详解Web3的四大核心要素:区块链、加密资产、智能合约和预言机

最近Web3突然成为了热点,传统科技行业和新兴区块链行业的领导者带着各自对互联网历史和未来的不同视角,纷纷参与了这场讨论。
在具体讨论Web3之前,我们先快速回顾一下这个概念是如何演变的。
“Web 3.0”这个概念最初是由HTTP的发明者Tim Berners-Lee在互联网泡沫时期提出的,是指一个集成的通信框架,互联网数据可以跨越各个应用和系统实现机器可读。Web 3.0通常也被称作为“语义网”(Semantic Web)。
到了2014年,以太坊联合创始人Gavin Wood在一篇名为《DApp:Web 3.0是什么》的博客文章中重新定义了Berner-Lee提出的这个词,用来指代一种区块链技术,可以基于“无须信任的交互系统”在“各方之间实现创新的交互模式”。
Gavin Wood这篇文章的重点并不是加密资产,而是共识引擎和密码学等协议和技术。这些协议和技术可以实现更强大的网络社会合约。他之后又阐述了Web3的终极目标,那就是“更少信任,更多事实”。
而现在,许多人对这个概念都有不同的见解,传统科技企业和新兴区块链行业都在不停思考Web3的核心价值主张和协议是什么,以及它对未来的信任模式会产生哪些影响。
本文将根据互联网的发展史来定义Web3,详细介绍Web3技术栈的关键技术,并探讨Web3的当前和未来发展。
术语注释:本文中的“Web3”与“Web 3.0”应区别开来,Web 3.0通常指Berner-Lee的语义网。
互联网的发展史:从Web 1.0到Web 2.0再到Web3
要充分理解Web3的含义,就必须先看互联网的发展史,以及Web3与前两个发展阶段的不同之处。
Web 1.0(1994-2004)
Web 1.0是互联网的第一个发展阶段,这个阶段从1994年一直延续到2004年,期间出现了Twitter和Facebook等社交媒体巨头。虽然大众在1994年左右才接触到Web 1.0,但实际上早在1968年,一个名为“ARPANET”(全称是Advanced Research Projects Agency Network)的美国政府项目就启动了Web 1.0。ARPANET最初是由军方承包商和大学教授组成的一个小型网络,他们在其中互相交换数据。
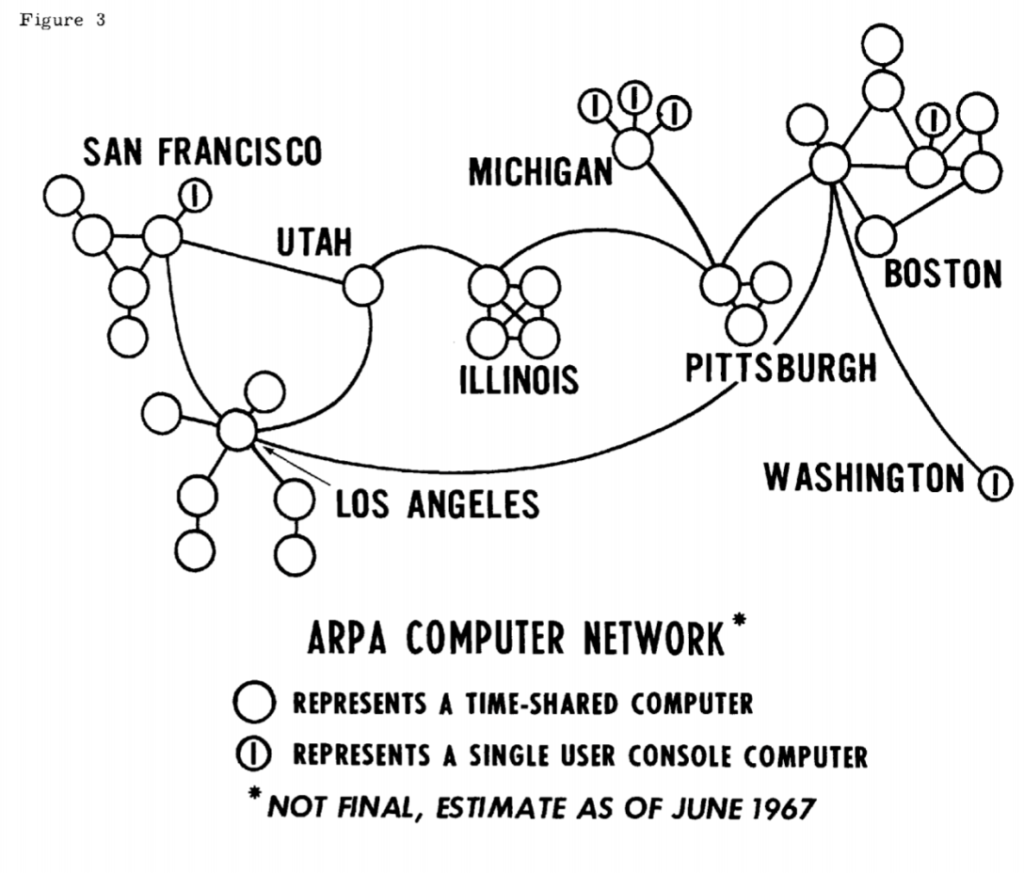
1967年的ARPANET。图中的每个节点都是加州大学伯克利分校、斯坦福大学、加州大学洛杉矶分校、密西根大学、卡内基梅隆大学或麻省理工大学的一个计算机节点。
Web 1.0主要是静态的HTML网页,用户之间很少交互。虽然有AOL(美国在线)等门户网站以及私人聊天室和BBS等论坛,但总的来说当时的互联网仍没有什么交互或支付交易功能。

Web 1.0的披萨订购网页。必胜客在Web 1.0时代是一家创新的企业,他们发布了自己的网站,消费者可以在网站上买披萨,不过支付只能在线下完成。
Web1.0并非完全没有交互或支付功能,只是这些功能因为转账基础设施无法保障安全性而受到很大限制。在Web 1.0时代中最具创新力的企业就是必胜客。他们在1995年开发了一个订购披萨的网页,消费者可以在页面中下单,等到披萨送到后再付现金。

美国在线(AOL)早期的广告,AOL也是最早的门户网站之一,向数百万用户寄去他们的软件CD,并赠送10小时的免费使用时间。
虽然AOL在他们1995年的广告中宣称用户可以在网站上给母亲订花,购买比赛门票或写一篇关于恐龙的研究报告,但涉及到网上付款环节时还是需要运营商的辅助,因为当时在线支付交易普遍无法保障安全性和加密性。
Web 2.0(2004年至今)
互联网在2004年左右经历了蜕变,由于当时互联网在网速、光纤基础设施和搜索引擎等方面都取得了发展,因此用户对社交、音乐、视频分享和支付交易的需求大幅上升。
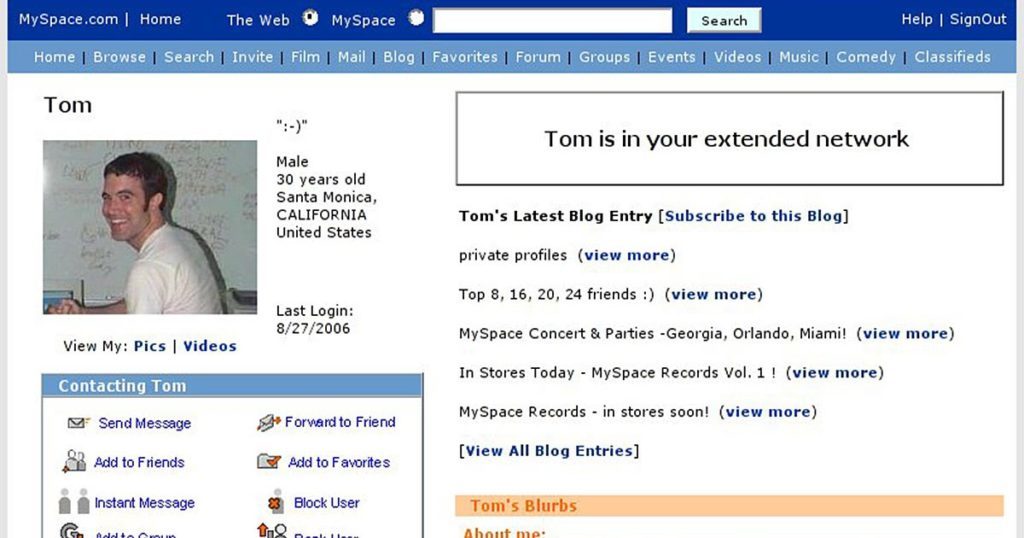
早期Web 2.0公司MySpace创始人Tom Anderson的MySpace主页。所有注册了Myspace账号的用户第一个自动添加的好友就是Tom。
用户对社交属性的需求也催生出了如今许多互联网企业。Facebook、MySpace和Twitter等社交媒体平台为用户提供了社交功能;Naspter等数据分享软件满足了用户对音乐和视频的需求;Google为用户搜索海量互联网信息提供了捷径。美国银行等传统机构则满足了用户的支付交易和电子转账需求,并采用了256-bit AES等新型加密标准。
这种更具互动性的全新互联网体验为用户带来了许多新的功能,并提升了用户体验。但问题也随之而来,并且直到今天也一直无法彻底解决,那就是:用户如果要使用这些新功能,就必须授权中心化的第三方平台管理大量数据。因此这些中心化的实体在数据和内容权限方面被赋予了巨大的权力和影响力。
而这个模式一直运行到今天。仅在美国,谷歌、YouTube、Facebook和亚马逊在2021年10月的共合计访问次数就达到了235.6亿次。
Web3(2008年之后)
在2008年,中本聪发布了比特币白皮书,在其中指出了区块链技术的核心基础并发明了点对点的digital currency,由此掀起了Web 2.0的改革浪潮。比特币彻底颠覆了我们对数字化交易的概念,并首次提出了一种无需可信中间方的安全在线交易模式。中本聪写道:“需要基于加密证明,而非信任,来建立电子支付系统。”
直到智能合约被发明后,去中心化的互联网模式才真正进入公众视野。如果说比特币实现了点对点支付,智能合约扩展了可编程协议的概念,实现了保险、游戏、身份管理和供应链等更高级的用例,那么这一切会如何影响互联网用户体验和数字化交互呢?智能合约用户可以直接、安全地交互,因此打造了一个更加公平、透明且基于加密事实的新型互联网。
Gavin Wood将这个升级版的互联网称作“Web3”,即“一个安全的、由社会运行的系统”。
简而言之,Web3就是一个去中心化的互联网,旨在打造出一个全新的合约系统,并颠覆个人和机构达成协议的方式。Web3复刻了第一版互联网(即Web 1.0)的去中心化基础架构,Web 1.0的特色是用户自己架设博客网站以及RSS feed。在此基础上,Web3还结合了Web 2.0丰富的交互体验,比如社交媒体平台。Web 1.0和Web 2.0相结合,就形成了Web3的数字化生态,在其中用户可以真正拥有自己的数据,并且交易受到了加密技术保障。用户无需再信任品牌背书,而是可以依赖确定的软件代码逻辑来严格执行协议。
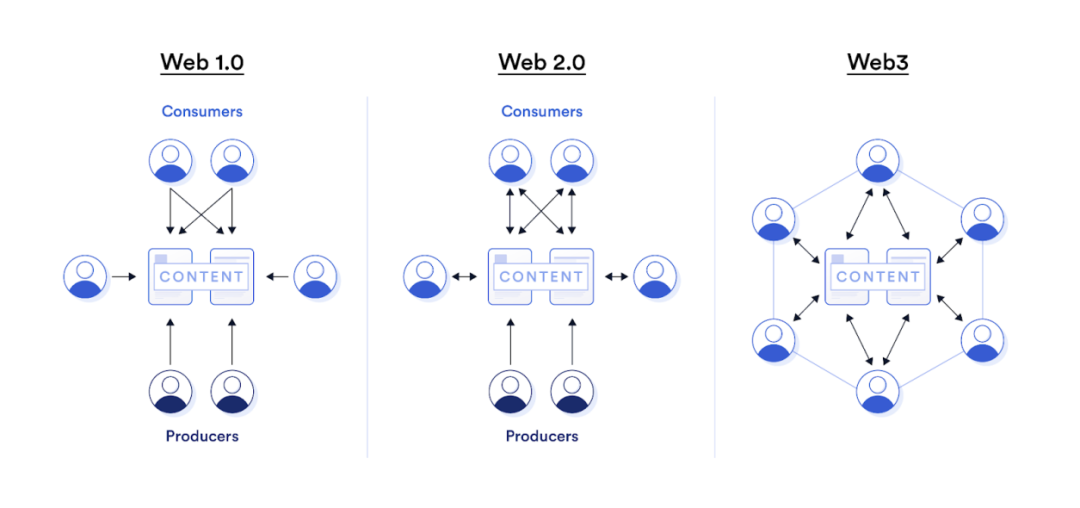
Web 1.0、Web 2.0和Web3中内容消费者与创作者之间的互动关系。
Web3的核心要素:区块链、加密资产、智能合约和预言机
Web3模式的去中心化技术栈不断发展壮大,涵盖区块链、智能合约、预言机、加密钱包以及存储网络等各种技术。下文将详细阐述Web3技术栈的关键构成要素。
区块链
区块链是安全性和去中心化水平都极高的网络,人们可以在一个共享账本中储存数据、交换价值并记录交易活动,而且这个账本不受任何中心化实体控制。区块链网络是Web3的支柱,提供了安全的执行层,可以在其中创建、发行并交易加密资产,并且开发可编程的智能合约。区块链是Web3的结算层。
加密资产
加密资产是数字通证,利用了去中心化且防篡改的区块链网络环境,充分保障了交易的安全性。加密资产是Web3去中心化应用(dApp)的原生货币,也可以用于支付Web3服务并参与Web3治理。
在区块链技术出现以前,通证往往指用来购买和交易产品或服务的价值单位,比如高速公路收费站的通行证、游乐园的门票和游戏代币。在这些早期用例中,服务提供方通过发放通证,让用户直接提前支付服务费用。
Web3应用中的通证也是发放给Web3内容创作者的价值单位,但区别是这些价值单位是以数字化且可编程的形式存在的,而且其功能远不止价值交换。在Web3中,通证可以表示对某一协议、项目或区块链的投资。通证也可以在这个项目或协议中用来支付或保障服务。另外,通证还可以让持有者参与到协议或项目的治理。
智能合约和去中心化应用(dApp)
智能合约是区块链上不可篡改的程序,利用“如果x是真实的,则执行y”的代码逻辑自动执行交易。可编程的智能合约可以创建去中心化的应用,或者叫“dApp”。去中心化应用是基于加密经济的协议,为Web3的发展奠定了基础,并将Web3交付到了用户手中。
dApp与Web 2.0的应用以及Web 1.0的静态HTML网页不一样,它们不由任何一个人或组织运行,而是由去中心化的区块链网络运行。去中心化应用看似简单,但却能够打造出点对点金融服务(DeFi)、数据驱动的保险产品以及P2E游戏等非常复杂的自动化系统。
预言机
智能合约要充分实现其潜力,就必须能够与区块链网络以外的数据和系统交互。预言机能够将区块链连接至真实世界中的数据和系统,并提供关键的基础架构,打造一个具有互操作性且统一的Web3生态。
Chainlink预言机网络不仅能够为DeFi应用传输金融市场数据,还能够执行一系列安全的链下计算,比如可验证的随机数和去中心化执行,以最终实现动态NFT以及自动化水平极高的dApp。另外,随着跨链互操作性协议(CCIP)的不断发展,预言机网络将连接各个快速发展的区块链生态和L2扩容方案,使其安全地实现交互。
预言机对Web3技术栈进行了扩充,传输链下数据和服务,以推动智能合约创新;实现跨链互操作性,以确保各条区块链无缝连接。Chainlink的预言机基础架构也为Web 2.0后端系统进入Web3世界提供了入口,为传统系统提供抽象层,轻松接入任何公链和私有链。最终,预言机将为传统系统带来去中心化计算和加密保障,并在Web 2.0和Web3之间搭建桥梁。
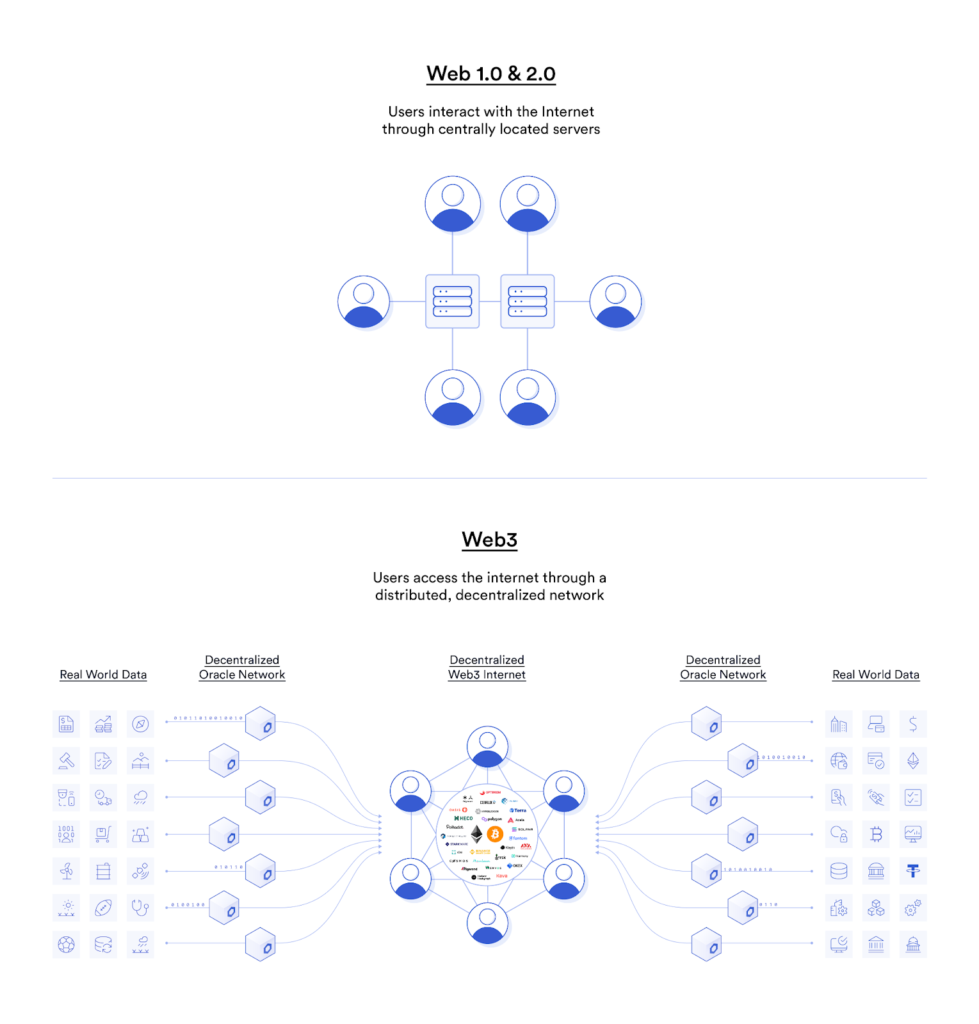
Web3由去中心化的计算网络组成,这些网络通过Chainlink预言机连接。
Web3的应用
Web3兼具去中心化和交互性,打造了一个全新的互联网模式。在其中,用户可以绕过中介直接交互。dApp用户无需许可即可访问金融工具,以点对点的方式交易加密资产,获得参数型保险理赔,通过NFT交易可验证所有权的数字艺术品,并且在游戏中赚钱。所有这些活动都可以完全绕过中间方直接展开。
Web3的建设者希望通过这个创新的架构,打造出更加公平和开放的互联网,用户可以在其中直接展开交互和交易。目前,采用了区块链、智能合约和去中心化预言机网络这三种核心技术的Web3应用已经实现了丰富的用例,颠覆了房地产、教育、金融、游戏和医疗等各个行业,并势必在未来将颠覆更多其他行业。
去中心化金融
Web3技术让个人可以创建并参与金融协议,并实现了前所未有的包容性、安全性和透明性。这种创新的经济模式还有一个广为人知的名字,那就是去中心化金融(DeFi)。
DeFi协议与传统金融服务不同,利用了去中心化的区块链基础设施以及预言机安全的数据输入,帮助用户在透明且防篡改的链上市场中直接交易。用去中心化的货币市场Aave举个例子:Aave集成了Chainlink预言机后为智能合约保障了超过120亿美元的价值。协议采用了非托管的模式,其用户可以点对点地进行借贷。货币市场是经济健康运行的关键支柱。链上货币市场将控制权去中心化,并且利用了预定义的智能合约逻辑,能够降低参与门槛和单点失效风险,并避免系统性风险和储备金不足的情况。
DeFi最大的一个创新就是可组合性。开发者可以将不同的开源协议组合成一个更加复杂的金融工具,比如利用超额抵押贷款协议打造无损储蓄游戏、开发去中心化stablecoin以及盘活闲置资金生成利息收益。
DeFi的创新金融应用是目前Web3最引人注目的发展,然而Web3远不止金融交易,还包括互联网世界中从娱乐到社交媒体再到浏览器等各个领域。
NFT、游戏和元宇宙
NFT、区块链游戏和元宇宙(metaverse)是Web3生态中异军突起的力量。NFT为数字资产提供了可验证的所有权,让这些数字商品拥有与实物资产同样的独特性。有了NFT,数字资产即使外观一模一样,也可以互相区分开来,这就像现实世界中两本一模一样的书可以通过它们各自独特的标记和磨损痕迹区分开来。
这对于数字艺术品、元宇宙应用和游戏来说意义重大。目前,Bored Ape Yacht Club(BAYC)等NFT项目正在不断推广NFT和数字艺术品;而Axie Infinity等区块链游戏也在逐渐颠覆传统游戏行业的玩家经济模式。实现这一转型在本质上需要区块链提供底层结算层、NFT智能合约提供可验证的艺术品所有权以及去中心化的预言机提供可验证的随机数、智能合约自动化和链下数据等关键服务。
参数型保险
去中心化参数型保险是区块链另一个有意思的用例。Arbol和Etherisc等区块链保险项目目前正在采用创新的模式,通过Chainlink Data Feeds将智能合约接入链下数据,为用户提供自动化的农作物保险和航班保险等各类创新保险产品。我们来看一个案例:
假设某一季节中的降雨量必须超过20英寸,才能保障农作物不欠收。一个农民希望买保险来对冲恶劣天气造成的不利影响。通常,他必须要经过漫长的理赔流程,并且要依靠中心化的保险机构来核实降雨量。
然而在Web3的世界里,无论你在什么地方,只要能上网,都能轻松买到保险。有了Arbol的链上农作物保险,保费和赔偿金额都会基于预定义的参数自动生成,并且会基于Chainlink提供的天气数据,通过保险智能合约自动支付赔偿金。因此,保险流程会非常高效迅速,并基于简单的二元逻辑判断农民是否应获得理赔。物联网传感器在当季记录的降雨量是否低于20英寸?如果是,则立即支付赔偿金给农民。如果否,则不支付赔偿金给农民。
这个模式还可以应用于航运险和火灾险等其他领域,而区块链参数保险目前已经应用在了参数型航班保险中。
Web3的未来将如何发展?
Chainlink的联合创始人Sergey Nazarov在近期关于Chainlink未来发展的演讲中提到,Web3生态的大趋势已经形成,并且在近期进入了主流视野:“如今Web3的应用场景覆盖了DeFi、NFT和通证化所有权这几个领域,但是这一切才刚开始。现在仍是加密技术发展的初期,之后这项技术会渗透至人们日常生活的方方面面以及所有行业的各个角落。”
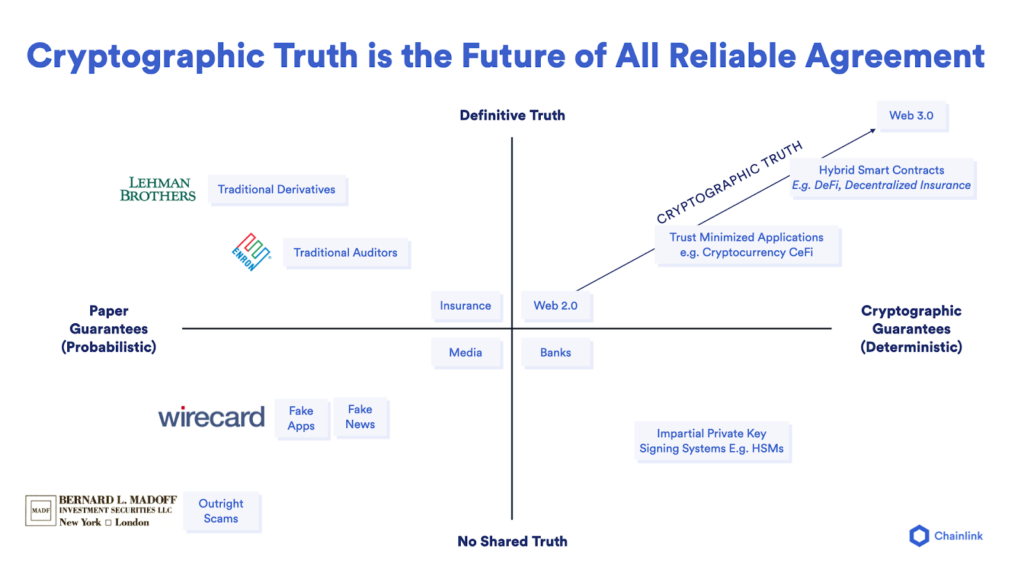
随着大家逐渐意识到加密技术的力量,它们将抛弃缺乏确定性的中心化服务提供方,转而拥抱信任最小化的Web3服务。
Web3这个词实际上指代了基于去中心化技术的新型互联网体验。而Web3已经开始颠覆我们在投资、交易、游戏和艺术等各个领域的交互方式。全球各地有越来越多的用户和机构已经开始意识到无须信任的交互和基于加密技术保障的协议是多么重要。虽然Web3仍处于发展初期,但它有潜力将互联网恢复成当初设计者所希望的那样:完全透明、可靠且易于使用。Sergey在演讲中说道:“Web3在速度、效率和成本上将逐渐赶上Web 2.0系统,并且它还具有Web 2.0没有的优势,那就是信任最小化的加密保障。”
欢迎查看开发者文档,加入Discord上的技术讨论,或联系Chainlink专家,立刻开始用Chainlink开发智能合约应用。
要了解更多关于Chainlink的咨询,请访问Chainlink官网,并关注Chainlink官方推特,获得Chainlink最新的消息和公告。



