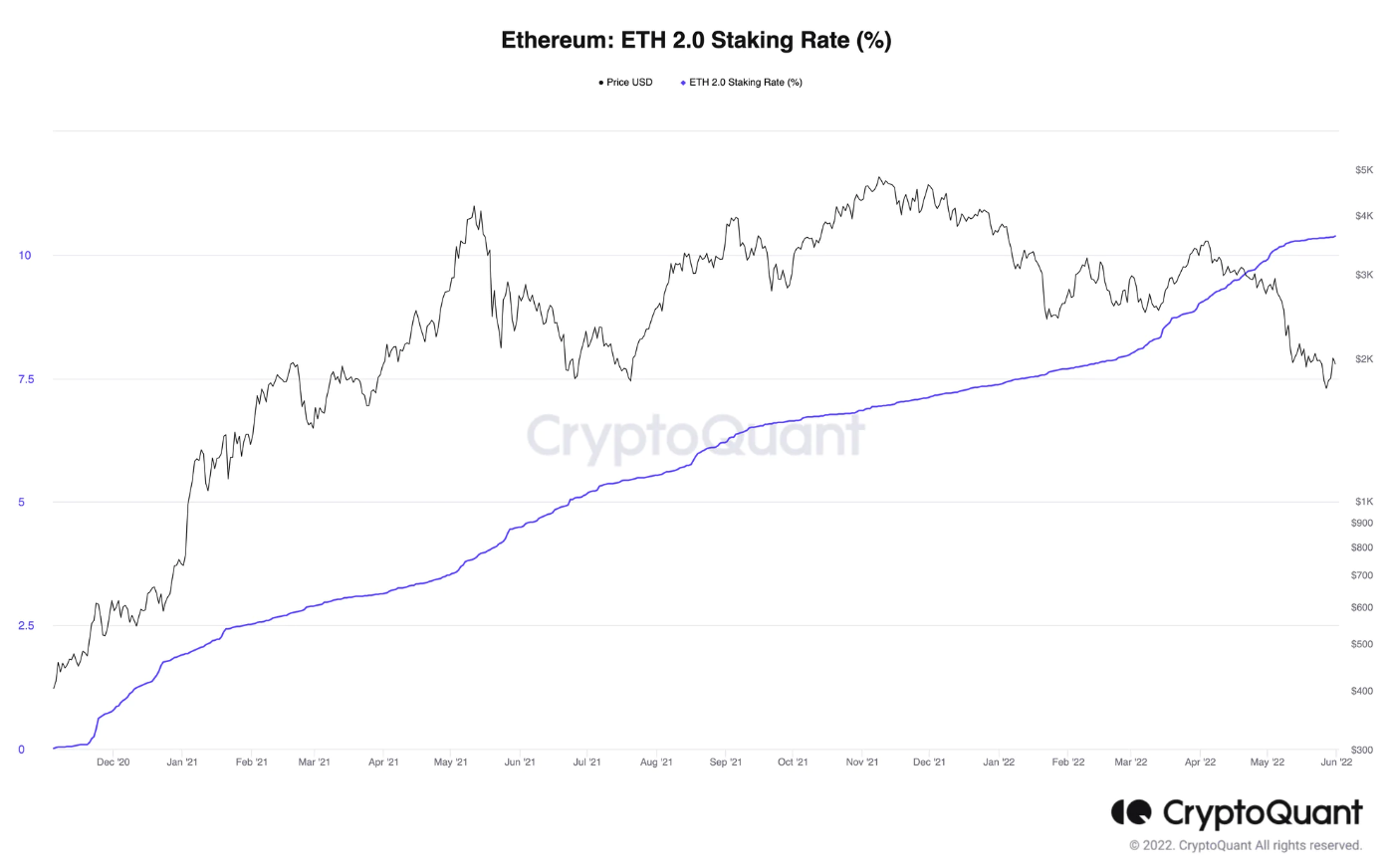
资料来源:CryptoQuant
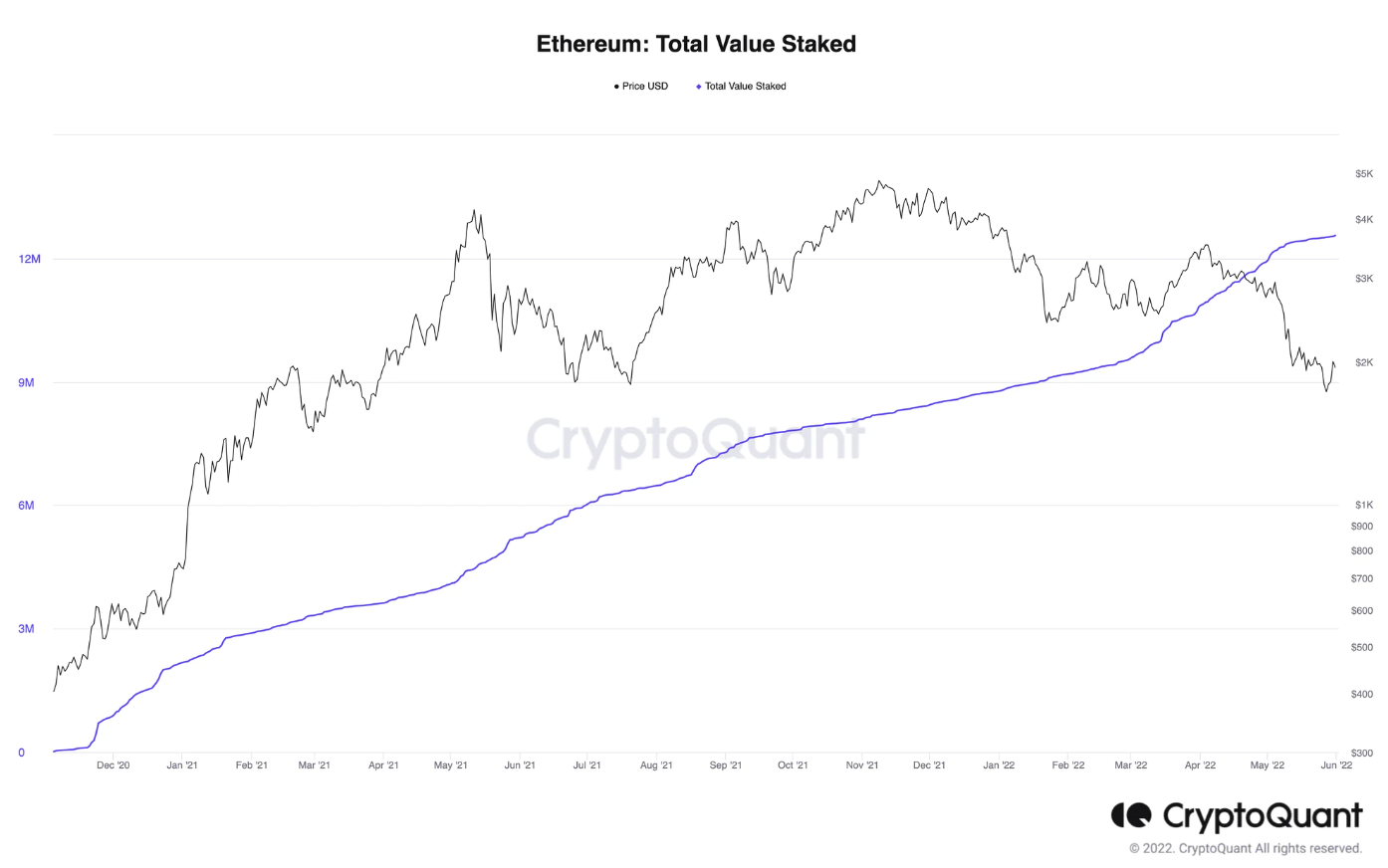
资料来源:CryptoQuant
质押流入图显示了一些流入的高峰时间点。一些大的流入发生在 2020 年 12 月和 2022 年 3 月。
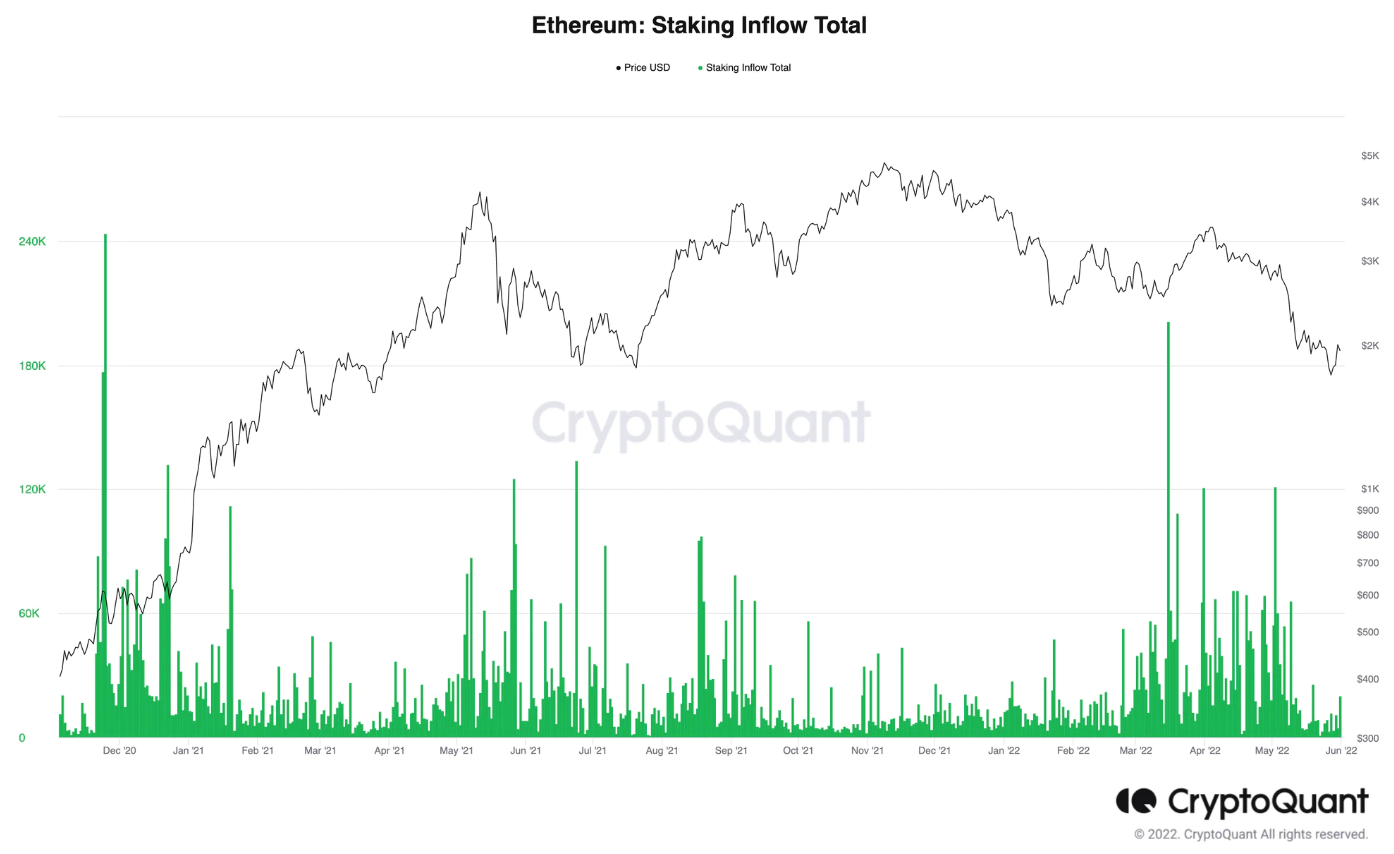
资料来源:CryptoQuant
Kraken 是 ETH2.0 的第一个参与者。中心化交易所是在质押市场上仍有优势。它们可以把它们的现有用户变成 ETH 2.0 的购买者。
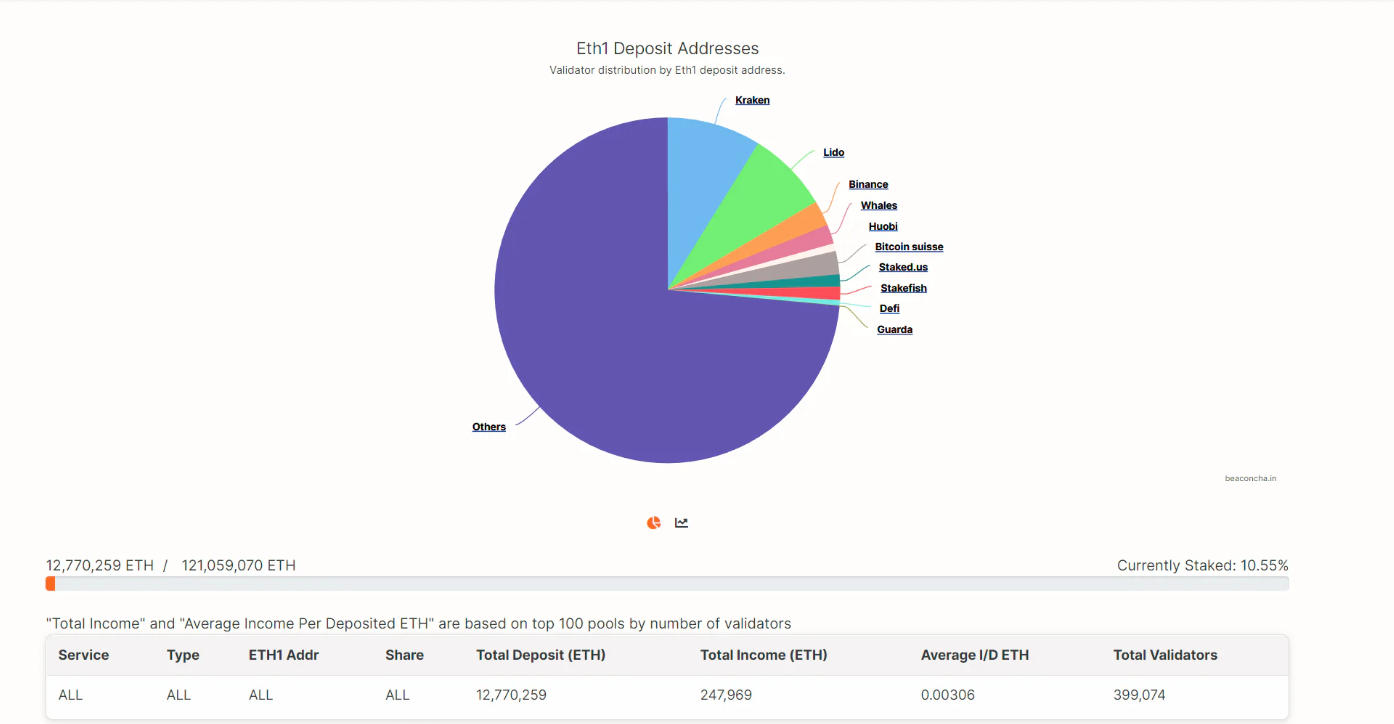
资料来源:以太坊 2.0 信标链(第 0 阶段)区块链浏览器——质押池服务概述
对于液态质押来说,Lido 在市场上占主导地位。液态质押衍生品帮助用户将其质押资产变现,从而提高资本效率。
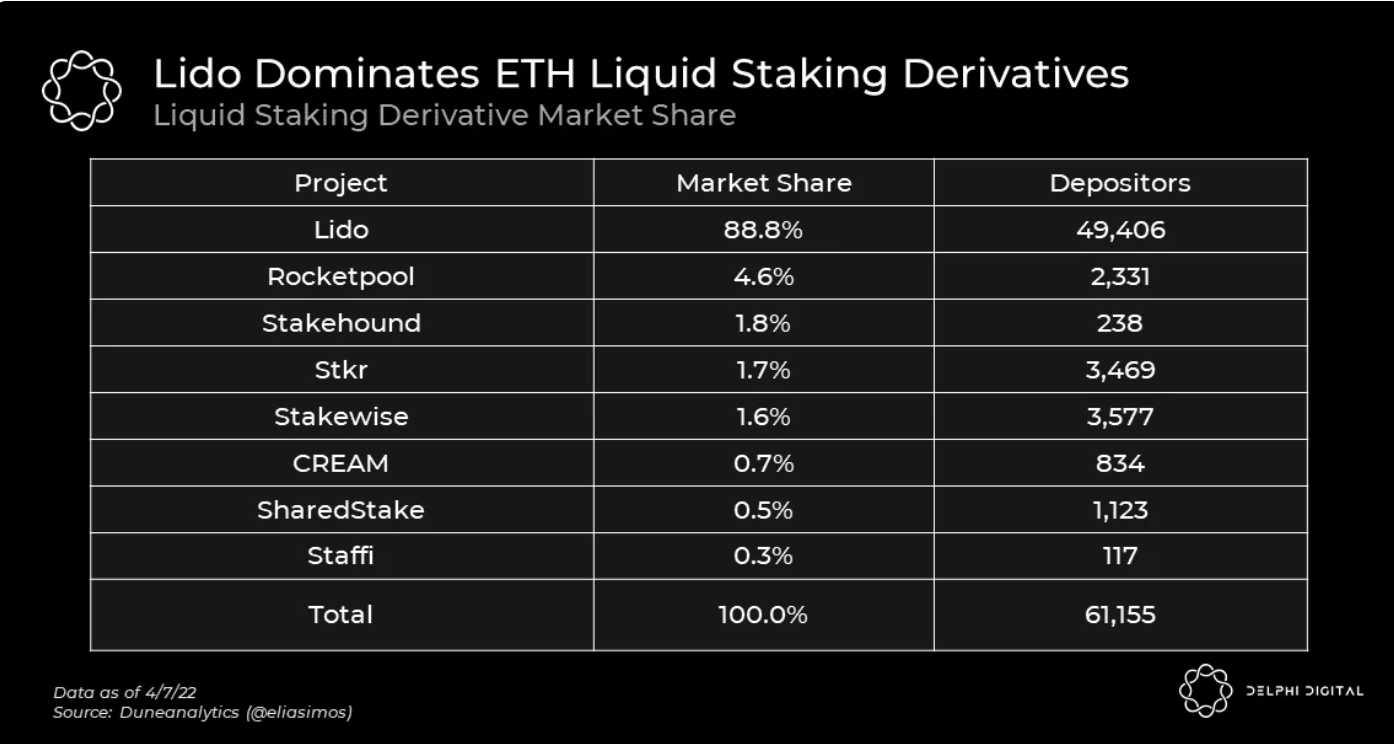
资料来源:Delphi Digital
竞争链
很多支持智能合约的区块链因考虑到 TPS 和可持续性而使用权益证明。
它们有不同的规则。一些区块链允许用户将他们的质押委托给活跃的验证者。这些验证者运行节点,并从委托抵押中收取佣金费用。用户要想撤回他们的质押就需要等待一段时间才能取消委托。
目前,以太坊 2.0 的质押率是最低的。
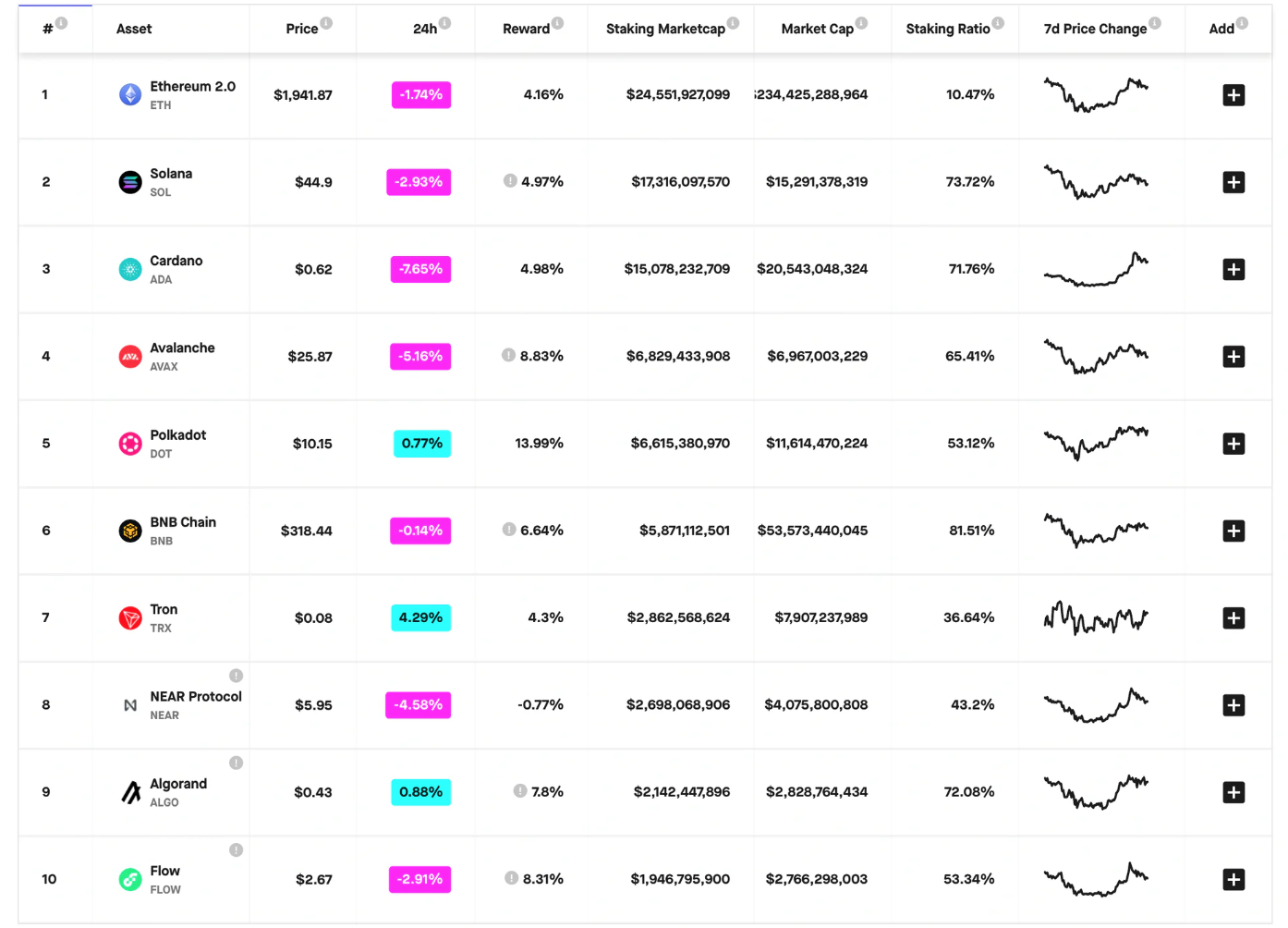
资料来源:Staking Rewards
节点供应商
运行自己的质押节点将会面临很多风险,并且需要大量的资金来启动。个人很难维持一个 24/7 的在线服务器,并且不做错事造成惩罚。为了帮助个人更容易地进行质押和赚取奖励,市场上出现了质押即服务。节点供应商将负责管理基础设施,用户只需要把他们的资金在节点供应商提供的平台上进行质押即可。
节点供应商提供节点操作服务。他们向个人和液态质押衍生品提供服务。对个人而言,节点提供商每月收取节点操作费或佣金费。而对流动质押衍生品而言,节点提供者通常会得到质押奖励的一个百分比。Lido 解释了他们如何选择节点运营商。
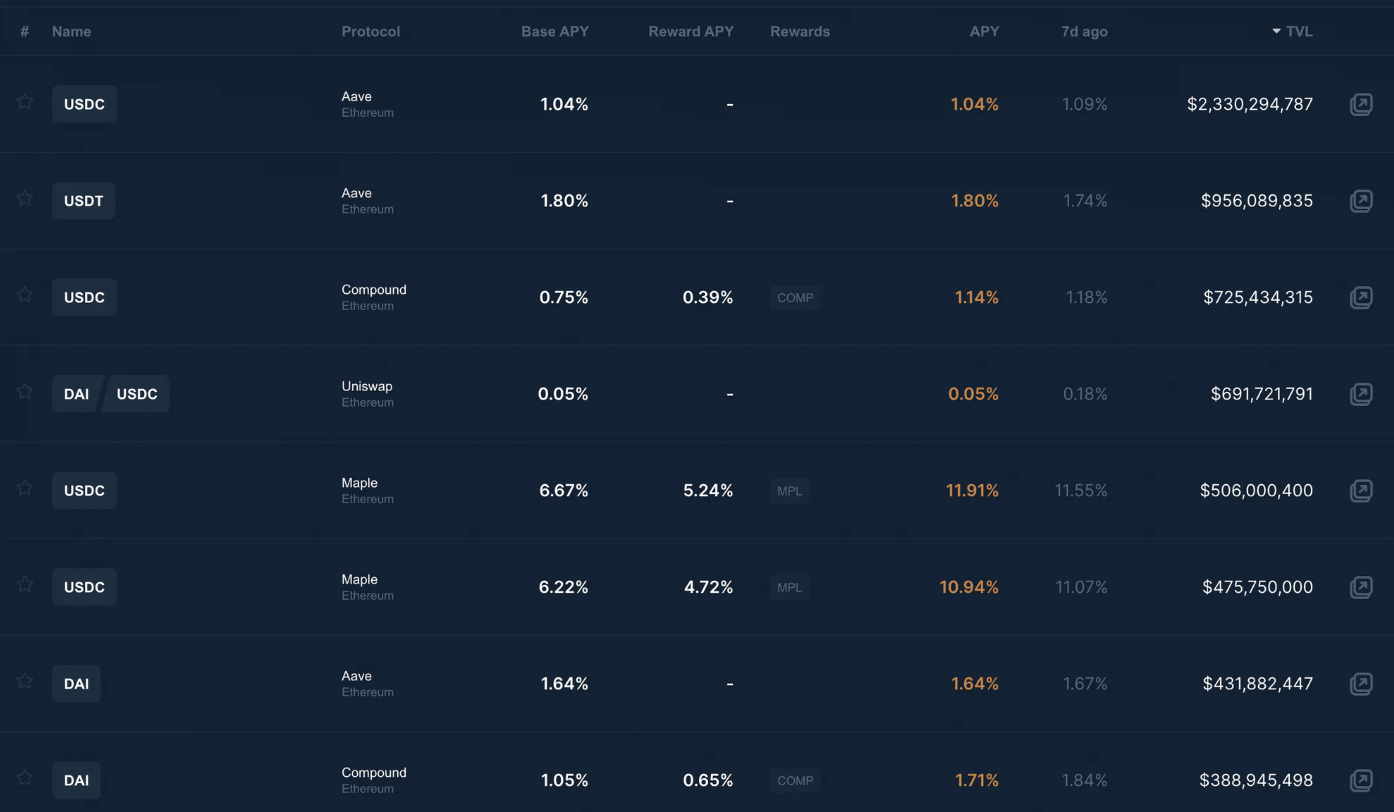
市场上有很多节点提供商,它们在以下方面有所不同:
费用
支持的资产
可靠性和安全性
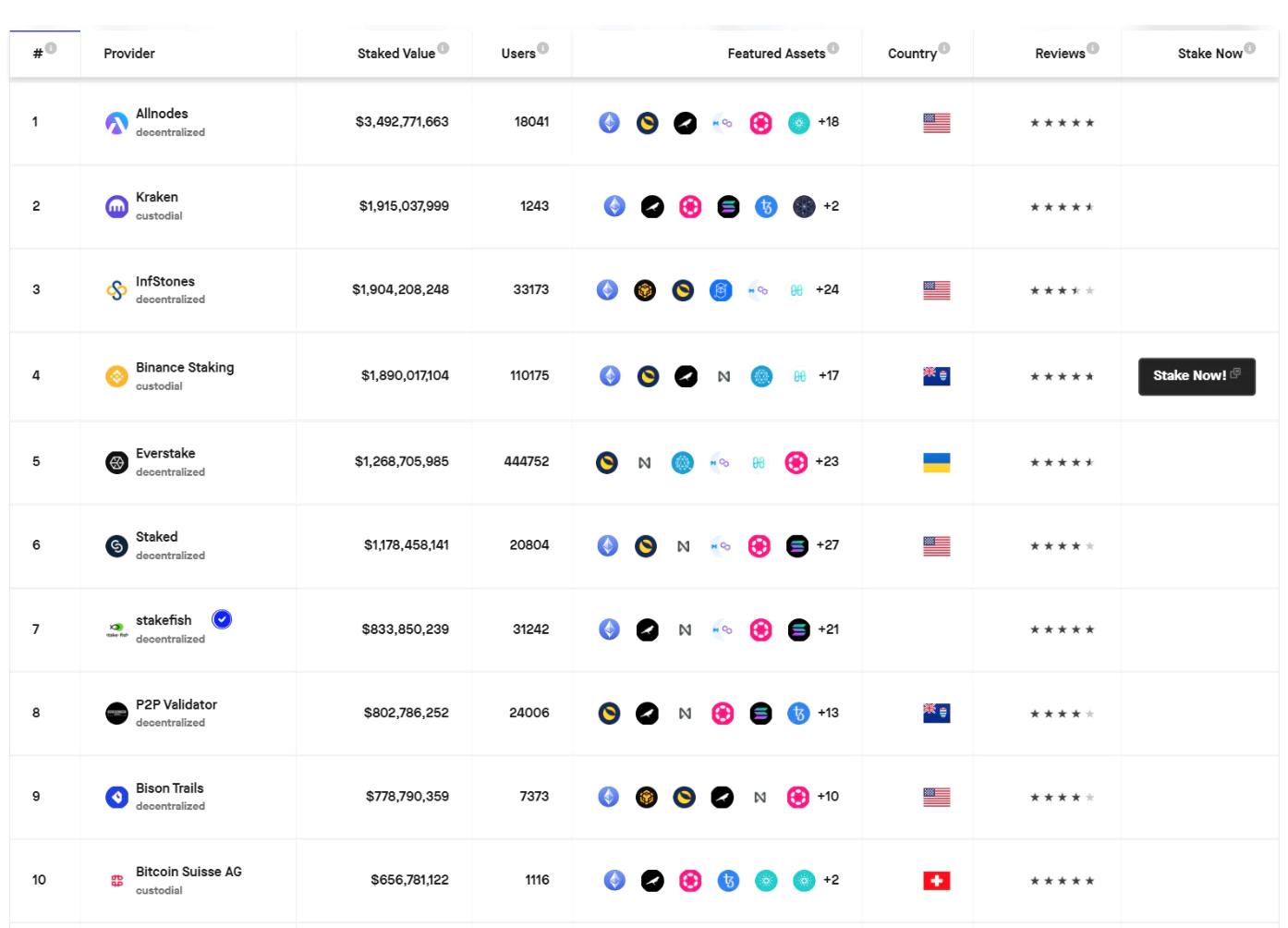
来源:Staking Rewards
一些大玩家已经建立了庞大的用户群,良好的声誉,以及安全的运营记录。在这种情况下,新玩家很难占据大量的市场份额。大的市场参与者认为小的参与者的机会有以下几点:
更好的用户体验
支持长尾资产
提供除质押以外的服务,如生态系统更新、简单的金融工程师工具、信息网站和数据分析工具
尽管小玩家很难与大玩家竞争,但是与此同时,大玩家确实也面临着一些挑战:
中心化风险
合规性
安全和运营风险
去中心化是一个网络的关键。@djrtwo 在他的文章《液态质押衍生品的风险》中对此提出质疑。如果几个节点供应商在网络中拥有主要利益,那么这些节点供应商就是联合垄断的一个阶层。
要建立一个去中心化和无许可的产品,合规是一个大问题。Stake.fish 在《2021 年质押生态系统报告》中认为,“由于质押在某种意义上看起来像固定收益,这可能会招致监管者认为验证者比矿工更接近于金融实体。如果发生这种情况,那么验证者将没有办法保持合规,而不成为一个完全许可的托管人并守护委托人的访问权(这在技术上可能又是不可能执行的)。”
节点运营商把安全放在第一位,因为安全事故会造成资产损失。2021 年 1 月,ETH2 验证者由于一个错误而被罚没。以下是 ETH2 验证器的近期遭受罚没的历史。
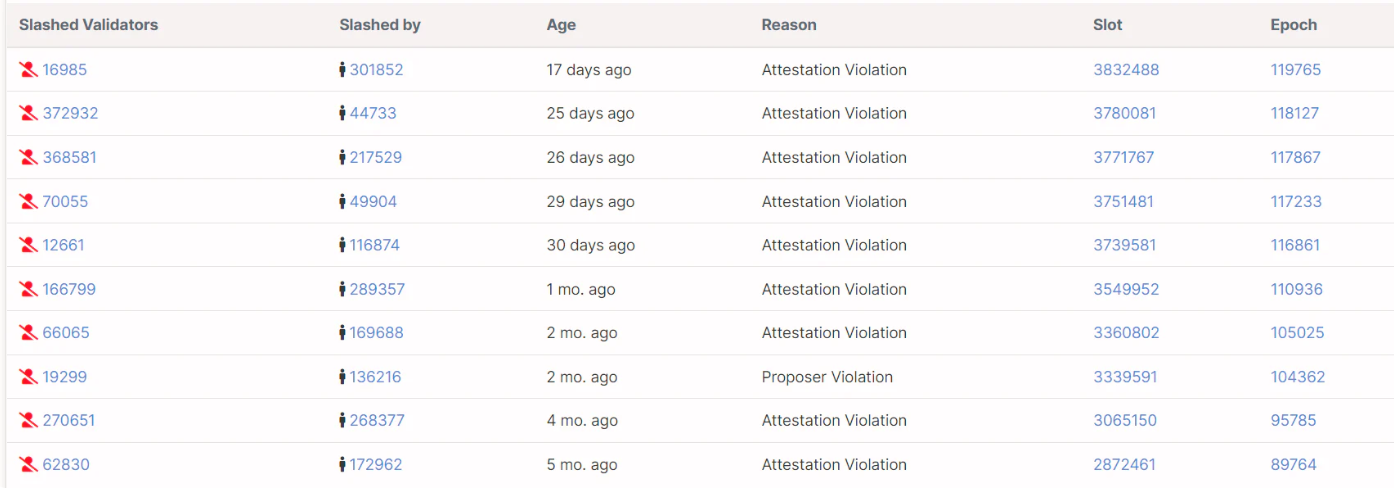
资料来源:beaconcha.in
节点供应商正试图通过秘密共享验证器(SSV)等新技术来提高基础设施的稳定性。秘密共享验证器网络是一种可以达到主动冗余的技术。网络中的所有验证者都会主动产生新的区块。该机制就像一个多签名的钱包。
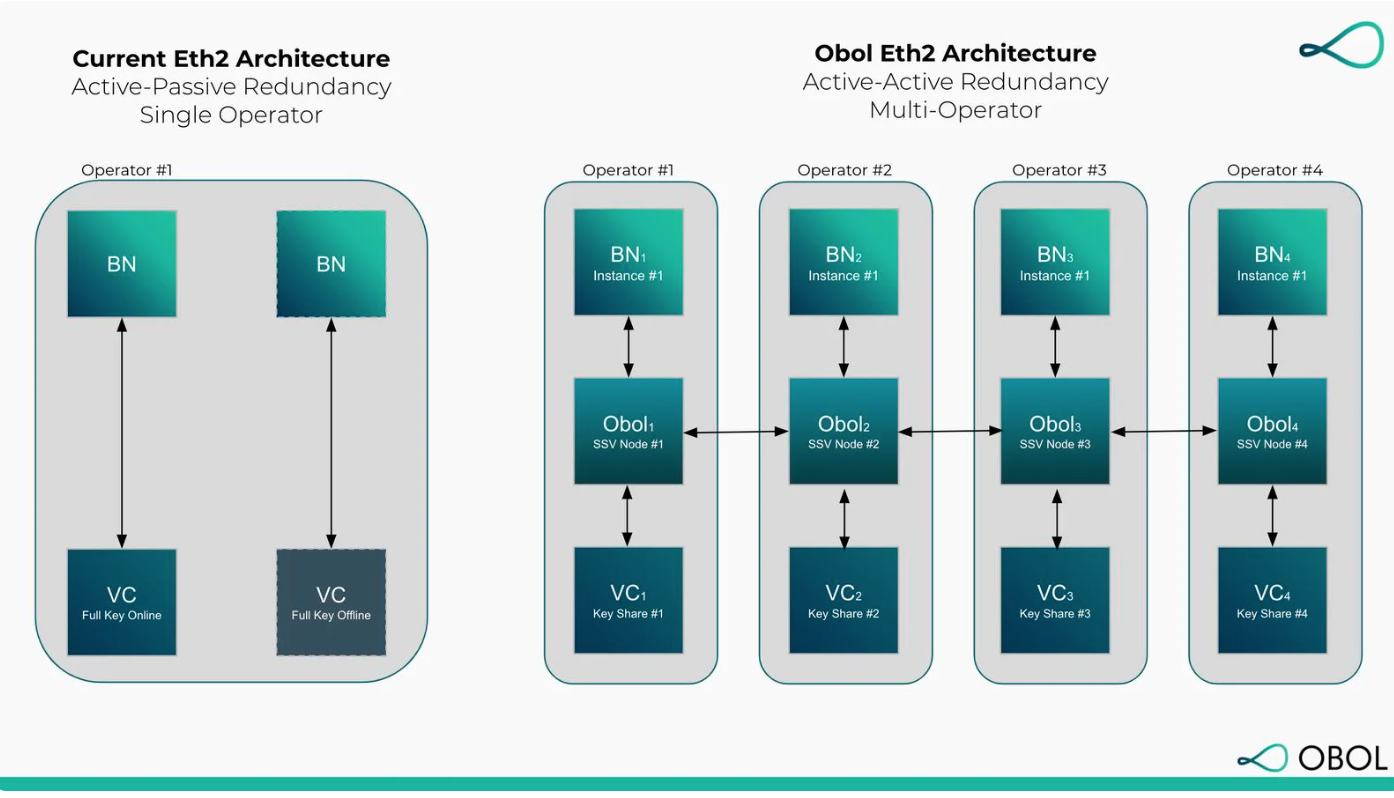
资料来源:OBOL
其他用于防止罚没的技术是本地罚没保护数据库,它记录了导致罚没的信息,以及记录了所有收到的证明和区块的远程罚没器。
从 Staking Rewards 的调查来看,用户确实更关心的是 节点供应商的信誉而不是成本,而节点供应商正在努力提高它们的可靠性,从而更好的建立它们的声誉。
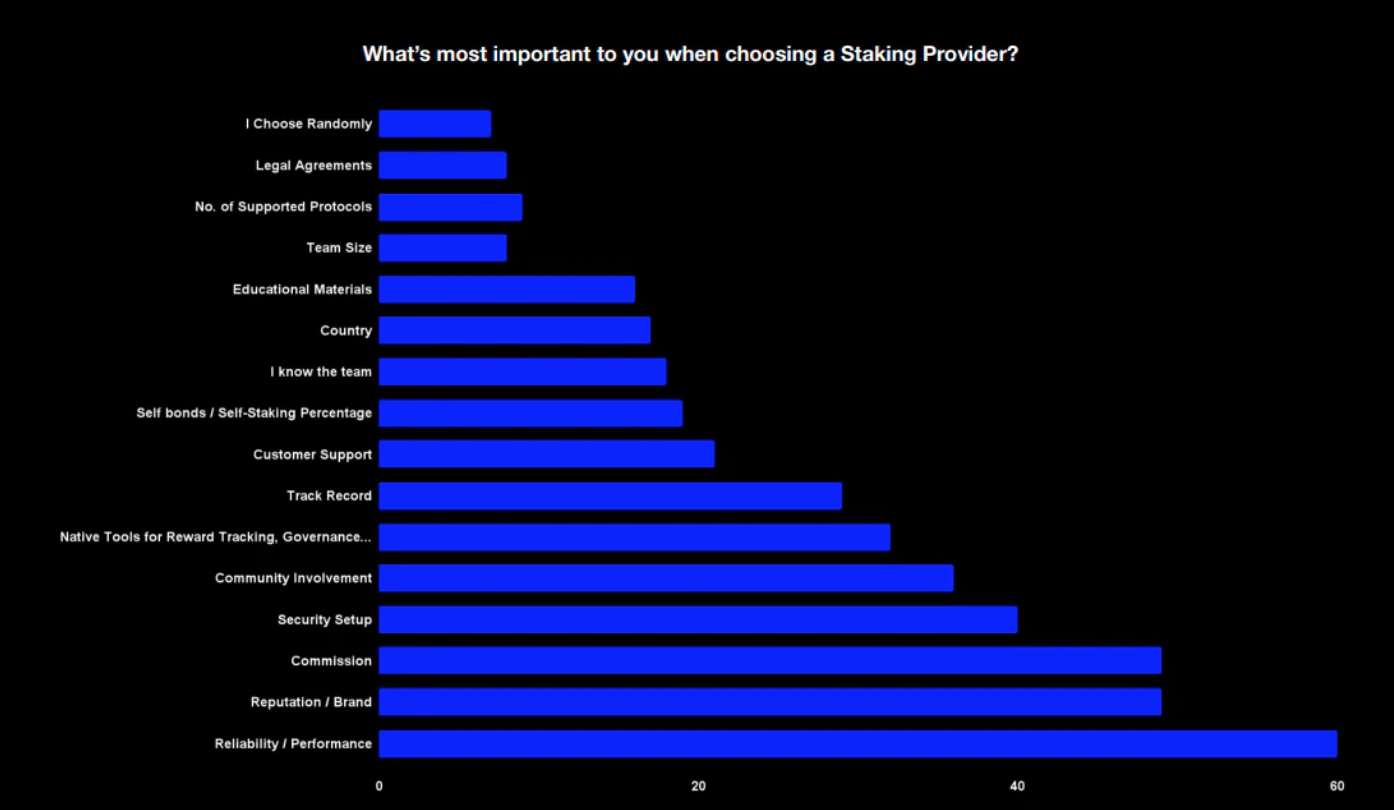
来源:Staking Rewards
液态质押池
用户在选择了最佳的质押节点供应商后,他们所面临的下一个问题就是如何提高资本效率。用户需要将资产锁定在质押节点中,但每年只能获得 10% 的收益。在加密货币世界里,到处都有机会。将资产锁定在质押池中的机会成本是巨大的。因此,用户正在努力提高资本效率。液态押池可以帮助用户几乎即时的获得流动资金。
液态质押池有两个功能:
降低用户的质押要求
大大增加被质押资产的流动性
为了增加被质押资产的流动性,液态质押池为用户铸造新的代币。例如,在 Lido 抵押 ETH 后,Lido 为用户铸造 stETH。用户可以在去中心化交易所上用 ETH 交换 stETH。以下是 stETH 的定价图。
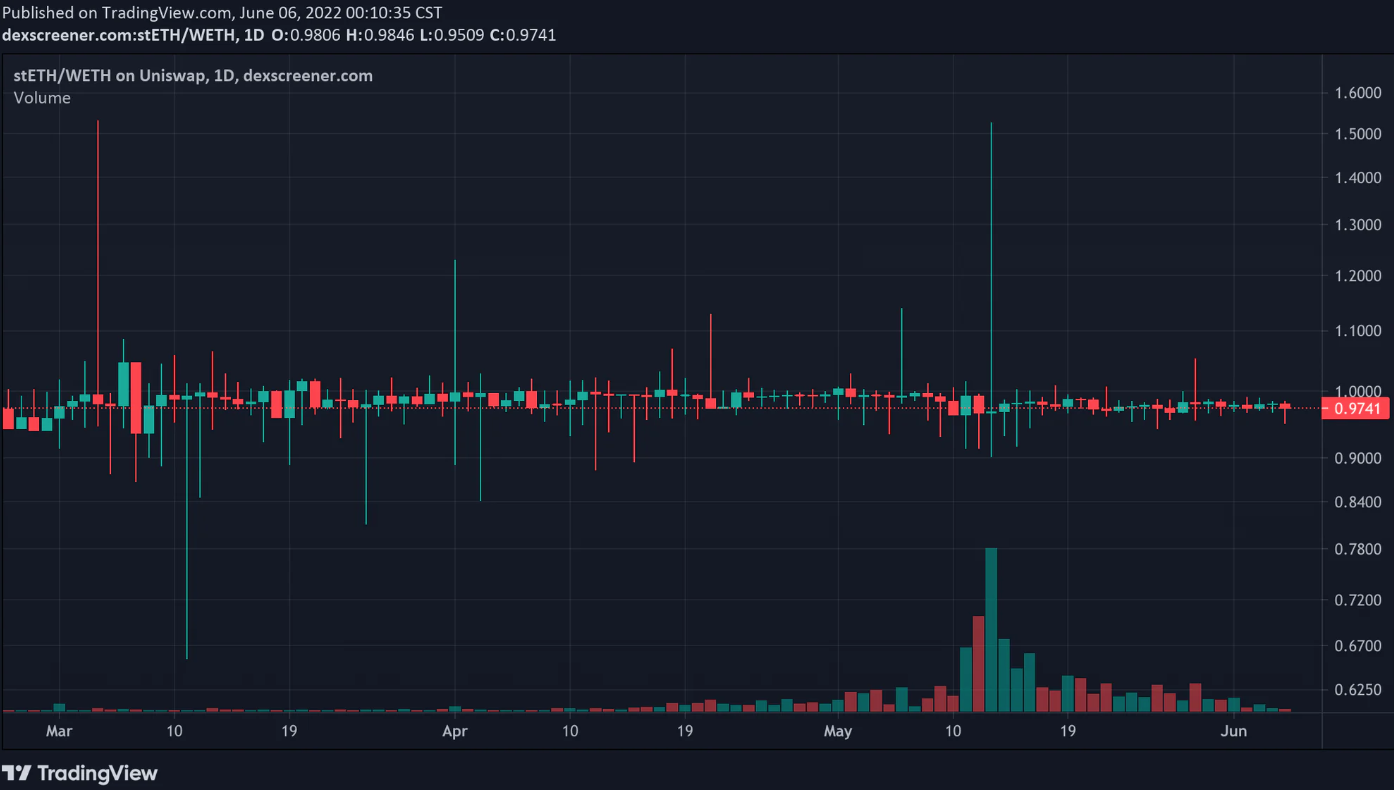
资料来源:Dex Screener
stETH 就像一个债券。1 个 stETH 可以在不可预知的未来赎回 1 个 ETH。我们不确定以太坊何时会在质押节点发布已质押资产,因为发布已质押资产需要在 ETH2.0 合并后进行硬分叉来更新。
接下来的几个图表显示,Lido 主导了 ETH 的质押市场,并确保了很大一部分市场份额。
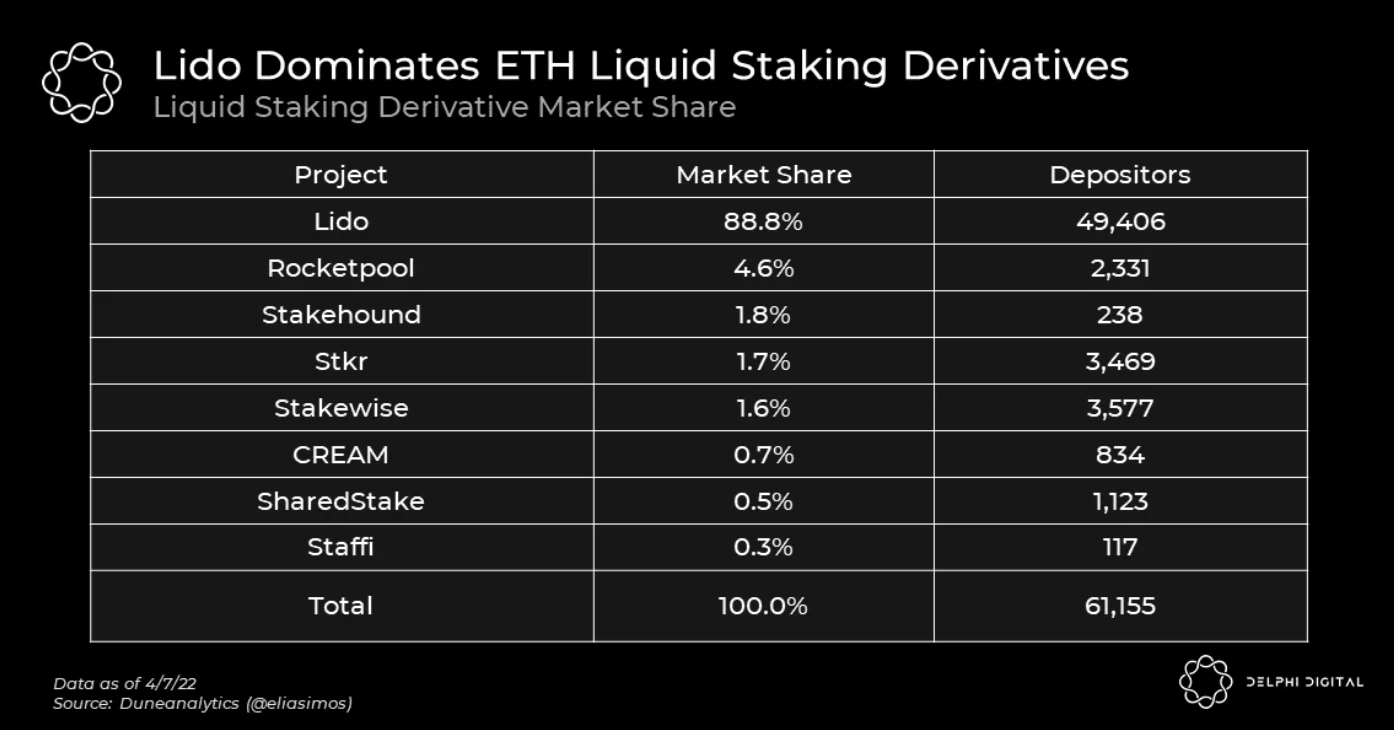
资料来源:Delphi Digital
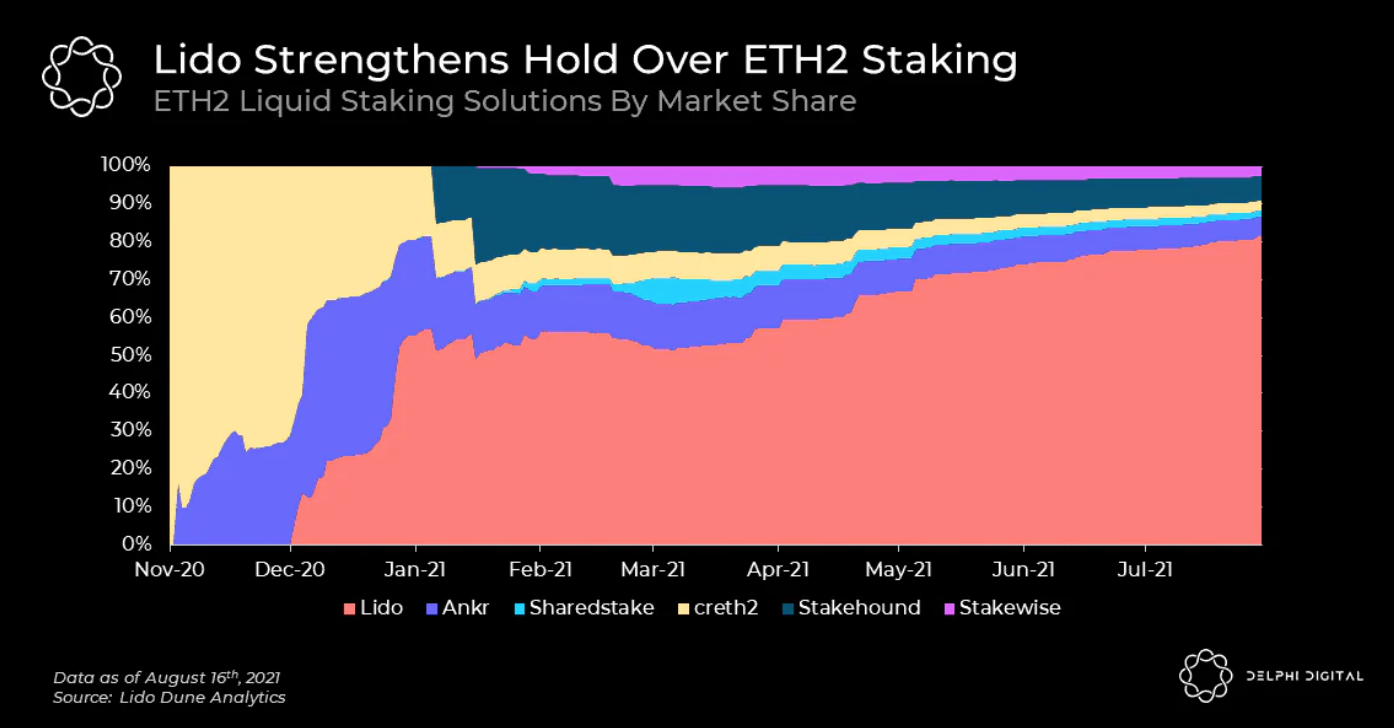
资料来源:Delphi Digital
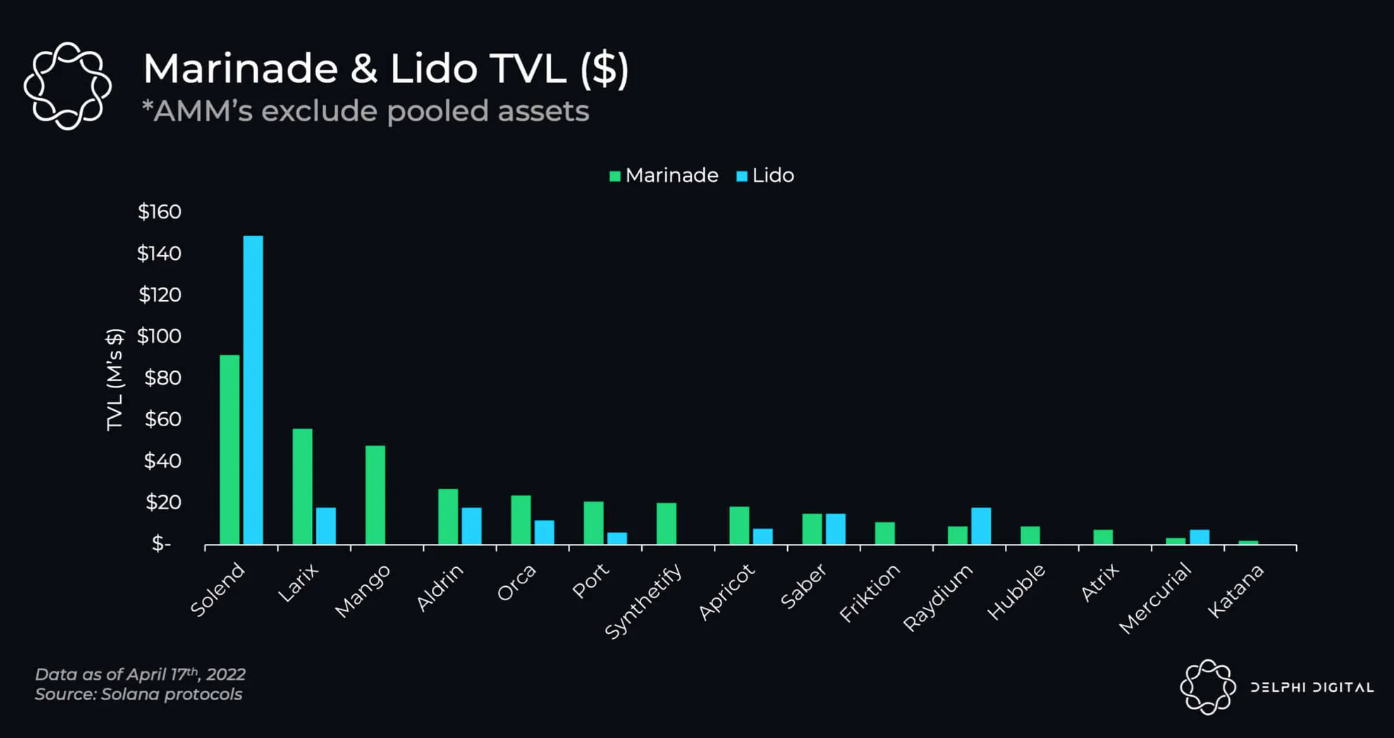
然而,Marinade 代替 Lido 主导了 Solana 的液态质押市场。
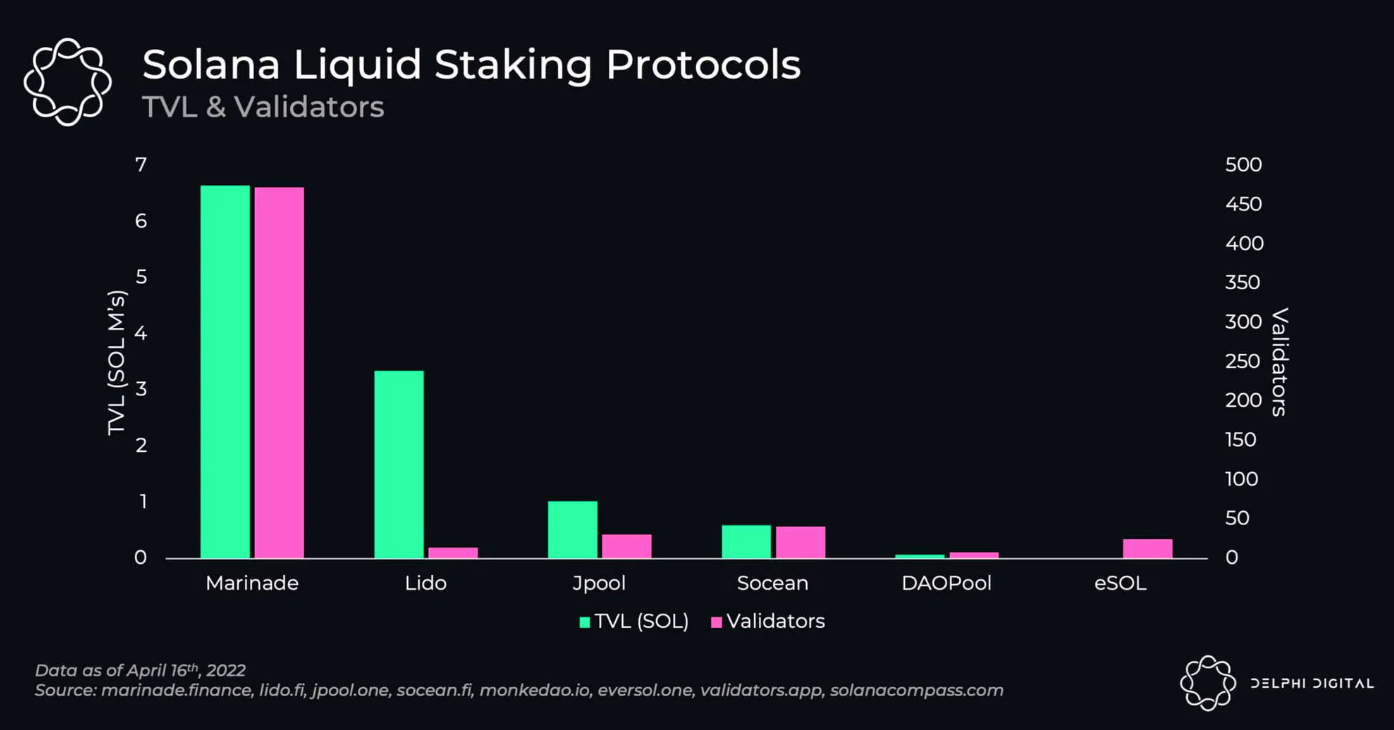
资料来源:Delphi Digital
以下是 Solana 的液态质押的费用明细。
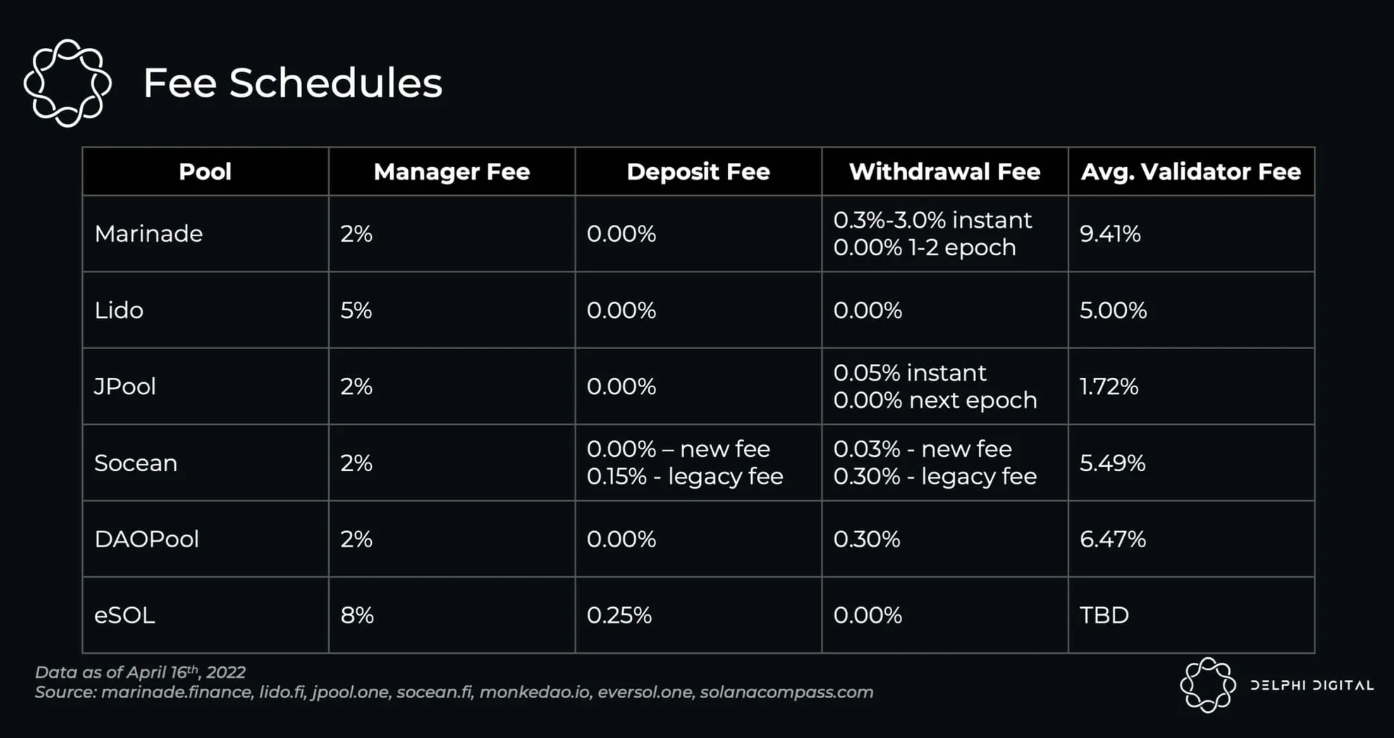
资料来源:Delphi Digital
除了费用和声誉,效用是另一个要点。更多的合作关系意味着在去中心化交易所和借贷平台的流动资产的流动性更深。Marinade 与 DeFi 项目的合作关系最多。
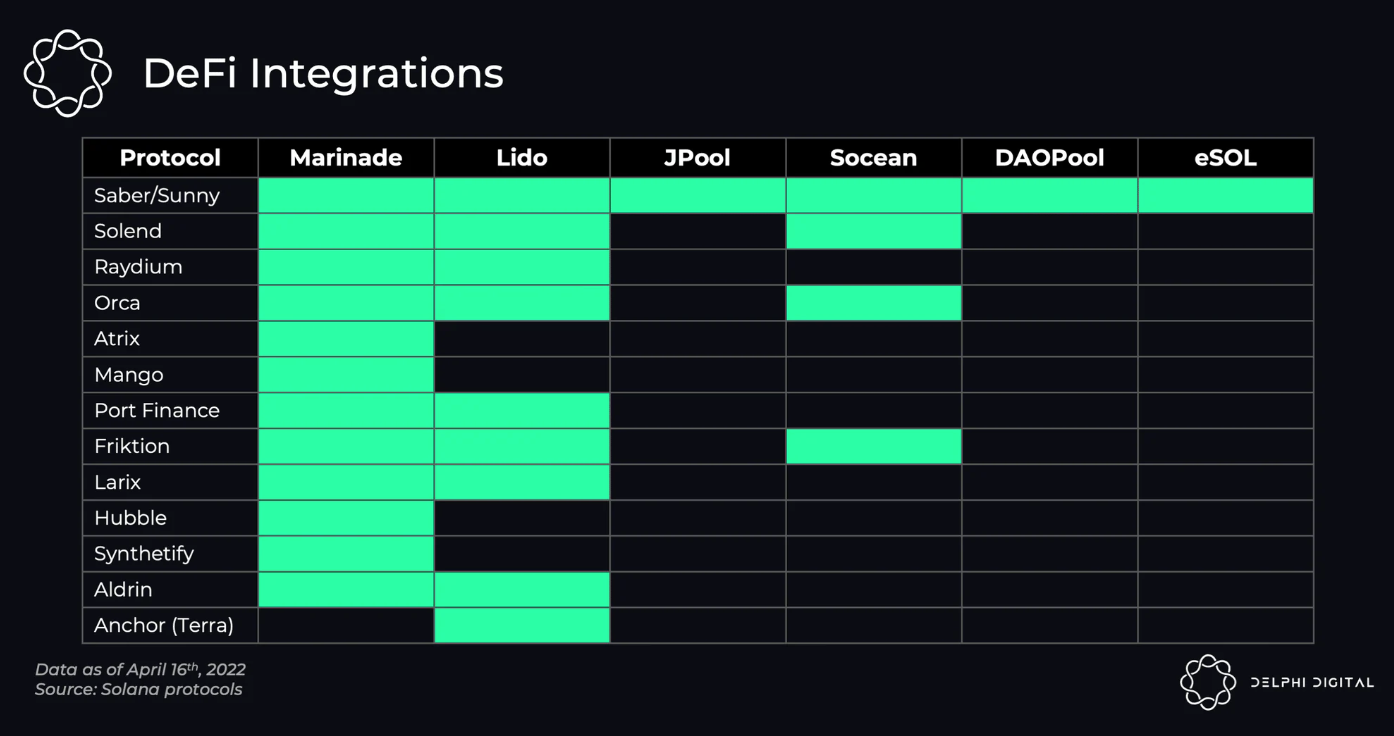
资料来源:Delphi Digital
资料来源:Delphi Digital
金融
大多数 DeFi 的用户都非常关注协议的年化收益率。那有没有什么方法可以推动我们的质押收益率,但仍然享受较低的风险呢?答案是有的。杠杆挖矿(leverage farming)可以做到这一点。
大多数杠杆收益农场使用 2~3 倍的杠杆,并提供大约 7% 的年化收益率。当然,它们也确实面临着清算的风险。
这一过程的基本操作是,他们在 Aave 上存入 stETH,通过 Aave 借入 WETH。然后他们用 WETH 换取更多的 StETH 并重复上述步骤。
另一个有趣的项目是 Staking Rewards 的 SR20。SR20 是一个包含前 20 个 PoS 资产的指数,按总质押价值加权。该指数也在持续累积质押奖励。下面的图表展示了该指数中加密货币的分配情况。
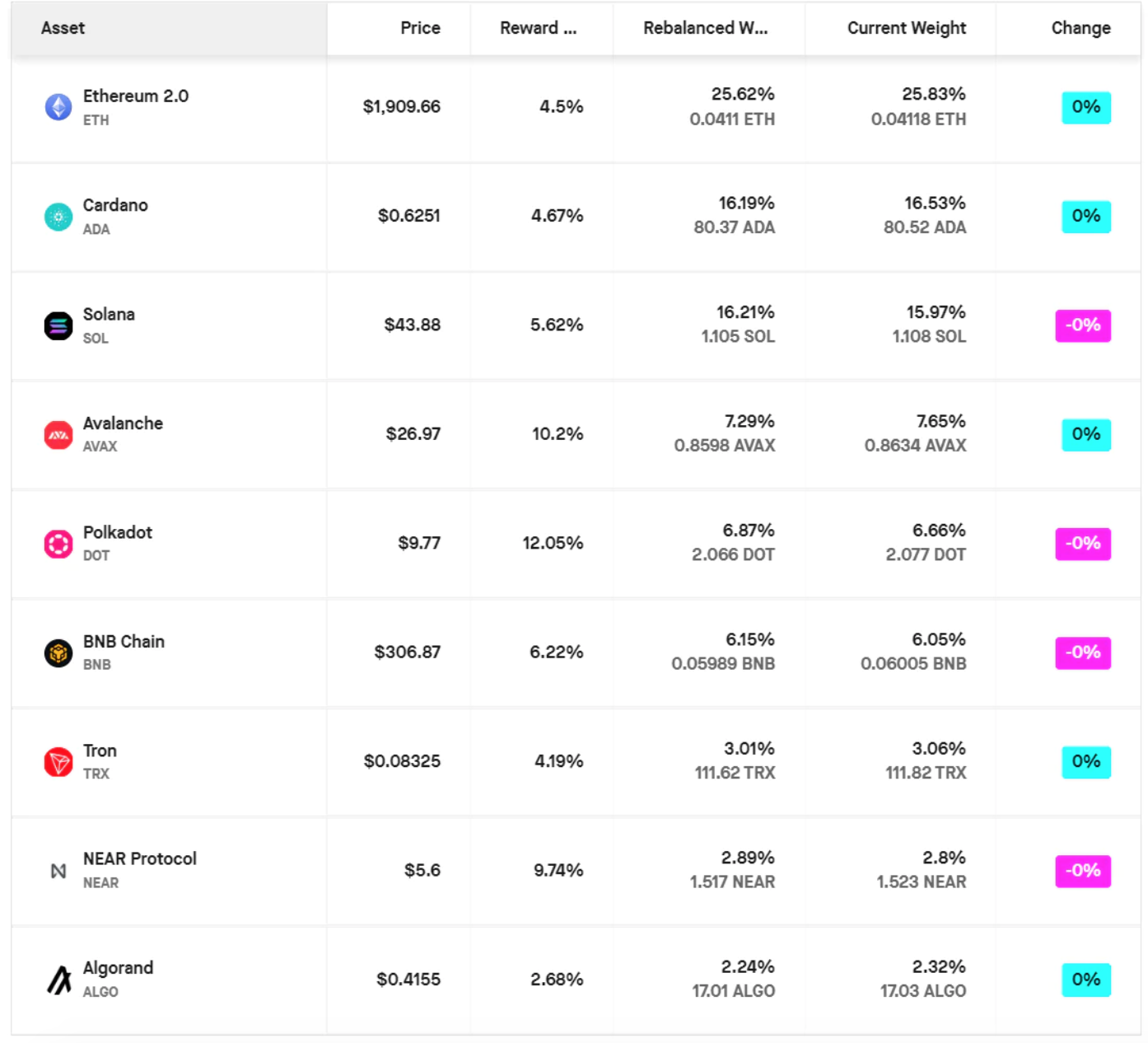
来源:Staking Rewards
目前的指数价格是 304.41 美元,奖励率是 6.54%。质押回报率 YOY 为 9.44%。下面是 SR20 的价格图。
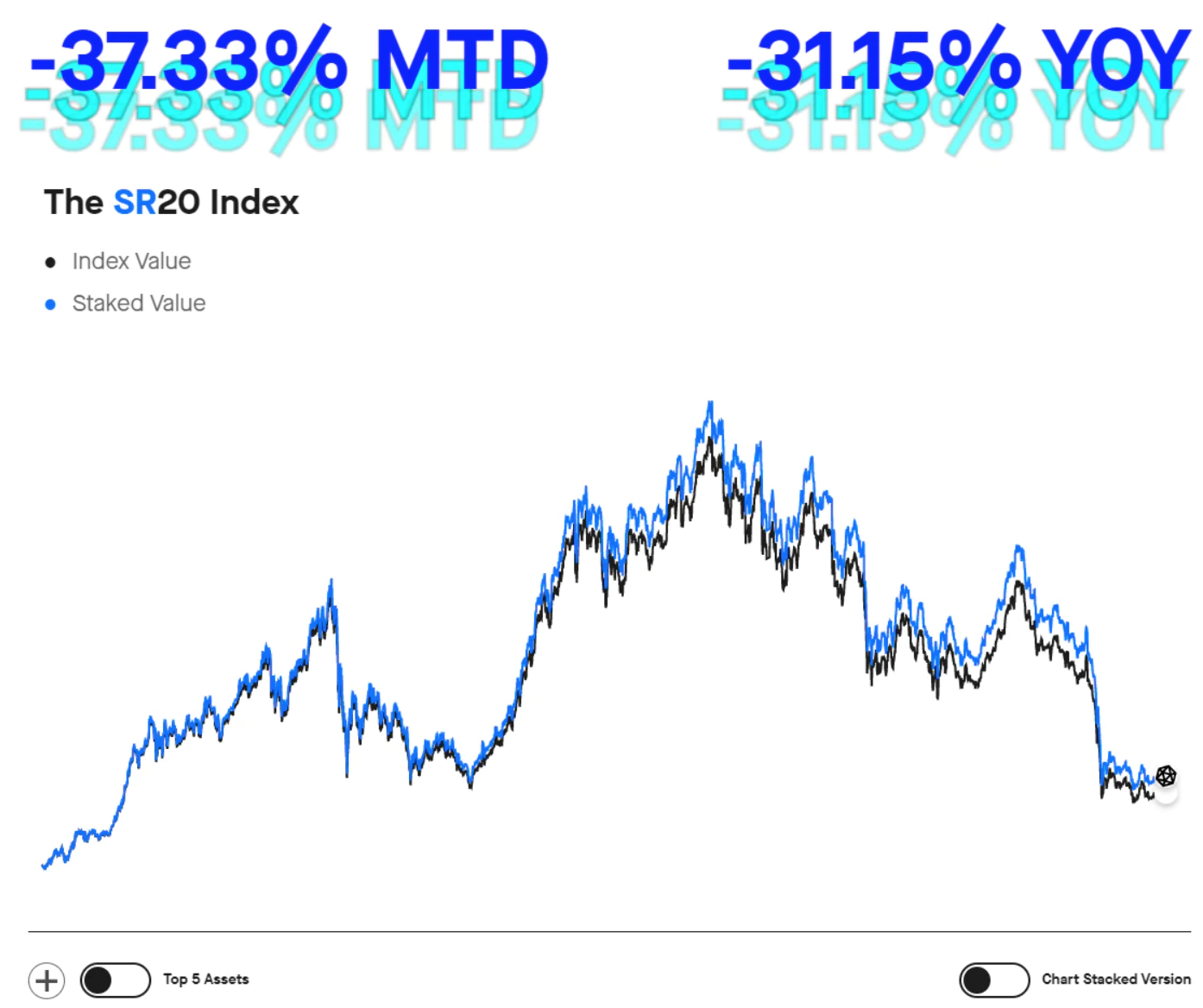
资料来源:Staking Rewards
为了避免罚没风险,也有针对验证者的保险产品。Lido 与 Unslashed Finance 合作,在 2021 年 2 月为价值约 2 亿美元的以太坊质押提供保险,以避免被罚没。

来源:Lido Medium
质押市场接下来将如何发展
当前,质押的生态系统已经逐步建立。大玩家已经在市场上获得了强大的地位。总的质押市场将继续增长,因为与其他 PoS 资产相比,ETH 的质押比例仍然很低。我们对质押市场的未来持乐观态度。
质押资产类似于购买国债。机构和大鲸鱼都愿意购买这些资产。但是国债和质押之间的一个很大的区别是,质押的回报是不固定的。质押的奖励会根据网络条件而变化。为了使年化收益率更加稳定,我们预计会有固定的年化收益率和长期质押资产的出现。
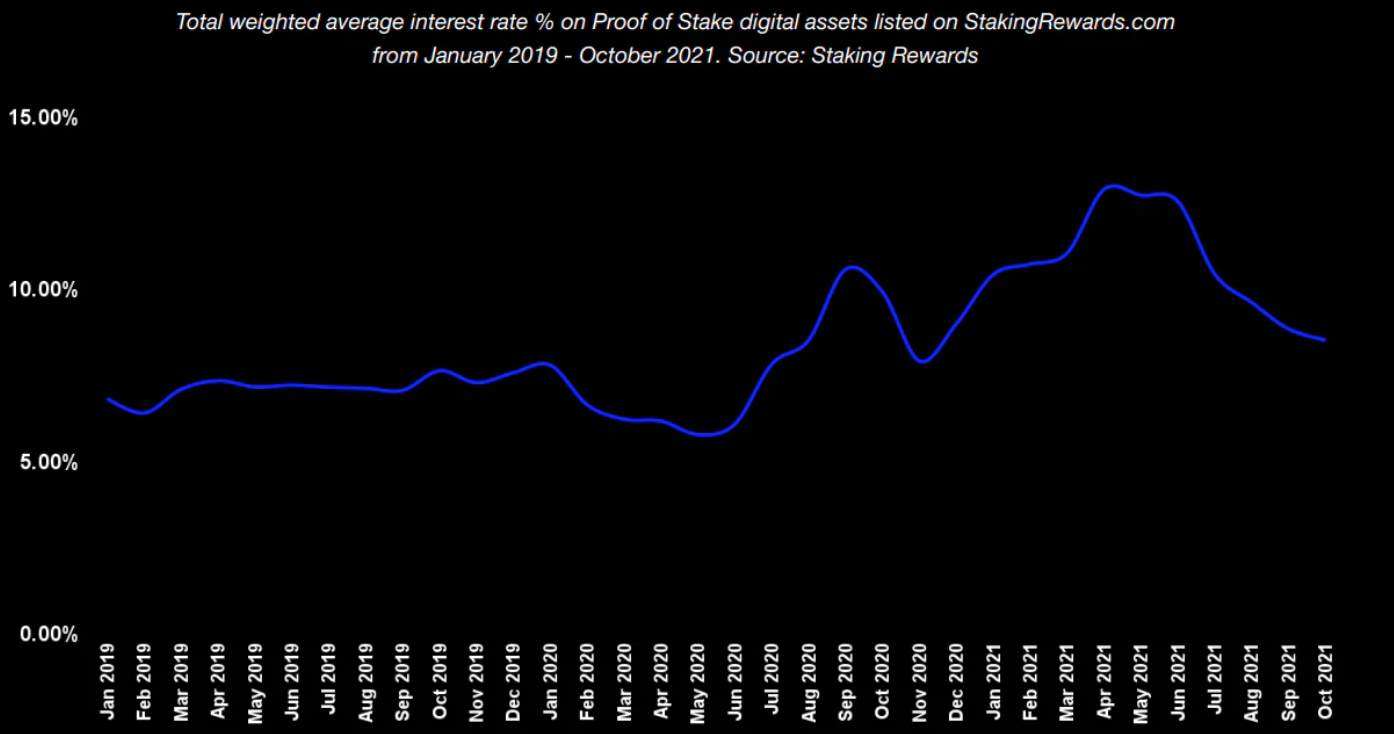
目前液态质押协议的代币经济学无法捕捉到真正的价值。随着收入和总锁仓量的上升,这些液态质押协议的代币价格逐渐下降。我们需要一个更好的代币经济学设计来支持质押协议。目前,质押协议的收入不与代币持有人分享,这使得代币成为一个纯粹的治理代币。
新玩家的两个机会是更好的用户体验和长尾资产支持。在官方文件的帮助下,设置一个节点是很容易的,而真正困难的部分是运营和客户管理。为了更好地支持这些新玩家,提供一些工具包是必要的,这与 VPN 市场类似。晚一步进入市场的小玩家可以提供更低的费用,以及更好的用户体验。
一个特定的数据分析工具也是必要的。对于质押者来说,他们关心的是活跃度历史,质押比例历史,罚没历史等。这些数据与我们使用的普通数据集不同。我们使用的普通数据集通常关注的是交易。为了更好地支持投机者,市场需要一个新的数据分析工具。



