读懂StarkWare: dYdX和iMMUTABLE背后的Layer2方案解决商
撰文:msfew@Foresight Ventures
StarkWare 简介
StarkWare 主要解决了区块链的可扩展性和隐私. StarkWare 开发了一个完整的解决方案, 使用 STARK 技术, 通过 zk-Rollups 和 Validium 模式组成 Volition 来生成和验证计算完整性的证明. StarkWare 的密码证明可以做到零知识、简洁、透明和后量子安全. StarkWare 所研发的产品主要有: StarkNet, StarkEx, Cairo.
主要特点
可拓展性
StarkWare 允许区块链通过依赖在云中的链下证明者生成的加密证明进行大规模扩展, 然后通过链上智能合约进行验证.
隐私性
zk-STARK 证明不会透露输入的私人信息. 结合其他加密工具, zk-STARK 可以完全且可证明地保护用户数据.
用户体验
通过 iMMUTABLE 和 dYdX 的例子, 我们就可以体验到 StarkWare 所提供方案极强的拓展能力. DiversiFi 的支付 TPS 可以达到 18k, iMMUTABLE 的 NFT 铸造费用仅需 0.2 美分, dYdX 的交易费用缩减到了1/50. 秒确认, 费率几乎为0, 带来了极佳的用户体验.
里程碑
2018: STARK 白皮书发布, 以太坊基金会 Grant
2019: 第一个 Demo 发布 (扩大以太坊效率200倍), StarkEx Alpha 发布测试网, 第二个 Demo 发布 (扩大以太坊效率700倍)
2020: DeversiFi (StarkEx 1.0) 发布主网, VeeDo (基于Stark的VDF) 发布主网, StarkEx Rollup 发布主网, ethSTARK发布, Cairo (图灵完备的针对STARK语言) 以及其 PlayGround 发布, Ziggy STARK (后量子安全的安全签名) 发布, StarkEx 2.0 发布主网
2021: StarkNet 公布, dYdX 与 Immutable X (均为StarkWare的客户) 项目发布主网
iMMUTABLE 与 StarkWare
iMMUTABLE 是第一个 Layer 2 的 NFT 交易平台. Tik Tok 在9月份与 iMMUTABLE 开展了合作, 发布了一系列 NFT.
由于以太坊的本地吞吐量上限为4交易/秒, 限制了任何希望扩展的 DApp. 对于 NFT 来说, 吞吐量瓶颈甚至比普通 Token 更大: 使用 NFT, 一千个 Token 实际上消耗区块链资源的千倍于单个 Token. iMMUTABLE 希望用以太坊原生解决方案来享受以太坊的安全, 开发工具和网络效果, 所以采取了 StarkWare 提供的解决方案.
StarkWare 提供的解决方案的独特功能之一是它能够以多种数据可用性模式进行部署: zk-Rollups 或 Validium. 两者都是基于有效性证明的, 但是在 zk-Rollups 中, 所有数据都在链上提交, 而在 Validium 中, 数据被保存在链外, 并且只有对最新状态的提交, 以及该状态有效性证明的链上提交. iMMUTABLE 以 Validium 模式开始, 提供更低的 gas fee. 由于政策法规规定, 数据可用性委员会 (DAC) 确保用户始终可以访问他们的数据. 所以 iMMUTABLE 切换到了 Volition 的新数据可用性模式, 该模式将允许用户以单一事务粒度选择数据的存储位置——链上 (zk-Rollups) 或链下 (Validium). 同时这样的做法也最大化了性能的拓展.
在 Tik Tok 与 iMMUTABLE 的合作博客文章中, Tik Tok 特别提到了 StarkWare 是第一个碳中和的 L2 拓展解决方案. 在传统互联网公司的视角里, 环保是很重要的, 不环保是很容易受到抨击的, 因此 L2 高性能和节约资源的特性也能吸引传统互联网公司的目光, 给他们铺平道路, 光明正大入局加密货币领域.
StarkWare 提供给 iMMUTABLE 的解决方案最终让 Tik Tok 这个目前最热门的公司找上了 iMMUTABLE 进行合作. StarkWare 所提供的两种部署模式给了客户数据保存方式的灵活性, 不仅符合法规, 同时也让性能得以拓展. 更重要的是, 性能的拓展也让以太坊饱受争议的能耗问题得到了解决, 这会是 Layer 2 的胜利, 更是 StarkWare 的胜利. 在未来, 我们一定会看到更多的传统企业选择以太坊以及 StarkWare 的方式进入区块链领域.
StarkWare 应用为何有如此高的性能?
StarkWare 的 Prover 有各种数学优化和 StarkWare 首先提出的一些优化算法, 同时开发所用的 Cairo 语言有专门数学相关的优化。除此之外交互数据送到 Prover 之前会用 StarkEx 引擎先协调一遍待证明的数据以及批处理. 整个运行流程都做到了全覆盖的优化. 具体细节会在后文中详细探讨.
StarkWare 应用的去中心化程度?
StarkWare 的 StarkNet 上的共识为 zk-STARK. zk-Rollups 不一定是去中心化, 无准入限制的. 但是 StarkWare 所使用的 zk-STARK 是无准入限制的, 与以太坊等公链一样. 在 StarkWare 所做的应用中间过程是会存在一些中心化的服务器来提供一些服务. 但这在一个完整应用的开发中是必要且无法去除的. 就像 uniswap 必须得有个中心化的域名和前端一样. 所以 StarkWare 所做的 dYdX, StarkNet 等依然是去中心化的.
zkSync 和 StarkWare 对比
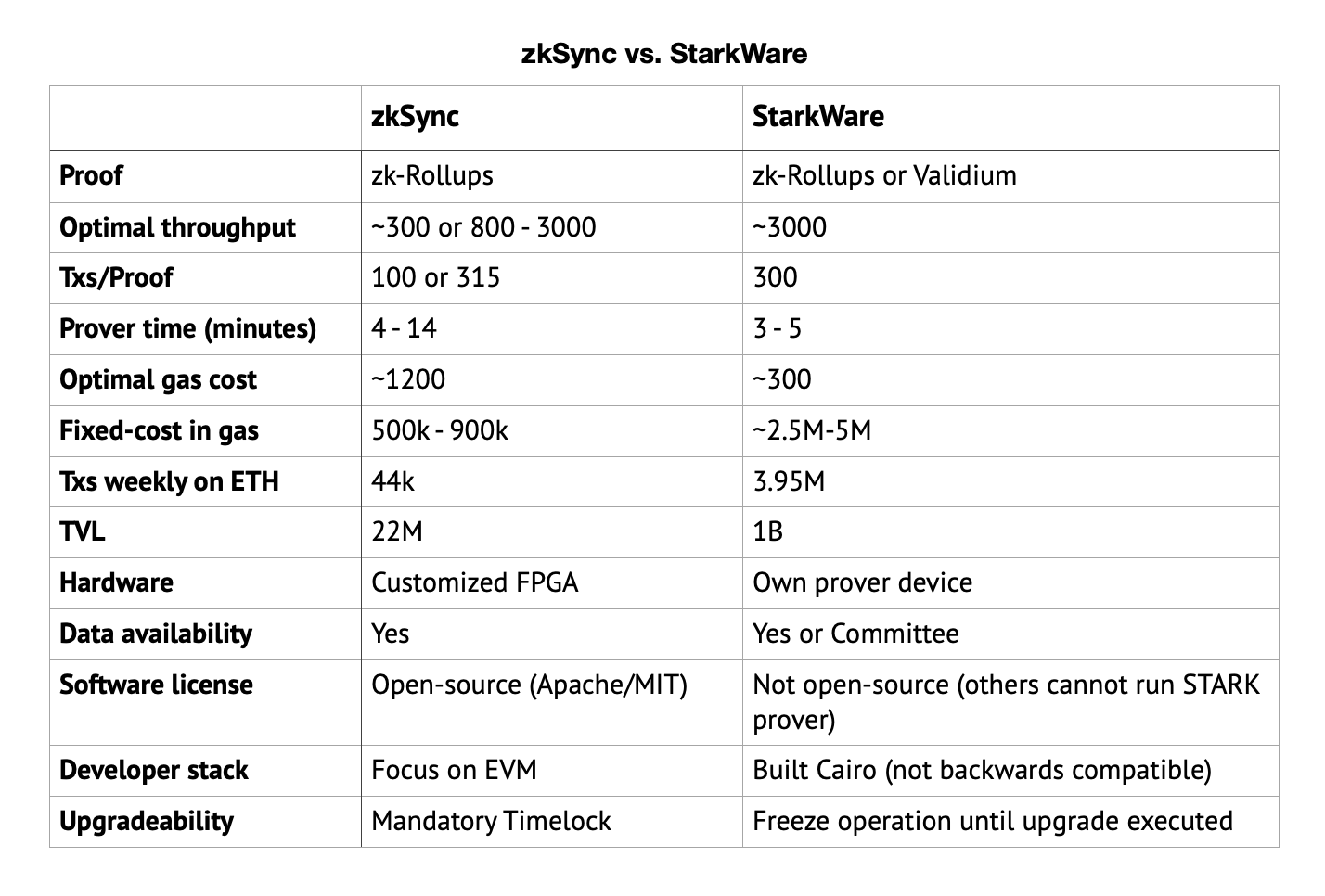 目前来看, StarkWare 无论是从性能还是目前的运行状况, 都领先于 zkSync. zkSync 和 StarkWare 最大的区别还是运作理念. zkSync 的项目都是开源的, 而且团队说自己被替代掉也无所谓, 只要能推动社区和以太坊的发展. StarkWare 公司是 toB 中心化的运作方式, STARK 证明器目前只能 StarkWare 公司使用, 而且做 Cairo 这个语言其实也是不那么对以太坊生态有利的做法 (对开发者友好的做法应该是和 zkSync 或 Optimistic 一样去做 EVM 兼容).
目前来看, StarkWare 无论是从性能还是目前的运行状况, 都领先于 zkSync. zkSync 和 StarkWare 最大的区别还是运作理念. zkSync 的项目都是开源的, 而且团队说自己被替代掉也无所谓, 只要能推动社区和以太坊的发展. StarkWare 公司是 toB 中心化的运作方式, STARK 证明器目前只能 StarkWare 公司使用, 而且做 Cairo 这个语言其实也是不那么对以太坊生态有利的做法 (对开发者友好的做法应该是和 zkSync 或 Optimistic 一样去做 EVM 兼容).
zk-Rollups 与 STARK 证明
StarkWare 所使用的技术包含了 zk-Rollups 以及 zk-STARK. 这两者不是同一个事物. STARK 即为 zk-STARK, 是零知识证明的一种.
StarkWare 倾向于称自己的解决方案为 Validity Rollups, 因为方案中不一定是用 zk-Rollups. Validity Rollups 包含了 Validium 和 zk-Rollups. 这两个的区别就是用户数据是否上链.
https://immutablex.medium.com/eli5-nft-scaling-solutions-b1de4ad82461
STARK 通过允许开发人员将计算和存储移出链来提高可伸缩性. 链外服务将能够生成 STARK 证明, 证明链外计算的完整性. 然后, 这些证据被放回链上, 供任何利益相关方验证计算. 使用 STARK 将大部分计算工作移出链, 允许现有区块链基础设施以指数级扩展, 同时保持计算完整性.
以太坊数据上链大致流程: 1000笔交易发送给以太坊每个节点 → 每个节点读取1000笔交易 → 节点更新1000笔交易
zk-STARK 数据上链流程: 1000笔交易发送给 zk-STARK → zk-STARK 作为证明者, 生成1个证明 (*生成阶段) → 节点作为验证者读取证明, 更新
*生成阶段: 通常 zk-STARK 证明需要以下过程生成证明. 验证者的证明过程分为两步: 第一步为计算完整性声明经过算术后生成代数中间代码表示, 第二步为经过测试后生成 FRI (StarkWare Co-Founder 2017年所著论文中对证明的优化方法) , 之后经过加密算法后输出可拓展的公开透明知识论据 (也就是 STARK). 简而言之就是通过安全可信的环境以及优化算法生成一个可信并且高性能的证明.
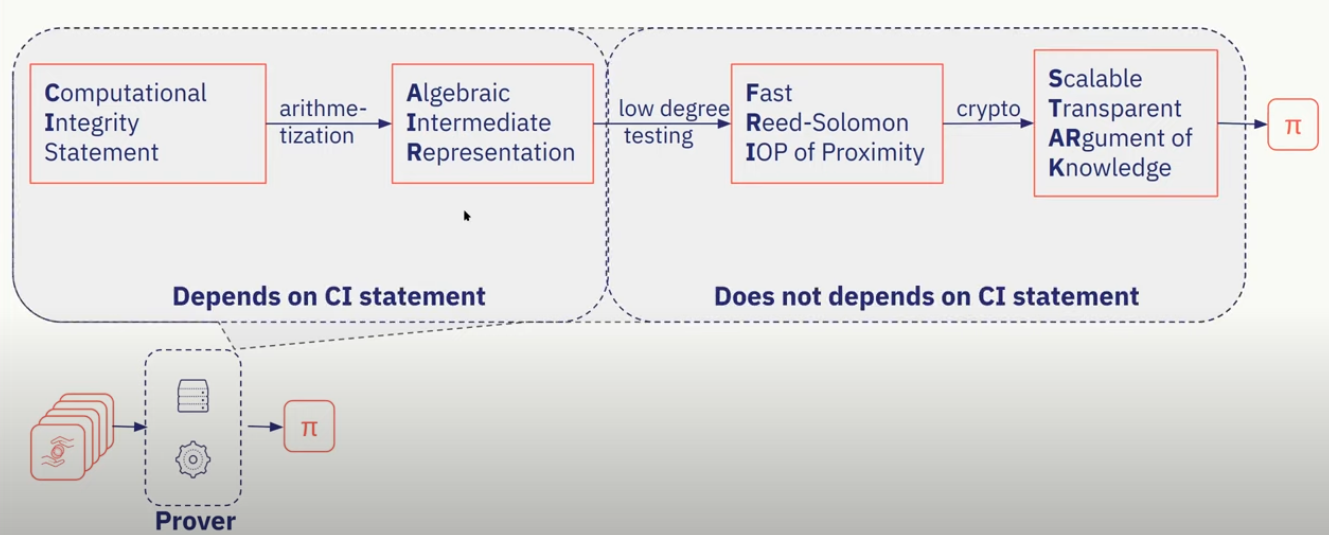
zk-Rollups 与其他 L2 方案比较
根据严格定义来说, StarkWare 很多文档中所使用的词汇 zk-Rollups 并不是一定采用零知识证明, 正确的描述是 Validity Proofs (包含 zk-Rollups 和 Validium, 因为 StarkWare 提供两种模式). 为了避免术语的变动影响理解, 本文依照 StarkWare 的文档均将其相关表述为 zk-Rollups.
侧链 (Polygon 或 xDai)
优点: 即使用户进行了大量交易, 主链上发生的只有两个, 即存款和取款. 由于侧链上的交易成本低于以太坊本身, 因此可以得到可扩展性.
缺点: 授予创建新区块的权力会带来停止生产区块的权力. 侧链可以有阻止用户提取资金的权力.
状态通道
优点: 状态通道的一个例子就是闪电网络. 当参与者将在长时间内交换大量状态更新时,状态通道非常有用. 具有很强的隐私性, 因为之间的状态只在通道内发生. 具有即时终结性, 只要结束就立马终结.
缺点: 状态通道非常依赖于有效性, 比较适用于有一组确定参与者的应用程序.
Plasma
优点: Plasma 非常适合处理 NFT, 因为每个 NFT 都有一个唯一的 ID. 侧链的问题之一是共识机制可以停止出块甚至锁定用户资金; Plasma 用户可以调用 Block root, 因此如果共识机制停止创建 Block, 用户仍然可以向以太坊索取资金.
缺点: 如果许多用户同时退出他们的 Plasma 链, 他们可能会淹没根链并使网络拥塞. 诸如欺诈活动或网络攻击之类的事情可能会导致如此大规模的外流. 另一个缺点是缺乏复杂性, 用户无法像在侧链上那样执行相同类型的复杂操作, 无法模拟完整以太坊环境.
zk-Rollups
优点: 每次转账的费用很低. 比 Plasma 和 Optimistic Rollups 更快. 数据量更少带来更高的吞吐量和可扩展性. 缺点:初始设置不去中心化 (STARK 中没有初始设置), 量子计算可能构成未来的黑客威胁 (STARK 可以抗量子计算机)
对比完各个 L2 解决方案后, 我们可以发现 zk-Rollups 或许是最接近区块链升级扩容的完美解决方案. 同时 zk-Rollup 的为数不多的几个缺点会在 StarkWare 采用的 zk-STARK 中得到修正.
STARK 与其他 ZK 性能比较
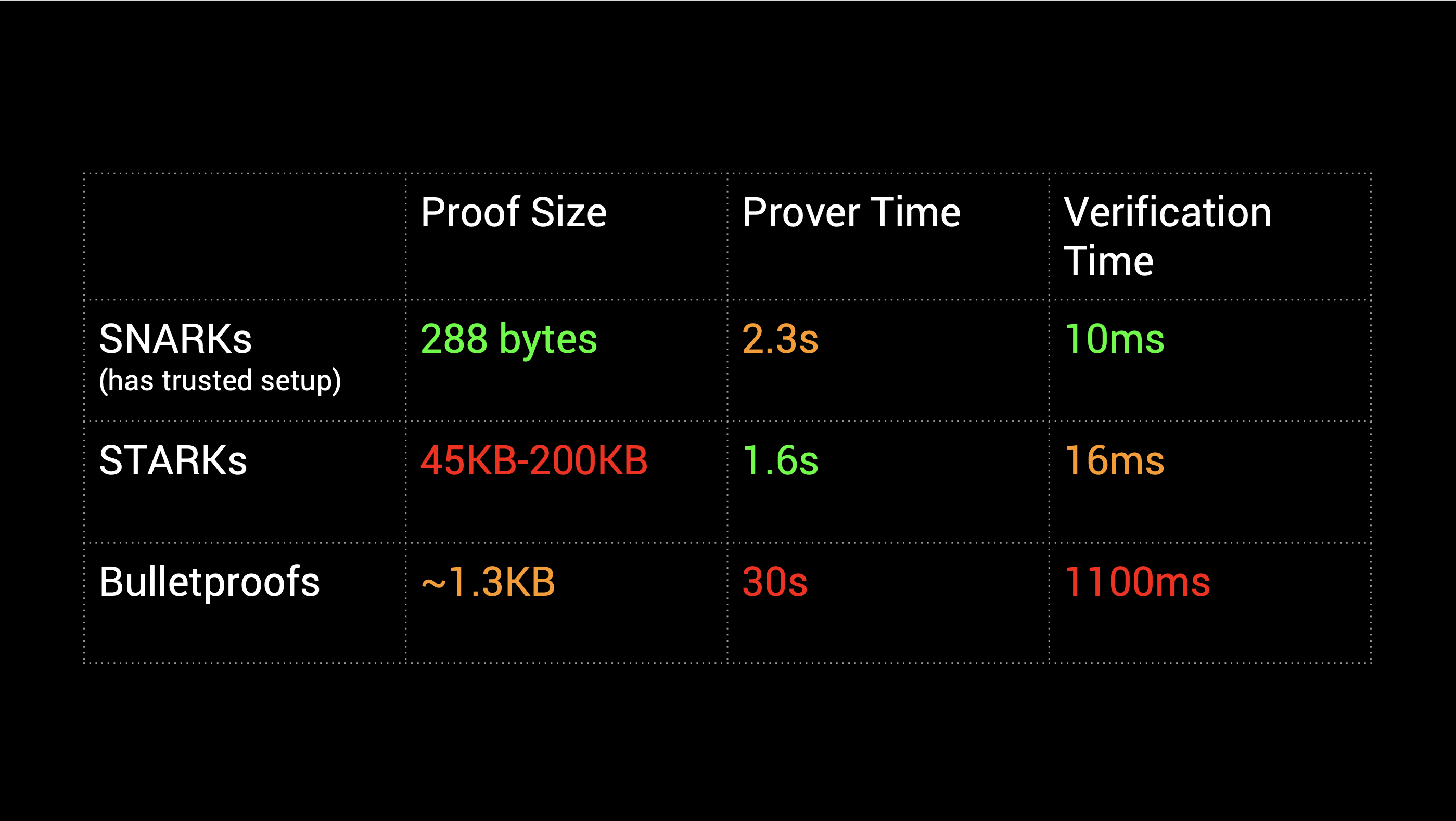
ZK 证明中主要有 SNARK, STARK, Bulletproof 三种. Bulletproofs 和 STARK 不需要可信设置, STARK 使用公开可验证的随机性来创建不受信任的可验证计算系统. 其中 STARK 相较于其他两种, 证明大小大非常多, 但在计算时的大小和证明速度上有很大优势. 同时 STARK 的安全性更高, 可以抗量子攻击.
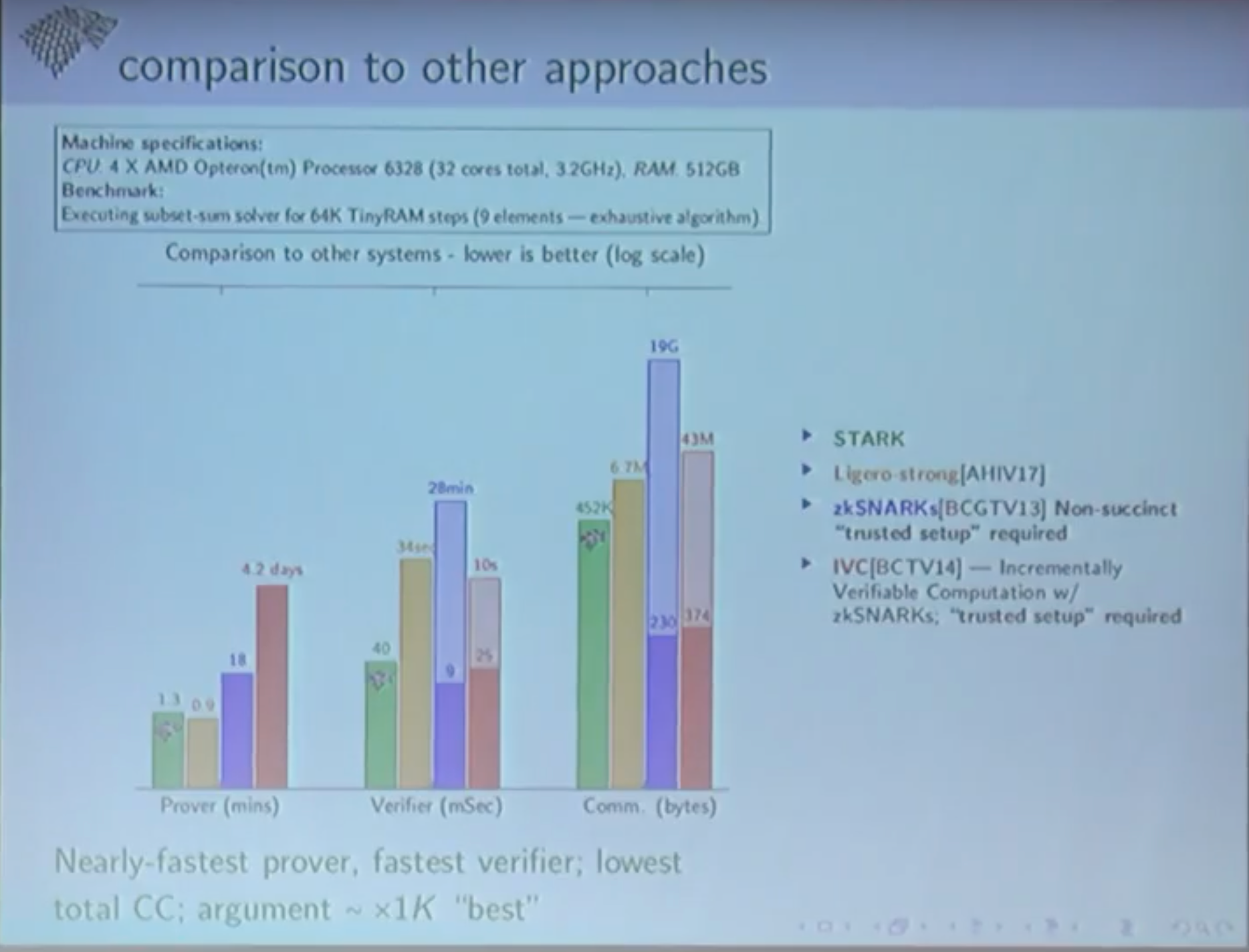
上图是 StarkWare 的 Co-Founder 在宣讲时放出的图. 他们测试时使用的 STARK 证明用图里服务器配置运行, 对比其他几种包括 SNARK 算法的性能都高出很多.
StarkNet
StarkNet Alpha 会在 11 月上线以太坊主网.
区块链浏览器: https://voyager.online
简介
StarkNet 是一个去中心化, 无需许可即可加入且抗审查的 L2 zk-Rollups, 支持以太坊上的通用计算. 它基于图灵完备的 Cairo 语言. 开发人员可以构建应用程序来实现 App 业务逻辑并部署在 StarkNet 上; 用户可以将交易以与以太坊正常交易相同的方式发送到 StarkNet 来执行. StarkNet 节点和参与者将受到经济激励, 以确保网络高效公平运行.
所有 StarkNet 交易将定期进行批处理, 交易在 STARK 证明中得到证明, 最终在以太坊上进行验证. 由于验证 STARK 证明所需的计算工作量与以太坊证明的计算量相比, 呈指数级小, 因此 StarkNet 可以将以太坊扩展几个数量级. 由于所有 StarkNet 状态转换都将经过 STARK 验证,因此以太坊只接受最终有效的状态转换.
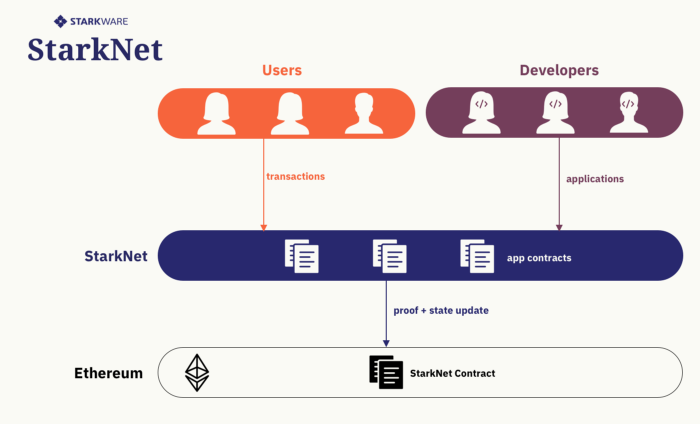
主要特点: 性能可拓展性, 开发便利, 针对以太坊生态的可组合性.
网络生态
编程语言 Cairo: Cairo 是一门图灵完备的高级编程语言和框架, 可以用于生成 STARK 证明. 开发人员可以使用 Cairo 来定义任何业务逻辑, 将交易送到 Shared Prover Service 对逻辑进行链下验证并在链上进行验证. Cairo 已在主网上适合进行正式的项目开发, 可供开发人员使用.
链下验证服务 Shared Prover Service: 在交易上链之前, 交易会送到 Sharp 进行验证, 判断应用程序执行的完整性, 并且计算出分摊证明验证的 gas 费用.
开源证明器 ethSTARK: ethSTARK 提供零知识和后量子安全签名. ethSTARK 在主网上的一个证明中处理 30 万笔交易, TPS 达到了 3000. Rollup gas 效率也突破了世界纪录达到 315 gas/tx, 比以太坊 L1 上的交易便宜几个数量级. 这项技术是 StarkNet 去中心化证明层的基石.
第三方项目: 目前主要的第三方库有 StarkNet.js . StarkNet.js 的作用类似于 Web3.js , 是用于前端获取合约内容时使用的. 以太坊客户端团队正在做 StarkNet 的完整节点实现. 同时目前 StarkNet 网络审计软件包括 CryptoExperts 和 LEAN proof.
使用案例
DeversiFi: 交易 TPS 9k, 支付 TPS 18k.
iMMUTABLE: NFT 铸造 gas 0.2美分, 每日 L2 交易 > 每周 L1 交易.
dYdX: 每笔交易费用缩减50倍.
StarkEx
简介
StarkEx 类似一个底层引擎, 构成组件来支持使用 STARK 的应用.
StarkEx 是可用于生产环境的 L2 可扩展性引擎, 自 2020 年 6 月起部署在以太坊主网上. StarkEx 利用 STARK 技术为 DeFi 和游戏等应用程序提供可扩展的自托管交易. StarkEx 支持广泛的用例: 现货交易, 永续交易以及 NFT 铸造和交易. 在主网部署之前,超过 5000 万笔 StarkEx 交易在公共和私人以太坊测试网上结算.
StarkEx 目前支持 ETH 代币, ERC-20, ERC-721 代币和合成资产. 此外, 它可以支持其他兼容 EVM 的区块链上的代币.
特点
可扩展性和计算完整性 应用程序可以依赖 StarkEx 和底层 STARK 基础设施来扩展, 同时 StarkEx 确保计算完整性. 通过 SHARP(共享证明器)技术, gas 成本在所有基于 StarkEx 的应用程序中均摊销.
多样化的部署模式 StarkEx 可以部署 zk-Rollups 模式 (在链上发布数据) 或 Validium 模式 (通过侧链验证数据可用性). 还有即将推出的模式: Volition, 允许用户为自己选择数据可用性模式.
钱包整合 StarkWare 通过 Ledger, Authereum 和 WalletConnect 提供本地支持. StarkWare 还通过与 Web3 兼容的密钥生成 (适用于许多其他现有钱包) 提供 MetaMask 集成.
架构与业务逻辑
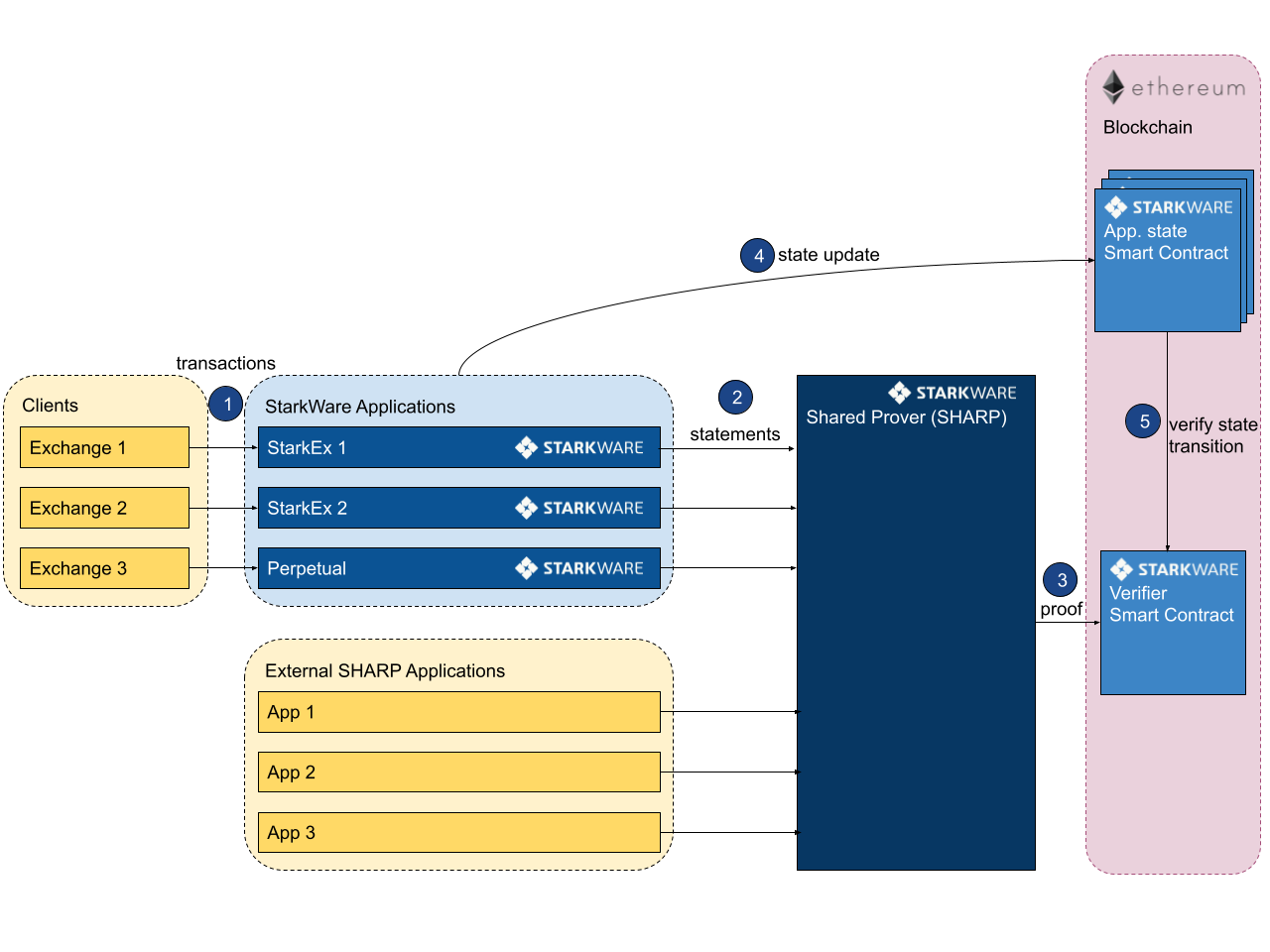
上图是一个使用了 StarkNet 和 StarkEx 的典型应用的架构图. 假设这个应用是一个叫 Starkswap 的 DEX.
最左侧黄色框内的应用 —— 操作整个应用
这个链下组件接收用户交易并定义业务逻辑和执行顺序. 它将交易传递给 StarkEx 服务.
这个组件是应用的中心化前端, 通常为 Web 或客户端.
淡蓝色框内的 StarkEx 服务 —— 批处理和协调
一个链下组件, 负责批处理一组操作并根据操作更新系统状态. 对于每个批次, 它会将这批操作 (通过 Cairo 语言执行, 先把 Solidity 的字节码转化成 Cairo 语言的智能合约, 在到 Cairo 语言环境中运行) 发送到 SHARP 以证明其有效性. 一旦证明得到验证, 它就会在链上发布新的状态. 状态由默克尔树表示. 每个 Vault 的结构和内容根据实现的特定业务逻辑而有所不同. 默克尔树根代表要提交到链上的状态.
SHARP —— 共享证明器 (由 StarkWare 专门为应用定制)
SHARP 是 Cairo 语言的共享证明服务. 它接收来自不同应用程序的证明请求并输出证明以证明 Cairo 代码执行的有效性. 输出证明可以在多个证明请求之间共享.
这个组件此前的名字叫 Generic Prover Service. 所以组件本质上是一个后端服务器, 包含了一些特定服务. 推测是部署在 StarkWare 的中心化服务器上.
StarkEx 合约 ( Verifier 合约) —— 状态更新、存款和取款
该合约有两个主要功能. 第一个功能是在验证满足有效性条件后更新系统的状态, 第二个功能是以非托管方式管理进出 StarkEx 的存款和取款 (任何情况下, 用户都可以提取他们的资金).
这个组件是以太坊上的一个智能合约.
Starkswap 的业务逻辑如下:
处理请求 淡蓝色方框内的 StarkWare 应用程序处理客户请求, 将这些交易转换为可证明的陈述, 并将这些发送给深蓝色方框内的 SHARP. 所有请求发送与处理都通过图中第一步的 API以及第二步中的批处理语句发送 (一个批次可以编译多个请求).
SHARP 证明 深蓝色的 SHARP 构造证明.
登记证明 SHARP 将证明传输到粉色框中的第三步的链上验证者智能合约.
注册状态转换 第四步中, StarkWare 应用程序在 Starkswap 智能合约上进行应用状态转换. 第五步中, 为确保转换的有效性 (SHARP 的验证), Starkswap 的智能合约确认转换语句已在 Verifier 智能合约中注册.
功能与加密算法
https://docs.starkware.co/starkex-v3/crypto/stark-curve
功能细节:
链下状态:
余额树和顺序树. 通过默克尔树, 保证了资金状态的安全和可信, 以及避免了双花问题.
Flow Description:
链上账户 (账户的余额在链外存储和管理, 除非资金移入/移出链上账户. 从 L1 的角度来看, 这些账户的资金都存储在 StarkEx 智能合约下.)
链下账户 (所有余额指令作为 L1 交易到达. 链上账户的一个特殊属性是它不需要私钥 (stark 的私钥), 所以智能合约是此类账户的"所有者". 因此, L1 用户和应用程序可以通过 StarkEx 进行交易并与任何挂单匹配. 链上交易模式实现了 StarkEx 应用程序和 L1 应用程序之间的互操作性,可用于 DeFi Pooling 或由流动性聚合器使用).
StarkEx 特定概念:
在 StarkEx 中有很多概念与以太坊不同, 因此开发需要额外的学习.
https://docs.starkware.co/starkex-v3/starkex-deep-dive/starkex-specific-concepts
除此之外, StarkEx 还有信息加密, 批量闪电贷, DeFi pooling 等的特定操作.
加密算法:
STARK Elliptic Curve, Pedersen Hash Function, KDF. 通过使用以上的加密算法以及参考 https://github.com/authereum/starkware-monorepo/tree/starkex-3.0/packages/starkware-provider#walletconnect 的实例, 第三方钱包可以集成 StarkEx.
Cairo
简介
Cairo 是第一个生成 STARK 证明的生产级平台. 它是图灵完备的, 而且非常高效. 要在 StarkNet 上部署高性能并且低 gas 费的 Layer 2 应用组件就需要使用 Cairo 来编写应用程序. Cairo 语言不是一门专门的合约语言, 但是可以并且主要用来写类似合约的内容.
zk-Rollups 当前的缺点是通用计算: 将智能合约逻辑直接移植到 rollups 中更具挑战性,因此只有有限的功能可用,例如转移和交易. 然而, Cairo 填补了这个空缺, 可以将智能合约逻辑直接移植到 rollups 中. zkSync 和 Optimistic 的做法分别是让 rollups 做到 EVM 兼容和 EVM equivalency (更加全面并且进一步的 EVM 兼容).
特点
计算完整性
计算完整性是代表了在没有监管的情况下, 能保证计算的公正性. 保证 Computational Integrity 的方法有五种: 银行委托问责制 (基于信誉, 审计等), 计算可重放性 (例如比特币和其他 L1 公开所有交易), 可信执行环境 (例如英特尔的 SGX), 欺诈证明 (Optimistic rollups, 介于委托问责和计算可重放性之间), 密码学证明 (zk-STARK). Cairo 语言经过多篇论文以及数学证明的验证, 可以安全可信地生成 zk-STARK 的证明来保证计算完整性.
AIR (代数中间代码表示)
在 STARK 证明的过程中, 需要用到很多设计代数证明的运算以及符号, Cairo 会通过编译器把编程语言转化为 Cairo 字节代码, 生成一个 AIR 来包含所有的数学证明步骤, 最终生成结果. Cario 语言有配套的 AIR 可视化工具, 来查看证明中的细节.
语言设计
Cario 语言的设计遵循 Minimal Variable Language 的原则, 讲究恰到好处. 同时做到了语言的表达性 (便于开发者阅读) 以及 STARK 证明的生成效率. Cario 语言的设计也并非过于复杂, 仅有三个寄存器 (PC, 分配指针, 帧指针), 和简洁的指令集. Cario 语言也支持一些必要的功能, 包括函数, 递归, 分支, 判断等. Cario 语言设计的感觉更加符合数学证明的逻辑, 更加工整.
工具链
编译器 (https://github.com/NethermindEth/warp) , 虚拟机, 代码编辑环境插件 (VSCode上的代码提示插件 https://github.com/ericglau/cairo-ls), 跟踪程序, 代码示例 (https://github.com/starkware-libs/cairo-examples).
语言生态
目前 Cairo 语言的生态可以说非常全面但年轻. 在工具链方面一应俱全, 根据这些工具的 GitHub 星数可以判断出并没有收获很大的关注, 但是仓库的开发者在持续更新, 基本在一到两周内都有新的提交. 未来 Cairo 语言会更加开放, 培养更多开发者后, 在 StarkEx 引擎上写 Cairo 代码的工作很可能从 StarkWare 移交到开源开发者手里, 这样对 StarkWare 应用的去中心化会有很大的意义.
更重要的是 OpenZeppelin 正在做 Cairo 语言的 ERC-20, ERC-721 等基础模版的实现 (https://github.com/OpenZeppelin/cairo-contracts). 这个实现的意义就是能方便开发者在此实现的基础上开发, 能让开发者放心且大胆地拷贝此实现, 迅捷开发并且不用过于担心安全性. 从仓库的 commit 来看, OpenZeppelin 目前有专人来为 Cairo 语言做支持, 证明 OpenZeppelin 对 StarkWare 生态的重视.
总结
作为一家 Layer 2 解决方案提供商, StarkWare 做出了 dYdX 和 iMMUTABLE 这样的爆款产品. 在各种解决方案中, StarkWare 的 zk-STARK 技术支持了 Layer 2 上最大的交易数量. 从 Prover 的数学优化, Cairo 语言的数学优化, 到 StarkEx 引擎的证明协调, StarkNet 作为一个去中心化 zk-STARK 网络, 提供了极高的性能, 做到完全运行流程的优化. StarkWare 通过前沿的技术和完整的技术服务, 支撑了 Layer 2 应用庞大的交易量, 未来也必将拥抱开源, 做到更去中心化, 帮助了以太坊 2.0 的建设.
相关链接:
iMMUTABLE: https://www.immutable.com/blog/design-architecture, https://medium.com/starkware/starkex-now-for-nfts-bfdc9f4655a2
Layer 2: https://academy.moralis.io/blog/comparing-layer-2-ethereum-scaling-solutions, https://www.bcskill.com/index.php/archives/965.html, https://l2beat.com/faq/
ZK: https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/59145/zk-snarks-vs-zk-starks-vs-bulletproofs-updated/63778, https://consensys.net/blog/blockchain-explained/zero-knowledge-proofs-starks-vs-snarks/, https://medium.com/unitychain/reveal-mysterious-zk-starks-42d00679c05b
StarkNet: https://medium.com/starkware/on-the-road-to-starknet-a-permissionless-stark-powered-l2-zk-rollup-83be53640880, https://starkware.co/product/starknet/, https://medium.com/starkware/starknet-alpha-is-coming-to-mainnet-b825829eaf32
StarkEx: https://docs.starkware.co/starkex-v3/architecture/solution-architecture
Cairo: https://medium.com/starkware/hello-cairo-3cb43b13b209, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QPNp8w9rx7o, https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.14534
zkSync: https://www.reddit.com/r/ethereum/comments/q8q822/ama_were_matter_labs_the_team_behind_zksync_the/, https://members.delphidigital.io/reports/ethereum-layer-2-rollup-debate-optimism-starkware-arbitrum-and-zksync/, https://twitter.com/KyberNetwork/status/1372593913786109953, https://blog.kyber.network/research-trade-offs-in-rollup-solutions-a1084d2b444
General: https://academy.moralis.io/blog/what-is-starkware-and-starks



